Sertindole: Difference between revisions
m (Protected "Sertindole": Protecting pages from unwanted edits ([edit=sysop] (indefinite) [move=sysop] (indefinite))) |
Kiran Singh (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Drugbox| | {{Drugbox| verifiedrevid = 464389408 | ||
| IUPAC_name = ''1-[2-[4-[5-chloro-1-(4-fluorophenyl)-<BR>indol-3-yl]-1-piperidyl]ethyl]<BR>imidazolidin-2-one'' | | IUPAC_name = ''<nowiki>1-[2-[4-[5-chloro-1-(4-fluorophenyl)-</nowiki><BR><nowiki>indol-3-yl]-1-piperidyl]ethyl]</nowiki><BR>imidazolidin-2-one'' | ||
| image = | | image =Sertindole2DACS.png | ||
| width = | | width = 250 | ||
| image2 =Sertindole3Dan.gif | |||
| width2 = 250 | |||
<!--Clinical data--> | |||
| Drugs.com = {{drugs.com|international|sertindole}} | |||
| legal_status = approved for marketing in approx 20 countries | |||
| routes_of_administration = Oral | |||
<!--Pharmacokinetic data--> | |||
| bioavailability = 75%<ref name = Rev>{{cite journal|title=Drug safety and efficacy evaluation of sertindole for schizophrenia|journal=Expert Opinion on Drug Safety|date=November 2012|volume=11|issue=6|pages=1047–1062|doi=10.1517/14740338.2012.726984|pmid=22992213|author=Karamatskos, E; Lambert, M; Mulert, C; Naber, D}}</ref> | |||
| protein_bound = 99.5%<ref name = Rev/> | |||
| metabolism = [[Hepatic]] (mostly via [[CYP2D6]] and [[CYP3A4]])<ref name = TGA/><ref name = Rev2>{{cite journal|title=Sertindole in the Management of Schizophrenia|journal=Journal of Central Nervous System Disease|author=Juruena, MF; de Sena, EP; de Oliveira, IR|date=May 2011|volume=3|pages=75–85|doi=10.4137/JCNSD.S5729|pmid=23861640|pmc=3663609|url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3663609/pdf/jcnsd-3-2011-075.pdf}}</ref> | |||
| elimination_half-life = 3 days<ref name = TGA/> | |||
| excretion = [[Faeces|Faecal]] (the majority), [[Renal]] (4% metabolites; 1% unchanged)<ref name = TGA/> | |||
<!--Identifiers--> | |||
| CASNo_Ref = {{cascite|correct|CAS}} | |||
| CAS_number_Ref = {{cascite|correct|??}} | |||
| CAS_number = 106516-24-9 | | CAS_number = 106516-24-9 | ||
| ATC_prefix = N05 | | ATC_prefix = N05 | ||
| ATC_suffix = AE03 | | ATC_suffix = AE03 | ||
| PubChem = 60149 | | PubChem = 60149 | ||
| DrugBank = | | IUPHAR_ligand = 98 | ||
| C=24 | H=26 | Cl=1 | F=1 | N=4 | O=1 | | DrugBank_Ref = {{drugbankcite|correct|drugbank}} | ||
| DrugBank = DB06144 | |||
| ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| ChemSpiderID = 54229 | |||
| UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} | |||
| UNII = GVV4Z879SP | |||
| KEGG_Ref = {{keggcite|correct|kegg}} | |||
| KEGG = D00561 | |||
| ChEBI_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} | |||
| ChEBI = 9122 | |||
| ChEMBL_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} | |||
| ChEMBL = 12713 | |||
<!--Chemical data--> | |||
| C=24 | H=26 | Cl=1 | F=1 | N=4 | O=1 | |||
| molecular_weight = 440.941 | | molecular_weight = 440.941 | ||
| | | smiles = Fc1ccc(cc1)n3c2ccc(Cl)cc2c(c3)C5CCN(CCN4C(=O)NCC4)CC5 | ||
| | | InChI = 1/C24H26ClFN4O/c25-18-1-6-23-21(15-18)22(16-30(23)20-4-2-19(26)3-5-20)17-7-10-28(11-8-17)13-14-29-12-9-27-24(29)31/h1-6,15-17H,7-14H2,(H,27,31) | ||
| | | StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | ||
