|
|
| (65 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
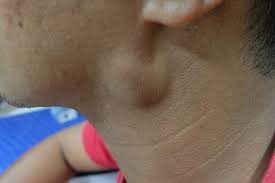
| | [[File:ImageLymphadenopathy.jpg|300px|thumb|right|Lymphadenopathy]] |
| | |
| __NOTOC__ | | __NOTOC__ |
| {{SI}} | | {{Lymphadenopathy}} |
| {{CMG}} {{shyam}} {{AE}} {{MV}} {{RT}} | | {{CMG}},{{shyam}};{{AE}} {{ADS}}, {{RT}} [[Ogechukwu Hannah Nnabude, MD]] |
|
| |
| {{SK}} Lymph nodes enlarged; Enlarged lymph nodes; Lymphadenitis; Swollen lymph nodes; Swollen/enlarged lymph nodes
| |
|
| |
| ==Overview==
| |
| '''Lymphadenopathy''' (also known as "enlarged lymph nodes") refers to [[lymph nodes]] which are abnormal in size, number or consistency. Common causes of lymphadenopathy are [[infection]], [[autoimmune]] disease, or [[malignancy]]. Lymphadenopathy may be classified according to distribution into 2 groups: generalized lymphadenopathy and localized lymphadenopathy. The pathogenesis of lymphadenopathy is characterized by the inflammation of lymph nodes. This process is primarily due to an elevated rate of trafficking of [[lymphocytes]] into the node from the blood, exceeding the rate of outflow from the node. Lymph nodes may also be enlarged secondarily as a result of the activation and proliferation of antigen-specific T and [[B cells]] (clonal expansion). Lymphadenopathy is very common, the estimated incidence of lymphadenopathy among children in the United States ranges from 35%- 45%. Patients of all age groups may develop lymphadenopathy. Lymphadenopathy is more commonly observed among children. Common complications of lymphadenopathy, may include: [[Abscess|abscess formation]], [[superior vena cava syndrome]], and [[intestinal obstruction]]. Diagnostic criteria for [[malignant]] lymphadenopathy, may include: node > 2 cm, node that is draining, hard, or fixed to underlying tissue, atypical location (e.g. [[supraclavicular]] node), associated risk factors (e.g. [[HIV AIDS|HIV]] or [[Tuberculosis|TB]]), fever and/or weight loss, and [[splenomegaly]]. On the other hand, diagnostic criteria for [[benign]] lymphadenopathy, may include: node < 1 cm, node that is mobile, soft-or tender, and is not fixed to underlying tissue, typical location (e.g. supraclavicular node), no associated risk factors, and palpable and painful enlargement. Laboratory findings consistent with the diagnosis of lymphadenopathy, may include: elevated lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), mild neutropenia, and [[leukocytosis]]. There is no treatment for lymphadenopathy; the mainstay of therapy is treating the underlying condition.
| |
| | |
| ==Classification==
| |
| *Lymphadenopathy may be classified according to distribution into 2 groups:<ref name="pmid24753638">{{cite journal |vauthors=Mohseni S, Shojaiefard A, Khorgami Z, Alinejad S, Ghorbani A, Ghafouri A |title=Peripheral lymphadenopathy: approach and diagnostic tools |journal=Iran J Med Sci |volume=39 |issue=2 Suppl |pages=158–70 |year=2014 |pmid=24753638 |pmc=3993046 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="AA">Lymph node enlargment. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lymph_node Accessed on May 9, 2016</ref>
| |
| | |
| :*Generalized lymphadenopathy
| |
| :*Localized lymphadenopathy
| |
| | |
| ==Pathophysiology==
| |
| *The pathogenesis of lymphadenopathy is characterized by the inflammation of lymph nodes. This process is primarily due to an elevated rate of trafficking of lymphocytes into the node from the blood, exceeding the rate of outflow from the node.<ref name="pmid24753638">{{cite journal |vauthors=Mohseni S, Shojaiefard A, Khorgami Z, Alinejad S, Ghorbani A, Ghafouri A |title=Peripheral lymphadenopathy: approach and diagnostic tools |journal=Iran J Med Sci |volume=39 |issue=2 Suppl |pages=158–70 |year=2014 |pmid=24753638 |pmc=3993046 |doi= |url=}}</ref>
| |
| *The inmune response between the antigen and lymphocyte that leads to cellular proliferation and enlargement of the lymph nodes.
| |
| *Lymph nodes may also be enlarged secondarily as a result of the activation and proliferation of antigen-specific T and B cells (clonal expansion).
| |
| *On gross pathology, characteristic findings of lymphadenopathy, include:
| |
| :*Enlarged lymph node
| |
| :*Soft greasy yellow areas within capsule
| |
| *On microscopic histopathological analysis, characteristic findings of lymphadenopathy will depend on the aetiology.
