Orthostatic hypotension: Difference between revisions
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
**Adverse effects of certain [[medications]] | **Adverse effects of certain [[medications]] | ||
[[Image:barereflex.jpg]] | [[Image:barereflex.jpg|none|200x]] | ||
==Causes== | ==Causes== | ||
Revision as of 15:36, 13 February 2021
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Sogand Goudarzi, MD [2]; Norina Usman, M.B.B.S[3]
Synonyms and keywords: Postural hypotension; orthostatic intolerance; head rush; dizzy spell
Overview
Orthostatic hypotension or postural hypotension is defined as a reduction of systolic blood pressure of at least 20 mm Hg or 10 mm Hg in diastolic blood pressure within 3 minutes of standing. A similar fall during head-up tilt test at 60 degrees also defines orthostatic hypotension. Orthostatic hypotension may be asymptomatic or may cause symptoms of lightheadedness, dizziness, blurred vision or cognitive impairment. It may have acute or chronic causes. Management of orthostatic hypotension may be challenging, in particular in patients with orthostatic hypotension and concomitant supine hypertension. [1][2][3].
Classification
- Based on the underlying pathophysiology correlated to a postural drop in blood pressure, orthostatic hypotension can be classified into:
Initial orthostatic hypotension (iOH)
- It is most common in healthy adolescents
- It is demarcated as a brief BP decrease of >40 mmHg systolic or >20 mmHg diastolic with symptomatic cerebral hypoperfusion within five to fifteen seconds after standing, typically resolves by twenty seconds.
Neurogenic orthostatic hypotension (nOH)
- In Neurogenic orthostatic hypotension, the sympathetic noradrenergic nerves continually fail to facilitate the reflexive cardiovascular responses essential to sustain blood pressure in response to orthostatic stress.
- It is described as a constant BP decrease of >20 mmHg systolic or >10 mmHg diastolic, without or with symptoms, within three minutes of head-up tilt or standing.
Delayed orthostatic hypotension (dOH)
- Delayed orthostatic hypotension (dOH) is demarcated as a fall in blood pressure that accomplishes neurogenic orthostatic hypotension criteria but ensues after three minutes.
Neurally mediated syncope (vOH)
- It is also recognized as vasodepressor or vasovagal syncope, It involves a paroxysmal extraction of sympathetic vasopressor tone, frequently during prolonged standing, in patients with an effective autonomic nervous system.
Cardiovascular orthostatic hypotension (cOH)
- Cardiovascular orthostatic hypotension occurs from intravascular hypovolemia or reduced cardiac output along with compensatory tachycardia.
Orthostatic pseudohypotension (pOH)
- It is stated as apparent orthostatic hypotension when baseline supine blood pressure is raised, which may be due to a short time at rest to create a valid baseline, related recumbent hypertension, or fluctuation of baseline blood pressure with labile hypertension[4][5][6][7].
