Sandbox:iqra: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Iqra Qamar (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Iqra Qamar (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
==Physical Examination== | ==Physical Examination== | ||
=== | ===Appearance of the Patient=== | ||
* | *Patient appears well in the earlier stages of the disease | ||
* | *Patient appears ill in the late stages of the disease due to multi-organ involvement | ||
* | ===Vital Signs=== | ||
*[[Fever]] higher than 38 after the exclusion of [[infection]] | |||
*[[Tachycardia]]/[[bradycardia]] depends on the accompanying complication | |||
*[[Tachypnea]]/[[bradypnea]] depends on the accompanying complication | |||
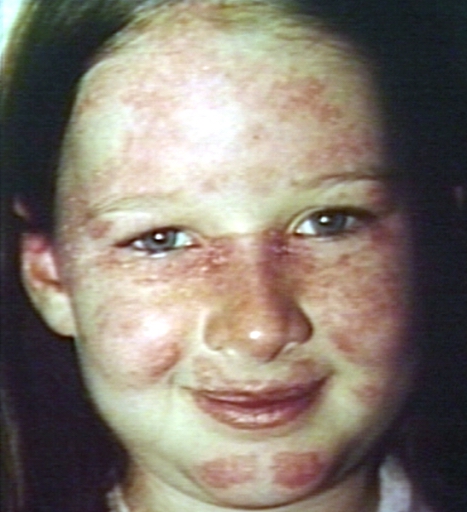
===Skin=== | === Skin<ref name="pmid25077888">{{cite journal |vauthors=Parodi A, Cozzani E |title=Cutaneous manifestations of lupus erythematosus |journal=G Ital Dermatol Venereol |volume=149 |issue=5 |pages=549–54 |year=2014 |pmid=25077888 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid26985173">{{cite journal |vauthors=Szczęch J, Rutka M, Samotij D, Zalewska A, Reich A |title=Clinical characteristics of cutaneous lupus erythematosus |journal=Postepy Dermatol Alergol |volume=33 |issue=1 |pages=13–7 |year=2016 |pmid=26985173 |pmc=4793050 |doi=10.5114/pdia.2014.44031 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid19824738">{{cite journal |vauthors=Walling HW, Sontheimer RD |title=Cutaneous lupus erythematosus: issues in diagnosis and treatment |journal=Am J Clin Dermatol |volume=10 |issue=6 |pages=365–81 |year=2009 |pmid=19824738 |doi=10.2165/11310780-000000000-00000 |url=}}</ref> === | ||
* [[ | *[[Cyanosis]] | ||
* [[ | **Secondary to [[respiratory]] complications | ||
* [[ | *[[Jaundice]] | ||
* | **Secondary to [[hepatitis]] | ||
* [[ | *[[Pallor]] | ||
* [[ | **Secondary to [[anemia]] | ||
* [[ | *Generalised [[erythema]] | ||
* | *[[Bruises]] | ||
* | **Secondary to [[thrombocytopenia]] | ||
* [[ | *[[Urticaria]] | ||
* [[ | *[[Bullous|Bullous lesions]] | ||
* [[ | *[[Sclerodactyly]] | ||
* [[ | *Skin [[Ulcerations|ulceration]] | ||
* | *[[Malar rash]]: the classic lupus ‘butterfly’ rash | ||
* | ** [[Erythema|Erythematous]], elevated [[Lesions|lesion]], [[Pruritis|pruritic]] or painful, in a [[malar]] distribution, commonly precipitated by exposure to sunlight | ||
* Annular or psoriasiform skin [[lesions]] | |||
** Small, [[erythematous]], slightly scaly [[papules]] that evolve into either a psoriasiform (papulosquamous) or annular form and tend to involve shoulders, forearms, neck, and upper torso | |||
* [[Scarring]] [[chronic]] [[alopecia]] | |||
** Mostly present on face, neck, and scalp | |||
* [[Telangiectasias]] | |||
* Dyspigmentation ([[hyperpigmentation]] or [[hypopigmentation]]) of skin in [[scar]] places | |||
* Follicular plugging | |||
** Discrete, [[erythematous]], slightly infiltrated [[plaques]] covered by a well-formed adherent scale that extends into dilated [[hair follicles]] | |||
* [[Nodules]] | |||
** Can be firm (Lupus profundus) and painful | |||
* Photodistributed [[lesions]] with chronic pink indurated plaques or broad [[lesions]] that are slow to heal (more seen in lupus tumidus) | |||
* Thin hair that easily fractures (lupus hair) | |||
* Irregularly shaped raised white plaques, areas of erythema, silvery white scarred [[lesions]], and [[ulcers]] with surrounding [[erythema]] on the soft or hard palate or buccal [[mucosa]] | |||
