Pericarditis resident survival guide: Difference between revisions
Rim Halaby (talk | contribs) (→Don'ts) |
Rim Halaby (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
{{Family tree/start}} | {{Family tree/start}} | ||
{{familytree | | | | | | | | | | A01 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | A01= <div style="float: left; text-align: left; width: 30em; padding:1em;"> '''Characterize the symptoms:'''<br> | {{familytree | | | | | | | | | | A01 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | A01= <div style="float: left; text-align: left; width: 30em; padding:1em;"> '''Characterize the symptoms:'''<br> | ||
❑ [[Chest pain]] | ❑ [[Chest pain]] | ||
:❑ Sudden onset | :❑ Sudden onset | ||
:❑ Sharp or dull, aching and pressure like | :❑ Sharp or dull, aching and pressure like | ||
| Line 64: | Line 64: | ||
:❑ [[Orthopnea]] <br> | :❑ [[Orthopnea]] <br> | ||
:❑ [[Dizziness]] <BR> | :❑ [[Dizziness]] <BR> | ||
:❑ | :❑ [[Hoarseness]] ([[recurrent laryngeal nerve]] compression) <br> | ||
:❑ [[Hiccups]] ([[phrenic nerve]] compression) <BR> | :❑ [[Hiccups]] ([[phrenic nerve]] compression) <BR> | ||
:❑ [[Abdominal pain]] ([[mesenteric ischemia]]) <BR> | :❑ [[Abdominal pain]] ([[mesenteric ischemia]]) <BR> | ||
| Line 82: | Line 82: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
'''Obtain a detailed history:'''<br> | '''Obtain a detailed history:'''<br> | ||
❑ Infections | ❑ Infections | ||
:❑ [[Pneumonia]] | :❑ [[Pneumonia]] | ||
:❑ [[Tuberculosis]] | :❑ [[Tuberculosis]] | ||
| Line 125: | Line 125: | ||
{{familytree | | | | | | | | | | B01 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | B01=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; padding:1em;"> '''Examine the patient:'''<br> | {{familytree | | | | | | | | | | B01 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | B01=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; padding:1em;"> '''Examine the patient:'''<br> | ||
'''Vitals''' | '''Vitals''' | ||
:❑ [[Pulse]] | :❑ [[Pulse]] | ||
::❑ [[Tachycardia]] (typical) | ::❑ [[Tachycardia]] (typical) | ||
| Line 140: | Line 140: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
'''Cardiovascular examination:''' <br> | '''Cardiovascular examination:''' <br> | ||
'''Auscultation''' <br> | '''Auscultation''' <br> | ||
:❑ Heart sounds | :❑ Heart sounds | ||
| Line 159: | Line 159: | ||
'''Percussion:''' <br> | '''Percussion:''' <br> | ||
:❑ Cardiac dullness beyond the apical point of maximal impulse (in [[pericardial effusion]]) <br> | :❑ Cardiac dullness beyond the apical point of maximal impulse (in [[pericardial effusion]]) <br> | ||
'''Respiratory examination:''' <br> | '''Respiratory examination:''' <br> | ||
:❑ [[Wheeze]] or [[rales]]<br> | :❑ [[Wheeze]] or [[rales]]<br> | ||
:❑ [[Pleural effusion]]<br> | :❑ [[Pleural effusion]]<br> | ||
---- | ---- | ||
'''Abdominal examination:''' | '''Abdominal examination:''' | ||
:❑ Pulsatile [[hepatomegaly]] (in [[constrictive pericarditis]]) | :❑ Pulsatile [[hepatomegaly]] (in [[constrictive pericarditis]]) | ||
:❑ [[Ascites]]<br> | :❑ [[Ascites]]<br> | ||
| Line 183: | Line 183: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
'''Order [[electrocardiogram]] (urgent):'''<br> | '''Order [[electrocardiogram]] (urgent):'''<br> | ||
❑ [[Pericarditis electrocardiogram|Typical findings in pericarditis]] | ❑ [[Pericarditis electrocardiogram|Typical findings in pericarditis]] | ||