Pathophysiology
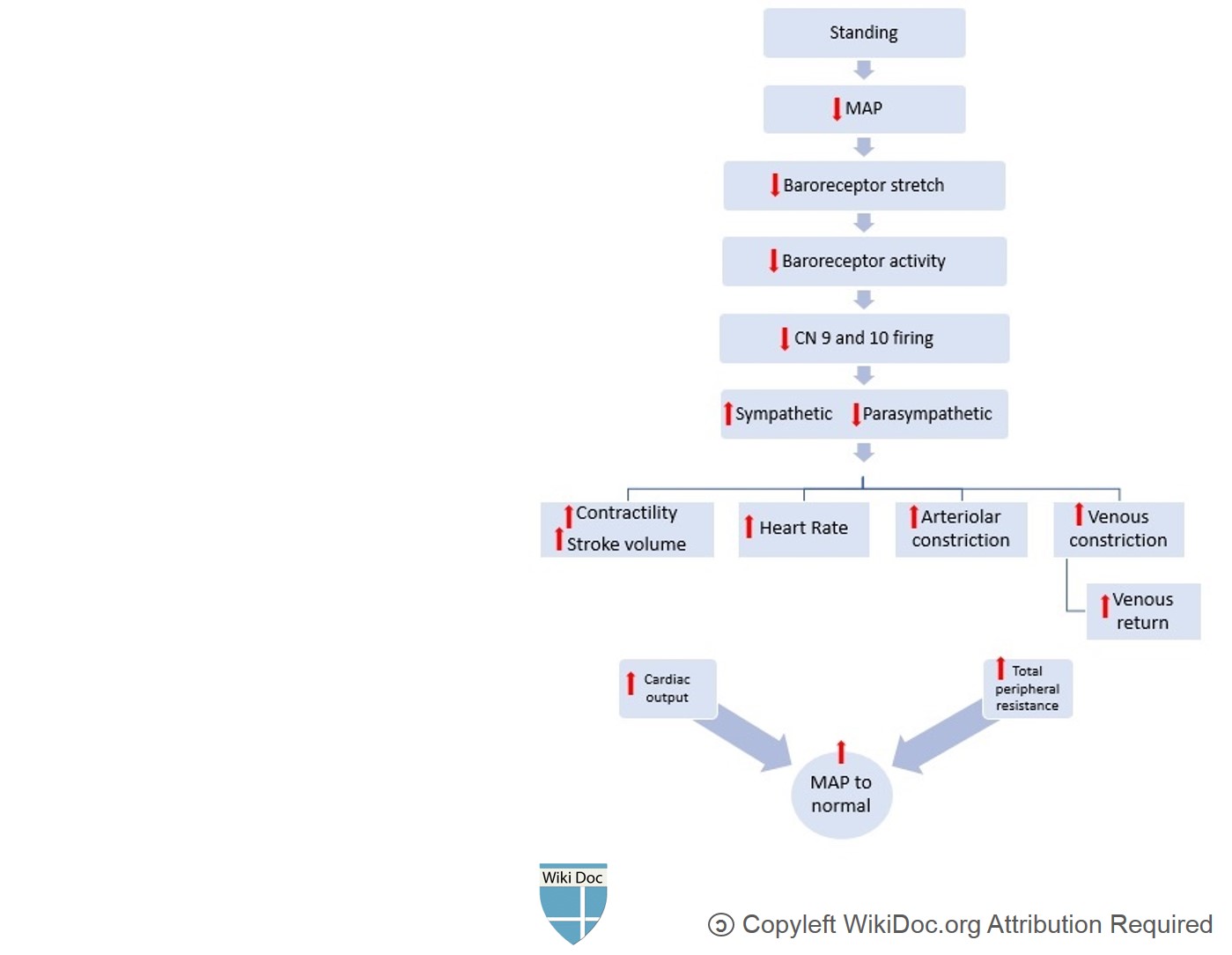
- In standing position, 500 to 1000 mL of blood pools in the lower extremities and splanchnic circulation, causing a rapid decline in venous return to the heart.
- Decreased ventricular filling pressures lower cardiac output and systemic blood pressure. [8][9][10][11][12].
- Baroreceptors located mainly in the aorta and carotid arteries are very sensitive to fluctuations in blood pressure. A fall in blood pressure decreases the stretching of baroreceptors, thus decreasing their firing. The decreased firing of baroreceptors increases sympathetic and decreases parasympathetic outflow.
- This compensatory reflex increases heart rate, contractility and peripheral vascular resistance (i.e., both arteriolar and venous vasoconstriction). These changes result in increased venous return and increased cardiac output, and limit the decline in blood pressure. This compensatory reflex is known as baroreflex.
- Any disruption in this pathway can cause a significant decline in blood pressure upon standing (i.e., orthostatic hypotension), causing symptoms of cerebral hypoperfusion including nausea, dizziness, headache, lightheadedness, blurred vision, and impaired cognition.