| | | StdInChI = 1S/C24H26ClFN4O/c25-18-1-6-23-21(15-18)22(16-30(23)20-4-2-19(26)3-5-20)17-7-10-28(11-8-17)13-14-29-12-9-27-24(29)31/h1-6,15-17H,7-14H2,(H,27,31) | ||
| | | StdInChIKey_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | ||
| | | StdInChIKey = GZKLJWGUPQBVJQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| | |legal_AU=S4 | ||
}} | |pregnancy_AU=C}} | ||
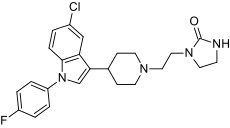
'''Sertindole''' (brand names: '''Serdolect''', and '''Serlect''') is an [[antipsychotic]] medication. Sertindole was developed by the Danish pharmaceutical company [[H. Lundbeck]] and marketed under license by [[Abbott Labs]]. Like other [[atypical antipsychotic]]s, it has activity at [[dopamine]] and [[serotonin]] receptors in the brain. It is used in the treatment of [[schizophrenia]]. It is classified chemically as a [[phenylindole]] derivative. | |||
Sertindole is not approved for use in the United States. | |||
==Medical Uses== | |||
Sertindole appears effective as an antipsychotic in schizophrenia.<ref>{{cite journal|last=Lewis|first=R|author2=Bagnall, AM |author3=Leitner, M |title=Sertindole for schizophrenia.|journal=Cochrane database of systematic reviews (Online)|date=Jul 20, 2005|issue=3|pages=CD001715|pmid=16034864|doi=10.1002/14651858.CD001715.pub2}}</ref> | |||
==Adverse Effects== | |||
'''Very common (>10% incidence) adverse effects include:'''<ref name = "TGA">{{cite web|title=PRODUCT INFORMATION SERDOLECT® TABLETS|work=TGA eBusiness Services|publisher=Lundbeck Australia Pty Ltd|date=16 January 2013|accessdate=27 October 2013|url=https://www.ebs.tga.gov.au/ebs/picmi/picmirepository.nsf/pdf?OpenAgent&id=CP-2010-PI-07697-3|format=PDF}}</ref> | |||
* Headache | |||
* Ejaculation failure | |||
* Insomnia | |||
* Dizziness | |||
''' | '''Common (1-10% incidence) adverse effects include:'''<ref name = "TGA" /> | ||
* Urine that tests positive for red and/or white blood cells | |||
* Sedation (causes less sedation than most antipsychotic drugs according to a recent meta-analysis of the efficacy and tolerability of 15 antipsychotic drugs. Causes only slightly [and non-significantly] more sedation than [[amisulpride]] and [[paliperidone]]<ref name = "Maudsley">{{cite isbn|9780470979488}}</ref><ref name = Lancet/>) | |||
* Ejaculation disorder | |||
* Erectile dysfunction | |||
* Orthostatic hypotension<ref name = "Maudsley" /> | |||
* Weight gain (which it seems to possess a similar propensity for causing as [[quetiapine]]<ref name = "Lancet" />) | |||
'''Uncommon (0.1-1% incidence) adverse effects include:'''<ref name = "TGA" /> | |||
{{Colbegin|3}} | |||
* Substernal chest pain | |||
* Face oedema | |||
* Flu syndrome | |||
* Neck rigidity | |||
* Pallor | |||
* Peripheral vascular disorder | |||
* Syncope | |||
* [[Torsades de Pointes]] | |||
* Vasodilation | |||
* Suicide attempt | |||
* Amnesia | |||
* Anxiety | |||
* Ataxia | |||
* Confusion | |||
* Incoordination | |||
* Libido decreased | |||
* Libido increased | |||
* Miosis | |||
* Nystagmus | |||
* Personality disorder | |||
* Psychosis | |||
* Reflexes decreased | |||
* Reflexes increased | |||
* Stupor | |||
* Suicidal tendency | |||
* Urinary retention | |||
* Vertigo | |||
* Diabetes mellitus | |||
* Abnormal stools | |||
* Gastritis | |||
* Gingivitis | |||
* Glossitis | |||