:❑ [[ST segment elevation]] in leads I, II, aVL, aVF, and V3-V6 | :❑ [[ST segment elevation]] in leads I, II, aVL, aVF, and V3-V6 | ||
| Line 192: | Line 192: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
'''Order imaging (urgent):'''<br> | '''Order imaging (urgent):'''<br> | ||
❑ [[Chest X-ray]] <br> | ❑ [[Chest X-ray]] <br> | ||
:❑ Clear lung fields (typical) | :❑ Clear lung fields (typical) | ||
| Line 210: | Line 210: | ||
{{familytree | | | | | | | | | | |!| | | | | | | | | }} | {{familytree | | | | | | | | | | |!| | | | | | | | | }} | ||
{{familytree | | | | | | | | | | C01 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | C01=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; padding:1em;">'''Diagnosis of acute pericarditis'''<br> | {{familytree | | | | | | | | | | C01 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | C01=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; padding:1em;">'''Diagnosis of acute pericarditis'''<br> | ||
''' | '''At least two of the following criteria:'''<br> | ||
❑ Characteristic [[chest pain]] <br> | ❑ Characteristic [[chest pain]] <br> | ||
:❑ Sharp and pleuritic that is improved by sitting up and leaning forward | :❑ Sharp and pleuritic that is improved by sitting up and leaning forward | ||
| Line 226: | Line 226: | ||
{{familytree | | | | | | |!| | | | | | | |!| | | | | | | }} | {{familytree | | | | | | |!| | | | | | | |!| | | | | | | }} | ||
{{familytree | | | | | | E01 | | | | | | D02 | | | | | | E01= Elevated [[cardiac enzymes]] <BR> or <BR> Global or regional myocardial dysfunction on echo | D02=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; padding:1em;">'''Suspicion of diagnosis of [[acute pericarditis]]'''<br> | {{familytree | | | | | | E01 | | | | | | D02 | | | | | | E01= Elevated [[cardiac enzymes]] <BR> or <BR> Global or regional myocardial dysfunction on echo | D02=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; padding:1em;">'''Suspicion of diagnosis of [[acute pericarditis]]'''<br> | ||
❑ Ongoing [[fever]] <BR> | ❑ Ongoing [[fever]] <BR> | ||
❑ Poor response to treatment<br> | ❑ Poor response to treatment<br> | ||
Revision as of 15:23, 24 March 2014
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Mugilan Poongkunran M.B.B.S [2]
| Pericarditis Resident Survival Guide Microchapters |
|---|
| Overview |
| Causes |
| Diagnosis |
| Treatment |
| Do's |
| Don'ts |
Synonyms and keywords: Myopericarditis, perimyocarditis
Overview
Pericarditis is the inflammation of the fibroelastic sac surrounding the heart (pericardium). Pericarditis is divided into acute (<6 weeks), subacute (6 weeks to 6 months) and chronic (>6 months) and it can be dry, fibrinous or effusive independently of the etiology. Myopericarditis, or perimyocarditis refers to acute pericarditis associated with myocardial inflammation that leads to global or regional myocardial dysfunction and elevation in the concentration of troponins, creatine kinase MB, myoglobin and tumour necrosis factor.[1] Always suspect pericarditis in the presence of pleuritic chest pain and pericardial friction rub. NSAIDs are the mainstay of the treatment of acute pericarditis; ibuprofen is the most preferred drug due to its favorable effect on the coronary flow.[2]
Causes
Life Threatening Causes
Life-threatening causes include conditions which may result in death or permanent disability within 24 hours if left untreated.