- Although many pathologic causes may alter this normal physiologic response to standing, the most common pathophysiologic mechanisms include:
- Autonomic dysfunction affecting the baroreflex (i.e. baroreflex dysfunction)
- Volume depletion
- Adverse effects of certain medications
Causes
Common causes of orthostsic hypotension include: [13][14][15][16].
| Causes of orthostatic hypotension |
| Cardiac diseases |
| Intravascular volume depletion |
| Venous pooling/venous vasodilation |
| Autonomic nervous system disorders |
|
|
| Endocrine |
|
| Medications |
| Miscellaneous |
| Medication-induced Orthostatic Hypotension | |
| Mechanism | Examples |
| Vasodilation through Alpha-1 blockade | |
| Vasodilation (Others) | |
| Volume depletion | |
| Sympathetic blockade | |
| Dopamin agonists and other anti-Parkinsonian medications | |
| Others | |
Differentiating Orthostatic Hypotension from Other Diseases
Orthostatic hypotension must be differentiated from neurogenic syncope, cardiogenic syncope, situational syncope, multiple system atrophy with orthostatic hypotension, neurally mediated hypotension, postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS) and vasovagal syncope[17][18][19][20][21][22][23].
| Disease | History and Physical Examination | Diagnostic approach | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lightheadedness | Fatigue | Autonomic symptoms | Fever | Nausea/vomiting | Diminished Vision | Dizziness | Slurred Speech | Tachycardia | Altered mentation | Loss of Consciousness | Weakness | Neurological Deficit | Labs and CSF findings | ECG | CT/MRI | Gold standard test | |
| Multiple system atrophy with orthostatic hypotension | + | + | + | - | - | + | + | + | - | + | - | + | + | - | - | Atrophy of brain stem and cerebellum | Clinical assesment |
| Neurally mediated hypotension | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | + | - | + | - | + | - | - | - | - | Clinical assesment |
| Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS) | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | Clinical assesment |
| Neurologic syncope | + | - | + | - | + | +/- | + | - | - | - | + | +/- | - | - | - | - | Clinical assessment |
| Cardiac syncope | + | + | + | _ | + | + | + | + | + | +/- | + | + | - | - | + | - | ECG, Holter monitor, Echocardiography |
| Situational syncope | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | +/- | +/- | +/- | + | +/- | - | - | - | - | Clinical assessment syncope occurs during defecation, micturition or coughing |
| Vasovagal syncope (also known as cardio-neurogenic syncope) | + | + | + | - | + | +/- | + | + | - | + | + | +/- | - | + | + | - | ECG, Echocardiogram, Exercise stress test. |
Epidemiology and Demographics
Incidence
- The approximation of orthostatic hypotension‐associated hospitalization is 36 per 100,000 adults, and the rate can be as high as 233 per 100,000 patients >75 years of age[24].
Prevalence
- The overall prevalence of orthostatic hypotension depends on age as it increases with age in the general population.
- The prevalence ranges from 5% in patients <50 years of age to 30% in those >70 years of age.
- It is ~20% in > 65-year-old patients[25][26].
Age
- Orthostatic Hypotension is commonly seen in individuals older than 50 years of age.
Gender
- Orthostatic hypotension affects men and women equally.
Risk Factors
Common risk factors in the development of orthostatic hypotension include:[27][28]
- Age (>65)
- Medications
- Autonomic neuropathies, such asParkinson's disease, diabetes
- Volume depletion
- Postpartum period
- Prolong bedrest.
Screening
- Orthostatic hypotension, screening consists of blood pressure measurements in supine (or sitting) and standing position during clinical consultations[29].
Natural History, Complications, and Prognosis
Natural History
- The symptoms of orthostatic hypotension mainly develop in the elderly, and start with generalized symptoms of dizziness, lightheadedness, or syncope and less frequently with headache, leg buckling, or chest pain[30][1].
Complications
Common complications of orthostatic hypotension include:[31][32]
- Symptomatic orthostatic hypotension may cause falling.
- The risk of recurrent falls is particularly higher in frail older adults.
- According to various studies, orthostatic hypotension may be a risk factor for:
- Cardiovascular and all-cause mortality
- Cardiovascular events
- Congestive heart failure
- Atrial fibrillation
- Cognitive decline or dementia
- Anxiety, depression, and impaired quality of life
Prognosis
- Depending on the underlying cause of orthostatic hypotension, the prognosis may vary.