| |
| *Common findings, include:<ref name="pmid24753638">{{cite journal |vauthors=Mohseni S, Shojaiefard A, Khorgami Z, Alinejad S, Ghorbani A, Ghafouri A |title=Peripheral lymphadenopathy: approach and diagnostic tools |journal=Iran J Med Sci |volume=39 |issue=2 Suppl |pages=158–70 |year=2014 |pmid=24753638 |pmc=3993046 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="AA">Lymph node enlargment. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lymph_node Accessed on May 9, 2016</ref>
| |
| | |
| '''Non-specific reactive follicular [[hyperplasia]] (NSRFH)'''
| |
| :*Large spaced cortical follicles
| |
| :*Tingible body [[macrophages]], normal dark/light GC pattern
| |
| '''Lymph node metastasis'''
| |
| :*Foreign cell population (usually in subcapsular sinuses)
| |
| :*+/-nuclear [[atypia]]
| |
| :* +/-malignant architecture
| |
| '''Toxoplasmosis'''
| |
| :*Large [[follicles]]
| |
| :*Epithelioid cells perifollicular & intrafollicular
| |
| :*Reactive GCs
| |
| :*Monocytoid cell clusters
| |
| '''Cat-scratch disease'''
| |
| :*PMNs in necrotic area
| |
| :*"Stellate" (or serpentine) shaped micro-abscesses
| |
| :*Presence of granulomas
| |
| '''Dermatopathic lymphadenopathy'''
| |
| :*Melanin-laden histiocytes
| |
| :*Histiocytosis
| |
| '''Systemic lupus erythematosus lymphadenopathy'''
| |
| :*Blue hematoxylin bodies
| |
| :*[[Necrosis]]
| |
| :*No PMNs
| |
| | |
| ==Causes==
| |
| | |
| ===Common Causes===
| |
| {{columns-list|2|
| |
| *[[Acute lymphatic leukemia]]
| |
| *[[Addison's disease]]
| |
| *[[Adult T cell leukemia]]
| |
| *[[African sleeping sickness]]
| |
| *[[Aids]]
| |
| *[[Bartonella]]
| |
| *[[Bejel]]
| |
| *[[Borrelia burgdorferi]]
| |
| *[[Boutonneuse fever]]
| |
| *[[Breast cancer]]
| |
| *[[Brucellosis]]
| |
| *[[Cat scratch disease]]
| |
| *[[Chagas' disease]]
| |
| *[[Chronic lymphatic leukemia]]
| |
| *[[Coccidioidomycosis]]
| |
| *[[Colorectal cancer]]
| |
| *[[Congenital toxoplasmosis]]
| |
| *[[Cowpox]]
| |
| *[[Coxsackie virus infections]]
| |
| *[[Cryptococcosis]]
| |
| *[[Cutaneous leishmaniasis ]]
| |
| *[[Cutaneous T cell lymphoma]]
| |
| *[[Cystic hygroma]]
| |
| *[[Cytomegalovirus infection]]
| |
| *[[Dengue]]
| |
| *[[Diphtheria]]
| |
| *[[Epstein-barr virus]]
| |
| *[[Epstein-barr virus]]
| |
| *[[Erysipelas]]
| |
| *[[Erythroderma]]
| |
| *[[Ethotoin]]
| |
| *[[Filaria]]
| |
| *[[Fungal blastomycosis]]
| |
| *[[Gamma heavy chain disease]]
| |
| *[[German measles]]
| |
| *[[Granuloma inguinale]]
| |
| *[[Hemangiopericytoma]]
| |
| *[[Hepatitis A]]
| |
| *[[Hepatitis B]]
| |
| *[[Herpes simplex]]
| |
| *[[Histoplasmosis]]
| |
| *[[Hiv-1 disease]]
| |
| *[[Hodgkin's lymphoma]]
| |
| *[[Human immunodeficiency virus]]
| |
| *[[Leukemia]]
| |
| *[[Lip cancer]]
| |
| *[[Listeriosis]]
| |
| *[[Lyme disease]]
| |
| *[[Lymphangioma]]
| |
| *[[Lymphangitis]]
| |
| *[[Lymphatic filariasis]]
| |
| *[[Lymphogranuloma venereum]]
| |
| *[[Lymphoma]]
| |
| *[[Malignant lymphoma]]
| |
| *[[Measles]]
| |
| *[[Melanoma]]
| |
| *[[Merkel cell carcinoma]]
| |
| *[[Mesenteric adenitis]]
| |
| *[[Moraxella catarrhalis]]
| |
| *[[Mucocutaneous leishmaniasis]]
| |
| *[[Opisthorchiasis]]
| |
| *[[Pancoast tumor]]
| |
| *[[Paracoccidioidomycosis]]
| |
| *[[Plague]]
| |
| *[[Plasma cell leukemia]]
| |
| *[[Pneumoconiosis]]
| |
| *[[Primary autoimmune haemolytic anaemia]]
| |
| *[[Protozoa]]
| |
| *[[Pseudolymphoma]]
| |
| *[[Rat-bite fever]]
| |
| *[[Reticuloendotheliosis]]
| |
| *[[Rhabditida infections]]
| |
| *[[Rhabdomyosarcoma]]
| |
| *[[Rickettsiae]]
| |
| *[[Rubella]]
| |
| *[[Sarcoidosis]]
| |
| *[[Scrub typhus]]
| |
| *[[Secondary deposits from a local malignancy]]
| |
| *[[Secondary syphilis]]
| |
| *[[Sennetsu fever]]
| |
| *[[Septicaemia]]
| |
| *[[Serum sickness]]
| |
| *[[Smallpox]]
| |
| *[[Sporotrichosis]]
| |
| *[[Spotted fevers]]
| |
| *[[Stomach cancer]]
| |
| *[[Toxoplasma]]
| |
| *[[Toxoplasmosis]]
| |
| *[[Trypanosomiasis]]
| |
| *[[Tuberculosis]]
| |
| *[[Tularemia]]
| |
| *[[Typhus fever]]
| |
| *[[Varicella]]
| |
| *[[Visceral leishmaniasis]]
| |
| *[[Waldenström macroglobulinemia]]
| |
| *[[Western equine encephalitis]]
| |
| *[[Whipple's disease]]
| |
| *[[Wuchereria bancrofti]]
| |
| *[[Yaws]]
| |
| *[[Yersinia pestis]]
| |
| }}
| |
| | |
| ===Causes by Organ System===
| |
| {| style="width:80%; height:100px" border="1"
| |
| | style="width:25%" bgcolor="LightSteelBlue" ; border="1" |'''Cardiovascular'''
| |
| | style="width:75%" bgcolor="Beige" ; border="1" | [[Apo a-i deficiency]]
| |
| |-
| |
| | bgcolor="LightSteelBlue" | '''Chemical/Poisoning'''
| |
| | bgcolor="Beige" | [[Anthrax]], [[Black widow spider venom]], [[Zinc]]
| |
| |-
| |
| |- bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Dental'''
| |
| | bgcolor="Beige" | [[Lip cancer]]
| |
| |-
| |
| |- bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Dermatologic'''
| |
| | bgcolor="Beige" | [[Aphthous stomatitis]], [[Asymmetric periflexural exanthem ]] , [[Dermatomyositis]], [[Erysipelas]], [[Erythroderma]], [[Gingivostomatitis]], [[Infantile papular acrodermatitis]], [[Leprosy]], [[Mastitis]], [[Measles]], [[Melanoma]], [[Mumps]], [[Sarcoidosis]], [[Spotted fevers]], [[Yaws]]
