Tissue factor: Difference between revisions
m (Robot: Automated text replacement (-{{reflist}} +{{reflist|2}}, -<references /> +{{reflist|2}}, -{{WikiDoc Cardiology Network Infobox}} +)) |
(→Thromboplastin: Reworded 2 sentences to clarify) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ | {{Refimprove|date=August 2015}} | ||
{{Infobox_gene}} | |||
'''Tissue factor''', also called '''platelet tissue factor''', '''factor III''', '''thromboplastin''', or '''[[cluster of differentiation|CD142]]''' is a [[protein]] encoded by the '''F3''' [[gene]] present in [[endothelium|subendothelial tissue]] and [[leukocyte]]s. Its role in the clotting process is the initiation of [[thrombin]] formation from the [[zymogen]] [[prothrombin]]. Thromboplastin defines the cascade that leads to the activation of [[factor X]] - the tissue factor pathway. In doing so it has replaced the previously named extrinsic pathway in order to eliminate ambiguity. | |||
| | |||
}} | |||
{{ | |||
== Function == | |||
The '''F3''' gene encodes coagulation factor III which is a cell surface [[glycoprotein]]. This factor enables cells to initiate the blood coagulation cascades, and it functions as the high-affinity receptor for the [[coagulation factor VII]]. The resulting complex provides a catalytic event that is responsible for initiation of the coagulation protease cascades by specific limited proteolysis. Unlike the other cofactors of these protease cascades, which circulate as nonfunctional precursors, this factor is a potent initiator that is fully functional when expressed on cell surfaces. There are 3 distinct domains of this factor: extracellular, transmembrane, and cytoplasmic. This protein is the only one in the coagulation pathway for which a congenital deficiency has not been described.<ref>{{cite web | title = Entrez Gene: F3 coagulation factor III (thromboplastin, tissue factor)| url = https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=2152| accessdate = }}</ref> In addition to the membrane-bound tissue factor, soluble form of tissue factor was also found which results from [[alternative splicing|alternatively spliced]] tissue factor mRNA transcripts, in which [[exon]] 5 is absent and exon 4 is spliced directly to exon 6.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Guo W, Wang H, Zhao W, Zhu J, Ju B, Wang X | title = Effect of all-trans retinoic acid and arsenic trioxide on tissue factor expression in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells | journal = Chin. Med. J. | volume = 114 | issue = 1 | pages = 30–4 | year = 2001 | pmid = 11779431 | doi = }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Bogdanov VY, Balasubramanian V, Hathcock J, Vele O, Lieb M, Nemerson Y | title = Alternatively spliced human tissue factor: a circulating, soluble, thrombogenic protein | journal = Nat. Med. | volume = 9 | issue = 4 | pages = 458–62 | date = April 2003 | pmid = 12652293 | doi = 10.1038/nm841 }}</ref> | |||
=== Coagulation === | |||
[[Image:Coagulation full.svg|thumb|left|300px|The coagulation cascade.]] | |||
TF is the cell surface receptor for the [[serine protease]] factor VIIa. | |||
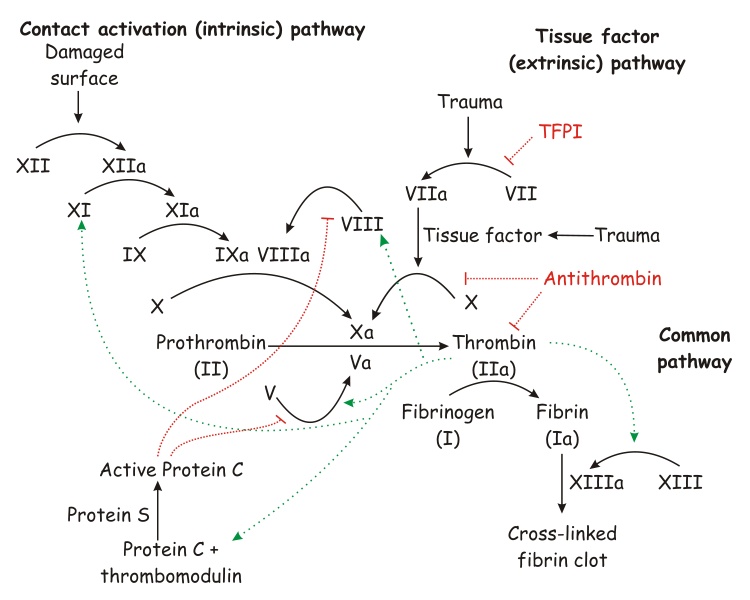
The best known function of tissue factor is its role in [[blood coagulation]]. The complex of TF with [[factor VII]]a catalyzes the conversion of the inactive protease [[factor X]] into the active protease [[factor Xa]]. | |||