Diagnosis
Diagnostic study of choice
- Orthostatic vitals are the best diagnostic tests that are simple and easy to perform in a clinical setting.
- Blood pressure and heart rate should be measured within 2-5 minutes of standing after a 5-minute period of supine rest.
- Orthostatic hypotension is diagnosed when there is:
- At least a 20 mmHg decline in systolic blood pressure
- At least 10 mmHg decline in diastolic blood pressure
- The absence of the normal rise in heart rate on standing is a diagnostic clue to the presence of autonomic dysfunction; however, an increased heart rate cannot exclude autonomic failure.
History and Symptoms
- When evaluating a patient with orthostatic hypotension, the following features in history may provide a clue to the diagnosis:
- Use of certain medications known to cause orthostatic hypotension.
- Recent history of volume depletion (such as fever, fluid restriction, vomiting, diarrhea, hemorrhage)
- Medical history of common diseases causing orthostatic hypotension, such as congestive heart failure, diabetes, Parkinson's disease, malignancies.
- History of alcohol consumption
- Particular attention should be made to the presence of neurologic symptoms (e.g., parkinsonism, ataxia, peripheral neuropathy) or symptoms of autonomic dysfunction (e.g. abnormal pupillary response, chronic constipation, erectile dysfunction, urinary incontinence)
- Symptoms of orthostatic hypotension are prominent immediately upon standing, might improve in sitting position, and disappear in the supine position (i.e., postural symptoms) [33][34].
- Symptoms may also be seen in association with meals, exercise, and prolonged standing
- Symptoms are due to cerebral hypoperfusion
- Symptoms usually last for few minutes
- The most common symptoms are lightheadedness and dizziness upon standing.
- Other symptoms include:
Physical Examination
Common physical examination findings of orthostatic hypotension include checking the blood pressure, pulse, and symptoms while having the patient in the standing and sitting position[35].
Laboratory Findings
There are no diagnostic laboratory findings associated with orthostatic hypotension. While the definitive diagnosis of orthostatic hypotension is made clinically, other tests contribute to understanding the risks of disease and may provide clues to the selection of treatment options. These tests include those that access the underlying cause that may be altered in patients suffering from orthostatic hypotension. Addressing these conditions may improve the quality of life of a patient.
Electrocardiogram
An ECG may be helpful in the diagnosis of cardiovascular causes of orthostatic hypotension.
X-ray
There are no x-ray findings associated with orthostatic hypotension.
Echocardiography
Echocardiography may be helpful in the diagnosis of orthostatic hypotension. Findings on an echocardiography diagnostic of orthostatic hypotension include cardiac structural changes such as left ventricular hypertrophy, development of diastolic dysfunction, and decrease right chamber volume [36].
CT scan
CT scan may be helpful in the diagnosis of orthostatic hypotension. Findings on CT scan diagnostic of orthostatic hypotension include the presence of a cerebral tumor or communicating hydrocephalus[37].
MRI
Brain MRI may be helpful in the diagnosis of orthostatic hypotension. Findings on MRI suggestive of orthostatic hypotension include:
Other Imaging Findings
There are no other diagnostic studies associated with orthostatic hypotension.
Other Diagnostic Studies
There are no other diagnostic studies associated with orthostatic hypotension.
Treatment
- Asymptomatic hypotension is a common finding in practice and does not require any treatment.
- There is no specific target blood pressure goals in the management of orthostatic hypotension.
- However, management is targeted to alleviate symptoms, prevention of future falls, and excessive supine hypertension.
- Management of orthostatic hypotension can be categorized into lifestyle modifications and medical therapy.
- Education of the patient and non-pharmacological treatments are the cornerstone of treatment of orthostatic hypotension.
| Drop of systolic BP > 20 mmHg (30 for hypertensive patients) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symptomatic | Asymptomatic | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-pharmacological treatment | Observation and follow-up | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Persistance of symtoms | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pharmacological Treatment | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| No supine hypertension or chronic heart failure | Supine hypertension or chronic heart failure: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fludrocortisone Midodrine | Midodrine | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Non Pharmacological Therapy
- Education of the patient and non-pharmacological treatments are the cornerstone of treatment of orthostatic hypotension.[38][39][40][41][42][1][43]
- Cessation of orthostatic hypotension inducing drugs such as antihypertensives s in patients with mean blood pressure below target value is recommended.