Common Causes
- Autoimmune: Rheumatoid arthritis, Sjögren’s syndrome, SLE, systemic sclerosis, systemic vasculitis
- Bacterial: Coxiella burnetii, pneumococcus, staphylococcus, streptococcus, tuberculosis[3]
- Cardiovascular: Dressler's syndrome, postpericardiotomy syndrome, post-traumatic pericarditis[4]
- Idiopathic
- Metabolic: Myxedema, uremia
- Neoplastic: Breast cancer, leukemia, lung cancer, lymphoma
- Viral: Adeno virus, CMV, coxsackie, EBV, echovirus, HBV, HIV, human herpes virus 6, influenza, mumps, parvovirus B19, rubella, varicella[3]
Diagnosis
Shown below is an algorithm summarizing the diagnostic approach to acute pericarditis in adults.[2][5][4]
Characterize the symptoms:
Symptoms associated with pericardial effusion:
❑ With a hemodynamically significant pericardial effusion
Other etiology associated symptoms: Obtain a detailed history:
❑ Medications ❑ Systemic illness ❑ Others | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Examine the patient: Vitals
Cardiovascular examination: Auscultation
Palpation:
Percussion:
Respiratory examination:
Abdominal examination:
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Order laboratory tests (urgent): ❑ CBC (leucocytosis) Order electrocardiogram (urgent): ❑ Typical findings in pericarditis
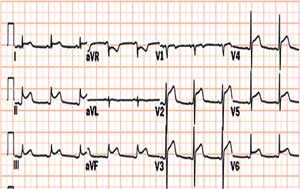 ❑ Electrical alternans (in cardiac tamponade) Order imaging (urgent):
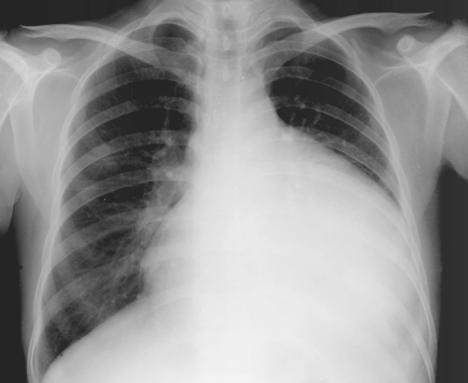
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Diagnosis of acute pericarditis At least two of the following criteria:
❑ Suggestive EKG changes
❑ Suggestive echocardiography changes
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yes | No or equivocal | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Elevated cardiac enzymes or Global or regional myocardial dysfunction on echo | Suspicion of diagnosis of acute pericarditis ❑ Ongoing fever | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| No | Yes | Yes | No | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Consider cardiac MRI (CMR))[7] | Consider alternative diagnosis and treat accordingly | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Acute pericarditis | Myopericarditis | Treat as acute pericarditis or myopericarditis if there is delayed enhancement on CMR | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Treatment
Treatment of Acute Pericarditis
Shown below is an algorithm summarizing the management of acute pericarditis in adults.[2][5][4]
| Acute pericarditis or myopericarditis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
High risk features ❑ Fever >38°C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Any one of the above high risk features | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yes | No | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inpatient treatment | Outpatient treatment | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stable | No pre-existing coronary artery disease | Pre-existing coronary artery disease | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Initiate medical therapy NSAIDs
❑ Indomethacin:
❑ Stop anticoagulants if patient develops pericardial effusion
Order tests to identify the specific etiology ❑ Order specifc tests based on the clinical suspicion Order pericardiocentesis: ❑ When there is
| Click here for management of cardiac tamponade ❑ Immediately transfer the patient to ICU Initiate medical therapy NSAIDs
❑ Indomethacin:
❑ Stop anticoagulants if patient develops pericardial effusion
Order tests to identify the specific etiology ❑ Order specifc tests based on the clinical suspicion | Initiate medical therapy NSAID's
❑ Indomethacin:
❑ Add gastroprotective agents
Life style modification ❑ In case of pericarditis, avoid sternous physical activity until symptom resolution | Intitate aspirin therapy
❑ Add gastroprotective agents
❑ Stop anticoagulants if patient develops pericardial effusion Steroids Life style modification ❑ In case of pericarditis, avoid sternous physical activity until symptom resolution | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Response to treatment | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yes | No | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Follow up ❑ Observe for recurrences or constriction | Hospital admission ❑ Indication that the underlying cause may not be viral or idiopathic in nature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Treatment of Recurrent Pericarditis
Shown below is an algorithm summarizing the management of recurrent pericarditis in adults which encompass the incessant type (relapses on discontinuation of anti-inflammatory) and the intermittent type (widely varying symptom free interval without medical therapy).[2][5][4]
| Recurrent pericarditis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Characterize the clinical, EKG and imaging findings ❑ Characteristic acute pericarditis symptoms
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Initiate medical therapy NSAIDs