Together with factor VIIa, tissue factor forms the tissue factor or extrinsic pathway of coagulation. This is opposed to the intrinsic (amplification) pathway which involves both activated [[factor IX]] and [[factor VIII]]. Both pathways lead to the activation of [[factor X]] (the common pathway) which combines with activated [[factor V]] in the presence of calcium and [[phospholipid]] to produce [[thrombin]] (thromboplastin activity). | |||
{{clear|left}} | |||
=== Cytokine signaling === | |||
TF is related to a protein family known as the [[cytokine receptor class II family]]. The members of this receptor family are activated by [[cytokines]]. Cytokines are small proteins that can influence the behavior of [[white blood cell]]s. Binding of VIIa to TF has also been found to start signaling processes inside the cell. The signaling function of TF/VIIa plays a role in [[angiogenesis]] and [[apoptosis]]. | |||
==Structure== | ==Structure== | ||
Tissue factor belongs to the [[cytokine receptor]] [[protein superfamily]] and consists of three [[protein domain|domain]]s:<ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Muller YA, Ultsch MH, de Vos AM | title = The crystal structure of the extracellular domain of human tissue factor refined to 1.7 Å resolution | journal = Journal of Molecular Biology | volume = 256 | issue = 1 | pages = 144–159 |date=Feb 1996 | pmid = 8609606 | doi = 10.1006/jmbi.1996.0073}}</ref> | |||
# an extracellular domain, which consists of two [[fibronectin]] type III modules whose hydrophobic cores merge in the domain-domain interface. This serves as a (probably rigid) template for [[factor VIIa]] binding. | |||
# a [[transmembrane]] domain. | |||
# a cytosolic domain of 21 amino acids length inside the cell which is involved in the signaling function of TF. | |||
Note that one of factor VIIa's domains, [[GLA domain]], binds in the presence of calcium to negatively charged [[phospholipids]], and this binding greatly enhances factor VIIa binding to tissue factor. | |||
== Tissue distribution == | |||
Some cells release TF in response to blood vessel damage (see next paragraph) and some do only in response to inflammatory mediators (endothelial cells/macrophages). | |||
TF is expressed by cells which are normally not exposed to flowing blood such as sub-endothelial cells (e.g. [[smooth muscle cell]]s) and cells surrounding blood vessels (e.g. [[fibroblast]]s). This can change when the blood vessel is damaged by for example physical injury or rupture of [[atherosclerotic plaque]]s. Exposure of TF expressing cells during injury allows the complex formation of TF with factor VII. Factor VII and TF form an equal molar complex in the presence of calcium ions and this leads to the activation of factor VII on a membrane surface. | |||
TF is the | |||
The | The inner surface of the blood vessel consists of endothelial cells. Endothelial cells do not express TF except when they are exposed to inflammatory molecules such as [[tumor necrosis factor-alpha]] (TNF-alpha). Another cell type that expresses TF on the cell surface in inflammatory conditions is the [[monocyte]] (a white blood cell). | ||
== Thromboplastin == | |||