| |
| |-
| |
| |- bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Drug Side Effect'''
| |
| | bgcolor="Beige" | [[Allopurinol]], [[Atenolol]], [[Bcg vaccine]], [[Captopril]], [[Carbamazepine]], [[Cephalosporins]], [[Certolizumab pegol]], [[Hydralazine]], [[Infliximab]], [[Oxaprozin]], [[Penicillin]], [[Penicillium marneffei]], [[Phenytoin]], [[Pinta]], [[Pneumococcal vaccine 13-valent ]] , [[Primidone]], [[Pyrimethamine]], [[Quinidine]], [[Sulfonamides]], [[Sulindac]], [[Tiagabine]], [[Typhoid vaccination]]
| |
| |-
| |
| |- bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Ear Nose Throat'''
| |
| | bgcolor="Beige" | [[Aphthous stomatitis]], [[Kikuchi's disease]], [[Lymphangioma]], [[Lymphangitis]], [[Lymphatic filariasis]], [[Lymphoma]], [[Malignant lymphoma]], [[Mesenteric adenitis]], [[Sinus histiocytosis]], [[Streptococcal pharyngitis]], [[Vincent's angina]]
| |
| |-
| |
| |- bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Endocrine'''
| |
| | bgcolor="Beige" | [[Castleman's disease]], [[Chediak-higashi syndrome]], [[Hyperthyroidism]]
| |
| |-
| |
| |- bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Environmental'''
| |
| | bgcolor="Beige" | No underlying causes
| |
| |-
| |
| |- bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Gastroenterologic'''
| |
| | bgcolor="Beige" | [[Brucellosis]], [[Colorectal cancer]], [[Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis]], [[Stomach cancer]], [[Whipple's disease]]
| |
| |-
| |
| |- bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Genetic'''
| |
| | bgcolor="Beige" | [[Chediak-higashi syndrome]], [[Churg-strauss syndrome]], [[Faisalabad histiocytosis]], [[Familial alphalipoprotein deficiency]], [[Familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis]], [[Familial histiocytic reticulosis]], [[Griscelli disease]], [[Lipogranulomatosis]], [[Rosai-dorfman disease]], [[Siccardi syndrome]], [[Sphingomyelinase deficiency]], [[Wt limb blood syndrome]], [[X-linked agammaglobulinaemia]], [[X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome]]
| |
| |-
| |
| |- bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Hematologic'''
| |
| | bgcolor="Beige" | [[Acute lymphatic leukemia]], [[Acute lymphoblastic leukemia]], [[Acute lymphocytic leukemia]], [[Addison's disease]], [[Adult t cell leukemia]], [[Apo a-i deficiency]], [[Autoimmune haemolytic anaemia]], [[Autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome type 1]], [[Caspase-8 deficiency]], [[Chancroid]], [[Chronic lymphatic leukemia]], [[Chronic lymphocytic leukemia]], [[Churg-strauss syndrome]], [[Cutaneous t cell lymphoma]], [[Familial alphalipoprotein deficiency]], [[Familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis]], [[Familial histiocytic reticulosis]], [[Hairy cell leukaemia]], [[Hemoblastosis]], [[Histiocytosis x]], [[Hodgkin's lymphoma]], [[Hyperimmunoglobulinemia d ]] , [[Kawasaki disease]], [[Large granular lymphocyte leukemia]], [[Lassa fever]], [[Leukemia]], [[Macroglobulinemia]], [[Myeloproliferative disorder]], [[Non-hodgkin's lymphoma]], [[Plasma cell leukemia]], [[Primary autoimmune haemolytic anaemia]], [[Pseudolymphoma]], [[Septicaemia]], [[Siccardi syndrome]], [[Sinus histiocytosis]], [[Waldenström macroglobulinemia]], [[Yersinia pestis]]
| |
| |-
| |
| |- bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Iatrogenic'''
| |
| | bgcolor="Beige" | [[Bcg vaccine]], [[Pneumococcal vaccine 13-valent ]] , [[Radiotherapy]], [[Typhoid vaccination]]
| |
| |-
| |
| |- bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Infectious Disease'''
| |
| | bgcolor="Beige" | [[African sleeping sickness]], [[Aids]], [[Bartonella]], [[Bejel]], [[Borrelia burgdorferi]], [[Boutonneuse fever]], [[Brucellosis]], [[Cat scratch disease]], [[Chagas' disease]], [[Coccidioidomycosis]], [[Congenital toxoplasmosis]], [[Cowpox]], [[Coxsackie virus infections]], [[Cryptococcosis]], [[Cutaneous leishmaniasis ]] , [[Cytomegalovirus infection]], [[Dengue]], [[Diphtheria]], [[Epstein-barr virus]], [[Erysipelas]], [[Erythroderma]], [[Ethotoin]], [[Filaria]], [[Fungal blastomycosis]], [[German measles]], [[Hepatitis a]], [[Hepatitis b]], [[Herpes simplex]], [[Herpes virus 2]], [[Histoplasmosis]], [[Hiv-1 disease]], [[Human immunodeficiency virus]], [[Infectious mononucleosis]], [[Inflammatory pseudotumor]], [[Influenza]], [[Lassa fever]], [[Leptospirosis]], [[Listeriosis]], [[Lyme disease]], [[Lymphangitis]], [[Lymphatic filariasis]], [[Lymphogranuloma venereum]], [[Measles]], [[Mesenteric adenitis]], [[Moraxella catarrhalis]], [[Mucocutaneous leishmaniasis]], [[Mumps]], [[Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare]], [[Mycobacterium chelonae]], [[Mycosis fungoides]], [[Onchocerciasis]], [[Opisthorchiasis]], [[Paracoccidioidomycosis]], [[Plague]], [[Pneumoconiosis]], [[Protozoa]], [[Rat-bite fever]], [[Rhabditida infections]], [[Rickettsiae]], [[Rubella]], [[Sarcoidosis]], [[Scrub typhus]], [[Secondary syphilis]], [[Sennetsu fever]], [[Septicaemia]], [[Serum sickness]], [[Sexually transmitted diseases]], [[Smallpox]], [[Sporotrichosis]], [[Spotted fevers]], [[Streptococcal pharyngitis]], [[Streptococcal tonsillitis]], [[Syphilis]], [[Systemic infection]], [[Three-day fever]], [[Toxoplasma]], [[Toxoplasmosis]], [[Trypanosomiasis]], [[Tuberculosis]], [[Tularemia]], [[Typhus fever]], [[Varicella]], [[Visceral leishmaniasis]], [[Western equine encephalitis]], [[Whipple's disease]], [[Wuchereria bancrofti]], [[Yaws]], [[Yersinia pestis]]
