Bifascicular block: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
m (Bot: Automated text replacement (-{{SIB}} + & -{{EH}} + & -{{EJ}} + & -{{Editor Help}} + & -{{Editor Join}} +)) |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
'''Associate Editor-In-Chief:''' {{CZ}} | '''Associate Editor-In-Chief:''' {{CZ}} | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
| Line 80: | Line 80: | ||
{{Circulatory system pathology}} | {{Circulatory system pathology}} | ||
{{Electrocardiography}} | {{Electrocardiography}} | ||
[[Category:Cardiology]] | [[Category:Cardiology]] | ||
Revision as of 22:54, 8 August 2012
| Bifascicular block | |
 | |
|---|---|
| ICD-10 | I45.2 |
| ICD-9 | 426.53 |
| Cardiology Network |
 Discuss Bifascicular block further in the WikiDoc Cardiology Network |
| Adult Congenital |
|---|
| Biomarkers |
| Cardiac Rehabilitation |
| Congestive Heart Failure |
| CT Angiography |
| Echocardiography |
| Electrophysiology |
| Cardiology General |
| Genetics |
| Health Economics |
| Hypertension |
| Interventional Cardiology |
| MRI |
| Nuclear Cardiology |
| Peripheral Arterial Disease |
| Prevention |
| Public Policy |
| Pulmonary Embolism |
| Stable Angina |
| Valvular Heart Disease |
| Vascular Medicine |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Associate Editor-In-Chief: Cafer Zorkun, M.D., Ph.D. [2]
Overview
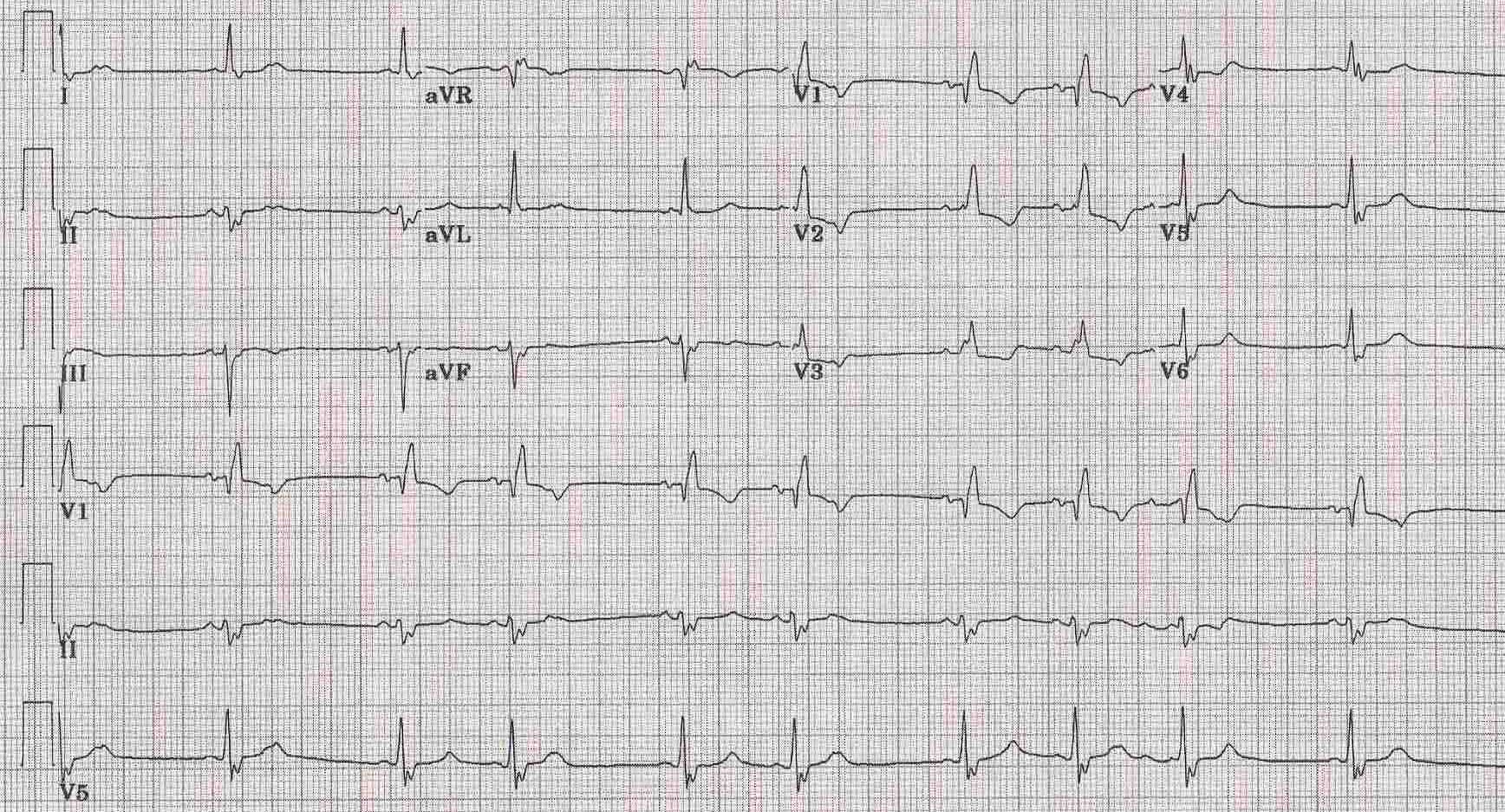
Bifascicular block is a conduction abnormality in the heart where two of the three main fascicles of the His/Purkinje system are blocked.