[[ | Historically, [[thromboplastin]] was a lab reagent, usually derived from placental sources, used to assay [[prothrombin time]]s (PT time). Thromboplastin, by itself, could activate the extrinsic coagulation pathway. When manipulated in the laboratory, a derivative could be created called partial thromboplastin, which was used to measure the intrinsic pathway. This test is called the [[Partial thromboplastin time|aPTT]], or activated partial thromboplastin time. It was not until much later that the subcomponents of thromboplastin and partial thromboplastin were identified. Thromboplastin contains phospholipids as well as tissue factor, both of which needed in the activation of the extrinsic pathway, whereas partial thromboplastin does not contain tissue factor. Tissue factor is not needed to activate the intrinsic pathway. | ||
=== | == Interactions == | ||
== | Tissue factor has been shown to [[Protein-protein interaction|interact]] with [[Factor VII]].<ref name=pmid12787023>{{cite journal | vauthors = Carlsson K, Freskgård PO, Persson E, Carlsson U, Svensson M | title = Probing the interface between factor Xa and tissue factor in the quaternary complex tissue factor-factor VIIa-factor Xa-tissue factor pathway inhibitor | journal = Eur. J. Biochem. | volume = 270 | issue = 12 | pages = 2576–82 | date = Jun 2003 | pmid = 12787023 | doi = 10.1046/j.1432-1033.2003.03625.x }}</ref><ref name=pmid9925787>{{cite journal | vauthors = Zhang E, St Charles R, Tulinsky A | title = Structure of extracellular tissue factor complexed with factor VIIa inhibited with a BPTI mutant | journal = J. Mol. Biol. | volume = 285 | issue = 5 | pages = 2089–104 | date = Feb 1999 | pmid = 9925787 | doi = 10.1006/jmbi.1998.2452 }}</ref> | ||
== Additional images == | |||
==Additional images== | |||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
Image:Tissue factor.png|Tissue factor | Image:Tissue factor.png|Tissue factor | ||
File:Fibrin-nach-Thromboplastin.jpg|Blood plasma after the addition of tissue factor | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==References== | == See also == | ||
{{reflist | *[[hemostasis]] | ||
==Further reading== | |||
== References == | |||
{{reflist}} | |||
== Further reading == | |||
{{refbegin | 2}} | {{refbegin | 2}} | ||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Gouault-Helimann M, Josso F | title = [Initiation in vivo of blood coagulation. The role of white blood cells and tissue factor (author's transl)] | journal = Nouv Presse Med | volume = 8 | issue = 40 | pages = 3249–53 | year = 1979 | pmid = 392457 | doi = }} | |||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Mackman N | title = Regulation of the tissue factor gene | journal = FASEB J. | volume = 9 | issue = 10 | pages = 883–9 | year = 1995 | pmid = 7615158 | doi = }} | |||
*{{cite journal | * {{cite journal | vauthors = McVey JH | title = Tissue factor pathway | journal = Best Practice & Research. Clinical Haematology | volume = 12 | issue = 3 | pages = 361–72 | year = 1999 | pmid = 10856975 | doi = }} | ||
*{{cite journal | * {{cite journal | vauthors = Konigsberg W, Kirchhofer D, Riederer MA, Nemerson Y | title = The TF:VIIa complex: clinical significance, structure-function relationships and its role in signaling and metastasis | journal = Thromb. Haemost. | volume = 86 | issue = 3 | pages = 757–71 | year = 2001 | pmid = 11583305 | doi = }} | ||
*{{cite journal | * {{cite journal | vauthors = Versteeg HH, Peppelenbosch MP, Spek CA | title = The pleiotropic effects of tissue factor: a possible role for factor VIIa-induced intracellular signalling? | journal = Thromb. Haemost. | volume = 86 | issue = 6 | pages = 1353–9 | year = 2001 | pmid = 11776298 | doi = }} | ||
*{{cite journal | * {{cite journal | vauthors = Fernandez PM, Rickles FR | title = Tissue factor and angiogenesis in cancer | journal = Curr. Opin. Hematol. | volume = 9 | issue = 5 | pages = 401–6 | year = 2002 | pmid = 12172458 | doi = 10.1097/00062752-200209000-00003 }} | ||
