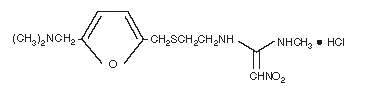Ranitidine (injection)
{{DrugProjectFormSinglePage |authorTag=Aparna Vuppala, M.B.B.S. [1] |genericName=Ranitidine |aOrAn=a |drugClass=H2 receptor blocker |indicationType=treatment |indication=heartburn associated with acid indigestion and sour stomach and prevents heartburn associated with acid indigestion and sour stomach brought on by certain foods and beverages |adverseReactions=headache, constipation, diarrhea, abdominal pain |blackBoxWarningTitle=Title |blackBoxWarningBody=ConditionName:
- Content
|fdaLIADAdult=*Ranitidine Injection is indicated in some hospitalized patients with pathological hypersecretory conditions or intractable duodenal ulcers, or as an alternative to the oral dosage form for short-term use in patients who are unable to take oral medication.
Dosage
- Parenteral Administration
- In some hospitalized patients with pathological hypersecretory conditions or intractable duodenal ulcers, or in patients who are unable to take oral medication, Ranitidine may be administered parenterally according to the following recommendations:
- Intramuscular Injection: 50 mg (2 mL) every 6 to 8 hours. (No dilution necessary.)
- Intermittent Intravenous Injection:
- a. Intermittent Bolus: 50 mg (2 mL) every 6 to 8 hours. Dilute Ranitidine Injection, 50 mg, in 0.9% sodium chloride injection or other compatible IV solution (see Stability) to a concentration no greater than 2.5 mg/mL (20 mL). Inject at a rate no greater than 4 mL/min (5 minutes).
- b. Intermittent Infusion: 50 mg (2 mL) every 6 to 8 hours. Dilute Ranitidine Injection, 50 mg, in 5% dextrose injection or other compatible IV solution (see Stability) to a concentration no greater than 0.5 mg/mL (100 mL). Infuse at a rate no greater than 5 to 7 mL/min (15 to 20 minutes).
- In some patients it may be necessary to increase dosage. When this is necessary, the increases should be made by more frequent administration of the dose, but generally should not exceed 400 mg/day.
- Continuous Intravenous Infusion: Add Ranitidine Injection to 5% dextrose injection or other compatible IV solution (see Stability). Deliver at a rate of 6.25 mg/hour (e.g., 150 mg [6 mL] of Ranitidine Injection in 250 mL of 5% dextrose injection at 10.7 mL/hour).
- For Zollinger-Ellison patients, dilute Ranitidine Injection in 5% dextrose injection or other compatible IV solution (see Stability) to a concentration no greater than 2.5 mg/mL. Start the infusion at a rate of 1.0 mg/kg/hour. If after 4 hours either a measured gastric acid output is >10 mEq/hour or the patient becomes symptomatic, the dose should be adjusted upward in 0.5-mg/kg/hour increments, and the acid output should be remeasured. Dosages up to 2.5 mg/kg/hour and infusion rates as high as 220 mg/hour have been used.
- Dosage Adjustment for Patients With Impaired Renal Function
- The administration of ranitidine as a continuous infusion has not been evaluated in patients with impaired renal function. On the basis of experience with a group of subjects with severely impaired renal function treated with Ranitidine, the recommended dosage in patients with a creatinine clearance <50 mL/min is 50 mg every 18 to 24 hours. Should the patient's condition require, the frequency of dosing may be increased to every 12 hours or even further with caution. Hemodialysis reduces the level of circulating ranitidine. Ideally, the dosing schedule should be adjusted so that the timing of a scheduled dose coincides with the end of hemodialysis.
- Elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, therefore caution should be exercised in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function
- Stability
- Undiluted, Ranitidine Injection tends to exhibit a yellow color that may intensify over time without adversely affecting potency. Ranitidine Injection is stable for 48 hours at room temperature when added to or diluted with most commonly used IV solutions, e.g., 0.9% sodium chloride injection, 5% dextrose injection, 10% dextrose injection, lactated ringer's injection, or 5% sodium bicarbonate injection.
