Cardiac electrophysiology: Difference between revisions
m (Robot: Automated text replacement (-{{WikiDoc Cardiology Network Infobox}} +, -<references /> +{{reflist|2}}, -{{reflist}} +{{reflist|2}})) |
Rim Halaby (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
{{CMG}} | {{CMG}} | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
'''Cardiac electrophysiology''' (also referred to as '''clinical cardiac electrophysiology''' , '''Arrhythmia Services''' , or '''electrophysiology''') is the science of the mechanisms, functions, and performance of the electrical activities of specific regions of the [[heart]]. | |||
'''Cardiac electrophysiology''' (also referred to as '''clinical cardiac electrophysiology''' , '''Arrhythmia Services''' , or '''electrophysiology''') is the science of the mechanisms, functions, and performance of the electrical activities of specific regions of the [[heart]]. | ==The Cardiac Conduction System== | ||
==[[Cardiac action potential|Normal Cardiac Action Potential]]== | |||
==Electrophysiology Studies and Therapeutic Modalities== | |||
===Overview=== | |||
An '''electrophysiologic study''' is a term used to describe a number of invasive (intracardiac) and non-invasive recording of spontaneous electrical activity as well as of cardiac responses to [[programmed electrical stimulation]]. These studies are performed to assess [[arrhythmias]], elucidate symptoms, evaluate abnormal [[electrocardiograms]], assess risk of developing arrhythmias in the future, and design treatment. These procedures increasingly include therapeutic methods (typically [[radiofrequency ablation]]) in addition to diagnostic and prognostic procedures. Other therapeutic modalities employed in this field include [[antiarrhythmic drug]] therapy and implantation of [[artificial pacemaker|pacemakers]] and [[implantable cardioverter-defibrillators]]. | An '''electrophysiologic study''' is a term used to describe a number of invasive (intracardiac) and non-invasive recording of spontaneous electrical activity as well as of cardiac responses to [[programmed electrical stimulation]]. These studies are performed to assess [[arrhythmias]], elucidate symptoms, evaluate abnormal [[electrocardiograms]], assess risk of developing arrhythmias in the future, and design treatment. These procedures increasingly include therapeutic methods (typically [[radiofrequency ablation]]) in addition to diagnostic and prognostic procedures. Other therapeutic modalities employed in this field include [[antiarrhythmic drug]] therapy and implantation of [[artificial pacemaker|pacemakers]] and [[implantable cardioverter-defibrillators]]. | ||
A specialist in cardiac electrophysiology is known as a cardiac electrophysiologist, or (more commonly) simply an electrophysiologist. Cardiac electrophysiology is considered a subspecialty of [[cardiology]], and in most countries requires two or more years of [[fellowship]] training beyond a general cardiology fellowship. They are trained to perform interventional cardiac EP procedures as well as surgical device implantations. | A specialist in cardiac electrophysiology is known as a cardiac electrophysiologist, or (more commonly) simply an electrophysiologist. Cardiac electrophysiology is considered a subspecialty of [[cardiology]], and in most countries requires two or more years of [[fellowship]] training beyond a general cardiology fellowship. They are trained to perform interventional cardiac EP procedures as well as surgical device implantations. | ||
==Diagnostic testing== | ===Diagnostic testing=== | ||
* Ambulatory electrocardiographic monitoring - Holter recording and interpretation, loop recording and interpretation; | * Ambulatory electrocardiographic monitoring - Holter recording and interpretation, loop recording and interpretation; | ||
| Line 34: | Line 33: | ||