* Periungual [[erythema]] | |||
** Dilated tortuous loops of [[capillaries]] and a prominent subcapillary venous plexus along | |||
** Involves the base of the nail and edges of the upper [[eyelid]] | |||
[[File:Systemic lupus erythematosus 055.jpg|300px]] | |||
'''For more pictures of the rash presentation in lupus, click [[Systemic lupus eryhthematosus physical examination:Gallery|here]].''' | |||
=== | ===HEENT=== | ||
* [[ | *[[Ophthalmology]]<ref name="pmid26367085">{{cite journal |vauthors=Preble JM, Silpa-archa S, Foster CS |title=Ocular involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus |journal=Curr Opin Ophthalmol |volume=26 |issue=6 |pages=540–5 |year=2015 |pmid=26367085 |doi=10.1097/ICU.0000000000000209 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid25904124">{{cite journal |vauthors=Silpa-archa S, Lee JJ, Foster CS |title=Ocular manifestations in systemic lupus erythematosus |journal=Br J Ophthalmol |volume=100 |issue=1 |pages=135–41 |year=2016 |pmid=25904124 |doi=10.1136/bjophthalmol-2015-306629 |url=}}</ref> | ||
* | **[[Nystagmus]] | ||
**Visual [[Retinal|retinal changes]] from systemic lupus erythematosus cytoid bodies, [[Retina|retinal]] [[haemorrhages]], serous exudate or [[haemorrhage]] in the [[choroid]], [[optic neuritis]] (not due to [[hypertension]], drugs or [[infection]]) | |||
**[[Cataract]] | |||
**[[Optic nerve atrophy]] | |||
**[[Icterus|Icteric sclera]] | |||
**[[Cotton wool spots]] in the [[retina]] in [[Ophthalmoscopy|ophthalmoscopic exam]] | |||
*Nasal [[ulcers]]<ref name="pmid1526055">{{cite journal |vauthors=Robson AK, Burge SM, Millard PR |title=Nasal mucosal involvement in lupus erythematosus |journal=Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci |volume=17 |issue=4 |pages=341–3 |year=1992 |pmid=1526055 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
**Mostly painless | |||
**Mostly in lower [[nasal septum]] and [[bilateral]] and parallel | |||
**Nasal perforation secondary to [[vasculitis]] may happen rarely | |||
*Oral [[ulcers]]<ref name="pmid23780804">{{cite journal |vauthors=Anyanwu CO, Ang CC, Werth VP |title=Oral mucosal involvement in bullous lupus |journal=Arthritis Rheum. |volume=65 |issue=10 |pages=2622 |year=2013 |pmid=23780804 |pmc=4333153 |doi=10.1002/art.38051 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid23248469">{{cite journal |vauthors=Ranginwala AM, Chalishazar MM, Panja P, Buddhdev KP, Kale HM |title=Oral discoid lupus erythematosus: A study of twenty-one cases |journal=J Oral Maxillofac Pathol |volume=16 |issue=3 |pages=368–73 |year=2012 |pmid=23248469 |pmc=3519212 |doi=10.4103/0973-029X.102487 |url=}}</ref> | |||
**Mostly painless | |||
**White plaques with areas of [[erythema]], or punched-out erosions or ulcers with surrounding [[erythema]] on the soft or hard palate or [[buccal mucosa]] | |||
=== | ===Neck<ref name="pmid19107085">{{cite journal |vauthors=Melikoglu MA, Melikoglu M |title=The clinical importance of lymphadenopathy in systemic lupus erythematosus |journal=Acta Reumatol Port |volume=33 |issue=4 |pages=402–6 |year=2008 |pmid=19107085 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid24722263">{{cite journal |vauthors=Sacre K, Escoubet B, Pasquet B, Chauveheid MP, Zennaro MC, Tubach F, Papo T |title=Increased arterial stiffness in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients at low risk for cardiovascular disease: a cross-sectional controlled study |journal=PLoS ONE |volume=9 |issue=4 |pages=e94511 |year=2014 |pmid=24722263 |pmc=3983200 |doi=10.1371/journal.pone.0094511 |url=}}</ref>=== | ||