- Ranitidine Injection Premixed in flexible plastic containers is sterile through the expiration date on the label when stored under recommended conditions.
Note: Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration before administration whenever solution and container permit. |offLabelAdultGuideSupport=There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Ranitidine in adult patients. |offLabelAdultNoGuideSupport= |offLabelPedGuideSupport=There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Ranitidine (injection) in pediatric patients. |offLabelPedNoGuideSupport=There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Ranitidine (injection) in pediatric patients.
|contraindications=*Ranitidine Injection is contraindicated for patients known to have hypersensitivity to the drug. |warnings=
Allergy alert
- Do not use if you are allergic to ranitidine or other acid reducers
- Do not use if you have trouble or pain swallowing food, vomiting with blood, or bloody or black stools. These may be signs of a serious condition.
- With other acid reducers
- If you have kidney disease, except under the advice and supervision of a doctor
- Ask a doctor before use if you have
- Frequent chest pain
- Frequent wheezing, particularly with heartburn unexplained weight loss
- Nausea or vomiting
- Stomach pain had heartburn over 3 months. This may be a sign of a more serious condition.
- Heartburn with lightheadedness, sweating, or dizziness chest pain or shoulder pain with shortness of breath; sweating; pain spreading to arms, neck or shoulders; or lightheadedness
- Stop use and ask a doctor if your heartburn continues or worsens you need to take this product for more than 14 days
- If pregnant or breast-feeding, ask a health professional before use.
- Keep out of reach of children.
Precautions
- Symptomatic response to therapy with Ranitidine does not preclude the presence of gastric malignancy.
- Since Ranitidine is excreted primarily by the kidney, dosage should be adjusted in patients with impaired renal function. Caution should be observed in patients with hepatic dysfunction since Ranitidine is metabolized in the liver.
- In controlled studies in normal volunteers, elevations in SGPT have been observed when H2-antagonists have been administered intravenously at greater-than-recommended dosages for 5 days or longer. Therefore, it seems prudent in patients receiving IV ranitidine at dosages ≥100 mg 4 times daily for periods of 5 days or longer to monitor SGPT daily (from day 5) for the remainder of IV therapy.
- Bradycardia in association with rapid administration of Ranitidine Injection has been reported rarely, usually in patients with factors predisposing to cardiac rhythm disturbances. Recommended rates of administration should not be exceeded .
- Rare reports suggest that Ranitidine may precipitate acute porphyric attacks in patients with acute porphyria. Ranitidine should therefore be avoided in patients with a history of acute porphyria.
|clinicalTrials=
- Transient pain at the site of IM injection has been reported. Transient local burning or itching has been reported with IV administration of Ranitidine.
- The following have been reported as events in clinical trials or in the routine management of patients treated with oral or parenteral Ranitidine. The relationship to therapy with Ranitidine has been unclear in many cases. Headache, sometimes severe, seems to be related to administration of Ranitidine.
- Central Nervous System
- Rarely, malaise, dizziness, somnolence, insomnia, and vertigo. Rare cases of reversible mental confusion, agitation, depression, and hallucinations have been reported, predominantly in severely ill elderly patients. Rare cases of reversible blurred vision suggestive of a change in accommodation have been reported. Rare reports of reversible involuntary motor disturbances have been received.
- Cardiovascular
- As with other H2-blockers, rare reports of arrhythmias such as tachycardia, bradycardia, asystole, atrioventricular block, and premature ventricular beats.
- Gastrointestinal
- Constipation, diarrhea, nausea/vomiting, abdominal discomfort/pain, and rare reports of pancreatitis.
- Hepatic
- In normal volunteers, SGPT values were increased to at least twice the pretreatment levels in 6 of 12 subjects receiving 100 mg intravenously 4 times daily for 7 days, and in 4 of 24 subjects receiving 50 mg intravenously 4 times daily for 5 days. There have been occasional reports of hepatocellular, cholestatic, or mixed hepatitis, with or without jaundice. In such circumstances, ranitidine should be immediately discontinued. These events are usually reversible, but in rare circumstances death has occurred. Rare cases of hepatic failure have also been reported.
