Pericarditis electrocardiogram
|
Pericarditis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Surgery |
|
Case Studies |
|
Pericarditis electrocardiogram On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Pericarditis electrocardiogram |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Pericarditis electrocardiogram |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Homa Najafi, M.D.[2]
Overview
The typical EKG finding in acute pericarditis is ST segment elevation in leads I, II, aVL, aVF, and V3-V6. Low-voltage QRS complexes may be observed in large pericardial effusion and constrictive pericarditis. Cardiac tamponade is characterized by electrical alternans.
Electrocardiogram
EKG Findings in Pericarditis
- Typical lead involvement: I, II, aVL, aVF, and V3-V6.
- The ST segment is always depressed in aVR, frequently in V1, and occasionally in V2. Occasionally, stage IV does not occur and there are permanent T wave inversions and flattenings. PR segment depression may be observed in this stage in leads other than aVR. This is known as 'Spodick's sign'.
- If EKG is first recorded in stage III, pericarditis cannot be differentiated by EKG from diffuse myocardial injury, "biventricular strain", or myocarditis.
- EKG in early repolarization is very similar to stage I. Unlike stage I, this EKG does not acutely evolve and J point elevations are usually accompanied by a slur, oscillation, or notch at the end of the QRS just before and including the J point (best seen with tall R and T waves - large in early repolarisation pattern).
- Pericarditis is likely if in lead V6 the J point is >25% of the height of the T wave apex (using the PR segment as a baseline).
- Increase in scar tissue, fluid and fibrin can reduce voltage, quasi-specific ST-T waves can present. The EKG abnormalities vary depending on the stage/severity of the pericarditis. Below are the stages/types of pericarditis.[1][2]
Shown below is an EKG image of pericarditis at several different stages:
- Stage I: ST elevation in all leads; PTa depression (depression between the end of the P wave and the beginning of the QRS complex)
- Stage II: Pseudonormalization (transition)
- Stage III: Inverted T waves
- Stage IV: Normalization
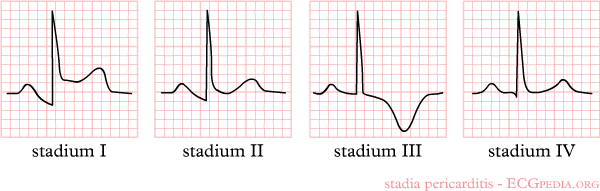
Copyleft image obtained courtesy of, http://en.ecgpedia.org/wiki/Main_Page
- Acute pericarditis (see also the PR interval and the EKG of cardiac transplantation): This variation of the disease in conjunction with myocarditis can lead to ST-T anomalies that are characteristic of the acute stages of pericarditis.
- Stage 1: Stage 1 of acute pericarditis, in and of itself, presents as "early repolarization" and acute infarction. It shows signs of anterior and inferior ST elevation on the EKG. There are usually no deviations in the QRS complex. This stage is largely characteristic of acute pericarditis when almost all of the leads are effected. Leads I, II, avL, avF, and V3-V6.
- Stage 2: During the early phase of this stage, ST segments should become baseline again; whereas, PR segments may have deviated. During the latter phase of stage 2, the ST segments that were previously elevated usually flatten and invert.
- Stage 3: Virtually all of the leads in stage 3 exhibit T wave inversion. Acute pericarditis cannot be diagnosed on an ECG of a stage 3 patient because its presentation is the same as myocardial injury and frank myocarditis.
- Stage 4: This stage presents itself on the EKG as a return to a pre-pericarditis state. Stage 4 does not always occur and in its absence, there can be residual T wave inversions that may be permanent, generalized or focal.
- Rate and Rhythm: Rapid heart rates are typical in patients with pericarditis, but in patients with uremic pericarditis slower rates are observed. Heart rhythms appear normal unless there is another complication such as cardiac disease, the presence of myocardial/pericardial tumor, or a metabolic disorder.
- Pericardial effusion (see also amplitude): These can present differently on the EKG depending on whether they are chronic vs large effusions. The former typically leads to low amplitude EKGs; whereas, the latter can show no voltage or various ECG abnormalities. ST-T wave abnormalities can be caused by superficial myocarditis or because of the accumulated fluid, they may be caused by the compression of the myocardium or ischemia. The primary cause of ST segment variation during pericardial effusions is usually the rapid accumulation of fluid. Large effusions can lead to the reduction of P wave voltage. Pleural effusions can cause a decrease in voltage, which occurs mainly on the left. Also, cirrhosis and congestive heart failure (CHF), which similarily involve the accumulation of fluid in the body, can decrease voltage in the absence of any pericardial disease.
