Receptor (biochemistry)
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Template:Otheruses3 In biochemistry, a receptor is a protein on the cell membrane or within the cytoplasm or cell nucleus that binds to a specific molecule (a ligand) such as a neurotransmitter or a hormone or other substance, and initiates the cellular response to the ligand. Ligand-induced changes in the behavior of receptor proteins result in physiological changes that constitute the biological actions of the ligands.
Overview
The shapes and actions of receptors are commonly determined by X-ray crystallography and computer modelling. These methods have increased the current understanding of drug action at binding sites on the receptors.
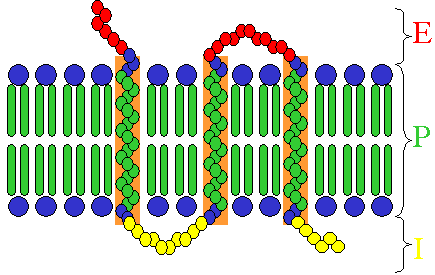
Receptors exist in different types, dependent on their ligand and function:
- Some receptor proteins are peripheral membrane proteins;
- Many hormone receptors and neurotransmitter receptors are transmembrane proteins: transmembrane receptors are embedded in the phospholipid bilayer of cell membranes, that allow the activation of signal transduction pathways in response to the activation by the binding molecule, or ligand.
- Metabotropic receptors are coupled to G proteins and affect the cell indirectly through enzymes which control ion channels.
- Ionotropic receptors contain a central pore which functions as a ligand-gated ion channel.
- Another major class of receptors are intracellular proteins such as those for steroid and intracrine peptide hormone receptors. These receptors often can enter the cell nucleus and modulate gene expression in response to the activation by the ligand.
Binding and activation
Ligand binding to a receptor is an equilibrium process: Ligands bind to an empty receptor and they dissociate from it (according to the law of mass action):
- (the brackets stand for concentrations)
A measure of how well a certain molecule fits into a given receptor is the binding affinity which is measured as the dissociation constant Kd (good fit means high affinity and a low Kd). The activation of the second messenger cascade and the final biological response is achieved only when at a certain time point a significant number of receptors are activated by bound ligands.
If the receptor exists in two states (see this picture), then the ligand binding must account for these two receptor states. For a more detailed discussion of two-state binding, which is thought to occur as an activation mechanism in many receptors see this link.
- Constitutive activity
Receptors which are active in the absence of a ligand. The constitutive activity of these receptors may be reversed by inverse agonist binding. Mutations in receptors that result in increased constitutive receptor signaling underlie some heritable diseases, such as precocious puberty (luteinizing hormone receptor mutations) and hyperthyroidism (thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor mutations). Psychostimulants act as inverse agonists at dopamine receptors.
For the use of statistical mechanics in a quantitative study of the ligand-receptor binding affinity, see the comprehensive article[1].
Agonists versus antagonists
Not every ligand that binds to a receptor also activates the receptor. The following classes of ligands exist:
- (Full) agonists are able to activate the receptor and result in a maximal biological response. Most natural ligands are full agonists
- Partial agonists are not able to activate the receptor maximally, resulting in a partial biological response compared to a full agonist.
- Antagonists bind to the receptor but do not activate it. This results in a receptor blockade that inhibits the binding of agonists.
- Inverse agonists are antagonists that are able to further reduce the receptor activation by decreasing its basal activity
Peripheral membrane protein receptors
Transmembrane receptors
Metabotropic receptors
G protein-coupled receptors
These receptors are also known as seven transmembrane receptors or 7TM receptors.
- Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (Acetylcholine and Muscarine)
- Adenosine receptors (Adenosine)
- Adrenoceptors (also known as Adrenergic receptors, for adrenaline, and other structurally related hormones and drugs)
- GABA receptors, Type-B (γ-Aminobutyric acid or GABA)
- Angiotensin receptors (Angiotensin)
- Cannabinoid receptors (Cannabinoids)
- Cholecystokinin receptors (Cholecystokinin)
- Dopamine receptors (Dopamine)
- Glucagon receptors (Glucagon)
- Metabotropic glutamate receptors (Glutamate)
- Histamine receptors (Histamine)
- Olfactory receptors (for the sense of smell)
- Opioid receptors (Opioids)
- Rhodopsin (a photoreceptor)
- Secretin receptors (Secretin)
- Serotonin receptors, except Type-3 (Serotonin, also known as 5-Hydroxytryptamine or 5-HT)
- Somatostatin receptors (Somatostatin)
- Calcium-sensing receptor (Calcium)
- Chemokine receptors (Chemokines)
- many more ...
Receptor tyrosine kinases
These receptors detect ligands and propagate signals via the tyrosine kinase of their intracellular domains. This family of receptors includes;
- Erythropoietin receptor (Erythropoietin)
- Insulin receptor (Insulin)
- Eph receptors
- Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor
- various other growth factor and cytokine receptors
- ....
Guanylyl cyclase receptors
- GC-A & GC-B: receptors for Atrial-natriuretic peptide (ANP) and other natriuretic peptides
- GC-C: Guanylin receptor
Ionotropic receptors
Ionotropic receptors are heteromeric or homomeric oligomers [2]. They are receptors that respond to extracellular ligands and receptors that respond to intracellular ligands.
