Satraplatin: Difference between revisions
m (Robot: Automated text replacement (-{{reflist}} +{{reflist|2}}, -<references /> +{{reflist|2}}, -{{WikiDoc Cardiology Network Infobox}} +)) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ | {{Drugbox | ||
| verifiedrevid = 447808729 | |||
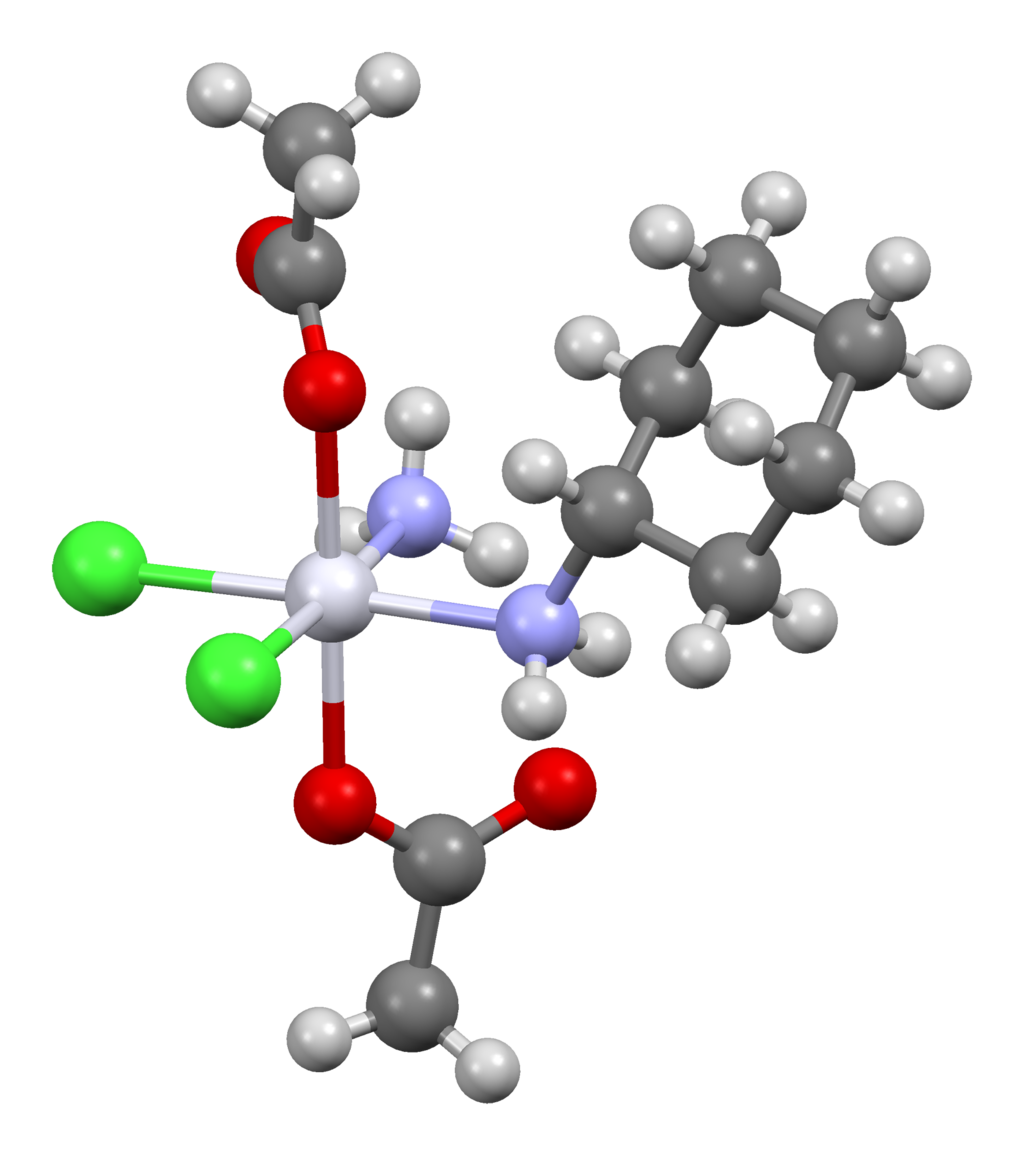
| IUPAC_name = (''OC''-6-43)-bis(acetato)amminedichloro(cyclohexylamine)platinum | |||
| image = Satraplatin.svg | |||
| image2 = Satraplatin-from-xtal-1995-Mercury-3D-balls.png | |||
<!--Clinical data--> | |||
| tradename = | |||
| pregnancy_AU = <!-- A / B1 / B2 / B3 / C / D / X --> | |||
| pregnancy_US = <!-- A / B / C / D / X --> | |||
| pregnancy_category = | |||
| legal_AU = <!-- S2, S3, S4, S5, S6, S7, S8, S9 or Unscheduled--> | |||
| legal_CA = <!-- Schedule I, II, III, IV, V, VI, VII, VIII --> | |||
| legal_UK = <!-- GSL, P, POM, CD, or Class A, B, C --> | |||
| legal_US = <!-- OTC / Rx-only / Schedule I, II, III, IV, V --> | |||
| legal_status = | |||
| routes_of_administration = Oral | |||
<!--Pharmacokinetic data--> | |||
| bioavailability = | |||
| protein_bound = | |||
| metabolism = | |||
| elimination_half-life = | |||
| excretion = | |||
== | <!--Identifiers--> | ||
| CAS_number_Ref = {{cascite|correct|??}} | |||
| CAS_number = 129580-63-8 | |||
| ATC_prefix = L01 | |||
| ATC_suffix = XA04 | |||
| PubChem = 123974 | |||
| DrugBank_Ref = {{drugbankcite|correct|drugbank}} | |||
| DrugBank = | |||
| UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} | |||
| UNII = 8D7B37T28G | |||
<!--Chemical data--> | |||
| C=10 | H=22 | Cl=2 | N=2 | O=4 | Pt=1 | |||
| molecular_weight = 500.277 g/mol | |||
| synonyms = BMY 45594<br>BMS 182751<br>(''OC''-6-43)-bis(acetato)amminedichlorocyclohexylamine platinum(IV) | |||
}} | |||
'''Satraplatin''' ([[International Nonproprietary Name|INN]], codenamed '''JM216''') is a [[platinum-based antineoplastic]] agent that is under investigation as one treatment of patients with advanced [[prostate cancer]] who have failed previous [[chemotherapy]]. It has not yet received approval from the U.S. [[Food and Drug Administration]].