- Cardiac tamponade (see also cardiac tamponade electrocardiogram): Generally has little EKG effect; however, in the acute form, tamponade may present on the EKG as any one of the stages of acute pericarditis.
- Electrical alternans: This occurs more often in cases of tamponade than in those of pericarditis (2:1). There is alternation of the QRS complex on the spatial axis. Alternation of the T wave, P wave, and PR segement are difficult to see and are uncommon. The removal of even a small amount of fluid can end alternation.
- Early Repolarization: This finding can be misleading and may look like pericarditis, when in fact it is not. A strong indication of pericarditis is "if the J point is more than 25% the height of the T wave apex."
- Constrictive pericarditis: Cases of constrictive pericarditis have nonspecific EKG abnormalities. Common abnormalities include: a slightly "low voltage QRS" segment combined with "flattened to inverted T waves", during stage 3 of acute/subacute constriction the T wave inversions remain or worsen and "P waves can be wide and bifid." It is not uncommon for patients to have normal EKGs. Many patients may only exhibit "nonspecific T wave abnormality." Other influencial factors that may effect the EKG in constrictive pericarditis are: fluid retention, ascites, and pleural effusions. The two most common arrhythmias that occur are atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter.
- QRS abnormality: Characteristic RV hypertrophy QRS abnormalities may develop as a result of disproportionate constriction or postpericardiectomy scarring. Also, "focal atrophy, scarring or inflammation" may cause "abnormal Q waves".
- Chronic constrictive pericarditis: Low voltage and myocardial atrophy, "frontal QRS axis" is usually vertical (becomes more vertical with increasing chronicity),
- Acute/subacute pericarditis: QRS axis appears as normal
- QRS abnormality: Characteristic RV hypertrophy QRS abnormalities may develop as a result of disproportionate constriction or postpericardiectomy scarring. Also, "focal atrophy, scarring or inflammation" may cause "abnormal Q waves".
EKG Examples
Shown below is an EKG with ST elevation in leads I, II, III, aVF, aVL, V2, V3, V4,V5, and V6 depicting acute pericarditis.
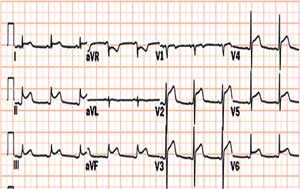
Copyleft image obtained courtesy of ECGpedia, http://en.ecgpedia.org/wiki/Main_Page
Shown below is an EKG with ST elevation in leads I, II, V2, V3, V4, V5, and V6 depicting acute pericarditis.
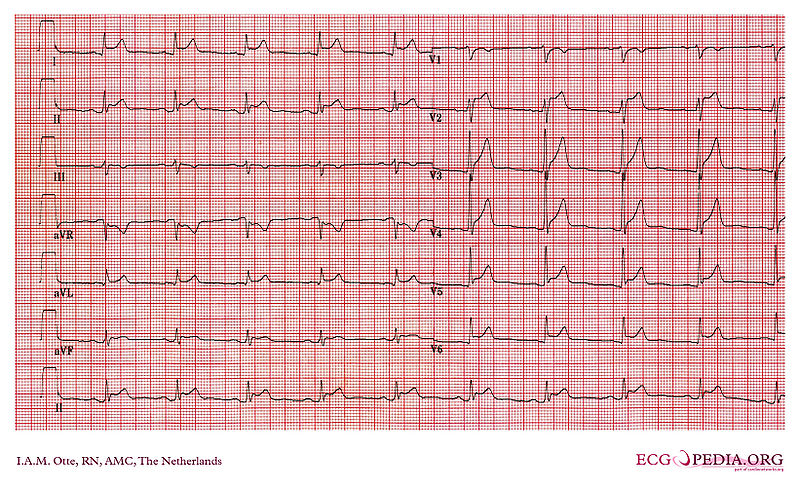
Copyleft image obtained courtesy of ECGpedia, http://en.ecgpedia.org/wiki/File:De-ECG000026.jpg
Shown below is an EKG with PTa depression in lead II depicting acute pericarditis.

Copyleft image obtained courtesy of ECGpedia, http://en.ecgpedia.org/wiki/Main_Page
Shown below is an EKG with ST elevation in leads II, aVF, V2, V3, V4, V5, and V6 depicting acute pericarditis.
