Left ventricular hypertrophy
Template:DiseaseDisorder infobox
| Cardiology Network |
 Discuss Left ventricular hypertrophy further in the WikiDoc Cardiology Network |
| Adult Congenital |
|---|
| Biomarkers |
| Cardiac Rehabilitation |
| Congestive Heart Failure |
| CT Angiography |
| Echocardiography |
| Electrophysiology |
| Cardiology General |
| Genetics |
| Health Economics |
| Hypertension |
| Interventional Cardiology |
| MRI |
| Nuclear Cardiology |
| Peripheral Arterial Disease |
| Prevention |
| Public Policy |
| Pulmonary Embolism |
| Stable Angina |
| Valvular Heart Disease |
| Vascular Medicine |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Associate Editor-In-Chief: Cafer Zorkun, M.D., Ph.D. [2]
Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is the thickening of the myocardium (muscle) of the left ventricle of the heart. While ventricular hypertrophy can occur naturally as a reaction to aerobic exercise and strength training, it is most frequently referred to as a pathological reaction to cardiovascular disease.
While LVH itself is not a disease, it is usually a marker for disease involving the heart. Disease processes that can cause LVH include any disease that increases the afterload that the heart has to contract against, and some primary diseases of the muscle of the heart.
Causes of increased afterload that can cause LVH include aortic stenosis, aortic insufficiency, and hypertension. Primary disease of the muscle of the heart that cause LVH are known as hypertrophic cardiomyopathies.
Complete Differential Diagnosis of Causes of Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
- Acromegaly
- Alcoholic cardiomyopathy
- Aortic coarctation
- Aortic regurgitation
- Aortic stenosis
- Chronic Renal Failure
- Familial dilated and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM)
- Idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy
- Mitral regurgitation
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus
- Restrictive cardiomyopathy
- Thalassemia
Diagnosis
The principal method to diagnose LVH is echocardiography, during which the thickness of the muscle of the heart can be measured. The electrocardiogram (ECG) often shows signs of increased voltage from the heart in individuals with LVH, so this is often used as a screening test to determine who should undergo further testing with an echocardiogram.
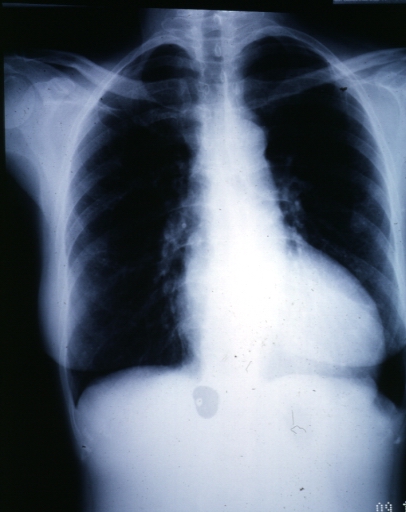
Chest x-ray
-
Chest X-ray: Left Ventricular Hypertrophy in a patient with aortic valve stenosis
Echocardiography
Two dimensional echocardiography can produce images of the left ventricle. The thickness of the left ventricle as visualized on echocardiography correlates with its actual mass. Normal thickness of the left ventricular myocardium is from 0.6 to 1.1 cm (as measured at the very end of diastole. If the myocardium is more than 1.1 cm thick, the diagnosis of LVH can be made.