* Increased appetite | |||
* Mouth ulceration | |||
* Rectal disorder | |||
* Rectal haemorrhage | |||
* Stomatitis | |||
* Tongue disorder | |||
* Ulcerative stomatitis | |||
* Anaemia | |||
* Ecchymosis | |||
* Hypochromic anaemia | |||
* Leukopenia | |||
* Hyperglycaemia | |||
* Hyperlipemia | |||
* Oedema | |||
* Bone pain | |||
* Myasthenia | |||
* Twitching | |||
* Bronchitis | |||
* Hyperventilation | |||
* Pneumonia | |||
* Sinusitis | |||
* Furunculosis | |||
* Herpes simplex | |||
* Nail disorder | |||
* Psoriasis | |||
* Pustular Rash | |||
* Skin discolouration | |||
* Skin hypertrophy | |||
* Skin ulcer | |||
* Abnormal vision | |||
* Keratoconjunctivitis | |||
* Lacrimation disorder | |||
* Otitis externa | |||
* Pupillary disorder | |||
* Taste perversion | |||
* Anorgasmia | |||
* Penis disorder (gs) | |||
* Urinary urgency | |||
* [[Hyperprolactinaemia]] (which it seems to cause with a higher propensity than most other atypical antipsychotics do<ref name = "Lancet" />) | |||
* Seizures | |||
* [[Galactorrhoea]] | |||
{{Colend}} | |||
'''Rare (<0.1% incidence) adverse effects include:'''<ref name = "TGA" /> | |||
* [[Neuroleptic malignant syndrome]] | |||
* [[Tardive dyskinesia]] | |||
'''Unknown frequency adverse events include:'''<ref name = "TGA" /> | |||
* Extrapyramidal side effects (EPSE; e.g. dystonia, akathisia, muscle rigidity, parkinsonism, etc. These adverse effects are probably uncommon/rare according to a recent meta-analysis of the efficacy and tolerability of 15 antipsychotic drugs which found it had the 2nd lowest effect size for causing EPSE<ref name = "Lancet">{{cite pmid|23810019}}</ref>) | |||
* Venous thromboembolism | |||
* QT interval prolongation (probably common; in a recent meta-analysis of the efficacy and tolerability of 15 antipsychotic drugs it was found to be the most prone to causing QT interval prolongation<ref name = "Lancet" />) | |||
==Pharmacology== | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|- | |||
! Biologic protein !! Binding affinity (K<sub>i</sub>[nM])<ref>{{cite web | title = PDSP K<sub>i</sub> Database | work = Psychoactive Drug Screening Program (PDSP) | author = Roth, BL; Driscol, J | url = http://pdsp.med.unc.edu/pdsp.php | publisher = University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and the United States National Institute of Mental Health | accessdate = 27 October 2013 | date = 12 January 2011}}</ref> !! Notes | |||
|- | |||
| [[5-HT1A receptor|5-HT<sub>1A</sub>]] || 280 || | |||
|- | |||
| [[5-HT1B receptor|5-HT<sub>1B</sub>]] || 60 || | |||
|- | |||
| [[5-HT1D receptor|5-HT<sub>1D</sub>]] || 96 || | |||
|- | |||
| [[5-HT1E receptor|5-HT<sub>1E</sub>]] || 430 || | |||
|- | |||
| [[5-HT1F receptor|5-HT<sub>1F</sub>]] || 360 || | |||
|- | |||
| [[5-HT2A receptor|5-HT<sub>2A</sub>]] || 0.39 || The receptor believed to mediate the ''atypicality'' of atypical antipsychotics.<ref name = GG>{{cite isbn|9780071624428}}</ref> | |||
|- | |||
| [[5-HT2C receptor|5-HT<sub>2C</sub>]] || 0.9 || Likely responsible for its propensity for causing weight gain.<ref name = GG/> | |||
|- | |||
| [[5-HT6 receptor|5-HT<sub>6</sub>]] || 5.4 || | |||
|- | |||
| [[5-HT7 receptor|5-HT<sub>7</sub>]] || 28 || | |||
|- | |||