* [[ | *[[Jugular venous distension]] | ||
* [[ | **Secondary to [[hypertension]] and cardiac complications | ||
*[[Lymphadenopathy]] | |||
** [[Lymph node|Lymph nodes]] are soft, non-tender, discrete | |||
** Usually detected in the [[cervical]], [[axillary]], and [[inguinal]] | |||
=== | ===Lungs<ref name="pmid21194884">{{cite journal |vauthors=Torre O, Harari S |title=Pleural and pulmonary involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus |journal=Presse Med |volume=40 |issue=1 Pt 2 |pages=e19–29 |year=2011 |pmid=21194884 |doi=10.1016/j.lpm.2010.11.004 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid26550810">{{cite journal |vauthors=Salvati F |title=[The involvement of pulmonary interstitial tissue in multisystemic lupus erythematosus: interdisciplinarity and role of the pneumologists] |language=Italian |journal=Clin Ter |volume=166 |issue=5 |pages=205–7 |year=2015 |pmid=26550810 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid25639532">{{cite journal |vauthors=Alamoudi OS, Attar SM |title=Pulmonary manifestations in systemic lupus erythematosus: association with disease activity |journal=Respirology |volume=20 |issue=3 |pages=474–80 |year=2015 |pmid=25639532 |pmc=4418345 |doi=10.1111/resp.12473 |url=}}</ref>=== | ||
*Fine and coarse [[crackles]] upon auscultation of the [[lung]] | |||
**May be due to [[pneumonitis]] | |||
*In case of [[pleural effusion]]: | |||
* [[ | **Asymmetric [[tactile fremitus]] | ||
* | **Asymmetric [[chest expansion]] | ||
=== | ===Heart<ref name="pmid24790989">{{cite journal |vauthors=Mak A, Kow NY |title=Imbalance between endothelial damage and repair: a gateway to cardiovascular disease in systemic lupus erythematosus |journal=Biomed Res Int |volume=2014 |issue= |pages=178721 |year=2014 |pmid=24790989 |pmc=3984775 |doi=10.1155/2014/178721 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid24722263">{{cite journal |vauthors=Sacre K, Escoubet B, Pasquet B, Chauveheid MP, Zennaro MC, Tubach F, Papo T |title=Increased arterial stiffness in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients at low risk for cardiovascular disease: a cross-sectional controlled study |journal=PLoS ONE |volume=9 |issue=4 |pages=e94511 |year=2014 |pmid=24722263 |pmc=3983200 |doi=10.1371/journal.pone.0094511 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid23052654">{{cite journal |vauthors=Canpolat N, Kasapcopur O, Caliskan S, Gokalp S, Bor M, Tasdemir M, Sever L, Arisoy N |title=Ambulatory blood pressure and subclinical cardiovascular disease in patients with juvenile-onset systemic lupus erythematosus |journal=Pediatr. Nephrol. |volume=28 |issue=2 |pages=305–13 |year=2013 |pmid=23052654 |doi=10.1007/s00467-012-2317-3 |url=}}</ref>=== | ||
* | *Chest [[tenderness]] or discomfort upon palpation | ||
* | **May be due to [[costochondritis]] | ||
*[[Diastolic murmurs|Diastolic murmur]], or [[Systolic murmurs|systolic murmur]] >3/6 due to [[valvular disease]] | |||
*Loud second heart sound (due to [[pulmonary hypertension]]) | |||
*Loud S1-S2 due to [[cardiomegaly]] | |||
*Decrease heart sounds if associated with [[pericardial effusion]] | |||