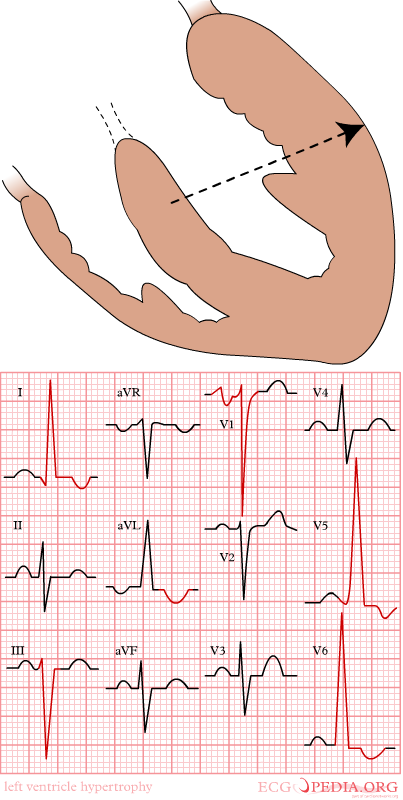
ECG criteria for LVH
There are multiple criteria used to diagnose LVH via electrocardiography. None of them are perfect. However, by using multiple different criteria the sensitivity and specificity are increased.
The Sokolow and Lyon criteria
- S in V1 + R in V5 or V6 (whichever is larger) =/> 35 mm
- R in aVL =/> 11 mm
The Cornell criteria1 for the ECG diagnosis of LVH involves measurement of the sum of the R wave in lead aVL and the S wave in lead V3. The Cornell criteria for LVH are:
- S in V3 + R in aVL > 28 mm (men)
- S in V3 + R in aVL > 20 mm (women)
Other voltage-based criteria for LVH include:
- Lead I: R wave > 14 mm
- Lead aVR: S wave > 15 mm
- Lead aVL: R wave > 12 mm
- Lead aVF: R wave > 21 mm
- Lead V5: R wave > 26 mm
- Lead V6: R wave > 20 mm
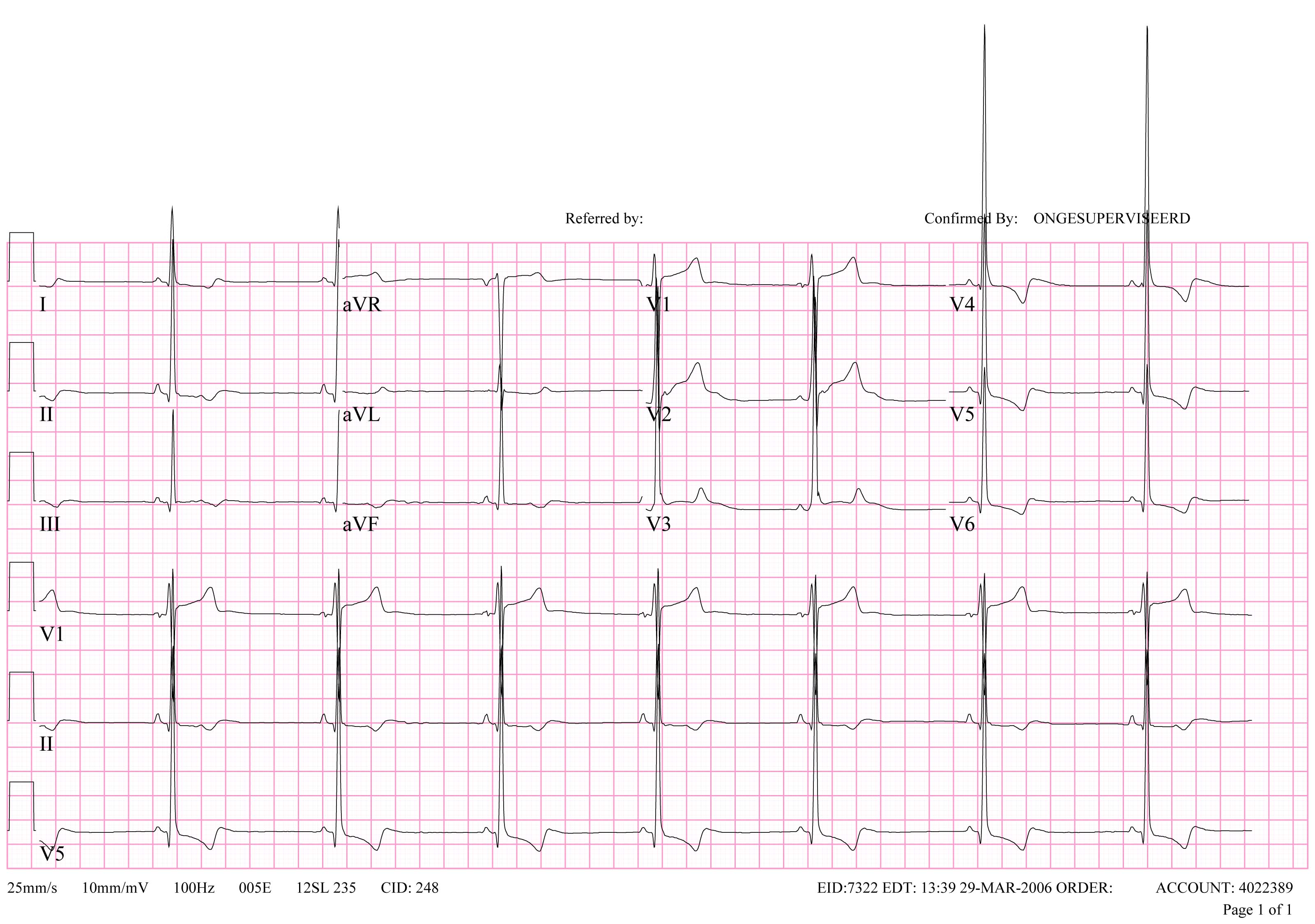
-
LVH: R in V5 is 26mm, S in V1 in 15mm. The sum is 41 mm which is more than 35 mm and therefore LVH is present according to the Sokolow-Lyon criteria.
-
ECG of patient with left ventricular hypertrophy according to the Sokolow-Lyon criteria