*{{cite journal | * {{cite journal | vauthors = Golino P | title = The inhibitors of the tissue factor:factor VII pathway | journal = Thromb. Res. | volume = 106 | issue = 3 | pages = V257–65 | year = 2002 | pmid = 12356487 | doi = 10.1016/S0049-3848(02)00079-8 }} | ||
*{{cite journal | * {{cite journal | vauthors = Engelmann B, Luther T, Müller I | title = Intravascular tissue factor pathway--a model for rapid initiation of coagulation within the blood vessel | journal = Thromb. Haemost. | volume = 89 | issue = 1 | pages = 3–8 | year = 2003 | pmid = 12540946 | doi = 10.1267/THRO03010003 | doi-broken-date = 2017-01-15 }} | ||
*{{cite journal | * {{cite journal | vauthors = Morrissey JH | title = Tissue factor: in at the start...and the finish? | journal = J. Thromb. Haemost. | volume = 1 | issue = 5 | pages = 878–80 | year = 2003 | pmid = 12871349 | doi = 10.1046/j.1538-7836.2003.00219.x }} | ||
*{{cite journal | * {{cite journal | vauthors = Yu JL, May L, Klement P, Weitz JI, Rak J | title = Oncogenes as regulators of tissue factor expression in cancer: implications for tumor angiogenesis and anti-cancer therapy | journal = Semin. Thromb. Hemost. | volume = 30 | issue = 1 | pages = 21–30 | year = 2004 | pmid = 15034795 | doi = 10.1055/s-2004-822968 }} | ||
*{{cite journal | * {{cite journal | vauthors = Fernandez PM, Patierno SR, Rickles FR | title = Tissue factor and fibrin in tumor angiogenesis | journal = Semin. Thromb. Hemost. | volume = 30 | issue = 1 | pages = 31–44 | year = 2004 | pmid = 15034796 | doi = 10.1055/s-2004-822969 }} | ||
*{{cite journal | * {{cite journal | vauthors = Mackman N | title = Role of tissue factor in hemostasis, thrombosis, and vascular development | journal = Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. | volume = 24 | issue = 6 | pages = 1015–22 | year = 2004 | pmid = 15117736 | doi = 10.1161/01.ATV.0000130465.23430.74 }} | ||
*{{cite journal | * {{cite journal | vauthors = Belting M, Ahamed J, Ruf W | title = Signaling of the tissue factor coagulation pathway in angiogenesis and cancer | journal = Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. | volume = 25 | issue = 8 | pages = 1545–50 | year = 2005 | pmid = 15905465 | doi = 10.1161/01.ATV.0000171155.05809.bf }} | ||
*{{cite journal | * {{cite journal | vauthors = Engelmann B | title = Initiation of coagulation by tissue factor carriers in blood | journal = Blood Cells Mol. Dis. | volume = 36 | issue = 2 | pages = 188–90 | year = 2007 | pmid = 16473535 | doi = 10.1016/j.bcmd.2005.12.020 }} | ||
*{{cite journal | * {{cite journal | vauthors = Furie B, Furie BC | title = Cancer-associated thrombosis | journal = Blood Cells Mol. Dis. | volume = 36 | issue = 2 | pages = 177–81 | year = 2007 | pmid = 16490369 | doi = 10.1016/j.bcmd.2005.12.018 }} | ||
*{{cite journal | * {{cite journal | vauthors = Mackman N | title = Alternatively spliced tissue factor - one cut too many? | journal = Thromb. Haemost. | volume = 97 | issue = 1 | pages = 5–8 | year = 2007 | pmid = 17200762 | doi = 10.1160/th06-11 }} | ||
*{{cite journal | * {{cite journal | vauthors = Wiiger MT, Prydz H | title = The changing faces of tissue factor biology. A personal tribute to the understanding of the "extrinsic coagulation activation" | journal = Thromb. Haemost. | volume = 98 | issue = 1 | pages = 38–42 | year = 2007 | pmid = 17597988 | doi = 10.1160/th07-04-0289 }} | ||