| |
| |-
| |
| |- bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Musculoskeletal/Orthopedic'''
| |
| | bgcolor="Beige" | [[Dermatomyositis]], [[Rhabdomyosarcoma]], [[Rheumatoid arthritis]]
| |
| |-
| |
| |- bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Neurologic'''
| |
| | bgcolor="Beige" | [[African sleeping sickness]], [[Western equine encephalitis]]
| |
| |-
| |
| |- bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Nutritional/Metabolic'''
| |
| | bgcolor="Beige" | [[Lipogranulomatosis]]
| |
| |-
| |
| |- bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Obstetric/Gynecologic'''
| |
| | bgcolor="Beige" | [[Breast cancer]], [[Lymphogranuloma venereum]]
| |
| |-
| |
| |- bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Oncologic'''
| |
| | bgcolor="Beige" | [[Acute lymphatic leukemia]], [[Acute lymphoblastic leukemia]], [[Acute lymphocytic leukemia]], [[Addison's disease]], [[Adult t cell leukemia]], [[Breast cancer]], [[Chronic lymphatic leukemia]], [[Chronic lymphocytic leukemia]], [[Colorectal cancer]], [[Cutaneous t cell lymphoma]], [[Cystic hygroma]], [[Epstein-barr virus]], [[Gamma heavy chain disease]], [[Granuloma inguinale]], [[Hemangiopericytoma]], [[Hodgkin's lymphoma]], [[Inflammatory pseudotumor]], [[Kikuchi's disease]], [[Leukemia]], [[Lip cancer]], [[Lymphangioma]], [[Lymphoma]], [[Malignant lymphoma]], [[Melanoma]], [[Merkel cell carcinoma]], [[Myeloproliferative disorder]], [[Non-hodgkin's lymphoma]], [[Pancoast tumor]], [[Plasma cell leukemia]], [[Primary autoimmune haemolytic anaemia]], [[Pseudolymphoma]], [[Reticuloendotheliosis]], [[Rhabdomyosarcoma]], [[Secondary deposits from a local malignancy]], [[Stomach cancer]], [[Systemic mastocytosis]], [[Waldenström macroglobulinemia]]
| |
| |-
| |
| |- bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Ophthalmologic'''
| |
| | bgcolor="Beige" | No underlying causes
| |
| |-
| |
| |- bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Overdose/Toxicity'''
| |
| | bgcolor="Beige" | No underlying causes
| |
| |-
| |
| |- bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Psychiatric'''
| |
| | bgcolor="Beige" | No underlying causes
| |
| |-
| |
| |- bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Pulmonary'''
| |
| | bgcolor="Beige" | [[Congenital tuberculosis]], [[Extrinsic allergic alveolitis]], [[Histoplasmosis]], [[Pancoast tumor]], [[Pneumoconiosis]], [[Tuberculosis]]
| |
| |-
| |
| |- bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Renal/Electrolyte'''
| |
| | bgcolor="Beige" | No underlying causes
| |
| |-
| |
| |- bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Rheumatology/Immunology/Allergy'''
| |
| | bgcolor="Beige" | [[Amyloidosis]], [[Extrinsic allergic alveolitis]], [[Hemangiopericytoma]], [[Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis]], [[Hemophagocytic reticulosis]], [[Juvenile chronic arthritis]], [[Rheumatoid arthritis]], [[Rheumatoid disease]], [[Still's disease]], [[Systemic lupus erythematosus]]
| |
| |-
| |
| |- bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Sexual'''
| |
| | bgcolor="Beige" | [[Aids]], [[Bejel]], [[Chancroid]], [[Herpes simplex]], [[Herpes virus 2]], [[Hiv-1 disease]], [[Human immunodeficiency virus]], [[Secondary syphilis]], [[Sexually transmitted diseases]], [[Syphilis]]
| |
| |-
| |
| |- bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Trauma'''
| |
| | bgcolor="Beige" | [[Snake bite ]] , [[Spider bite]]
| |
| |-
| |
| |- bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Urologic'''
| |
| | bgcolor="Beige" | [[Granuloma inguinale]]
| |
| |-
| |
| |- bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Miscellaneous'''
| |
| | bgcolor="Beige" | [[Tang hsi ryu syndrome]]
| |
| |-
| |
| |}
| |
| | |
| ===Causes in Alphabetical Order===
| |
| <div style="-moz-column-count:3; column-count:3;">
| |
| *[[Acute lymphoblastic leukemia]]
| |
| *[[Acute lymphocytic leukemia]]
| |
| *[[Addison's disease]]
| |
| *[[Adult t cell leukemia]]
| |
| *[[African sleeping sickness]]
| |
| *[[Aids]]
| |
| *[[Allopurinol]]
| |
| *[[Amyloidosis]]
| |
| *[[Angioimmunoblastic lymphadenopathy]]
| |
| *[[Anthrax]]
| |
| *[[Aphthous stomatitis]]
| |
| *[[Apo a-i deficiency]]
| |
| *[[Asymmetric periflexural exanthem ]]
| |
| *[[Atenolol]]
| |
| *[[Autoimmune haemolytic anaemia]]
| |
| *[[Autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome type 1]]
| |
| *[[Bartonella]]
| |
| *[[Bcg vaccine]]
| |
| *[[Bejel]]
| |
| *[[Black widow spider venom]]
| |
| *[[Borrelia burgdorferi]]
| |
| *[[Boutonneuse fever]]
| |
| *[[Breast cancer]]
| |
| *[[Brucellosis]]
| |
| *[[Captopril]]
| |
| *[[Carbamazepine]]
| |
| *[[Caspase-8 deficiency]]
| |
| *[[Castleman's disease]]
| |
| *[[Cat scratch disease]]
| |
| *[[Cephalosporins]]