=== | ===Abdomen<ref name="pmid20572299">{{cite journal |vauthors=Tian XP, Zhang X |title=Gastrointestinal involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus: insight into pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment |journal=World J. Gastroenterol. |volume=16 |issue=24 |pages=2971–7 |year=2010 |pmid=20572299 |pmc=2890936 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid27329649">{{cite journal |vauthors=Alves SC, Fasano S, Isenberg DA |title=Autoimmune gastrointestinal complications in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: case series and literature review |journal=Lupus |volume=25 |issue=14 |pages=1509–1519 |year=2016 |pmid=27329649 |doi=10.1177/0961203316655210 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid27055518">{{cite journal |vauthors=Fawzy M, Edrees A, Okasha H, El Ashmaui A, Ragab G |title=Gastrointestinal manifestations in systemic lupus erythematosus |journal=Lupus |volume=25 |issue=13 |pages=1456–1462 |year=2016 |pmid=27055518 |doi=10.1177/0961203316642308 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid28523968">{{cite journal |vauthors=Li Z, Xu D, Wang Z, Wang Y, Zhang S, Li M, Zeng X |title=Gastrointestinal system involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus |journal=Lupus |volume= |issue= |pages=961203317707825 |year=2017 |pmid=28523968 |doi=10.1177/0961203317707825 |url=}}</ref>=== | ||
* [[ | *[[Abdominal distention]] | ||
* [[ | *[[Ascites]] | ||
**Due to [[nephrotic syndrome]] | |||
*[[Abdominal pain]] | |||
**Due to [[Vasculitis|mesentric vasculitis]] | |||
*[[Hepatomegaly]] | |||
*[[Splenomegaly]] | |||
*Costo-vertebral angle tenderness | |||
=== | ===Extremities<ref name="pmid15580980">{{cite journal |vauthors=Zoma A |title=Musculoskeletal involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus |journal=Lupus |volume=13 |issue=11 |pages=851–3 |year=2004 |pmid=15580980 |doi=10.1191/0961203303lu2021oa |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid22956550">{{cite journal |vauthors=Gabba A, Piga M, Vacca A, Porru G, Garau P, Cauli A, Mathieu A |title=Joint and tendon involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus: an ultrasound study of hands and wrists in 108 patients |journal=Rheumatology (Oxford) |volume=51 |issue=12 |pages=2278–85 |year=2012 |pmid=22956550 |doi=10.1093/rheumatology/kes226 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid19591780">{{cite journal |vauthors=Grossman JM |title=Lupus arthritis |journal=Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol |volume=23 |issue=4 |pages=495–506 |year=2009 |pmid=19591780 |doi=10.1016/j.berh.2009.04.003 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid24862229">{{cite journal |vauthors=Zhu KK, Xu WD, Pan HF, Zhang M, Ni J, Ge FY, Ye DQ |title=The risk factors of avascular necrosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a meta-analysis |journal=Inflammation |volume=37 |issue=5 |pages=1852–64 |year=2014 |pmid=24862229 |doi=10.1007/s10753-014-9917-y |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid23731640">{{cite journal |vauthors=Voulgari PV, Kosta P, Argyropoulou MI, Drosos AA |title=Avascular necrosis in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus |journal=Joint Bone Spine |volume=80 |issue=6 |pages=665 |year=2013 |pmid=23731640 |doi=10.1016/j.jbspin.2013.03.018 |url=}}</ref>=== | ||
* [[ | *[[Clubbing]] | ||
*[[Cyanosis]] | |||
*[[Muscle weakness|Muscle atrophy or weakness]] | |||
*[[Livedo reticularis]] | |||
**Reddish-cyanotic, reticular pattern on the skin of the arms, legs, and torso, particularly with cold exposure | |||
*[[Arthritis]] | |||