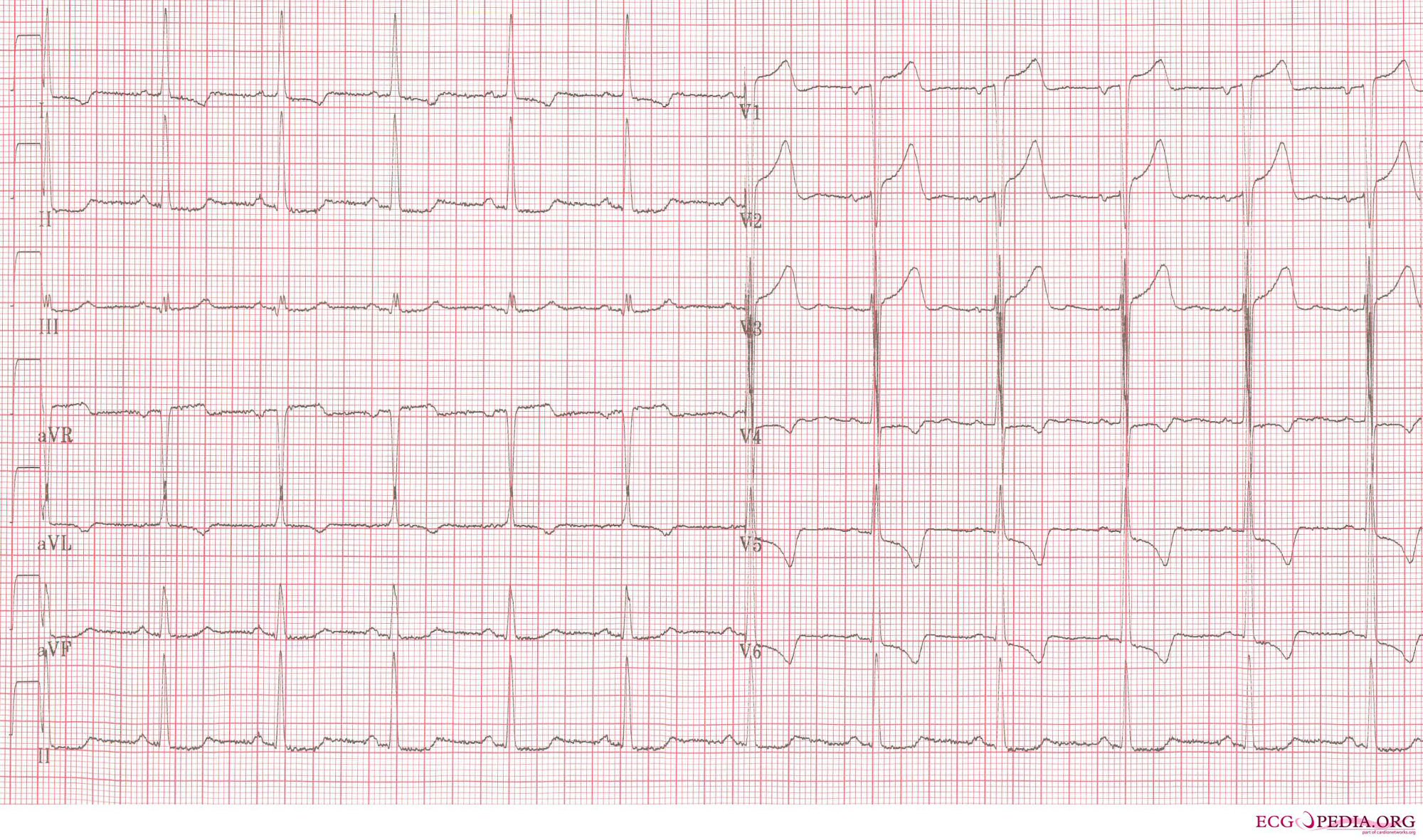
-
Another example of extreme left ventricular hypertrophy in a patient with severe aortic valve stenosis
-
ECG of a patient with LVH and subendocardial ischemia leading to positive cardiovascular markers in blood testing
See also
References
- Sokolow Sokolow M, Lyon TP: The ventricular complex in left verntricular hypterfophy as obtained by unipolar precordial and limb leads. Am Heart J 37: 161, 1949
- Sundström J, Lind L, Arnlöv J, Zethelius B, Andrén B, Lithell HO. Echocardiographic and electrocardiographic diagnoses of left ventricular hypertrophy predict mortality independently of each other in a population of elderly men Circulation. 2001 May 15;103(19):2346-51. PMID 11352882
- Levy D, Salomon M, D'Agostino RB, Belanger AJ, Kannel WB.Prognostic implications of baseline electrocardiographic features and their serial changes in subjects with left ventricular hypertrophy. Circulation. 1994 Oct;90(4):1786-93.Related Articles, Links PMID 7923663
- Casale PN, Devereux RB, Alonso DR, Campo E, Kligfield P (1987). "Improved sex-specific criteria of left ventricular hypertrophy for clinical and computer interpretation of electrocardiograms: validation with autopsy findings". Circulation. 75 (3): 565–72. PMID 2949887.
- Marriott, Henry J. L.; Wagner, Galen S. (2001). Marriott's practical electrocardiography. Hagerstwon, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 0683307460.
- Hammill S. C. Electrocardiographic diagnoses: Criteria and definitions of abnormalities, Chapter 18, MAYO Clinic, Concise Textbook of Cardiology, 3rd edition, 2007 ISBN 0-8493-9057-5
Additional resources
- ECGpedia: Course for interpretation of ECG
- The whole ECG - A basic ECG primer
- 12-lead ECG library
- Simulation tool to demonstrate and study the relation between the electric activity of the heart and the ECG
- ECG information from Children's Hospital Heart Center, Seattle
- ECG Challenge from the ACC D2B Initiative
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Diseases and Conditions Index
- A history of electrocardiography
- EKG Interpretations in infants and children