- Musculoskeletal
- Rare reports of arthralgias and myalgias.
- Hematologic
- Blood count changes (leukopenia, granulocytopenia, and thrombocytopenia) have occurred in a few patients. These were usually reversible. Rare cases of agranulocytosis, pancytopenia, sometimes with marrow hypoplasia, and aplastic anemia and exceedingly rare cases of acquired immune hemolytic anemia have been reported.
- Endocrine
- Controlled studies in animals and humans have shown no stimulation of any pituitary hormone by Ranitidine and no antiandrogenic activity, and cimetidine-induced gynecomastia and impotence in hypersecretory patients have resolved when Ranitidine has been substituted. However, occasional cases of impotence and loss of libido have been reported in male patients receiving Ranitidine, but the incidence did not differ from that in the general population. Rare cases of breast symptoms and conditions, including galactorrhea and gynecomastia, have been reported in both males and females.
- Integumentary
- Rash, including rare cases of erythema multiforme. Rare cases of alopecia and vasculitis.
- Respiratory
- A large epidemiological study suggested an increased risk of developing pneumonia in current users of histamine-2–receptor antagonists (H2RAs) compared to patients who had stopped H2RA treatment, with an observed adjusted relative risk of 1.63 (95% CI, 1.07–2.48). However, a causal relationship between use of H2RAs and pneumonia has not been established.
- Other
- Rare cases of hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., bronchospasm, fever, rash, eosinophilia), anaphylaxis, angioneurotic edema, acute interstitial nephritis, and small increases in serum creatinine.
|drugInteractions=
- Ranitidine has been reported to affect the bioavailability of other drugs through several different mechanisms such as competition for renal tubular secretion, alteration of gastric pH, and inhibition of cytochrome P450 enzymes.
- Procainamide: Ranitidine, a substrate of the renal organic cation transport system, may affect the clearance of other drugs eliminated by this route. High doses of ranitidine (e.g., such as those used in the treatment of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome) have been shown to reduce the renal excretion of procainamide and N-acetylprocainamide resulting in increased plasma levels of these drugs. Although this interaction is unlikely to be clinically relevant at usual ranitidine doses, it may be prudent to monitor for procainamide toxicity when administered with oral ranitidine at a dose exceeding 300 mg per day.
- Warfarin: There have been reports of altered prothrombin time among patients on concomitant warfarin and ranitidine therapy. Due to the narrow therapeutic index, close monitoring of increased or decreased prothrombin time is recommended during concurrent treatment with ranitidine.
- Ranitidine may alter the absorption of drugs in which gastric pH is an important determinant of bioavailability. This can result in either an increase in absorption (e.g., triazolam, midazolam, glipizide) or a decrease in absorption (e.g., ketoconazole, atazanavir, delavirdine, gefitinib). Appropriate clinical monitoring is recommended.
- Atazanavir: Atazanavir absorption may be impaired based on known interactions with other agents that increase gastric pH. Use with caution. See atazanavir label for specific recommendations.
- Delavirdine: Delavirdine absorption may be impaired based on known interactions with other agents that increase gastric pH. Chronic use of H2-receptor antagonists with delavirdine is not recommended.
- Gefitinib: Gefitinib exposure was reduced by 44% with the coadministration of ranitidine and sodium bicarbonate (dosed to maintain gastric pH above 5.0). Use with caution.
- Glipizide: In diabetic patients, glipizide exposure was increased by 34% following a single 150-mg dose of oral ranitidine. Use appropriate clinical monitoring when initiating or discontinuing ranitidine.
- Ketoconazole: Oral ketoconazole exposure was reduced by up to 95% when oral ranitidine was coadministered in a regimen to maintain a gastric pH of 6 or above. The degree of interaction with usual dose of ranitidine (150 mg twice daily) is unknown.