<ref>{{cite journal |title=The status of platinum anticancer drugs in the clinic and in clinical trials |journal=Dalton Transactions |volume=39 |pages=8113–27 |year=2010 |doi=10.1039/C0DT00292E |last1=Wheate |first1=Nial J. |authorlink1=Nial J. Wheate |last2=Walker |first2=Shonagh |last3=Craig |first3=Gemma E. |last4=Oun |first4=Rabbab |issue=35 |pmid=20593091 }}</ref> First mentioned in the medical literature in 1993,<ref>{{cite journal |author=Kelland LR, Abel G, McKeage MJ, ''et al.'' |title=Preclinical antitumor evaluation of bis-acetato-ammine-dichloro-cyclohexylamine platinum(IV): an orally active platinum drug |journal=Cancer Res |volume=53 |issue=11 |pages=2581–6 |year=1993 |pmid=8388318 |url=http://cancerres.aacrjournals.org/cgi/reprint/53/11/2581.pdf |format=PDF}}</ref> satraplatin is the first orally active platinum-based chemotherapeutic drug;<ref>{{cite journal |author=Choy H, Park C, Yao M |title=Current status and future prospects for satraplatin, an oral platinum analogue |journal=Clin Cancer Res |volume=14 |issue=6 |pages=1633–8 |year=2008 |pmid=18347164 |doi=10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-2176}}</ref> other available platinum analogues—[[cisplatin]], [[carboplatin]], and [[oxaliplatin]]—must be given [[intravenous therapy|intravenously]]. | |||
The drug has also been used in the treatment of lung and ovarian cancers. The mode of action is that the compound binds to the [[DNA]] of cancer cells rendering them incapable of [[Mitosis|dividing]]. <ref> http://www.spectrumpharm.com/satraplatin.html </ref> | It is made available in the United States jointly by [[Spectrum Pharmaceuticals]] and GPC Biotech under the name SPERA (SatraPlatin Expanded Rapid Access). | ||
The drug has also been used in the treatment of lung and ovarian cancers. The proposed mode of action is that the compound binds to the [[DNA]] of cancer cells rendering them incapable of [[Mitosis|dividing]].<ref>[http://www.spectrumpharm.com/satraplatin.html Satraplatin — Spectrum Pharmaceuticals<!-- Bot generated title -->]</ref> | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist | {{reflist}} | ||
{{Chemotherapeutic agents}} | |||
{{Platinum compounds}} | |||
[[Category:Coordination compounds]] | |||
[[Category:Platinum compounds]] | |||
[[Category:Acetates]] | |||
[[Category:Platinum-based antineoplastic agents]] | |||
{{antineoplastic-drug-stub}} | |||
{{ | |||
Revision as of 20:34, 12 April 2015