**Symmetrical | |||
**Polyarticular | |||
**Mostly involve knees, carpal joints, and joints of the fingers, especially the proximal [[interphalangeal]] (PIP) joint | |||
**Decrease range of motion in affected joints | |||
*Joints [[erythema]] | |||
**Due to [[synovitis]] | |||
*Joint effusion | |||
*Muscle [[atrophy]] | |||
*[[Fasciculations]] in the upper/lower extremity | |||
*[[Claudication]] | |||
*Loss of digit or limb | |||
=== | ===Neuromuscular<ref name="pmid19366083">{{cite journal |vauthors=Cojocaru IM, Cojocaru M, Tănăsescu R, Burcin C, Atanasiu AN, Silosi I |title=Detection of autoantibodies to ribosome P in lupus patients with neurological involvement |journal=Rom J Intern Med |volume=46 |issue=3 |pages=239–42 |year=2008 |pmid=19366083 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid22594009">{{cite journal |vauthors=Madrane S, Ribi C |title=[Central neuropsychiatric involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus] |language=French |journal=Rev Med Suisse |volume=8 |issue=337 |pages=848–53 |year=2012 |pmid=22594009 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid7555923">{{cite journal |vauthors=Sivri A, Hasçelik Z, Celiker R, Başgöze O |title=Early detection of neurological involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus patients |journal=Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol |volume=35 |issue=4 |pages=195–9 |year=1995 |pmid=7555923 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid19217587">{{cite journal |vauthors=Juncal Gallego L, Almuíña Simón C, Muíños Esparza LF, Díaz Soto R, Ramil Fraga C, Quiroga Ordóñez E |title=[Systemic lupus erythematosus with fulminant neurological involvement] |language=Spanish; Castilian |journal=An Pediatr (Barc) |volume=70 |issue=2 |pages=202–4 |year=2009 |pmid=19217587 |doi=10.1016/j.anpedi.2008.09.009 |url=}}</ref>=== | ||
*Patient is usually oriented to persons, place, and time based on the disease course | |||
* [[ | *[[Cognitive impairment]] | ||
* | *[[Hallucination|Hallucinations]] | ||
* | **[[Visual hallucinations|Visual]] | ||
* | **[[Auditory hallucinations|Auditory]] | ||
* | *Memory deficit | ||
* | **Loose associations | ||
**Impoverished thought content | |||
**Illogical thinking | |||
**Bizarre disorganised or catatonic behaviour | |||
</div>}} | </div>}} | ||
{{Familytree|boxstyle=width: 700px; text-align: left; font-size: 100%; padding: 0px;| |!| | | |}} | {{Familytree|boxstyle=width: 700px; text-align: left; font-size: 100%; padding: 0px;| |!| | | |}} | ||
Revision as of 17:43, 30 March 2018
SLE resident survival guide:
SLE Presentation
Less common Presentation
| |||||||||||
Focused History
| |||||||||||
Physical ExaminationAppearance of the Patient
Vital Signs
Skin[4][5][6]
HEENT
Neck[12][13]
Lungs[14][15][16]
Heart[17][13][18]
Abdomen[19][20][21][22]
Extremities[23][24][25][26][27]
Neuromuscular[28][29][30][31]
| |||||||||||
Laboratory Workup
| |||||||||||
Imaging StudyChest Radiograph
Echocardiography
Abdominal Ultrasonography
Chest CT Scan
Abdominal CT Scan
Positron Emission Tomography
| |||||||||||
Other InvestigationLymph Node Biopsy
Bone Marrow Biopsy
Discontinuation of Nonessential Medications
Trial of Empiric Antibiotics
Naproxen Test
| |||||||||||
- ↑ Tench CM, McCurdie I, White PD, D'Cruz DP (2000). "The prevalence and associations of fatigue in systemic lupus erythematosus". Rheumatology (Oxford). 39 (11): 1249–54. PMID 11085805.