- Avoidance of certain factors that aggravate hypotension such as heat, alcohol intake.
- Consumption of large meals induces splanchnic vasodilation thereby resulting in hypotension postprandially.
- Fractionated meals are recommended in patients with postprandial symptoms.
| Non-Pharmacological methods | Mechanism of alleviating hypotension | Recommendations |
|---|---|---|
| Elastic stockings |
|
|
| Physical Maneuvers |
|
|
| Head up tilt sleeping |
|
|
| Intravascular volume |
|
|
| Intake of cold water |
|
|
Medical Therapy
- Pharmacological: Some drugs that are used in the treatment of orthostatic hypotension include fludrocortisone (Florinef), erythropoietin, midodrine and Pyridostigmine bromide (Mestinon)[44][45][46][47]
Initial Therapy
- Preferred regimen (1): Fludrocortisone acetate at a dose of 0.1 mg per day, administered in the morning, which can eventually be increased up to 0.3 mg per day.
- Considered first-line regimen for hypotension in the absence of heart failure and supine hypertension
- Preferred regimen (2): Midodrine 2.5 to 10 mg three times a day.
- Max dose should not exceed 40 mg/day.
- Preferred regimen (2): Droxidopa starts at 100 mg and escalates to 600 mg three times per day.
- Patients should not take droxidopa within four to five hours of bedtime in order to limit supine hypertension.
Secondline Therapy
- Preferred regimen (1): Erythropoietin is administered SC or IV at doses between 25 to 75 units/kg three times a week.
- Preferred regimen (1): Methylxanthine caffeine 100 to 250 mg three times a day with meals.
- Preferred regimen (1): Pyridostigmine initiated at a dose of 30 mg three times daily, up to a maximum dose of 90 mg three times daily.
- Preferred regimen (1): Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are rarely effective as monotherapy
- They can supplement treatment with fludrocortisone or a sympathomimetic agent.
Thirdline Therpay
- Preferred regimen (1): Atomoxetine
- Preferred regimen (1): Vasopressin analogs (desmopressin (DDAVP))
- Preferred regimen (1): Yohimbine a single dose of yohimbine (5.4 mg).
- Yohimbine has limited availability in the United States.
- Preferred regimen (1): Somatostatin subcutaneous doses range from 25 to 200 mcg.
- Preferred regimen (1): Ergotamine-caffeine (1 mg/100 mg) up to twice-daily dosing in patients with orthostatic hypotension.
- Preferred regimen (1): Metoclopramide and domperidone
Primary Prevention
Effective measures for the primary prevention of orthostatic hypotension include:
ABCDEF method
- A. Abdominal compression: Wear an abdominal binder when out of bed
- B. A bolus of water/elevate Bed: On bad days, drink two 8-ounce glasses of cold water prior to prolonged standing and sleep with the head of the bed raised about 4 inches
- C. Counter-maneuvers: While standing, contract the lower abdominal muscles for about 30 seconds
- D. Drugs: Midodrine, Pyridostigmine, or Fludrocortisone can be used to elevate blood pressure (acknowledge any medications currently taken that can lower blood pressure)
- E. Education & Exercise: Note any symptoms that indicate a fall in blood pressure while standing, recognize conditions that lower blood pressure (i.e. heavy metals, temperature changes, exercise, change in position)
- F. Fluids: Stay hydrated
References
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 1.2 Bradley JG, Davis KA (2003). "Orthostatic hypotension". Am Fam Physician. 68 (12): 2393–8. PMID 14705758.
- ↑ Rutan GH, Hermanson B, Bild DE, Kittner SJ, LaBaw F, Tell GS (1992). "Orthostatic hypotension in older adults. The Cardiovascular Health Study. CHS Collaborative Research Group". Hypertension. 19 (6 Pt 1): 508–19. doi:10.1161/01.hyp.19.6.508. PMID 1592445.