Most commonly, it refers to a combination of right bundle branch block (RBBB) and either left anterior fascicular block (LAFB) or left posterior fascicular block (LPFB).
Some authors consider left bundle branch block (LBBB) to be a technical bifascicular block, since the block occurs above the bifurcation of the left anterior and left posterior fascicles of the left bundle branch.
ACC / AHA Guidelines- Recommendations for Permanent Pacing in Chronic Bifascicular Block (DO NOT EDIT) [1]
| “ |
Class I1. Permanent pacemaker implantation is indicated for advanced second-degree AV block or intermittent third-degree AV block. (Level of Evidence: B) 2. Permanent pacemaker implantation is indicated for type II second-degree AV block. (Level of Evidence: B) 3. Permanent pacemaker implantation is indicated for alternating bundle-branch block. (Level of Evidence: C) Class IIa1. Permanent pacemaker implantation is reasonable for syncope not demonstrated to be due to AV block when other likely causes have been excluded, specifically ventricular tachycardia (VT). (Level of Evidence: B) 2. Permanent pacemaker implantation is reasonable for an incidental finding at electrophysiological study of a markedly prolonged HV interval (greater than or equal to 100 milliseconds) in asymptomatic patients. (Level of Evidence: B) 3. Permanent pacemaker implantation is reasonable for an incidental finding at electrophysiological study of pacing-induced infra-His block that is not physiological. (Level of Evidence: B) Class IIb1. Permanent pacemaker implantation may be considered in the setting of neuromuscular diseases such as myotonic muscular dystrophy, Erb dystrophy (limb-girdle muscular dystrophy), and peroneal muscular atrophy with bifascicular block or any fascicular block, with or without symptoms. (Level of Evidence: C) Class III1. Permanent pacemaker implantation is not indicated for fascicular block without AV block or symptoms. (Level of Evidence: B) 2. Permanent pacemaker implantation is not indicated for fascicular block with first-degree AV block without symptoms. (Level of Evidence: B) |
” |
External links
- Template:GPnotebook
- http://sprojects.mmi.mcgill.ca/heart/ecg970516-7dx.html
- http://library.med.utah.edu/kw/ecg/mml/ecg_12lead047.html
Additional Reading
- Moss and Adams' Heart Disease in Infants, Children, and Adolescents Hugh D. Allen, Arthur J. Moss, David J. Driscoll, Forrest H. Adams, Timothy F. Feltes, Robert E. Shaddy, 2007 ISBN 0781786843
- Braunwald's Heart Disease, Libby P, 8th ed., 2007, ISBN 978-1-41-604105-4
- Hurst's the Heart, Fuster V, 12th ed. 2008, ISBN 978-0-07-149928-6
- Willerson JT, Cardiovascular Medicine, 3rd ed., 2007, ISBN 978-1-84628-188-4
Sources
- The ACC/AHA/HRS 2008 Guidelines for Device-Based Therapy of Cardiac Rhythm Abnormalities [1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Epstein AE, DiMarco JP, Ellenbogen KA, Estes NAM III, Freedman RA, Gettes LS, Gillinov AM, Gregoratos G, Hammill SC, Hayes DL, Hlatky MA, Newby LK, Page RL, Schoenfeld MH, Silka MJ, Stevenson LW, Sweeney MO. ACC/AHA/HRS 2008 guidelines for device-based therapy of cardiac rhythm abnormalities: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (Writing Committee to Revise the ACC/AHA/NASPE 2002 Guideline Update for Implantation of Cardiac Pacemakers and Antiarrhythmia Devices). Circulation. 2008; 117: 2820–2840. PMID 18483207