- Midazolam: Oral midazolam exposure in 5 healthy volunteers was increased by up to 65% when administered with oral ranitidine at a dose of 150 mg twice daily. However, in another interaction study in 8 volunteers receiving IV midazolam, a 300 mg oral dose of ranitidine increased midazolam exposure by about 9%. Monitor patients for excessive or prolonged sedation when ranitidine is coadministered with oral midazolam.
- Triazolam: Triazolam exposure in healthy volunteers was increased by approximately 30% when administered with oral ranitidine at a dose of 150 mg twice daily. Monitor patients for excessive or prolonged sedation.
|FDAPregCat=B |useInPregnancyFDA=*Teratogenic Effects: Reproduction studies have been performed in rats and rabbits at oral doses up to 160 times the human oral dose and have revealed no evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the fetus due to ranitidine. There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed. |AUSPregCat=B1 |useInPregnancyAUS= There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Ranitidine (injection) in women who are pregnant. |useInLaborDelivery=There is no FDA guidance on use of Ranitidine (injection) during labor and delivery. |useInNursing=*Ranitidine is secreted in human milk. Caution should be exercised when Ranitidine is administered to a nursing mother. |useInPed=*The safety and effectiveness of Ranitidine Injection have been established in the age-group of 1 month to 16 years for the treatment of duodenal ulcer. Use of Ranitidine in this age-group is supported by adequate and well-controlled studies in adults, as well as additional pharmacokinetic data in pediatric patients, and an analysis of the published literature.
- Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients for the treatment of pathological hypersecretory conditions have not been established.
- Limited data in neonatal patients (less than 1 month of age) receiving ECMO suggest that Ranitidine may be useful and safe for increasing gastric pH for patients at risk of gastrointestinal hemorrhage.
|useInGeri=*Clinical studies of Ranitidine Injection did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they responded differently from younger subjects. However, in clinical studies of oral formulations of Ranitidine, of the total number of subjects enrolled in US and foreign controlled clinical trials, for which there were subgroup analyses, 4,197 were 65 and over, while 899 were 75 and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
- This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, caution should be exercised in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function
|useInGender=There is no FDA guidance on the use of Ranitidine (injection) with respect to specific gender populations. |useInRace=There is no FDA guidance on the use of Ranitidine (injection) with respect to specific racial populations. |useInRenalImpair=There is no FDA guidance on the use of Ranitidine (injection) in patients with renal impairment. |useInHepaticImpair=There is no FDA guidance on the use of Ranitidine (injection) in patients with hepatic impairment. |useInReproPotential=There is no FDA guidance on the use of Ranitidine (injection) in women of reproductive potentials and males. |useInImmunocomp=There is no FDA guidance one the use of Ranitidine (injection) in patients who are immunocompromised.
|administration=* injection |monitoring=*False-positive tests for urine protein with MULTISTIX® may occur during therapy with Ranitidine, and therefore testing with sulfosalicylic acid is recommended.
|IVCompat=There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Ranitidine (injection) in the drug label.