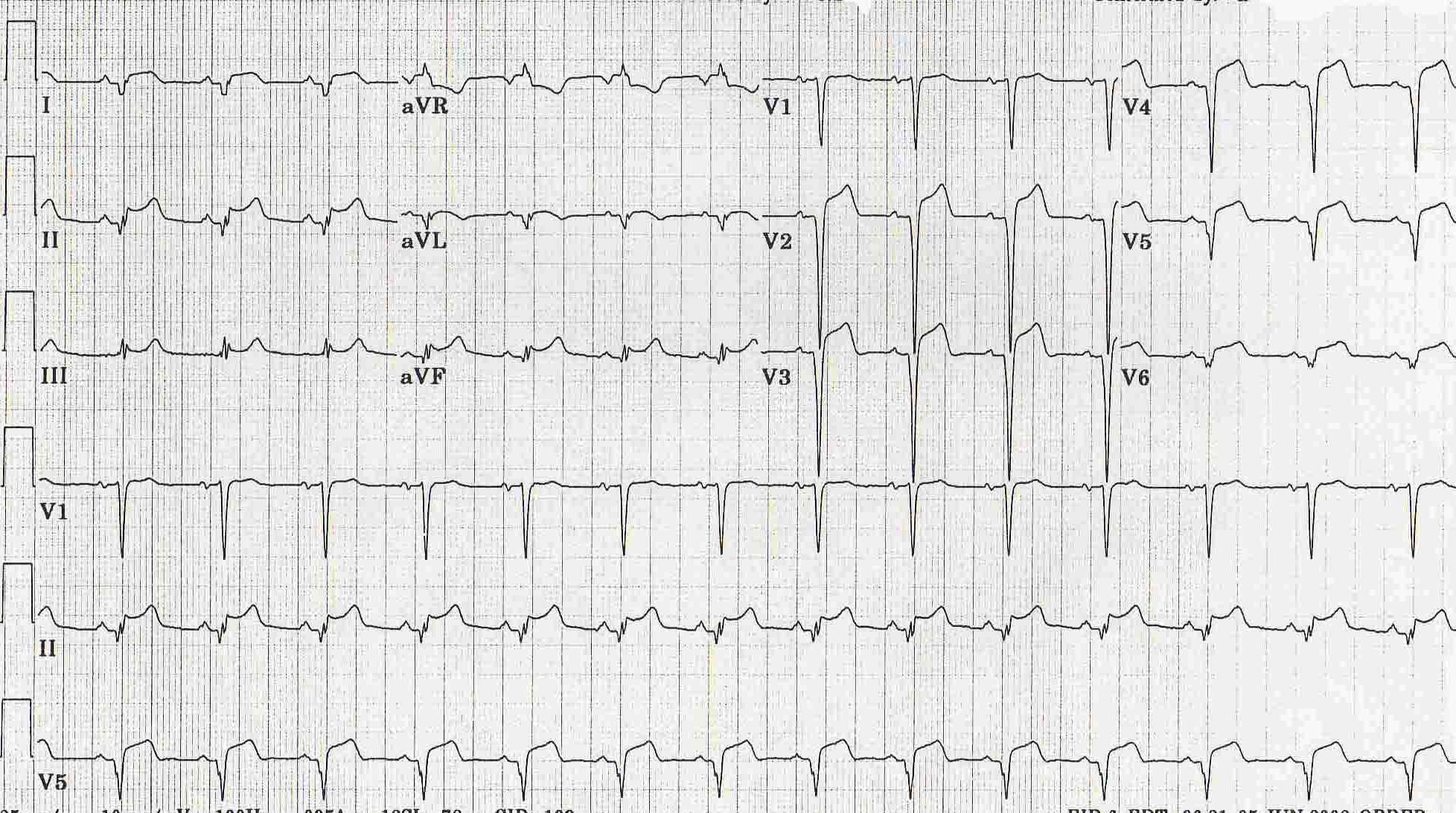
Copyleft image obtained courtesy of ECGpedia, http://en.ecgpedia.org/wiki/Main_Page
EKG Examples
Shown below is an EKG demonstrating PTa depression (depression between the end of the P wave and the beginning of the QRS complex) and absence of ST elevation depicting acute pericarditis.
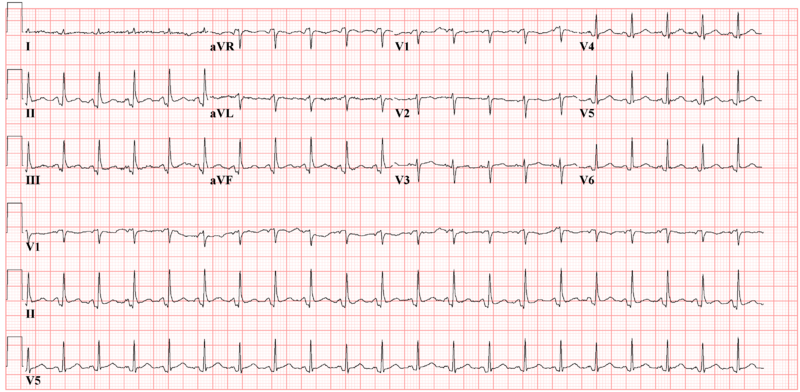
Copyleft image obtained courtesy of ECGpedia,http://en.ecgpedia.org/wiki/File:De-Ptadepressieecg.png
Shown below is an EKG demonstrating PTa depression depicting acute pericarditis.