| |
| *[[Certolizumab pegol]]
| |
| *[[Chagas' disease]]
| |
| *[[Chancroid]]
| |
| *[[Chediak-higashi syndrome]]
| |
| *[[Chronic lymphatic leukemia]]
| |
| *[[Chronic lymphocytic leukemia]]
| |
| *[[Churg-strauss syndrome]]
| |
| *[[Coccidioidomycosis]]
| |
| *[[Colorectal cancer]]
| |
| *[[Congenital toxoplasmosis]]
| |
| *[[Congenital tuberculosis]]
| |
| *[[Cowpox]]
| |
| *[[Coxsackie virus]] infections
| |
| *[[Cryptococcosis]]
| |
| *[[Cutaneous leishmaniasis ]]
| |
| *[[Cutaneous t cell lymphoma]]
| |
| *[[Cystic hygroma]]
| |
| *[[Cytomegalovirus infection]]
| |
| *[[Dengue]]
| |
| *[[Dermatomyositis]]
| |
| *[[Diphtheria]]
| |
| *[[Epstein-barr virus]]
| |
| *[[Erysipelas]]
| |
| *[[Erythroderma]]
| |
| *[[Ethotoin]]
| |
| *[[Extrinsic allergic alveolitis]]
| |
| *[[Faisalabad histiocytosis]]
| |
| *[[Familial alphalipoprotein deficiency]]
| |
| *[[Familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis]]
| |
| *[[Familial histiocytic reticulosis]]
| |
| *[[Filaria]]
| |
| *[[Fungal blastomycosis]]
| |
| *[[Gamma heavy chain disease]]
| |
| *[[German measles]]
| |
| *[[Gingivostomatitis]]
| |
| *[[Gold]]
| |
| *[[Granuloma inguinale]]
| |
| *[[Griscelli disease]]
| |
| *[[Hairy cell leukaemia]]
| |
| *[[Hemangiopericytoma]]
| |
| *Hemoblastosis
| |
| *[[Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis]]
| |
| *[[Hemophagocytic reticulosis]]
| |
| *[[Hepatitis]] a
| |
| *[[Hepatitis]]b
| |
| *[[Herpes simplex]]
| |
| *[[Herpes virus 2]]
| |
| *[[Histiocytosis x]]
| |
| *[[Histoplasmosis]]
| |
| *[[Hiv-1 disease]]
| |
| *[[Hodgkin's lymphoma]]
| |
| *[[Human immunodeficiency virus]]
| |
| *[[Hydralazine]]
| |
| *[[Hyperimmunoglobulinemia d ]]
| |
| *[[Hyperthyroidism]]
| |
| *[[Infantile papular acrodermatitis]]
| |
| *[[Infectious mononucleosis]]
| |
| *[[Inflammatory pseudotumor]]
| |
| *[[Infliximab]]
| |
| *[[Influenza]]
| |
| *[[Juvenile chronic arthritis]]
| |
| *[[Kawasaki disease]]
| |
| *[[Kikuchi's disease]]
| |
| *[[Large granular lymphocyte leukemia]]
| |
| *[[Lassa fever]]
| |
| *[[Leprosy]]
| |
| *[[Leptospirosis]]
| |
| *[[Leukemia]]
| |
| *[[Lip cancer]]
| |
| *[[Lipogranulomatosis]]
| |
| *[[Listeriosis]]
| |
| *[[Local bacterial infection]]
| |
| *[[Lyme disease]]
| |
| *[[Lymphangioma]]
| |
| *[[Lymphangitis]]
| |
| *[[Lymphatic filariasis]]
| |
| *[[Lymphogranuloma venereum]]
| |
| *[[Lymphoma]]
| |
| *[[Macroglobulinemia]]
| |
| *[[Malignant lymphoma]]
| |
| *[[Mastitis]]
| |
| *[[Measles]]
| |
| *[[Melanoma]]
| |
| *[[Merkel cell carcinoma]]
| |
| *[[Mesenteric adenitis]]
| |
| *[[Metastasis]]
| |
| *[[Moraxella catarrhalis]]
| |
| *[[Mucocutaneous leishmaniasis]]
| |
| *[[Mumps]]
| |
| *[[Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare]]
| |
| *[[Mycobacterium chelonae]]
| |
| *[[Mycosis fungoides]]
| |
| *[[Myeloproliferative disorder]]
| |
| *[[Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma]]
| |
| *[[Onchocerciasis]]
| |
| *[[Opisthorchiasis]]
| |
| *[[Oxaprozin]]
| |
| *[[Pancoast tumor]]
| |
| *[[Paracoccidioidomycosis]]
| |
| *[[Penicillin]]
| |
| *[[Penicillium marneffei]]
| |
| *[[Phenytoin]]
| |
| *[[Pinta]]
| |
| *[[Plague]]
| |
| *[[Plasma cell leukemia]]
| |
| *[[Pneumococcal vaccine 13-valent ]]
| |
| *[[Pneumoconiosis]]
| |
| *[[Primary autoimmune haemolytic anaemia]]
| |
| *[[Primidone]]
| |
| *[[Protozoa]]
| |
| *[[Pseudolymphoma]]
| |
| *[[Pyrimethamine]]
| |
| *[[Quinidine]]
| |
| *[[Radiotherapy]]
| |
| *[[Rat-bite fever]]
| |
| *[[Reticuloendotheliosis]]
| |
| *Rhabditida infections
| |
| *[[Rhabdomyosarcoma]]
| |
| *[[Rheumatoid arthritis]]
| |
| *[[Rheumatoid disease]]
| |
| *[[Rickettsiae]]
| |
| *[[Rosai-dorfman disease]]
| |
| *[[Rubella]]
| |
| *[[Sarcoidosis]]
| |
| *[[Scrub typhus]]
| |
| *[[Secondary deposits from a local malignancy]]
| |
| *[[Secondary syphilis]]
| |
| *[[Sennetsu fever]]
| |
| *[[Septicaemia]]
| |
| *[[Serum sickness]]
| |
| *[[Sexually transmitted diseases]]
| |
| *[[Siccardi syndrome]]
| |
| *[[Sinus histiocytosis]]
| |
| *[[Smallpox]]
| |
| *[[Snake bite ]]
| |
| *[[Sphingomyelinase deficiency]]
| |
| *[[Spider bite]]
| |
| *[[Sporotrichosis]]
| |
| *[[Spotted fevers]]
| |
| *[[Still's disease]]
| |
| *[[Stomach cancer]]
| |
| *[[Streptococcal pharyngitis]]
| |
| *[[Streptococcal tonsillitis]]
| |
| *[[Sulfonamides]]
| |
| *[[Sulindac]]
| |
| *[[Syphilis]]
| |
| *[[Systemic infection]]
| |
| *[[Systemic lupus erythematosus]]
| |
| *[[Systemic mastocytosis]]
| |
| *[[Tang hsi ryu syndrome]]
| |
| *[[Three-day fever]]
| |
| *[[Tiagabine]]
| |
| *[[Toxoplasma]]
| |
| *[[Toxoplasmosis]]
| |
| *[[Trypanosomiasis]]
| |
| *[[Tuberculosis]]
| |
| *[[Tularemia]]
| |
| *[[Typhoid vaccination]]
| |
| *[[Typhus fever]]
| |
| *[[Varicella]]
| |
| *[[Vincent's angina]]
| |
| *[[Visceral leishmaniasis]]
| |
| *[[Waldenström macroglobulinemia]]
| |
| *[[Western equine encephalitis]]
| |
| *[[Whipple's disease]]
| |
| *[[Wt limb blood syndrome]]
| |
| *[[Wuchereria bancrofti]]
| |
| *[[X-linked agammaglobulinaemia]]
| |
| *[[X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome]]
| |
| *[[Yaws]]
| |
| *[[Yersinia pestis]]
| |
| *[[Zinc]]
| |