*{{cite journal | |||
*{{cite journal | |||
}} | |||
{{refend}} | {{refend}} | ||
== External links == | |||
* {{OMIM|134390}} | * {{OMIM|134390}} | ||
* {{PDB Molecule of the Month| | * {{PDB Molecule of the Month|75|Tissue factor}} - March 2006 | ||
{{PDB Gallery|geneid=2152}} | |||
{{Coagulation}} | {{Coagulation}} | ||
{{Clusters of differentiation}} | {{Clusters of differentiation}} | ||
| Line 125: | Line 93: | ||
[[Category:Coagulation system]] | [[Category:Coagulation system]] | ||
[[Category:Clusters of differentiation|CD142]] | [[Category:Clusters of differentiation|CD142]] | ||
Revision as of 23:05, 2 December 2017
This article needs additional citations for verification. (August 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
| VALUE_ERROR (nil) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||
| Aliases | |||||||
| External IDs | GeneCards: [1] | ||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||
| Entrez |
|
| |||||
| Ensembl |
|
| |||||
| UniProt |
|
| |||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) |
|
| |||||
| RefSeq (protein) |
|
| |||||
| Location (UCSC) | n/a | n/a | |||||
| PubMed search | n/a | n/a | |||||
| Wikidata | |||||||
| |||||||
Tissue factor, also called platelet tissue factor, factor III, thromboplastin, or CD142 is a protein encoded by the F3 gene present in subendothelial tissue and leukocytes. Its role in the clotting process is the initiation of thrombin formation from the zymogen prothrombin. Thromboplastin defines the cascade that leads to the activation of factor X - the tissue factor pathway. In doing so it has replaced the previously named extrinsic pathway in order to eliminate ambiguity.
Function
The F3 gene encodes coagulation factor III which is a cell surface glycoprotein. This factor enables cells to initiate the blood coagulation cascades, and it functions as the high-affinity receptor for the coagulation factor VII. The resulting complex provides a catalytic event that is responsible for initiation of the coagulation protease cascades by specific limited proteolysis. Unlike the other cofactors of these protease cascades, which circulate as nonfunctional precursors, this factor is a potent initiator that is fully functional when expressed on cell surfaces. There are 3 distinct domains of this factor: extracellular, transmembrane, and cytoplasmic. This protein is the only one in the coagulation pathway for which a congenital deficiency has not been described.[1] In addition to the membrane-bound tissue factor, soluble form of tissue factor was also found which results from alternatively spliced tissue factor mRNA transcripts, in which exon 5 is absent and exon 4 is spliced directly to exon 6.[2][3]
Coagulation
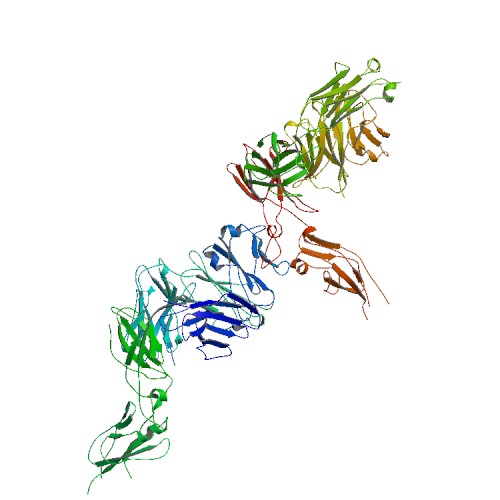
TF is the cell surface receptor for the serine protease factor VIIa.
The best known function of tissue factor is its role in blood coagulation. The complex of TF with factor VIIa catalyzes the conversion of the inactive protease factor X into the active protease factor Xa.
Together with factor VIIa, tissue factor forms the tissue factor or extrinsic pathway of coagulation. This is opposed to the intrinsic (amplification) pathway which involves both activated factor IX and factor VIII. Both pathways lead to the activation of factor X (the common pathway) which combines with activated factor V in the presence of calcium and phospholipid to produce thrombin (thromboplastin activity).
