Carotid artery stenosis: Difference between revisions
Varun Kumar (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
|||
| (28 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
Image = Carotid-artery-stenosis-001.jpg| | Image = Carotid-artery-stenosis-001.jpg| | ||
Caption = | | Caption = | | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{ | |||
{{Carotid artery stenosis}} | |||
{{CMG}}; '''Associate Editor-In-Chief:''' {{CZ}} | {{CMG}}; '''Associate Editor-In-Chief:''' {{CZ}} | ||
==Overview== | ==[[Carotid artery stenosis overview|Overview]]== | ||
==[[Carotid artery stenosis historical perspective|Historical Perspective]]== | |||
==[[Carotid artery stenosis classification|Classification]]== | |||
== | ==[[Carotid artery stenosis pathophysiology|Pathophysiology]]== | ||
Carotid stenosis | |||
==[[Carotid artery stenosis causes|Causes]]== | |||
==[[Carotid artery stenosis differential diagnosis|Differentiating Carotid artery stenosis from other Diseases]]== | |||
==[[Carotid artery stenosis epidemiology and demographics|Epidemiology and Demographics]]== | |||
== | ==[[Carotid artery stenosis risk factors|Risk Factors]]== | ||
== | ==[[Carotid artery stenosis screening|Screening]]== | ||
== | ==[[Carotid artery stenosis natural history, complications and prognosis|Natural History, Complications and Prognosis]]== | ||
==Diagnosis== | |||
[[Carotid artery stenosis diagnostic testing guidelines|Diagnostic Testing Guidelines]] | [[Carotid artery stenosis history and symptoms|History and Symptoms]] | [[Carotid artery stenosis physical examination|Physical Examination]] | [[Carotid artery stenosis laboratory findings|Laboratory Findings]] | [[Carotid artery stenosis electrocardiogram|Electrocardiogram]] | [[Carotid artery stenosis CT|CT]] | [[Carotid artery stenosis MRI|MRI]] | [[Carotid artery stenosis MRA|MRA]] | [[Carotid artery stenosis echocardiography or ultrasound|Echocardiography or Ultrasound]] | [[Carotid artery stenosis other imaging findings|Other Imaging Findings]] | [[Carotid artery stenosis other diagnostic studies|Other Diagnostic Studies]] | |||
==Treatment== | |||
[[Carotid artery stenosis medical therapy|Medical Therapy]] | [[Carotid artery stenosis surgery|Surgery]] | [[Carotid artery stenosis primary prevention|Primary Prevention]] | [[Carotid artery stenosis secondary prevention|Secondary Prevention]] | [[Carotid artery stenosis cost-effectiveness of therapy|Cost-Effectiveness of Therapy]] | [[Carotid artery stenosis future or investigational therapies|Future or Investigational Therapies]] | |||
==Case Studies== | |||
[[Carotid artery stenosis case study one|Case #1]] | |||
== | ==Related Chapters== | ||
*[[Ocular ischemic syndrome]] | *[[Ocular ischemic syndrome]] | ||
*[[External carotid artery]] | |||
*[[Common carotid artery]] | |||
*[[Internal carotid artery]] | |||
*[[Carotid artery dissection]] | |||
*[[Amaurosis fugax]] | |||
{{Circulatory system pathology}} | |||
{{ | |||
[[Category:Neurology]] | [[Category:Neurology]] | ||
| Line 87: | Line 57: | ||
[[Category:Emergency medicine]] | [[Category:Emergency medicine]] | ||
[[Category:Overview complete]] | [[Category:Overview complete]] | ||
[[Category:Disease]] | |||
[[nl:Carotisstenose]] | [[nl:Carotisstenose]] | ||
Latest revision as of 19:55, 30 January 2013
For patient information, click here
| Carotid artery stenosis | |
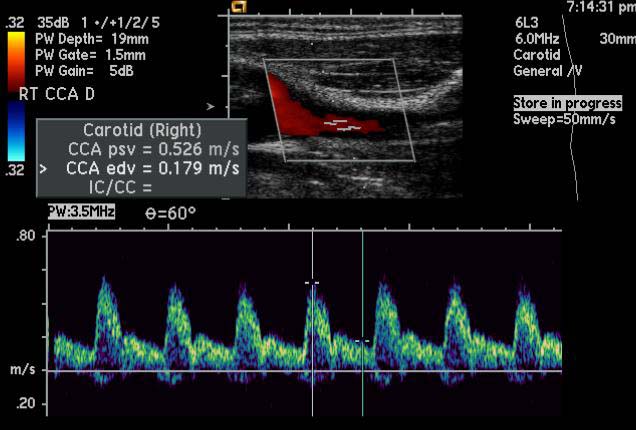 |
|---|
|
Carotid artery stenosis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
ACC/AHA Guideline Recommendations |
|
Periprocedural Management of Patients Undergoing Carotid Endarterectomy |
|
Atherosclerotic Risk Factors in Patients With Vertebral Artery Disease |
|
Occlusive Disease of the Subclavian and Brachiocephalic Arteries |
|
Case Studies |
|
Carotid artery stenosis On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Carotid artery stenosis |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Carotid artery stenosis |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor-In-Chief: Cafer Zorkun, M.D., Ph.D. [2]
Overview
Historical Perspective
Classification
Pathophysiology
Causes
Differentiating Carotid artery stenosis from other Diseases
Epidemiology and Demographics
Risk Factors
Screening
Natural History, Complications and Prognosis
Diagnosis
Diagnostic Testing Guidelines | History and Symptoms | Physical Examination | Laboratory Findings | Electrocardiogram | CT | MRI | MRA | Echocardiography or Ultrasound | Other Imaging Findings | Other Diagnostic Studies
Treatment
Medical Therapy | Surgery | Primary Prevention | Secondary Prevention | Cost-Effectiveness of Therapy | Future or Investigational Therapies
Case Studies
Related Chapters
- Ocular ischemic syndrome
- External carotid artery
- Common carotid artery
- Internal carotid artery
- Carotid artery dissection
- Amaurosis fugax