❑ Indomethacin:
❑ Stop anticoagulants if patient develops pericardial effusion
Life style modification ❑ Excercise restriction until symptom resolution | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Multiple relapses | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Positive response | No response | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Taper steroids ❑ Taper dose over a three-month period
❑ Add colchicine or NSAIDs at the end of tapering of steroids | ❑ Add azathioprine (75–100 mg/day) or cyclophosphamide | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treatment failure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pericardiectomy ❑ Maintain the patient on steroid free regimen for several weeks before the procedure ❑Order tests to identify the specific etiology and treat accordingly | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Etiology Specific Management
| Clinical subgroups | Specific investigations | Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Viral pericarditis | ❑ Perform testing for viral etiologies in immunocompromised and HIV infected patients not responding to intial management ❑ Diagnostic pericardiocentesis ❑ Analysis of pericardial fluid (transudate or exudate) ❑ PCR or in-situ hybridisation |
❑ CMV pericarditis: Hyperimmunoglobulin OD 4 ml/kg on day 0, 4,and 8; 2 ml/kg on day 12 and 16 ❑ Coxsackie B pericarditis: Interferon alpha or beta 2,5 Mio. IU/m2 surface area s.c. 3 x per week ❑ Adenovirus and parvovirus B19 perimyocarditis: Immunoglobulin 10 g IV at day 1 and 3 for 6-8 hours |
| Purulent pericarditis | ❑ Diagnostic pericardiocentesis in cases of high clinical suspicion ❑ Gram stain, acid fast stain, fungal stain, and cultures of the pericardial fluid ❑ Protein, glucose and cell count of the pericardial fluid ❑ Gram stain, acid fast stain, fungal stain, and cultures of other body fluids |
❑ Therapeutic pericardiocentesis or pericardial window ❑ Pericardiectomy may be used in treatment of recurrent pericardial effusion and in patients with dense adhesions, loculated and thick purulent effusion ❑ Antimicrobial therapy in case of bacterial etiology ❑ Intiate antistaphylococcal antibiotic plus aminoglycoside, followed by tailored antibiotic therapy according to pericardial fluid and blood cultures ❑ Empiric regimen can be started for the following ❑ Immunosuppression ❑ Concurrent infection at another body site ❑ Presence of intravascular lines or prosthetic devices ❑ Recent antimicrobial therapy ❑ Antifungal therapy in case of fungal etiology |
| Tuberculous pericarditis | ❑ Diagnostic pericardiocentesis in all suspected tuberculous pericarditis patients ❑ PCR of pericardial fluid ❑ High adenosine deaminase activity and interferon gamma concentration in pericardial effusion ❑ Pericardial biopsy (rapid diagnosis) ❑ Tuberculin skin test (not helpful) ❑ CT scan and/or MRI of the chest ❑ Culture of sputum, gastric aspirate, and/or urine ❑ Enzyme-linked immunospot (ELISPOT) ❑ Serum titres of antimyolemmal and antimyosin antibodies |
❑Anti-tuberculosis chemotherapy ❑ Emperic therapy in TB endemic areas and in cases with high clinical suspicion ❑ Pericardiectomy is warranted in the setting of persistent constrictive pericarditis or when no general improvement after 4-8 weeks following antituberculosis chemotherapy ❑ Prednisone can be used. |
| Neoplastic pericarditis | ❑ CT scan and/or MRI of the chest ❑ Diagnostic pericardiocentesis when other tests couldnt identify malignancy ❑ Cytology and tumour markers ❑ Pericardial biopsy |
❑ Systemic antineoplastic treatment ❑ Assess the life expectancy of the patients before proceeding with the treatment ❑ Better prognosis patients should be treated more aggressively ❑ Advanced malignancy should be treated palliatively with pericardiocentesis ❑ Recurrence of pericardial effusion is prevented using any of the following techniques ❑ Prolonged pericardiocentesis ❑ Pericardial sclerosis ❑ Pericardiotomy ❑ Intrapericardial chemotherapy |
| Pericarditis in renal failure | ❑ Renal function test ❑ Diagnostic pericardiocentesis ❑ Pericardial biopsy |
❑ Uremic pericarditis ❑ Hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis ❑ Heparin-free haemodialysis should be used ❑ Dialysis-associated pericarditis ❑ Pericardiocentesis for large effusion ❑ Pericardiotomy in non resolving effusion |
| Pericarditis in systemic autoimmune disease | ❑ Diagnostic pericardiocentesis ❑ Elevated lymphocytes and mononuclear cells > 5000/mm3 ❑ Antisarcolemmal antibodies ❑ Exclusion of viral and bacterial etiologies |
❑ NSAIDs or aspirin or colchicine ❑ Systemic corticosteroid can be used ❑ Intrapericardial steroids has less side effects and is highly effective |
Do's
- Always suspect acute pericarditis based on a history of characteristic pleuritic chest pain and on a pericardial friction rub finding. Pericarditis should also be suspected in a patient with persistent fever and pericardial effusion or new unexplained cardiomegaly.