* [[Electrophysiologic study]] (EPS) consists in the insertion of pacing and recording electrodes either in the oesophagus (intra-oesophageal EPS) or, through blood vessels, directly into the heart chambers (intra-cardiac EPS) in order to measure electrical properties of the heart and, in the case of intra-cardiac EPS, to electrically stimulate it in the attempt to induce arrhythmias for diagnostic purposes ("programmed electrical stimulation"). | * [[Electrophysiologic study]] (EPS) consists in the insertion of pacing and recording electrodes either in the oesophagus (intra-oesophageal EPS) or, through blood vessels, directly into the heart chambers (intra-cardiac EPS) in order to measure electrical properties of the heart and, in the case of intra-cardiac EPS, to electrically stimulate it in the attempt to induce arrhythmias for diagnostic purposes ("programmed electrical stimulation"). | ||
==Medical treatment== | ===Medical treatment=== | ||
* Initital administration and monitoring of the effect of drugs for treatment of heart rhythm disorders. Electrophysiologists are often involved when severe or life threatening [[arrhythmias]] are being treated, or when multiple drugs must be used to treat an arrhythmia. | * Initital administration and monitoring of the effect of drugs for treatment of heart rhythm disorders. Electrophysiologists are often involved when severe or life threatening [[arrhythmias]] are being treated, or when multiple drugs must be used to treat an arrhythmia. | ||
==Catheter ablation== | ===Catheter ablation=== | ||
* Ablation therapy - Catheter based creation of lesions in the heart (with radiofrequency energy, cryotherapy (destructive freezing), or ultrasound energy) to cure or control arrhythmias (see [[radiofrequency ablation]]). Ablation is usually performed during the same procedure as the electrophysiology study which induces and confirms the diagnosis of the arrhythmia for which ablation therapy is sought. | * Ablation therapy - Catheter based creation of lesions in the heart (with radiofrequency energy, cryotherapy (destructive freezing), or ultrasound energy) to cure or control arrhythmias (see [[radiofrequency ablation]]). Ablation is usually performed during the same procedure as the electrophysiology study which induces and confirms the diagnosis of the arrhythmia for which ablation therapy is sought. | ||
| Line 44: | Line 43: | ||
* "Complex" ablations include ablation for arrhythmias such as [[multifocal atrial tachycardia]], [[atrial fibrillation]], and [[ventricular tachycardia]]. In addition to the apparatus used for a "non-complex" ablation, these procedures often make use of sophisticated computer mapping systems to localize the source of the abnormal rhythm and to direct delivery of ablation lesions. | * "Complex" ablations include ablation for arrhythmias such as [[multifocal atrial tachycardia]], [[atrial fibrillation]], and [[ventricular tachycardia]]. In addition to the apparatus used for a "non-complex" ablation, these procedures often make use of sophisticated computer mapping systems to localize the source of the abnormal rhythm and to direct delivery of ablation lesions. | ||
==Surgical Procedures: Pacemaker and Defibrillator | ===Surgical Procedures: Pacemaker and Defibrillator Implantation and Follow Up=== | ||
* Implantation of single and dual chamber pacemakers and defibrillators | * Implantation of single and dual chamber pacemakers and defibrillators | ||
* Implantation of "biventricular" pacemakers and defibrillators for patients with congestive heart failure | * Implantation of "biventricular" pacemakers and defibrillators for patients with congestive heart failure | ||
| Line 51: | Line 50: | ||
'''Scope of practice, tests and procedures:''' | '''Scope of practice, tests and procedures:''' | ||
==[[Mechanism of Arrhythmias]]== | ==[[Mechanism of Arrhythmias]]== | ||
Revision as of 15:19, 28 October 2012
| Cardiac electrophysiology | |
 | |
|---|---|
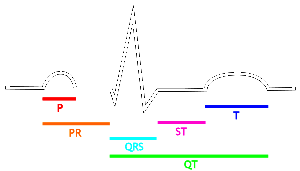
| Drawing of the EKG, with labels of intervals |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
Cardiac electrophysiology (also referred to as clinical cardiac electrophysiology , Arrhythmia Services , or electrophysiology) is the science of the mechanisms, functions, and performance of the electrical activities of specific regions of the heart.