- ↑ Ooi WL, Barrett S, Hossain M, Kelley-Gagnon M, Lipsitz LA (1997). "Patterns of orthostatic blood pressure change and their clinical correlates in a frail, elderly population". JAMA. 277 (16): 1299–304. PMID 9109468.
- ↑ Schmoldt A, Benthe HF, Haberland G (1975). "Digitoxin metabolism by rat liver microsomes". Biochem Pharmacol. 24 (17): 1639–41. PMID https://doi.org/10.1007/s10286-016-0382-6 Check
|pmid=value (help). - ↑ Wieling W, Krediet CT, van Dijk N, Linzer M, Tschakovsky ME (2007). "Initial orthostatic hypotension: review of a forgotten condition". Clin Sci (Lond). 112 (3): 157–65. doi:10.1042/CS20060091. PMID 17199559.
- ↑ Freeman R, Wieling W, Axelrod FB, Benditt DG, Benarroch E, Biaggioni I; et al. (2011). "Consensus statement on the definition of orthostatic hypotension, neurally mediated syncope and the postural tachycardia syndrome". Clin Auton Res. 21 (2): 69–72. doi:10.1007/s10286-011-0119-5. PMID 21431947.
- ↑ Wieling W, Schatz IJ (2009). "The consensus statement on the definition of orthostatic hypotension: a revisit after 13 years". J Hypertens. 27 (5): 935–8. doi:10.1097/HJH.0b013e32832b1145. PMID 19390349.
- ↑ Lipsitz LA (1989). "Orthostatic hypotension in the elderly". N Engl J Med. 321 (14): 952–7. doi:10.1056/NEJM198910053211407. PMID 2674714.
- ↑ Low PA, Opfer-Gehrking TL, McPhee BR, Fealey RD, Benarroch EE, Willner CL; et al. (1995). "Prospective evaluation of clinical characteristics of orthostatic hypotension". Mayo Clin Proc. 70 (7): 617–22. doi:10.4065/70.7.617. PMID 7791382.
- ↑ Zaqqa M, Massumi A (2000). "Neurally mediated syncope". Tex Heart Inst J. 27 (3): 268–72. PMC 101078. PMID 11093411.
- ↑ Mathias CJ (1995). "Orthostatic hypotension: causes, mechanisms, and influencing factors". Neurology. 45 (4 Suppl 5): S6–11. PMID 7746371.
- ↑ Hollister AS (1992). "Orthostatic hypotension. Causes, evaluation, and management". West J Med. 157 (6): 652–7. PMC 1022100. PMID 1475949.
- ↑ Jiang W, Davidson JR. (2005). "Antidepressant therapy in patients with ischemic heart disease". Am Heart J. 150 (5): 871–81. PMID 16290952.
- ↑ Delini-Stula A, Baier D, Kohnen R, Laux G, Philipp M, Scholz HJ. (1999). "Undesirable blood pressure changes under naturalistic treatment with moclobemide, a reversible MAO-A inhibitor--results of the drug utilization observation studies". Pharmacopsychiatry. 32 (2): 61–7. PMID 10333164.
- ↑ Jones RT. (2002). "Cardiovascular system effcts of marijuana". J Clin Pharmacol. 42 (11 Suppl): 58S–63S. PMID 12412837.
- ↑ Hohmann M, Künzel W (1991). "Orthostatic hypotension and birthweight". Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 248 (4): 181–9. doi:10.1007/bf02390357. PMID 1898124.
- ↑ Poewe W, Seppi K, Fitzer-Attas CJ, Wenning GK, Gilman S, Low PA; et al. (2015). "Efficacy of rasagiline in patients with the parkinsonian variant of multiple system atrophy: a randomised, placebo-controlled trial". Lancet Neurol. 14 (2): 145–52. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(14)70288-1. PMID 25498732.
- ↑ Brignole M (2005). "Neurally-mediated syncope". Ital Heart J. 6 (3): 249–55. PMID 15875516.