|drugBox={{Drugbox2 | Verifiedfields = changed | Watchedfields = changed | verifiedrevid = 458460406 | IUPAC_name = N-(2-[(5-[(dimethylamino)methyl]furan-2-yl)methylthio]ethyl)-N'-methyl-2-nitroethene-1,1-diamine; dimethyl [(5-{[(2-{[1-(methylamino)-2-nitroethenyl]amino}ethyl)sulfanyl]methyl}furan-2-yl)methyl]amine | image = Ranitidine Structural Formulae.png | width = 200 | image2 = Ranitidine-A-3D-balls.png
| tradename = Ranitidine | Drugs.com = Monograph | MedlinePlus = a601106 | licence_US = Ranitidine | pregnancy_AU = B1 | pregnancy_US = B | legal_AU = S2 | legal_US = OTC/RX | legal_status = P/POM (UK) | routes_of_administration = Oral, IV
| bioavailability = 39 to 88% | protein_bound = 15% | metabolism = Hepatic | elimination_half-life = 2–3 hours | excretion = 30–70% Renal
| CASNo_Ref =
| CAS_number_Ref =
| CAS_number = 66357-35-5
| ATC_prefix = A02
| ATC_suffix = BA02
| ATC_supplemental =
A02BA07 (WHO) (ranitidine bismuth citrate)
| PubChem = 657345
| IUPHAR_ligand = 1234
| DrugBank_Ref =
| DrugBank = DB00863
| ChemSpiderID_Ref =
| ChemSpiderID = 571454
| UNII_Ref =
| UNII = 884KT10YB7
| KEGG_Ref =
| KEGG = D00422
| ChEBI_Ref =
| ChEBI = 8776
| ChEMBL_Ref =
| ChEMBL = 1790041
| C=13 | H=22 | N=4 | O=3 | S=1
| molecular_weight = 314.4 g/mol
| smiles = [O-][N+](=O)\C=C(\NC)NCCSCc1oc(cc1)CN(C)C
| InChI = 1/C13H22N4O3S/c1-14-13(9-17(18)19)15-6-7-21-10-12-5-4-11(20-12)8-16(2)3/h4-5,9,14-15H,6-8,10H2,1-3H3/b13-9-
| InChIKey = VMXUWOKSQNHOCA-LCYFTJDEBT
| StdInChI_Ref =
| StdInChI = 1S/C13H22N4O3S/c1-14-13(9-17(18)19)15-6-7-21-10-12-5-4-11(20-12)8-16(2)3/h4-5,9,14-15H,6-8,10H2,1-3H3
| StdInChIKey_Ref =
| StdInChIKey = VMXUWOKSQNHOCA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
}}
|mechAction=* Ranitidine is a competitive, reversible inhibitor of the action of histamine at the histamine H2-receptors, including receptors on the gastric cells. Ranitidine does not lower serum Ca++ in hypercalcemic states. Ranitidine is not an anticholinergic agent.
|structure=* The active ingredient in Ranitidine Injection is ranitidine hydrochloride (HCl), a histamine H2-receptor antagonist. Chemically it is N[2-[5-[(dimethylamino)methyl]-2-furanyl]methyl]thio]ethyl]-N′-methyl-2-nitro-1,1-ethenediamine, hydrochloride. It has the following structure:
- The empirical formula is C13H22N4O3S●HCl, representing a molecular weight of 350.87.
- Ranitidine HCl is a white to pale yellow, granular substance that is soluble in water.
- Ranitidine Injection is a clear, colorless to yellow, nonpyrogenic liquid. The yellow color of the liquid tends to intensify without adversely affecting potency. The pH of the injection solution is 6.7 to 7.3.
- Sterile Injection for Intramuscular or Intravenous Administration
- Each 1 mL of aqueous solution contains ranitidine 25 mg (as the hydrochloride); phenol 5 mg as preservative; and 0.96 mg of monobasic potassium phosphate and 2.4 mg of dibasic sodium phosphate as buffers.
|PD=:

- In a group of 10 known hypersecretors, ranitidine plasma levels of 71, 180, and 376 ng/mL inhibited basal acid secretion by 76%, 90%, and 99.5%, respectively.
- It appears that basal- and betazole-stimulated secretions are most sensitive to inhibition by Ranitidine, while pentagastrin-stimulated secretion is more difficult to suppress.
- Effects on Other Gastrointestinal Secretions:
- Pepsin: Ranitidine does not affect pepsin secretion. Total pepsin output is reduced in proportion to the decrease in volume of gastric juice.
- Intrinsic Factor: Ranitidine has no significant effect on pentagastrin-stimulated intrinsic factor secretion.
- Serum Gastrin: Ranitidine has little or no effect on fasting or postprandial serum gastrin.
- Other Pharmacologic Actions:
- Gastric bacterial flora―increase in nitrate-reducing organisms, significance not known.
- Prolactin levels―no effect in recommended oral or IV dosage, but small, transient, dose-related increases in serum prolactin have been reported after IV bolus injections of 100 mg or more.
- Other pituitary hormones―no effect on serum gonadotropins, TSH, or GH. Possible impairment of vasopressin release.
- No change in cortisol, aldosterone, androgen, or estrogen levels.