Extracellular ligands
| Receptor | Ligand | Ion current |
| Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor | Acetylcholine, Nicotine | Na+, K+, Ca2+ [2] |
| Glycine receptor (GlyR) | Glycine, Strychnine | Cl- > HCO-3 [2] |
| GABA receptors: GABA-A, GABA-C | GABA | Cl- > HCO-3 [2] |
| Glutamate receptors: NMDA receptor, AMPA receptor, and Kainate receptor | Glutamate | Na+, K+, Ca2+ [2] |
| 5-HT3 receptor | Serotonin | Na+, K+ [2] |
| P2X receptors | ATP | Ca2+, Na+, Mg2+ [2] |
Intracellular ligands
| Receptor | Ligand | Ion current |
| cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channels | cGMP (vision), cAMP and cGTP (olfaction) | Na+, K+ [2] |
| IP3 receptor | IP3 | Ca2+ [2] |
| Intracellular ATP receptors | ATP (closes channel)[2] | K+ [2] |
| Ryanodine receptor | Ca2+ | Ca2+ [2] |
The entire repertoire of human plasma membrane receptors is listed at the Human Plasma Membrane Receptome (http://receptome.stanford.edu).
Intracellular receptors
Transcription factors
Various
- Ionotropic receptors (IP3 receptor above)
- sigma1 (neurosteroids)
- G protein-coupled receptors [3]
Role in Genetic Disorders
Many genetic disorders involve hereditary defects in receptor genes. Often, it is hard to determine whether the receptor is nonfunctional or the hormone is produced at decreased level; this gives rise to the "pseudo-hypo-" group of endocrine disorders, where there appears to be a decreased hormonal level while in fact it is the receptor that is not responding sufficiently to the hormone.
Receptor Regulation
Cells can increase (upregulate) or decrease (downregulate) the number of receptors to a given hormone or neurotransmitter to alter its sensitivity to this molecule. This is a locally acting feedback mechanism.
- Receptor desensitization
Ligand-bound desensitation of receptors was first characterized by Katz and Thesleff in the nicotine acetylcholine receptor[4][5] Prolonged or repeat exposure to a stimulus often results in decreased responsiveness of that receptor for a stimulus. Receptor desensitization results in altered affinity for the ligand.[4] Receptor desensitization can modeled by a two-state model that also predicts that antagonists combined with agonists can prevent receptor desensitization [6] See this link [2] for detailed molecular description
Desensitation may be accomplished by
- Receptor phosphorylation.[7]
- Uncoupling of receptor effector molecules.
- Receptor sequestration (internalization).[7]
In immune system
The main receptors in the immune system are pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), Toll-like receptors (TLRs), killer activated and killer inhibitor receptors (KARs and KIRs), complement receptors, Fc receptors, B cell receptors and T cell receptors. [8]
See also
- Signal transduction
- Neuropsychopharmacology
- Schild regression for ligand receptor inhibition
- Ki Database
References
- ↑ Vu-Quoc, L., Configuration integral (statistical mechanics), 2008.
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 2.11 Medical Physiology, Boron & Boulpaep, ISBN 1-4160-2328-3, Elsevier Saunders 2005. Updated edition. Page 90.
- ↑ Gobeil F, et al. (2006) G-protein-coupled receptors signalling at the cell nucleus: an emerging paradigm. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2006 Mar-Apr;84(3-4):287-97. PMID 16902576
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Y. Sun, R. Olson, M. Horning, N. Armstrong, M. Mayer and E. Gouaux. (2002) Mechanism of glutamate receptor desensitization Nature 417, 245-253
- ↑ S. Pitchford, J.W. Day, A. Gordon and D. Mochly-Rosen. (1992) Acetylcholine receptor desensitization is Regulate by activation-induced extracellular adenosine accumulation. The Journal of Neuroscience, 1.311): 4540-4544.
- ↑ Lanzara, "Optimal Agonist/Antagonist Combinations Maintain Receptor Response by Preventing Rapid Beta-1 adrenergic Receptor Desensitization" Intl. J. Pharmacol., 1(2): 122-131, 2005.[http://www.bio-balance.com/ijp.pdf
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 G. Boulay, L. Chrbtien, D.E. Richard, AND G. Guillemettes. (1994) Short-Term Desensitization of the Angiotensin II Receptor of Bovine Adrenal Glomerulosa Cells Corresponds to a Shift from a High to a Low Affinity State. Endocrinology Vol. 135. No. 5 2130-2136
- ↑ Lippincott's Illustrated Reviews: Immunology. Paperback: 384 pages. Publisher: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; (July 1, 2007). Language: English. ISBN-10: 0781795435. ISBN-13: 978-0781795432. Page 20
External links
- IUPHAR GPCR Database and Ion Channels Compendium
- Cell+surface+receptors at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
ar:مستقبل (كيمياء حيوية) cs:Receptor da:Receptor de:Rezeptor it:Recettore he:קולטן nl:Receptor sk:Receptor sl:Receptor (biokemija) fi:Reseptori (biokemia) sv:Receptor th:รีเซพเตอร์ uk:Рецептор