Cytokine signaling
TF is related to a protein family known as the cytokine receptor class II family. The members of this receptor family are activated by cytokines. Cytokines are small proteins that can influence the behavior of white blood cells. Binding of VIIa to TF has also been found to start signaling processes inside the cell. The signaling function of TF/VIIa plays a role in angiogenesis and apoptosis.
Structure
Tissue factor belongs to the cytokine receptor protein superfamily and consists of three domains:[4]
- an extracellular domain, which consists of two fibronectin type III modules whose hydrophobic cores merge in the domain-domain interface. This serves as a (probably rigid) template for factor VIIa binding.
- a transmembrane domain.
- a cytosolic domain of 21 amino acids length inside the cell which is involved in the signaling function of TF.
Note that one of factor VIIa's domains, GLA domain, binds in the presence of calcium to negatively charged phospholipids, and this binding greatly enhances factor VIIa binding to tissue factor.
Tissue distribution
Some cells release TF in response to blood vessel damage (see next paragraph) and some do only in response to inflammatory mediators (endothelial cells/macrophages).
TF is expressed by cells which are normally not exposed to flowing blood such as sub-endothelial cells (e.g. smooth muscle cells) and cells surrounding blood vessels (e.g. fibroblasts). This can change when the blood vessel is damaged by for example physical injury or rupture of atherosclerotic plaques. Exposure of TF expressing cells during injury allows the complex formation of TF with factor VII. Factor VII and TF form an equal molar complex in the presence of calcium ions and this leads to the activation of factor VII on a membrane surface.
The inner surface of the blood vessel consists of endothelial cells. Endothelial cells do not express TF except when they are exposed to inflammatory molecules such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha). Another cell type that expresses TF on the cell surface in inflammatory conditions is the monocyte (a white blood cell).
Thromboplastin
Historically, thromboplastin was a lab reagent, usually derived from placental sources, used to assay prothrombin times (PT time). Thromboplastin, by itself, could activate the extrinsic coagulation pathway. When manipulated in the laboratory, a derivative could be created called partial thromboplastin, which was used to measure the intrinsic pathway. This test is called the aPTT, or activated partial thromboplastin time. It was not until much later that the subcomponents of thromboplastin and partial thromboplastin were identified. Thromboplastin contains phospholipids as well as tissue factor, both of which needed in the activation of the extrinsic pathway, whereas partial thromboplastin does not contain tissue factor. Tissue factor is not needed to activate the intrinsic pathway.
Interactions
Tissue factor has been shown to interact with Factor VII.[5][6]
Additional images
-
Tissue factor
-
Blood plasma after the addition of tissue factor
See also
References
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: F3 coagulation factor III (thromboplastin, tissue factor)".
- ↑ Guo W, Wang H, Zhao W, Zhu J, Ju B, Wang X (2001). "Effect of all-trans retinoic acid and arsenic trioxide on tissue factor expression in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells". Chin. Med. J. 114 (1): 30–4. PMID 11779431.
- ↑ Bogdanov VY, Balasubramanian V, Hathcock J, Vele O, Lieb M, Nemerson Y (April 2003). "Alternatively spliced human tissue factor: a circulating, soluble, thrombogenic protein". Nat. Med. 9 (4): 458–62. doi:10.1038/nm841. PMID 12652293.
- ↑ Muller YA, Ultsch MH, de Vos AM (Feb 1996). "The crystal structure of the extracellular domain of human tissue factor refined to 1.7 Å resolution". Journal of Molecular Biology. 256 (1): 144–159. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1996.0073. PMID 8609606.
- ↑ Carlsson K, Freskgård PO, Persson E, Carlsson U, Svensson M (Jun 2003). "Probing the interface between factor Xa and tissue factor in the quaternary complex tissue factor-factor VIIa-factor Xa-tissue factor pathway inhibitor". Eur. J. Biochem. 270 (12): 2576–82. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1033.2003.03625.x. PMID 12787023.