- No antiandrogenic action.
- No effect on count, motility, or morphology of sperm.
- Pediatrics: The ranitidine concentration necessary to suppress basal acid secretion by at least 90% has been reported to be 40 to 60 ng/mL in pediatric patients with duodenal or gastric ulcers.
- In a study of 20 critically ill pediatric patients receiving ranitidine IV at 1 mg/kg every 6 hours, 10 patients with a baseline pH≥4 maintained this baseline throughout the study. Eight of the remaining 10 patients with a baseline of pH≤2 achieved pH≥4 throughout varying periods after dosing. It should be noted, however, that because these pharmacodynamic parameters were assessed in critically ill pediatric patients, the data should be interpreted with caution when dosing recommendations are made for a less seriously ill pediatric population.
- In another small study of neonatal patients (n = 5) receiving ECMO, gastric pH<4 pretreatment increased to >4 after a 2-mg/kg dose and remained above 4 for at least 15 hours.
|PK=
- Absorption:
- Ranitidine is absorbed very rapidly after intramuscular (IM) injection. Mean peak levels of 576 ng/mL occur within 15 minutes or less following a 50-mg IM dose. Absorption from IM sites is virtually complete, with a bioavailability of 90% to 100% compared with intravenous (IV) administration. Following oral administration, the bioavailability of Ranitidine Tablets is 50%.
- Distribution:
- The volume of distribution is about 1.4 L/kg. Serum protein binding averages 15%.
- Metabolism:
- In humans, the N-oxide is the principal metabolite in the urine; however, this amounts to <4% of the dose. Other metabolites are the S-oxide (1%) and the desmethyl ranitidine (1%). The remainder of the administered dose is found in the stool. Studies in patients with hepatic dysfunction (compensated cirrhosis) indicate that there are minor, but clinically insignificant, alterations in ranitidine half-life, distribution, clearance, and bioavailability.
- Excretion:
- Following IV injection, approximately 70% of the dose is recovered in the urine as unchanged drug. Renal clearance averages 530 mL/min, with a total clearance of 760 mL/min. The elimination half-life is 2.0 to 2.5 hours.
- Four patients with clinically significant renal function impairment (creatinine clearance 25 to 35 mL/min) administered 50 mg of ranitidine intravenously had an average plasma half-life of 4.8 hours, a ranitidine clearance of 29 mL/min, and a volume of distribution of 1.76 L/kg. In general, these parameters appear to be altered in proportion to creatinine clearance
- Geriatrics: The plasma half-life is prolonged and total clearance is reduced in the elderly population due to a decrease in renal function. The elimination half-life is 3.1 hours .
- Pediatrics:There are no significant differences in the pharmacokinetic parameter values for ranitidine in pediatric patients (from 1 month up to 16 years of age) and healthy adults when correction is made for body weight. The pharmacokinetics of Ranitidine in pediatric patients are summarized in Table 1.
- Plasma clearance in neonatal patients (less than 1 month of age) receiving ECMO was considerably lower (3 to 4 mL/min/kg) than observed in children or adults. The elimination half-life in neonates averaged 6.6 hours as compared to approximately 2 hours in adults and pediatric patients.
|nonClinToxic=
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
- There was no indication of tumorigenic or carcinogenic effects in life-span studies in mice and rats at oral dosages up to 2,000 mg/kg/day.
- Ranitidine was not mutagenic in standard bacterial tests (Salmonella, Escherichia coli) for mutagenicity at concentrations up to the maximum recommended for these assays.
- In a dominant lethal assay, a single oral dose of 1,000 mg/kg to male rats was without effect on the outcome of 2 matings per week for the next 9 weeks.
|clinicalStudies=*Active Duodenal Ulcer: In a multicenter, double-blind, controlled, US study of endoscopically diagnosed duodenal ulcers, earlier healing was seen in the patients treated with oral Ranitidine as shown in Table 3
- In these studies, patients treated with oral Ranitidine reported a reduction in both daytime and nocturnal pain, and they also consumed less antacid than the placebo-treated patients.