The Cardiac Conduction System
Normal Cardiac Action Potential
Electrophysiology Studies and Therapeutic Modalities
Overview
An electrophysiologic study is a term used to describe a number of invasive (intracardiac) and non-invasive recording of spontaneous electrical activity as well as of cardiac responses to programmed electrical stimulation. These studies are performed to assess arrhythmias, elucidate symptoms, evaluate abnormal electrocardiograms, assess risk of developing arrhythmias in the future, and design treatment. These procedures increasingly include therapeutic methods (typically radiofrequency ablation) in addition to diagnostic and prognostic procedures. Other therapeutic modalities employed in this field include antiarrhythmic drug therapy and implantation of pacemakers and implantable cardioverter-defibrillators.
A specialist in cardiac electrophysiology is known as a cardiac electrophysiologist, or (more commonly) simply an electrophysiologist. Cardiac electrophysiology is considered a subspecialty of cardiology, and in most countries requires two or more years of fellowship training beyond a general cardiology fellowship. They are trained to perform interventional cardiac EP procedures as well as surgical device implantations.
Diagnostic testing
- Ambulatory electrocardiographic monitoring - Holter recording and interpretation, loop recording and interpretation;
- Tilt table testing;
- Signal-averaged electrocardiogram (SAECG) interpretation, also referred to as "late potentials" reading;
- Electrophysiologic study (EPS) consists in the insertion of pacing and recording electrodes either in the oesophagus (intra-oesophageal EPS) or, through blood vessels, directly into the heart chambers (intra-cardiac EPS) in order to measure electrical properties of the heart and, in the case of intra-cardiac EPS, to electrically stimulate it in the attempt to induce arrhythmias for diagnostic purposes ("programmed electrical stimulation").
Medical treatment
- Initital administration and monitoring of the effect of drugs for treatment of heart rhythm disorders. Electrophysiologists are often involved when severe or life threatening arrhythmias are being treated, or when multiple drugs must be used to treat an arrhythmia.
Catheter ablation
- Ablation therapy - Catheter based creation of lesions in the heart (with radiofrequency energy, cryotherapy (destructive freezing), or ultrasound energy) to cure or control arrhythmias (see radiofrequency ablation). Ablation is usually performed during the same procedure as the electrophysiology study which induces and confirms the diagnosis of the arrhythmia for which ablation therapy is sought.
- "Non-complex" ablations include ablation for arrhythmias such as: AV nodal reentrant tachycardia, Accessory pathway mediated tachycardia, atrial flutter. These procedures are usually performed using intracardiac catheters (as are used during an electrophysiologic study), fluoroscopy (a real-time X-ray camera), and electrical recordings from the inside of the heart.
- "Complex" ablations include ablation for arrhythmias such as multifocal atrial tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, and ventricular tachycardia. In addition to the apparatus used for a "non-complex" ablation, these procedures often make use of sophisticated computer mapping systems to localize the source of the abnormal rhythm and to direct delivery of ablation lesions.
Surgical Procedures: Pacemaker and Defibrillator Implantation and Follow Up
- Implantation of single and dual chamber pacemakers and defibrillators
- Implantation of "biventricular" pacemakers and defibrillators for patients with congestive heart failure
- Implantation of loop recorders (implanted ECG recorders for long term monitoring of ECG to allow for diagnosis of an arrhythmia)
- Clinical follow up and reprogramming of implanted devices
Scope of practice, tests and procedures:
Mechanism of Arrhythmias
Antiarrhythmic Medications
EP study basics
Diseases of the Conduction System and Bradyarrhythmias
Narrow Complex Tachycardias
Atrial Flutter
Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial Tachycardia
AV Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia
Circus Movement Tachycardia
Wide Complex Tachycardias
WPW Syndrome
Ventricular Tachycardia
Ventricular Tachyarrhythmias in Structurally Normal Hearts
Brugada Syndrome
Long QT Syndrome
Ventricular Tachyarrhythmias, Cardiac Arrest and Sudden Cardiac Death
Syncope
Indications for Pacemakers
Indications for an ICD
Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy
Arrhythmias in Pregnancy
See also
- Clinical cardiac electrophysiology
- Electrical conduction system of the heart
- Electrocardiogram (EKG)
- Electrophysiologic study
- Cardiology
- Cardiac arrhythmia
External links