| | |
| </div>
| |
| | |
| | |
| *Common causes of lymphadenopathy, include:<ref name="pmid24753638">{{cite journal |vauthors=Mohseni S, Shojaiefard A, Khorgami Z, Alinejad S, Ghorbani A, Ghafouri A |title=Peripheral lymphadenopathy: approach and diagnostic tools |journal=Iran J Med Sci |volume=39 |issue=2 Suppl |pages=158–70 |year=2014 |pmid=24753638 |pmc=3993046 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="AA">Lymph node enlargment. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lymph_node Accessed on May 9, 2016</ref>
| |
| | |
| :*'''Infections''' (acute suppurative)
| |
| ::*Fungal
| |
| ::*Mycobacterial
| |
| ::*Viral
| |
| ::*Protozoal (e.g. [[Toxoplasmosis|toxoplasma]])
| |
| ::*Bacterial (e.g. [[chlamydia]], [[Rickettsia rickettsii infection|rickettsia]], [[bartonella]])
| |
| :*'''Reactive'''
| |
| ::*Follicular hyperplasia
| |
| ::*Paracortical hyperplasia
| |
| ::*Sinus histiocytosis
| |
| ::*Granulomatous
| |
| ::*Neoplastic
| |
| ::*Drugs (e.g. cyclosporin, phenytoin, methotrexate)
| |
| ::*Lipid storage diseases
| |
| ::*IgG4-related sclerosing disease
| |
| | |
| ==Differentiating Lymphadenopathy from other Diseases==
| |
| * Lymphadenopathy must be differentiated from [[syphilis]], which may present as [[fever]], [[myalgias]], [[weight loss]], and [[lymph node]] enlargement.<ref name="pmid1590633">{{cite journal |vauthors=Deschenes J, Seamone CD, Baines MG |title=Acquired ocular syphilis: diagnosis and treatment |journal=Ann Ophthalmol |volume=24 |issue=4 |pages=134–8 |year=1992 |pmid=1590633 |doi= |url=}}</ref>
| |
| | |
| ==Epidemiology and Demographics==
| |
| * Lymphadenopathy is very common.
| |
| *The estimated incidence of lymphadenopathy among children in the United States ranges from 35%- 45%.<ref name="pmid24753638">{{cite journal |vauthors=Mohseni S, Shojaiefard A, Khorgami Z, Alinejad S, Ghorbani A, Ghafouri A |title=Peripheral lymphadenopathy: approach and diagnostic tools |journal=Iran J Med Sci |volume=39 |issue=2 Suppl |pages=158–70 |year=2014 |pmid=24753638 |pmc=3993046 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="AA">Lymph node enlargment. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lymph_node Accessed on May 9, 2016</ref>
| |
|
| |
|
| ===Age===
| |
| *Patients of all age groups may develop lymphadenopathy.
| |
| *Lymphadenopathy is more commonly observed among children.
| |
|
| |
|
| ===Gender===
| |
| *Lymphadenopathy affects men and women equally.
| |
| | | |
| ===Race===
| | {{SK}} Lymph nodes enlarged; Enlarged lymph nodes; Lymphadenitis; Swollen lymph nodes; Swollen/enlarged lymph nodes<br> |
| *There is no racial predilection for lymphadenopathy.<ref name="pmid24753638">{{cite journal |vauthors=Mohseni S, Shojaiefard A, Khorgami Z, Alinejad S, Ghorbani A, Ghafouri A |title=Peripheral lymphadenopathy: approach and diagnostic tools |journal=Iran J Med Sci |volume=39 |issue=2 Suppl |pages=158–70 |year=2014 |pmid=24753638 |pmc=3993046 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="AA">Lymph node enlargment. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lymph_node Accessed on May 9, 2016</ref>
| | '''For patient information, click [[Xyz (patient information)|here]]''' |
|
| |
|
| | ==Overview== |
|
| |
|
| ==Risk Factors== | | ==[[Lymphadenopathy classification|Classification]]== |
| *The most common risk factors in the development of lymphadenopathy, include:
| |
| :*Local soft-tissue infections
| |
| :*[[Upper respiratory tract infection]]
| |
| :*Foreign travel
| |
|
| |
|
| == Natural History, Complications and Prognosis== | | ==[[Lymphadenopathy pathophysiology|Pathophysiology]]== |
| *Patients with lymphadenopathy may be symptomatic or asymptomatic, depending on the aetiology.<ref name="pmid24753638">{{cite journal |vauthors=Mohseni S, Shojaiefard A, Khorgami Z, Alinejad S, Ghorbani A, Ghafouri A |title=Peripheral lymphadenopathy: approach and diagnostic tools |journal=Iran J Med Sci |volume=39 |issue=2 Suppl |pages=158–70 |year=2014 |pmid=24753638 |pmc=3993046 |doi= |url=}}</ref>
| |
| *Early clinical features include palpable [[tenderness]], pain, and [[fever]].<ref name="AA">Lymph node enlargment. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lymph_node Accessed on May 9, 2016</ref>
| |
|
| |
|
| *Common complications of lymphadenopathy, include:<ref name="AA">Lymph node enlargment. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lymph_node Accessed on May 9, 2016</ref>
| | ==Histopathology== |
| '''Mediastinal lymphadenopathy'''
| |
| * [[Superior vena cava syndrome]]
| |
| **[[Tracheal]] and bronchial obstruction
| |
| ** [[Dysphagia]]
| |
| ** [[Hemoptysis]]
| |
| * [[Uric acid nephropathy]]
| |
| * [[Hyperkalemia]]
| |
| * [[Hypercalcemia]]
| |
| * [[Hypocalcemia]]
| |
| * [[Hyperphosphatemia]]
| |
| * [[Renal failure]]
| |
| '''Abdominal lymphadenopathy'''
| |
| * [[Intestinal obstruction]]
| |
| '''Superficial lymphadenopathy'''
| |
| * [[Abscess]] formation
| |
| * [[Cellulitis]]
| |
| * [[Fistulas]] (seen in lymphadenitis that is due to [[tuberculosis]])
| |
| * [[Sepsis]]
| |
| *Prognosis will depend on the aetiology of the underlying disease.