- ↑ McKinley PS, Ouellette SC, Winkel GH (1995). "The contributions of disease activity, sleep patterns, and depression to fatigue in systemic lupus erythematosus. A proposed model". Arthritis Rheum. 38 (6): 826–34. PMID 7779127.
- ↑ Wang B, Gladman DD, Urowitz MB (1998). "Fatigue in lupus is not correlated with disease activity". J. Rheumatol. 25 (5): 892–5. PMID 9598886.
- ↑ Parodi A, Cozzani E (2014). "Cutaneous manifestations of lupus erythematosus". G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 149 (5): 549–54. PMID 25077888.
- ↑ Szczęch J, Rutka M, Samotij D, Zalewska A, Reich A (2016). "Clinical characteristics of cutaneous lupus erythematosus". Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 33 (1): 13–7. doi:10.5114/pdia.2014.44031. PMC 4793050. PMID 26985173.
- ↑ Walling HW, Sontheimer RD (2009). "Cutaneous lupus erythematosus: issues in diagnosis and treatment". Am J Clin Dermatol. 10 (6): 365–81. doi:10.2165/11310780-000000000-00000. PMID 19824738.
- ↑ Preble JM, Silpa-archa S, Foster CS (2015). "Ocular involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus". Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 26 (6): 540–5. doi:10.1097/ICU.0000000000000209. PMID 26367085.
- ↑ Silpa-archa S, Lee JJ, Foster CS (2016). "Ocular manifestations in systemic lupus erythematosus". Br J Ophthalmol. 100 (1): 135–41. doi:10.1136/bjophthalmol-2015-306629. PMID 25904124.
- ↑ Robson AK, Burge SM, Millard PR (1992). "Nasal mucosal involvement in lupus erythematosus". Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci. 17 (4): 341–3. PMID 1526055.
- ↑ Anyanwu CO, Ang CC, Werth VP (2013). "Oral mucosal involvement in bullous lupus". Arthritis Rheum. 65 (10): 2622. doi:10.1002/art.38051. PMC 4333153. PMID 23780804.
- ↑ Ranginwala AM, Chalishazar MM, Panja P, Buddhdev KP, Kale HM (2012). "Oral discoid lupus erythematosus: A study of twenty-one cases". J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 16 (3): 368–73. doi:10.4103/0973-029X.102487. PMC 3519212. PMID 23248469.
- ↑ Melikoglu MA, Melikoglu M (2008). "The clinical importance of lymphadenopathy in systemic lupus erythematosus". Acta Reumatol Port. 33 (4): 402–6. PMID 19107085.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Sacre K, Escoubet B, Pasquet B, Chauveheid MP, Zennaro MC, Tubach F, Papo T (2014). "Increased arterial stiffness in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients at low risk for cardiovascular disease: a cross-sectional controlled study". PLoS ONE. 9 (4): e94511. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0094511. PMC 3983200. PMID 24722263.
- ↑ Torre O, Harari S (2011). "Pleural and pulmonary involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus". Presse Med. 40 (1 Pt 2): e19–29. doi:10.1016/j.lpm.2010.11.004. PMID 21194884.
- ↑ Salvati F (2015). "[The involvement of pulmonary interstitial tissue in multisystemic lupus erythematosus: interdisciplinarity and role of the pneumologists]". Clin Ter (in Italian). 166 (5): 205–7. PMID 26550810.
- ↑ Alamoudi OS, Attar SM (2015). "Pulmonary manifestations in systemic lupus erythematosus: association with disease activity". Respirology. 20 (3): 474–80. doi:10.1111/resp.12473. PMC 4418345. PMID 25639532.