| File:Satraplatin.svg | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | BMY 45594 BMS 182751 (OC-6-43)-bis(acetato)amminedichlorocyclohexylamine platinum(IV) |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| E number | {{#property:P628}} |
| ECHA InfoCard | {{#property:P2566}}Lua error in Module:EditAtWikidata at line 36: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C10H22Cl2N2O4Pt |
| Molar mass | 500.277 g/mol |
| (verify) | |
Satraplatin (INN, codenamed JM216) is a platinum-based antineoplastic agent that is under investigation as one treatment of patients with advanced prostate cancer who have failed previous chemotherapy. It has not yet received approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.[1] First mentioned in the medical literature in 1993,[2] satraplatin is the first orally active platinum-based chemotherapeutic drug;[3] other available platinum analogues—cisplatin, carboplatin, and oxaliplatin—must be given intravenously.
It is made available in the United States jointly by Spectrum Pharmaceuticals and GPC Biotech under the name SPERA (SatraPlatin Expanded Rapid Access).
The drug has also been used in the treatment of lung and ovarian cancers. The proposed mode of action is that the compound binds to the DNA of cancer cells rendering them incapable of dividing.[4]
References
- ↑ Wheate, Nial J.; Walker, Shonagh; Craig, Gemma E.; Oun, Rabbab (2010). "The status of platinum anticancer drugs in the clinic and in clinical trials". Dalton Transactions. 39 (35): 8113–27. doi:10.1039/C0DT00292E. PMID 20593091.
- ↑ Kelland LR, Abel G, McKeage MJ; et al. (1993). "Preclinical antitumor evaluation of bis-acetato-ammine-dichloro-cyclohexylamine platinum(IV): an orally active platinum drug" (PDF). Cancer Res. 53 (11): 2581–6. PMID 8388318.
- ↑ Choy H, Park C, Yao M (2008). "Current status and future prospects for satraplatin, an oral platinum analogue". Clin Cancer Res. 14 (6): 1633–8. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-2176. PMID 18347164.
- ↑ Satraplatin — Spectrum Pharmaceuticals
- Pages with script errors
- CS1 maint: Explicit use of et al.
- CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list
- Pages with broken file links
- E number from Wikidata
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without InChI source
- Drugs with no legal status
- Coordination compounds
- Platinum compounds
- Acetates
- Platinum-based antineoplastic agents