- ↑ Zhang E, St Charles R, Tulinsky A (Feb 1999). "Structure of extracellular tissue factor complexed with factor VIIa inhibited with a BPTI mutant". J. Mol. Biol. 285 (5): 2089–104. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1998.2452. PMID 9925787.
Further reading
- Gouault-Helimann M, Josso F (1979). "[Initiation in vivo of blood coagulation. The role of white blood cells and tissue factor (author's transl)]". Nouv Presse Med. 8 (40): 3249–53. PMID 392457.
- Mackman N (1995). "Regulation of the tissue factor gene". FASEB J. 9 (10): 883–9. PMID 7615158.
- McVey JH (1999). "Tissue factor pathway". Best Practice & Research. Clinical Haematology. 12 (3): 361–72. PMID 10856975.
- Konigsberg W, Kirchhofer D, Riederer MA, Nemerson Y (2001). "The TF:VIIa complex: clinical significance, structure-function relationships and its role in signaling and metastasis". Thromb. Haemost. 86 (3): 757–71. PMID 11583305.
- Versteeg HH, Peppelenbosch MP, Spek CA (2001). "The pleiotropic effects of tissue factor: a possible role for factor VIIa-induced intracellular signalling?". Thromb. Haemost. 86 (6): 1353–9. PMID 11776298.
- Fernandez PM, Rickles FR (2002). "Tissue factor and angiogenesis in cancer". Curr. Opin. Hematol. 9 (5): 401–6. doi:10.1097/00062752-200209000-00003. PMID 12172458.
- Golino P (2002). "The inhibitors of the tissue factor:factor VII pathway". Thromb. Res. 106 (3): V257–65. doi:10.1016/S0049-3848(02)00079-8. PMID 12356487.
- Engelmann B, Luther T, Müller I (2003). "Intravascular tissue factor pathway--a model for rapid initiation of coagulation within the blood vessel". Thromb. Haemost. 89 (1): 3–8. doi:10.1267/THRO03010003 (inactive 2017-01-15). PMID 12540946.
- Morrissey JH (2003). "Tissue factor: in at the start...and the finish?". J. Thromb. Haemost. 1 (5): 878–80. doi:10.1046/j.1538-7836.2003.00219.x. PMID 12871349.
- Yu JL, May L, Klement P, Weitz JI, Rak J (2004). "Oncogenes as regulators of tissue factor expression in cancer: implications for tumor angiogenesis and anti-cancer therapy". Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 30 (1): 21–30. doi:10.1055/s-2004-822968. PMID 15034795.
- Fernandez PM, Patierno SR, Rickles FR (2004). "Tissue factor and fibrin in tumor angiogenesis". Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 30 (1): 31–44. doi:10.1055/s-2004-822969. PMID 15034796.
- Mackman N (2004). "Role of tissue factor in hemostasis, thrombosis, and vascular development". Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 24 (6): 1015–22. doi:10.1161/01.ATV.0000130465.23430.74. PMID 15117736.
- Belting M, Ahamed J, Ruf W (2005). "Signaling of the tissue factor coagulation pathway in angiogenesis and cancer". Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 25 (8): 1545–50. doi:10.1161/01.ATV.0000171155.05809.bf. PMID 15905465.
- Engelmann B (2007). "Initiation of coagulation by tissue factor carriers in blood". Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 36 (2): 188–90. doi:10.1016/j.bcmd.2005.12.020. PMID 16473535.
- Furie B, Furie BC (2007). "Cancer-associated thrombosis". Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 36 (2): 177–81. doi:10.1016/j.bcmd.2005.12.018. PMID 16490369.
- Mackman N (2007). "Alternatively spliced tissue factor - one cut too many?". Thromb. Haemost. 97 (1): 5–8. doi:10.1160/th06-11. PMID 17200762.
- Wiiger MT, Prydz H (2007). "The changing faces of tissue factor biology. A personal tribute to the understanding of the "extrinsic coagulation activation"". Thromb. Haemost. 98 (1): 38–42. doi:10.1160/th07-04-0289. PMID 17597988.
External links
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) 134390
- PDB Molecule of the Month Tissue factor - March 2006