- ↑ Trahair LG, Horowitz M, Jones KL (2014). "Postprandial hypotension: a systematic review". J Am Med Dir Assoc. 15 (6): 394–409. doi:10.1016/j.jamda.2014.01.011. PMID 24630686.
- ↑ Garland EM, Celedonio JE, Raj SR (2015). "Postural Tachycardia Syndrome: Beyond Orthostatic Intolerance". Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 15 (9): 60. doi:10.1007/s11910-015-0583-8. PMC 4664448. PMID 26198889.
- ↑ Cheshire WP (2017). "Syncope". Continuum (Minneap Minn). 23 (2, Selected Topics in Outpatient Neurology): 335–358. doi:10.1212/CON.0000000000000444. PMID 28375909.
- ↑ Dohrmann ML, Cheitlin MD (1986). "Cardiogenic syncope. Seizure versus syncope". Neurol Clin. 4 (3): 549–62. PMID 3528810.
- ↑ Aydin MA, Salukhe TV, Wilke I, Willems S (2010). "Management and therapy of vasovagal syncope: A review". World J Cardiol. 2 (10): 308–15. doi:10.4330/wjc.v2.i10.308. PMC 2998831. PMID 21160608.
- ↑ Palma JA, Kaufmann H (2017). "Epidemiology, Diagnosis, and Management of [[Neurogenic Orthostatic Hypotension]]". Mov Disord Clin Pract. 4 (3): 298–308. doi:10.1002/mdc3.12478. PMC 5506688. PMID 28713844. URL–wikilink conflict (help)
- ↑ Ricci F, De Caterina R, Fedorowski A (2015). "Orthostatic Hypotension: Epidemiology, Prognosis, and Treatment". J Am Coll Cardiol. 66 (7): 848–860. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2015.06.1084. PMID 26271068.
- ↑ Low PA (2008). "Prevalence of orthostatic hypotension". Clin Auton Res. 18 Suppl 1: 8–13. doi:10.1007/s10286-007-1001-3. PMID 18368301.
- ↑ Arnold, Amy C.; Shibao, Cyndya (2013). "Current Concepts in Orthostatic Hypotension Management". Current Hypertension Reports. 15 (4): 304–312. doi:10.1007/s11906-013-0362-3. ISSN 1522-6417.
- ↑ Canobbio, Mary M.; Warnes, Carole A.; Aboulhosn, Jamil; Connolly, Heidi M.; Khanna, Amber; Koos, Brian J.; Mital, Seema; Rose, Carl; Silversides, Candice; Stout, Karen (2017). "Management of Pregnancy in Patients With Complex Congenital Heart Disease: A Scientific Statement for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart Association". Circulation. 135 (8). doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000458. ISSN 0009-7322.
- ↑ Cremer A, Rousseau AL, Boulestreau R, Kuntz S, Tzourio C, Gosse P (2019). "Screening for orthostatic hypotension using home blood pressure measurements". J Hypertens. 37 (5): 923–927. doi:10.1097/HJH.0000000000001986. PMID 30418320.
- ↑ "StatPearls". 2020. PMID 28846238.
- ↑ Romero-Ortuno R, Cogan L, Foran T, Kenny RA, Fan CW (April 2011). "Continuous noninvasive orthostatic blood pressure measurements and their relationship with orthostatic intolerance, falls, and frailty in older people". J Am Geriatr Soc. 59 (4): 655–65. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2011.03352.x. PMID 21438868.
- ↑ Ricci, Fabrizio; Fedorowski, Artur; Radico, Francesco; Romanello, Mattia; Tatasciore, Alfonso; Di Nicola, Marta; Zimarino, Marco; De Caterina, Raffaele (2015). "Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality related to orthostatic hypotension: a meta-analysis of prospective observational studies". European Heart Journal. 36 (25): 1609–1617. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehv093. ISSN 0195-668X.