- Focus on excluding a significant effusion or tamponade. Suspect acute cardiac tamponade in any patient presenting with Beck's triad: hypotension, tachycardia, muffled heart sounds and distended neck veins (or elevated jugular venous pressure).[9]
- NSAIDs are the mainstay in the treatment of uncomplicated acute pericarditis and ibuprofen is the most preferred for its favourable effect on the coronary flow, fewer side effects, and the large dose range.
- Heparin is recommended under strict observation for patients who need anticoagulant therapy.
- Restrict systemic corticosteroid therapy to connective tissue diseases, autoreactive or uremic pericarditis. Intrapericardial application avoids systemic side effects and is highly effective. Use moderate initial dosing of steroids followed by a slow taper. Introduce ibuprofen or colchicine early during tapering of steroids.
- Analysis of pericardial effusion for different etiologies should be ordered according to the clinical presentation.
- Assess for the presence of coagulopathy or the intake of antithrombotic medications before choosing the modality of drainage of the pericardial fluid.
- Choose pericardiocentesis rather than surgical drainage as a therapeutic option unless the patient has an indication for surgical drainage. Consider surgical drainage in aortic dissection and myocardial rupture.[10]
- When surgical drainage is indicated but the patient has severe hypotension prohibiting the induction of anesthesia, perform pericardiocentesis in the operating room before surgery.[10]
- Monitor closely patients who underwent pericardiocentesis for postdrainage decompensation.
Don'ts
- When cardiac tamponade is suspected, do not delay its treatment.
- Avoid pericardiocentesis in cases where the diagnosis can be made based on systemic features or when the effusions are very small or resolving with anti-inflammatory treatment.
- Don't perform pericardiocentesis in aortic dissection and ruptured ventricular aneurysm and avoid it in cases of uncorrected coagulopathy, anticoagulant therapy, thrombocytopenia < 50,000/mm 3 , small, posterior, and loculated effusions.
References
- ↑ Imazio M (2012). "Contemporary management of pericardial diseases". Curr Opin Cardiol. 27 (3): 308–17. doi:10.1097/HCO.0b013e3283524fbe. PMID 22450720.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Maisch B, Seferović PM, Ristić AD, Erbel R, Rienmüller R, Adler Y; et al. (2004). "Guidelines on the diagnosis and management of pericardial diseases executive summary; The Task force on the diagnosis and management of pericardial diseases of the European society of cardiology". Eur Heart J. 25 (7): 587–610. doi:10.1016/j.ehj.2004.02.002. PMID 15120056.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Imazio M, Spodick DH, Brucato A, Trinchero R, Adler Y (2010). "Controversial issues in the management of pericardial diseases". Circulation. 121 (7): 916–28. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.844753. PMID 20177006.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 Lange RA, Hillis LD (2004). "Clinical practice. Acute pericarditis". N Engl J Med. 351 (21): 2195–202. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp041997. PMID 15548780.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Klein AL, Abbara S, Agler DA, Appleton CP, Asher CR, Hoit B; et al. (2013). "American Society of Echocardiography clinical recommendations for multimodality cardiovascular imaging of patients with pericardial disease: endorsed by the Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance and Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography". J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 26 (9): 965–1012.e15. doi:10.1016/j.echo.2013.06.023. PMID 23998693.
- ↑ "WHO launches World health report 2013". Euro Surveill. 18 (33): 20559. 2013. PMID 23968879.
- ↑ Khandaker MH, Espinosa RE, Nishimura RA; et al. (2010). "Pericardial disease: diagnosis and management". Mayo Clinic Proceedings. Mayo Clinic. 85 (6): 572–93. doi:10.4065/mcp.2010.0046. PMC 2878263. PMID 20511488. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 Goldfinger S (2014). "A randomized trial of colchicine for acute pericarditis". N Engl J Med. 370 (8): 780. doi:10.1056/NEJMc1315351#SA1. PMID 24552334.
- ↑ Sternbach, G.; Beck, C. "Claude Beck: cardiac compression triads". J Emerg Med. 6 (5): 417–9. PMID 3066820.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Schiavone WA (2013). "Cardiac tamponade: 12 pearls in diagnosis and management". Cleve Clin J Med. 80 (2): 109–16. doi:10.3949/ccjm.80a.12052. PMID 23376916.