| [[Alpha-1A adrenergic receptor|α<sub>1A</sub>]] || 1.8 || Likely responsible for the orthostatic hypotension seen in patients on sertindole.<ref name = GG/> | |||
|- | |||
| [[Alpha-2A adrenergic receptor|α<sub>2A</sub>]] || 640 || | |||
|- | |||
| [[Alpha-2B adrenergic receptor|α<sub>2B</sub>]] || 450 || | |||
|- | |||
| [[Alpha-2C adrenergic receptor|α<sub>2C</sub>]] || 450 || | |||
|- | |||
| [[Beta-1 adrenergic receptor|β<sub>1</sub>]] || 5000 || | |||
|- | |||
| [[Beta-2 adrenergic receptor|β<sub>2</sub>]] || 5000 || | |||
|- | |||
| [[Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M1|M<sub>1</sub>]] || >10000 || <ref name = GG/> | |||
|- | |||
| [[Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M3|M<sub>3</sub>]] || 2692 || | |||
|- | |||
| [[Dopamine D2 receptor|D<sub>2</sub>]] || 2.35 || Believed to be responsible for the drug's efficacy against positive symptoms.<ref name = GG/> | |||
|- | |||
| [[Dopamine D3 receptor|D<sub>3</sub>]] || 2.30 || | |||
|- | |||
| [[Dopamine D4 receptor|D<sub>4</sub>]] || 4.92 || | |||
|- | |||
| [[HERG]] || 3 || | |||
|- | |||
| [[Histamine H1 receptor|H<sub>1</sub>]] || 130 || | |||
|- | |||
| [[NK1 receptor|NK<sub>1</sub>]] || 1000 || | |||
|} | |||
==Safety and status== | |||
The | ===USA=== | ||
[[Abbott Labs]] first applied for U.S. [[Food and Drug Administration]] (FDA) approval for sertindole in 1996,<ref>[http://www.thepharmaletter.com/file/57165/zenecas-seroquel-nears-market-approval.html Zeneca's Seroquel Nears Market Approval] - The Pharma Letter, 16 July 1997</ref> but withdrew this application in 1998 following concerns over the increased risk of sudden death from [[Long QT syndrome|QTc prolongation]].<ref name="pharma1">[http://www.thepharmaletter.com/file/65187/abbott-labs-withdraws-sertindole-nda.html Abbott Labs Withdraws Sertindole NDA Sertindole] - The Pharma Letter, 12 Jan 1998</ref> In a trial of 2000 patients on taking sertindole, 27 patients died unexpectedly, including 13 sudden deaths.<ref name="who1">{{cite web |url=http://apps.who.int/medicinedocs/en/d/Js2256e/1.12.html#Js2256e.1.12 |title=WHO Pharmaceuticals Newsletter 1998, No. 03&04: Regulatory actions: Sertindole - approval application withdrawn |format= |work= |accessdate=}}</ref> Lundbeck cites the results of the Sertindole Cohort Prospective (SCoP) study of 10,000 patients to support its claim that although sertindole does increase the QTc interval, this is not associated with increased rates of cardiac arrhythmias, and that patients on sertindole had the same overall mortality rate as those on [[risperidone]].<ref>[http://sweden.lundbeck.com/investor/releases/ReleaseDetails/Release_1304142_EN.asp FDA Advisory Committee provides opinion on Serdolect for the treatment of schizophrenia] - Lundbeck press release, 8 Apr 2009</ref> Nevertheless in April 2009 an FDA advisory panel voted 13-0 that sertindole was effective in the treatment of schizophrenia but 12-1 that it had not been shown to be acceptably safe.<ref>[http://www.fda.gov/downloads/AdvisoryCommittees/CommitteesMeetingMaterials/Drugs/PsychopharmacologicDrugsAdvisoryCommittee/UCM198218.pdf Food and Drug Administration; Minutes of the Psychphamacological Drugs Advisory Committee, 7 Apr 2009]</ref> {{Asof|October 2010}}, the drug has not been approved by the FDA for use in the USA.<ref>[http://www.serdolect.com]</ref> | |||