| |
|
| |
|
| == Diagnosis == | | ==Causes== |
| ===Diagnostic Criteria===
| |
| ====Malignant Lymphadenopathy====
| |
| :*Node > 2 cm
| |
| :*Node that is draining, hard, or fixed to underlying tissue
| |
| :*Atypical location (e.g. [[supraclavicular]] node)
| |
| :*Risk factors (e.g. [[HIV AIDS|HIV]] or [[TB]])
| |
| :*[[Fever]] and/or weight loss
| |
| :*[[Splenomegaly]]
| |
| | |
| ====Benign Lymphadenopathy====
| |
| :*Node < 1 cm
| |
| :*Node that is mobile, soft-or tender, and is not fixed to underlying tissue
| |
| :*Common location (e.g. supraclavicular node)
| |
| :*No associated risk factors
| |
| :*Palpable and painful enlargement
| |
| | |
| === Symptoms ===
| |
| *Symptoms of lymphadenopathy may include the following:<ref name="pmid24753638">{{cite journal |vauthors=Mohseni S, Shojaiefard A, Khorgami Z, Alinejad S, Ghorbani A, Ghafouri A |title=Peripheral lymphadenopathy: approach and diagnostic tools |journal=Iran J Med Sci |volume=39 |issue=2 Suppl |pages=158–70 |year=2014 |pmid=24753638 |pmc=3993046 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="AA">Lymph node enlargment. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lymph_node Accessed on May 9, 2016</ref>
| |
| | |
| :*'''Constitutional symptoms'''
| |
| ::*[[Fever]]
| |
| ::*[[Weight loss]]
| |
| ::*[[Fatigue]]
| |
| ::*[[Night sweats]]
| |
| :* [[Malaise]]
| |
| :* [[Nausea]] and [[vomiting]]
| |
| :* [[Cachexia]]
| |
| *A directed history should be obtained to ascertain:<ref name="pmid24753638">{{cite journal |vauthors=Mohseni S, Shojaiefard A, Khorgami Z, Alinejad S, Ghorbani A, Ghafouri A |title=Peripheral lymphadenopathy: approach and diagnostic tools |journal=Iran J Med Sci |volume=39 |issue=2 Suppl |pages=158–70 |year=2014 |pmid=24753638 |pmc=3993046 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="AA">Lymph node enlargment. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lymph_node Accessed on May 9, 2016</ref>
| |
| | |
| :*Use of drugs causing lymphadenopathy
| |
| :*Travel to endemic areas
| |
| :*Occupational risk (e.g. Fishermen, slaughterhouse workers, hunters, trappers)
| |
| :*High risk behavior or high risk sexual behaviors (e.g. I.V drug abuse, multiple partners)
| |
| | |
| === Physical Examination ===
| |
| *Patients with lymphadenopathy may have a pale or normal appearance.
| |
| *Physical examination may be remarkable for:
| |
| ===Vitals===
| |
| * Temperature
| |
| :*High grade [[fever]]
| |
| :*Low grade [[fever]]
| |
| *[[Pulse]]
| |
| :*Rapid (e.g. acute [[infections]])
| |
| | |
| ===Skin===
| |
| * [[Rash]] may be present
| |
| * Color change (indicative of inflammation)
| |
| * Skin [[fistula]] draining pus may be present
| |
| * Ulcers
| |
| | |
| ===Head===
| |
| ====Palpating Anterior Cervical Lymph Nodes====
| |
| Lymph nodes should be examined in the following order:<ref name="pmid24753638">{{cite journal |vauthors=Mohseni S, Shojaiefard A, Khorgami Z, Alinejad S, Ghorbani A, Ghafouri A |title=Peripheral lymphadenopathy: approach and diagnostic tools |journal=Iran J Med Sci |volume=39 |issue=2 Suppl |pages=158–70 |year=2014 |pmid=24753638 |pmc=3993046 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="AA">Lymph node enlargment. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lymph_node Accessed on May 9, 2016</ref>
| |
| | |
| *[[Anterior]] [[Cervical]]
| |
| *[[Posterior]] [[Cervical]]
| |
| *Tonsillar
| |
| * Sub-Mandibular
| |
| *Sub-Mental
| |
| *Supra-clavicular
| |
| | |
| '''Characteristics''' to be noted while palpating lymph nodes:<ref name="AA">Lymph node enlargment. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lymph_node Accessed on May 9, 2016</ref>
| |
| *Size
| |
| *Pain/ tenderness
| |
| :*Increased tenderness (e.g infected lymph nodes)
| |
| *Consistency
| |
| *Matting
| |
|
| |
|
| ====Gallery==== | | ==[[Lymphadenopathy differential diagnosis|Differentiating Lymphadenopathy from other Diseases]]== |
| <div align="left">
| | ==[[Epidemiology and Demographics]]== |
| <gallery heights="175" widths="175">
| |
| Image:head_scc1.jpg|'''Cervical adenopathy''': massive right side cervical adenopathy and facial asymmetry due to metastatic, intraoral squamous cell cancer. Images Courtesy of Charlie Goldberg, M.D., UCSD School of Medicine and VA Medical Center, San Diego, CA.
| |
| Image:head_scc2.jpg|'''Cervical adenopathy''': massive right side cervical adenopathy and facial asymmetry due to metastatic, intraoral squamous cell cancer. Images Courtesy of Charlie Goldberg, M.D., UCSD School of Medicine and VA Medical Center, San Diego, CA.
| |
| Image:head_cervical_ln.jpg|'''Cervical adenopathy''': large right anterior cervical lymph node. Images Courtesy of Charlie Goldberg, M.D., UCSD School of Medicine and VA Medical Center, San Diego, CA.
| |
| Image: Lymphadenopathy 001.jpg| '''Cervical lymphadenopathy'''. Images Courtesy of Charlie Goldberg, M.D., UCSD School of Medicine and VA Medical Center, San Diego, CA.
| |
| Image:head_cneck_adenop1.jpg|'''Cervical Adenopathy''': multiple right sided cervical lymph nodes. Images Courtesy of Charlie Goldberg, M.D., UCSD School of Medicine and VA Medical Center, San Diego, CA.