- ↑ Palma JA, Norcliffe-Kaufmann L, Kaufmann H (2016). "An orthostatic hypotension mimic: The inebriation-like syndrome in Parkinson disease". Mov Disord. 31 (4): 598–600. doi:10.1002/mds.26516. PMC 4833617. PMID 26879239.
- ↑ Freeman R (2008). "Clinical practice. Neurogenic orthostatic hypotension". N Engl J Med. 358 (6): 615–24. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp074189. PMID 18256396.
- ↑ Stewart JM (May 2013). "Common syndromes of orthostatic intolerance". Pediatrics. 131 (5): 968–80. doi:10.1542/peds.2012-2610. PMC 3639459. PMID 23569093.
- ↑ Magnusson M, Holm H, Bachus E, Nilsson P, Leosdottir M, Melander O; et al. (2016). "Orthostatic Hypotension and Cardiac Changes After Long-Term Follow-Up". Am J Hypertens. 29 (7): 847–52. doi:10.1093/ajh/hpv187. PMID 26643688.
- ↑ Metzler M, Duerr S, Granata R, Krismer F, Robertson D, Wenning GK (2013). "Neurogenic orthostatic hypotension: pathophysiology, evaluation, and management". J Neurol. 260 (9): 2212–9. doi:10.1007/s00415-012-6736-7. PMC 3764319. PMID 23180176.
- ↑ Singer W, Opfer-Gehrking TL, McPhee BR, Hilz MJ, Bharucha AE, Low PA. (2003). "Acetylcholinesterase inhibition: a novel approach in the treatment of neurogenic orthostatic hypotension". J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 74 (9): 1294–8. PMID 12933939.
- ↑ Figueroa, J. J.; Basford, J. R.; Low, P. A. (2010). "Preventing and treating orthostatic hypotension: As easy as A, B, C". Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine. 77 (5): 298–306. doi:10.3949/ccjm.77a.09118. ISSN 0891-1150.
- ↑ Freeman, Roy; Abuzinadah, Ahmad R.; Gibbons, Christopher; Jones, Pearl; Miglis, Mitchell G.; Sinn, Dong In (2018). "Orthostatic Hypotension". Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 72 (11): 1294–1309. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2018.05.079. ISSN 0735-1097.
- ↑ Freeman, Roy; Abuzinadah, Ahmad R.; Gibbons, Christopher; Jones, Pearl; Miglis, Mitchell G.; Sinn, Dong In (2018). "Orthostatic Hypotension". Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 72 (11): 1294–1309. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2018.05.079. ISSN 0735-1097.
- ↑ Schmoldt A, Benthe HF, Haberland G (1975). "Digitoxin metabolism by rat liver microsomes". Biochem Pharmacol. 24 (17): 1639–41. PMID /10.1016/j.jacc.2015.06.1084 Check
|pmid=value (help). - ↑ Carlson JE (1999). "Assessment of orthostatic blood pressure: measurement technique and clinical applications". South Med J. 92 (2): 167–73. doi:10.1097/00007611-199902000-00002. PMID 10071663.
- ↑ Benditt DG, Nguyen JT (2009). "Syncope: therapeutic approaches". J Am Coll Cardiol. 53 (19): 1741–51. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2008.12.065. PMID 19422980.
- ↑ Wieling W, van Dijk N, Thijs RD, de Lange FJ, Krediet CT, Halliwill JR (2015). "Physical countermeasures to increase orthostatic tolerance". J Intern Med. 277 (1): 69–82. doi:10.1111/joim.12249. PMID 24697914.
- ↑ Low PA, Singer W (2008). "Management of neurogenic orthostatic hypotension: an update". Lancet Neurol. 7 (5): 451–8. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(08)70088-7. PMC 2628163. PMID 18420158.
- ↑ Maule S, Papotti G, Naso D, Magnino C, Testa E, Veglio F (2007). "Orthostatic hypotension: evaluation and treatment". Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 7 (1): 63–70. doi:10.2174/187152907780059029. PMID 17346129.
External Links
- John G. Bradley, M.D., and Kathy A. Davis, R.N. Orthostatic Hypotension American Family Physician
- DYNA Dysautonomia Youth Network of America, Inc.