===Europe=== | |||
In Europe, sertindole was approved and marketed in 19 countries from 1996,<ref name="who1"/> but its marketing authorization was suspended by the [[European Medicines Agency]] in 1998<ref>[http://www.nelm.nhs.uk/en/NeLM-Area/News/483119/483386/483398/ EU CHMP recommends lifting ban on atypical antipsychotic Serdolect (sertindole)] - National electronic Library for Medicines, NHS</ref> and the drug was withdrawn from the market. In 2002, based on new data, the EMA's [[CHMP]] suggested that Sertindole could be reintroduced for restricted use in clinical trials, with strong safeguards including extensive contraindications and warnings for patients at risk of cardiac dysrhythmias, a recommended reduction in maximum dose from 24 mg to 20 mg in all but exceptional cases, and extensive ECG monitoring requirement before and during treatment.<ref>[http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Referrals_document/Sertindole_36/WC500011855.pdf COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS OPINION FOLLOWING AN ARTICLE 36 REFERRAL: SERTINDOLE] - European Medicines Agency, 13 Sep 2002</ref><ref>[http://www.mhra.gov.uk/Safetyinformation/Safetywarningsalertsandrecalls/Safetywarningsandmessagesformedicines/CON019523 Restricted re-introduction of the atypical antipsychotic sertindole (Serdolect)] - [[Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency|MHRA]], 2002</ref> | |||
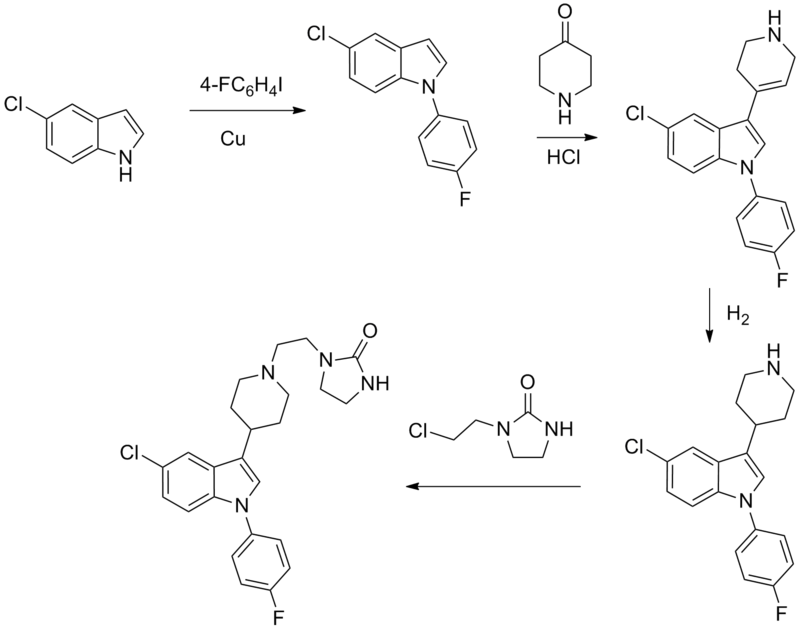
==Synthesis== | |||
[[File:Sertindole synthesis.png|center|thumb|700px|Sertindole synthesis:<ref>{{Cite doi|10.1021/jm00084a014}}</ref>]] | |||
==References== | |||
{{reflist|2}} | |||
{{Antipsychotics}} | {{Antipsychotics}} | ||
{{Serotonergics}} | |||
{{Dopaminergics}} | |||
[[Category:Drug]] | |||
[[Category:Atypical antipsychotics]] | [[Category:Atypical antipsychotics]] | ||
[[Category:Indoles]] | [[Category:Indoles]] | ||
[[Category:Withdrawn drugs]] | [[Category:Withdrawn drugs]] | ||
[[Category:Piperidines]] | [[Category:Piperidines]] | ||
[[Category:Organochlorides]] | |||
[[Category:Organofluorides]] | |||
[[Category:Ureas]] | |||
[[Category:Imidazolidinones]] | |||
Revision as of 17:36, 9 April 2015
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 75%[3] |
| Protein binding | 99.5%[3] |
| Metabolism | Hepatic (mostly via CYP2D6 and CYP3A4)[1][2] |
| Elimination half-life | 3 days[1] |
| Excretion | Faecal (the majority), Renal (4% metabolites; 1% unchanged)[1] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| E number | {{#property:P628}} |
| ECHA InfoCard | {{#property:P2566}}Lua error in Module:EditAtWikidata at line 36: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C24H26ClFN4O |
| Molar mass | 440.941 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Sertindole (brand names: Serdolect, and Serlect) is an antipsychotic medication. Sertindole was developed by the Danish pharmaceutical company H. Lundbeck and marketed under license by Abbott Labs. Like other atypical antipsychotics, it has activity at dopamine and serotonin receptors in the brain. It is used in the treatment of schizophrenia. It is classified chemically as a phenylindole derivative.
Sertindole is not approved for use in the United States.