- Pathological Hypersecretory Conditions (such as Zollinger-Ellison syndrome): Ranitidine inhibits gastric acid secretion and reduces occurrence of diarrhea, anorexia, and pain in patients with pathological hypersecretion associated with Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, systemic mastocytosis, and other pathological hypersecretory conditions (e.g., postoperative, "short-gut" syndrome, idiopathic). Use of oral Ranitidine was followed by healing of ulcers in 8 of 19 (42%) patients who were intractable to previous therapy.
- In a retrospective review of 52 Zollinger-Ellison patients given Ranitidine as a continuous IV infusion for up to 15 days, no patients developed complications of acid-peptic disease such as bleeding or perforation. Acid output was controlled to ≤10 mEq/h.
. |storage=* Store at 20° - 25° C (68° - 77° F)
- Avoid excessive heat or humidity
|packLabel= |fdaPatientInfo=* Adults and children 12 years and over:
- To relieve symptoms, swallow 1 tablet with a glass of water to prevent symptoms, swallow 1 tablet with a glass of water 30 to 60 minutes before eating food or drinking beverages that cause heartburn
- Can be used up to twice daily (do not take more than 2 tablets in 24 hours)
- TAMPER EVIDENT: DO NOT USE IF THE CARTON OR PRINTED FOIL UNDER CAP IS OPEN OR TORN.
|alcohol=* Alcohol-Ranitidine (injection) interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
|brandNames=*Ranitidine ®[1] |drugShortage= }} Synonyms / Brand Names: Ranitidine hydrochloride, Ranitidine HCL, Ranitidine Base, Rantidine HCL, Alquen, Alter-H2, Alvidina, Apo-Ranitidin, Artomil, Azuranit, Coralen, Digestosan, Ergan, Esofex, Fendibina, Gastrial, Gastridina, Gastrolav, Gastrosedol, Kuracid, Label, Lake, Logat, Melfax, Microtid, Mideran, Neugal, Noctone, Noktome, Normon, Novo-Radinine, Nu-Ranit, Pep-Rani, Ptinolin, Quadrin, Quantor, Radin, Ran H2, Ran Lich, Rani 2, Rani AbZ, Rani-BASF, Rani-Puren, Rani-Q, Rani-Sanorania, Rani-nerton, Raniben, Raniberl, Raniberta, Ranibloc, Ranic, Ranicux, Ranidil, Ranidin, Ranidine, Ranidura, Ranifur, Ranigasan, Ranigast, Ranigen, Ranilonga, Ranimerck, Raniogas, Raniplex, Ranisan, Ranitab, Ranitic, Ranitidin, Ranitidin 1A Pharma, Ranitidin AL, Ranitidin AWD, Ranitidin Arcana, Ranitidin Atid, Ranitidin Basics, Ranitidin Duncan, Ranitidin Dyna, Ranitidin Helvepharm, Ranitidin Heumann, Ranitidin Hexal, Ranitidin Merck, Ranitidin Millet, Ranitidin NM, Ranitidin Normon, Ranitidin PB, Ranitidin Stada, Ranitidin von ct, Ranitidin-Cophar, Ranitidin-Isis, Ranitidin-ratiopharm, Ranitidina Tamarang, Ranitidina predilu Grif, Ranitiget, Ranitin, Ranitine, Ranobel, Rantacid, Ranuber, Raticina, Regalil, Renatac, Rozon, Rubiulcer, Santanol, Serviradine, Sostril, Tanidina, Taural, Terposen, Toriol, Trigger, Ulcecur, Ulcex, Ulcirex, Ulcodin, Ulcolind Rani, Ulsaven, Ultidine, Viserul, Zandid, Ranitidine, Ranitidine 150, Ranitidine 75, Ranitidine In Plastic Container, Zantarac, Zantic
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Ranitidine (injection) |Label Name=Ranitidine (injection)06.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Ranitidine (injection) |Label Name=Ranitidine (injection)07.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Ranitidine (injection) |Label Name=Ranitidine (injection)08.png
}}