| |
| </gallery>
| |
| </div>
| |
|
| |
|
| === Laboratory Findings ===
| | ==Laboratory Evaluation of Lymphadenopathy== |
| *Laboratory findings consistent with the diagnosis of lymphadenopathy, may include:<ref name="pmid24753638">{{cite journal |vauthors=Mohseni S, Shojaiefard A, Khorgami Z, Alinejad S, Ghorbani A, Ghafouri A |title=Peripheral lymphadenopathy: approach and diagnostic tools |journal=Iran J Med Sci |volume=39 |issue=2 Suppl |pages=158–70 |year=2014 |pmid=24753638 |pmc=3993046 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="AA">Lymph node enlargment. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lymph_node Accessed on May 9, 2016</ref>
| |
| '''Complete Blood Count'''
| |
| :*Elevated [[lactate dehydrogenase]] (LDH)
| |
| :*Mild [[neutropenia]]
| |
| :*[[Leukocytosis]]
| |
| :*Elevated markers of [[inflammation]] and acute phase reactants (e.g. [[ESR]], C-reactive protein, [[ferritin]])
| |
|
| |
|
| ===Imaging Findings=== | | ==Diagnostic Radiological Testing== |
| '''Ultrasonography'''
| |
| *On ultrasound, characteristic findings of lymphadenopathy, include:<ref name="pmid24753638">{{cite journal |vauthors=Mohseni S, Shojaiefard A, Khorgami Z, Alinejad S, Ghorbani A, Ghafouri A |title=Peripheral lymphadenopathy: approach and diagnostic tools |journal=Iran J Med Sci |volume=39 |issue=2 Suppl |pages=158–70 |year=2014 |pmid=24753638 |pmc=3993046 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="radio">Lymph node enlargment. Radiopedia. http://radiopaedia.org/articles/lymph-node-enlargement Accessed on May 9, 2016 </ref><ref name="AA">Lymph node enlargment. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lymph_node Accessed on May 9, 2016</ref>
| |
| :*Increased lymph node size
| |
| '''CT'''
| |
| *On CT, characteristic findings of lymphadenopathy, include:<ref name="pmid24753638">{{cite journal |vauthors=Mohseni S, Shojaiefard A, Khorgami Z, Alinejad S, Ghorbani A, Ghafouri A |title=Peripheral lymphadenopathy: approach and diagnostic tools |journal=Iran J Med Sci |volume=39 |issue=2 Suppl |pages=158–70 |year=2014 |pmid=24753638 |pmc=3993046 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="radio">Lymph node enlargment. Radiopedia. http://radiopaedia.org/articles/lymph-node-enlargement Accessed on May 9, 2016 </ref><ref name="AA">Lymph node enlargment. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lymph_node Accessed on May 9, 2016</ref><ref name="pmid10670052">{{cite journal |vauthors=van den Brekel MW, Castelijns JA |title=Imaging of lymph nodes in the neck |journal=Semin Roentgenol |volume=35 |issue=1 |pages=42–53 |date=January 2000 |pmid=10670052 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid11264102">{{cite journal |vauthors=Sumi M, Ohki M, Nakamura T |title=Comparison of sonography and CT for differentiating benign from malignant cervical lymph nodes in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck |journal=AJR Am J Roentgenol |volume=176 |issue=4 |pages=1019–24 |date=April 2001 |pmid=11264102 |doi=10.2214/ajr.176.4.1761019 |url=}}</ref>
| |
|
| |
|
| :*Most nodes: 10 mm in short-axis
| |
| :*Sub-mental and sub-mandibular: 15 mm
| |
| :*Retropharyngeal: 8 mm
| |
| :*Loss of fatty hilum
| |
| :*Focal [[necrosis]]
| |
| :*Cystic necrotic nodes
| |
| :*Long-to-short axis ratio (>2cm - usually [[benign]])
| |
| *The upper limit in size of a normal node varies with location.
| |
|
| |
|
| '''PET/CT'''
| | ==Treatment== |
| *On PET/CT, lymphadenopathy can be further assessed via quantitation of FDG uptake, which is a surrogate of metabolic activity. Infectious, inflammatory, and neoplastic processes will show high FDG avidity on PET/CT. PET/CT is particularly useful for assessing response of lymph nodes to systemic chemotherapy.
| |
| '''MRI'''
| |
| *MRI is the most anatomically precise test for assessing lymphadenopathy. MRI is particularly useful for intraabdominal lymphadenopathy, which cannot be readily palpated via physical examination. MRI is more expensive than CT scan, so CT is preferred in general unless the clinical need for MRI arises.
| |
|
| |
|
| == Treatment ==
| |
| *There is no treatment for lymphadenopathy; the mainstay of therapy is treating the underlying condition.<ref name="pmid24753638">{{cite journal |vauthors=Mohseni S, Shojaiefard A, Khorgami Z, Alinejad S, Ghorbani A, Ghafouri A |title=Peripheral lymphadenopathy: approach and diagnostic tools |journal=Iran J Med Sci |volume=39 |issue=2 Suppl |pages=158–70 |year=2014 |pmid=24753638 |pmc=3993046 |doi= |url=}}</ref>
| |
| **Infectious lymphadenopathy responds well to prompt treatment with antibiotics, and usually leads to a complete recovery. However, it may take months, for swelling to disappear. The amount of time to recovery depends on the cause.<ref name="AA">Lymph node enlargment. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lymph_node Accessed on May 9, 2016</ref>
| |
| **Neoplastic (malignant) lymphadenopathy usually responds well to systemic chemotherapy.
| |
|
| |
|
| ==References== | | ==References== |
| Line 664: |
Line 38: |
| [[Category:Dermatology]] | | [[Category:Dermatology]] |
| [[Category:Medical signs]] | | [[Category:Medical signs]] |
| [[Category:Signs and symptoms]] | | [[Category: Signs and symptoms]] |
|
| |
|
| [[Category:Physical examination]] | | [[Category: Physical examination]] |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
| Line 672: |
Line 46: |
| {{WikiDoc Help Menu}} | | {{WikiDoc Help Menu}} |
| {{WikiDoc Sources}} | | {{WikiDoc Sources}} |
| [[Category:Up-To-Date]] | | [[Category: Up-To-Date]] |
| [[Category:Oncology]] | | [[Category:Oncology]] |
| [[Category:Medicine]] | | [[Category:Medicine]] |
| [[Category:Infectious disease]] | | [[Category:Infectious disease]] |
| [[Category:Hematology]] | | [[Category:Hematology]] |