Medical Uses
Sertindole appears effective as an antipsychotic in schizophrenia.[4]
Adverse Effects
Very common (>10% incidence) adverse effects include:[1]
- Headache
- Ejaculation failure
- Insomnia
- Dizziness
Common (1-10% incidence) adverse effects include:[1]
- Urine that tests positive for red and/or white blood cells
- Sedation (causes less sedation than most antipsychotic drugs according to a recent meta-analysis of the efficacy and tolerability of 15 antipsychotic drugs. Causes only slightly [and non-significantly] more sedation than amisulpride and paliperidone[5][6])
- Ejaculation disorder
- Erectile dysfunction
- Orthostatic hypotension[5]
- Weight gain (which it seems to possess a similar propensity for causing as quetiapine[6])
Uncommon (0.1-1% incidence) adverse effects include:[1]
- Substernal chest pain
- Face oedema
- Flu syndrome
- Neck rigidity
- Pallor
- Peripheral vascular disorder
- Syncope
- Torsades de Pointes
- Vasodilation
- Suicide attempt
- Amnesia
- Anxiety
- Ataxia
- Confusion
- Incoordination
- Libido decreased
- Libido increased
- Miosis
- Nystagmus
- Personality disorder
- Psychosis
- Reflexes decreased
- Reflexes increased
- Stupor
- Suicidal tendency
- Urinary retention
- Vertigo
- Diabetes mellitus
- Abnormal stools
- Gastritis
- Gingivitis
- Glossitis
- Increased appetite
- Mouth ulceration
- Rectal disorder
- Rectal haemorrhage
- Stomatitis
- Tongue disorder
- Ulcerative stomatitis
- Anaemia
- Ecchymosis
- Hypochromic anaemia
- Leukopenia
- Hyperglycaemia
- Hyperlipemia
- Oedema
- Bone pain
- Myasthenia
- Twitching
- Bronchitis
- Hyperventilation
- Pneumonia
- Sinusitis
- Furunculosis
- Herpes simplex
- Nail disorder
- Psoriasis
- Pustular Rash
- Skin discolouration
- Skin hypertrophy
- Skin ulcer
- Abnormal vision
- Keratoconjunctivitis
- Lacrimation disorder
- Otitis externa
- Pupillary disorder
- Taste perversion
- Anorgasmia
- Penis disorder (gs)
- Urinary urgency
- Hyperprolactinaemia (which it seems to cause with a higher propensity than most other atypical antipsychotics do[6])
- Seizures
- Galactorrhoea
Rare (<0.1% incidence) adverse effects include:[1]
Unknown frequency adverse events include:[1]
- Extrapyramidal side effects (EPSE; e.g. dystonia, akathisia, muscle rigidity, parkinsonism, etc. These adverse effects are probably uncommon/rare according to a recent meta-analysis of the efficacy and tolerability of 15 antipsychotic drugs which found it had the 2nd lowest effect size for causing EPSE[6])
- Venous thromboembolism
- QT interval prolongation (probably common; in a recent meta-analysis of the efficacy and tolerability of 15 antipsychotic drugs it was found to be the most prone to causing QT interval prolongation[6])
Pharmacology
| Biologic protein | Binding affinity (Ki[nM])[7] | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 5-HT1A | 280 | |
| 5-HT1B | 60 | |
| 5-HT1D | 96 | |
| 5-HT1E | 430 | |
| 5-HT1F | 360 | |
| 5-HT2A | 0.39 | The receptor believed to mediate the atypicality of atypical antipsychotics.[8] |
| 5-HT2C | 0.9 | Likely responsible for its propensity for causing weight gain.[8] |
| 5-HT6 | 5.4 | |
| 5-HT7 | 28 | |
| α1A | 1.8 | Likely responsible for the orthostatic hypotension seen in patients on sertindole.[8] |
| α2A | 640 | |
| α2B | 450 | |
| α2C | 450 | |
| β1 | 5000 | |
| β2 | 5000 | |
| M1 | >10000 | [8] |
| M3 | 2692 | |
| D2 | 2.35 | Believed to be responsible for the drug's efficacy against positive symptoms.[8] |
| D3 | 2.30 | |
| D4 | 4.92 | |
| HERG | 3 | |
| H1 | 130 | |
| NK1 | 1000 |
Safety and status
USA
Abbott Labs first applied for U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval for sertindole in 1996,[9] but withdrew this application in 1998 following concerns over the increased risk of sudden death from QTc prolongation.[10] In a trial of 2000 patients on taking sertindole, 27 patients died unexpectedly, including 13 sudden deaths.[11] Lundbeck cites the results of the Sertindole Cohort Prospective (SCoP) study of 10,000 patients to support its claim that although sertindole does increase the QTc interval, this is not associated with increased rates of cardiac arrhythmias, and that patients on sertindole had the same overall mortality rate as those on risperidone.[12] Nevertheless in April 2009 an FDA advisory panel voted 13-0 that sertindole was effective in the treatment of schizophrenia but 12-1 that it had not been shown to be acceptably safe.[13] As of October 2010[update], the drug has not been approved by the FDA for use in the USA.[14]