- ↑ Mak A, Kow NY (2014). "Imbalance between endothelial damage and repair: a gateway to cardiovascular disease in systemic lupus erythematosus". Biomed Res Int. 2014: 178721. doi:10.1155/2014/178721. PMC 3984775. PMID 24790989.
- ↑ Canpolat N, Kasapcopur O, Caliskan S, Gokalp S, Bor M, Tasdemir M, Sever L, Arisoy N (2013). "Ambulatory blood pressure and subclinical cardiovascular disease in patients with juvenile-onset systemic lupus erythematosus". Pediatr. Nephrol. 28 (2): 305–13. doi:10.1007/s00467-012-2317-3. PMID 23052654.
- ↑ Tian XP, Zhang X (2010). "Gastrointestinal involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus: insight into pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment". World J. Gastroenterol. 16 (24): 2971–7. PMC 2890936. PMID 20572299.
- ↑ Alves SC, Fasano S, Isenberg DA (2016). "Autoimmune gastrointestinal complications in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: case series and literature review". Lupus. 25 (14): 1509–1519. doi:10.1177/0961203316655210. PMID 27329649.
- ↑ Fawzy M, Edrees A, Okasha H, El Ashmaui A, Ragab G (2016). "Gastrointestinal manifestations in systemic lupus erythematosus". Lupus. 25 (13): 1456–1462. doi:10.1177/0961203316642308. PMID 27055518.
- ↑ Li Z, Xu D, Wang Z, Wang Y, Zhang S, Li M, Zeng X (2017). "Gastrointestinal system involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus". Lupus: 961203317707825. doi:10.1177/0961203317707825. PMID 28523968.
- ↑ Zoma A (2004). "Musculoskeletal involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus". Lupus. 13 (11): 851–3. doi:10.1191/0961203303lu2021oa. PMID 15580980.
- ↑ Gabba A, Piga M, Vacca A, Porru G, Garau P, Cauli A, Mathieu A (2012). "Joint and tendon involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus: an ultrasound study of hands and wrists in 108 patients". Rheumatology (Oxford). 51 (12): 2278–85. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kes226. PMID 22956550.
- ↑ Grossman JM (2009). "Lupus arthritis". Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 23 (4): 495–506. doi:10.1016/j.berh.2009.04.003. PMID 19591780.
- ↑ Zhu KK, Xu WD, Pan HF, Zhang M, Ni J, Ge FY, Ye DQ (2014). "The risk factors of avascular necrosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a meta-analysis". Inflammation. 37 (5): 1852–64. doi:10.1007/s10753-014-9917-y. PMID 24862229.
- ↑ Voulgari PV, Kosta P, Argyropoulou MI, Drosos AA (2013). "Avascular necrosis in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus". Joint Bone Spine. 80 (6): 665. doi:10.1016/j.jbspin.2013.03.018. PMID 23731640.
- ↑ Cojocaru IM, Cojocaru M, Tănăsescu R, Burcin C, Atanasiu AN, Silosi I (2008). "Detection of autoantibodies to ribosome P in lupus patients with neurological involvement". Rom J Intern Med. 46 (3): 239–42. PMID 19366083.
- ↑ Madrane S, Ribi C (2012). "[Central neuropsychiatric involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus]". Rev Med Suisse (in French). 8 (337): 848–53. PMID 22594009.
- ↑ Sivri A, Hasçelik Z, Celiker R, Başgöze O (1995). "Early detection of neurological involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus patients". Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol. 35 (4): 195–9. PMID 7555923.
- ↑ Juncal Gallego L, Almuíña Simón C, Muíños Esparza LF, Díaz Soto R, Ramil Fraga C, Quiroga Ordóñez E (2009). "[Systemic lupus erythematosus with fulminant neurological involvement]". An Pediatr (Barc) (in Spanish; Castilian). 70 (2): 202–4. doi:10.1016/j.anpedi.2008.09.009. PMID 19217587.