Europe
In Europe, sertindole was approved and marketed in 19 countries from 1996,[11] but its marketing authorization was suspended by the European Medicines Agency in 1998[15] and the drug was withdrawn from the market. In 2002, based on new data, the EMA's CHMP suggested that Sertindole could be reintroduced for restricted use in clinical trials, with strong safeguards including extensive contraindications and warnings for patients at risk of cardiac dysrhythmias, a recommended reduction in maximum dose from 24 mg to 20 mg in all but exceptional cases, and extensive ECG monitoring requirement before and during treatment.[16][17]
Synthesis
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 "PRODUCT INFORMATION SERDOLECT® TABLETS" (PDF). TGA eBusiness Services. Lundbeck Australia Pty Ltd. 16 January 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2013.
- ↑ Juruena, MF; de Sena, EP; de Oliveira, IR (May 2011). "Sertindole in the Management of Schizophrenia" (PDF). Journal of Central Nervous System Disease. 3: 75–85. doi:10.4137/JCNSD.S5729. PMC 3663609. PMID 23861640.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Karamatskos, E; Lambert, M; Mulert, C; Naber, D (November 2012). "Drug safety and efficacy evaluation of sertindole for schizophrenia". Expert Opinion on Drug Safety. 11 (6): 1047–1062. doi:10.1517/14740338.2012.726984. PMID 22992213.
- ↑ Lewis, R; Bagnall, AM; Leitner, M (Jul 20, 2005). "Sertindole for schizophrenia". Cochrane database of systematic reviews (Online) (3): CD001715. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001715.pub2. PMID 16034864.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Template:Cite isbn
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 PMID 23810019 (PMID 23810019)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ Roth, BL; Driscol, J (12 January 2011). "PDSP Ki Database". Psychoactive Drug Screening Program (PDSP). University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and the United States National Institute of Mental Health. Retrieved 27 October 2013.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 Template:Cite isbn
- ↑ Zeneca's Seroquel Nears Market Approval - The Pharma Letter, 16 July 1997
- ↑ Abbott Labs Withdraws Sertindole NDA Sertindole - The Pharma Letter, 12 Jan 1998
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 "WHO Pharmaceuticals Newsletter 1998, No. 03&04: Regulatory actions: Sertindole - approval application withdrawn".
- ↑ FDA Advisory Committee provides opinion on Serdolect for the treatment of schizophrenia - Lundbeck press release, 8 Apr 2009
- ↑ Food and Drug Administration; Minutes of the Psychphamacological Drugs Advisory Committee, 7 Apr 2009
- ↑ [1]
- ↑ EU CHMP recommends lifting ban on atypical antipsychotic Serdolect (sertindole) - National electronic Library for Medicines, NHS
- ↑ COMMITTEE FOR PROPRIETARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS OPINION FOLLOWING AN ARTICLE 36 REFERRAL: SERTINDOLE - European Medicines Agency, 13 Sep 2002
- ↑ Restricted re-introduction of the atypical antipsychotic sertindole (Serdolect) - MHRA, 2002
- ↑ Template:Cite doi
- Pages with script errors
- CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list
- Pages with incomplete PMID references
- Template:drugs.com link with non-standard subpage
- Drugs with non-standard legal status
- E number from Wikidata
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Chemical articles with unknown parameter in Infobox drug
- Pages using div col with unknown parameters
- Articles containing potentially dated statements from October 2010
- Articles with invalid date parameter in template
- All articles containing potentially dated statements
- Drug
- Atypical antipsychotics
- Indoles
- Withdrawn drugs
- Piperidines
- Organochlorides
- Organofluorides
- Ureas
- Imidazolidinones