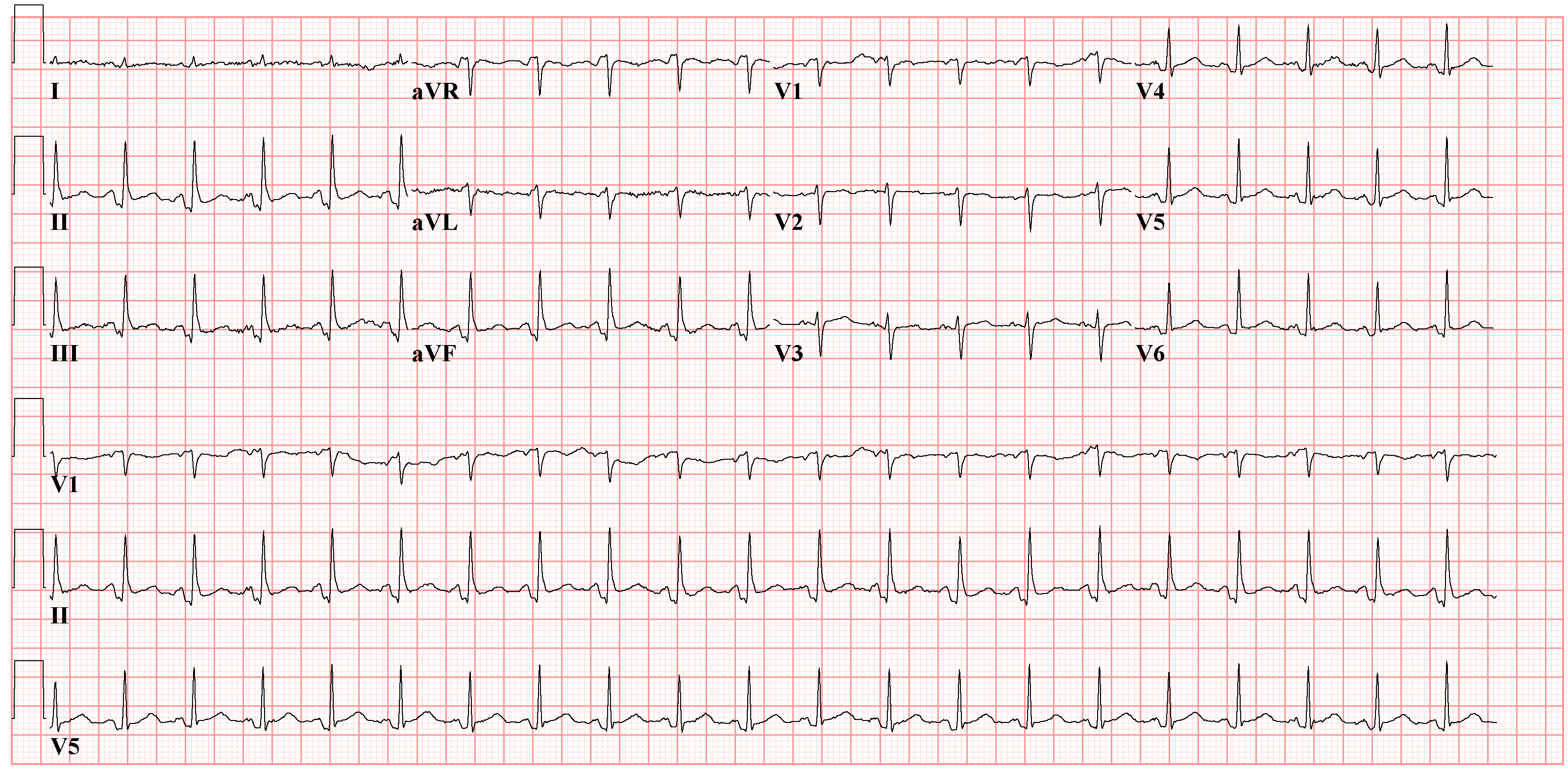
Copyleft image obtained courtesy of ECGpedia, http://en.ecgpedia.org/wiki/Main_Page
Shown below is an EKG demonstrating electrical alternans depicting pericarditis with effusion.
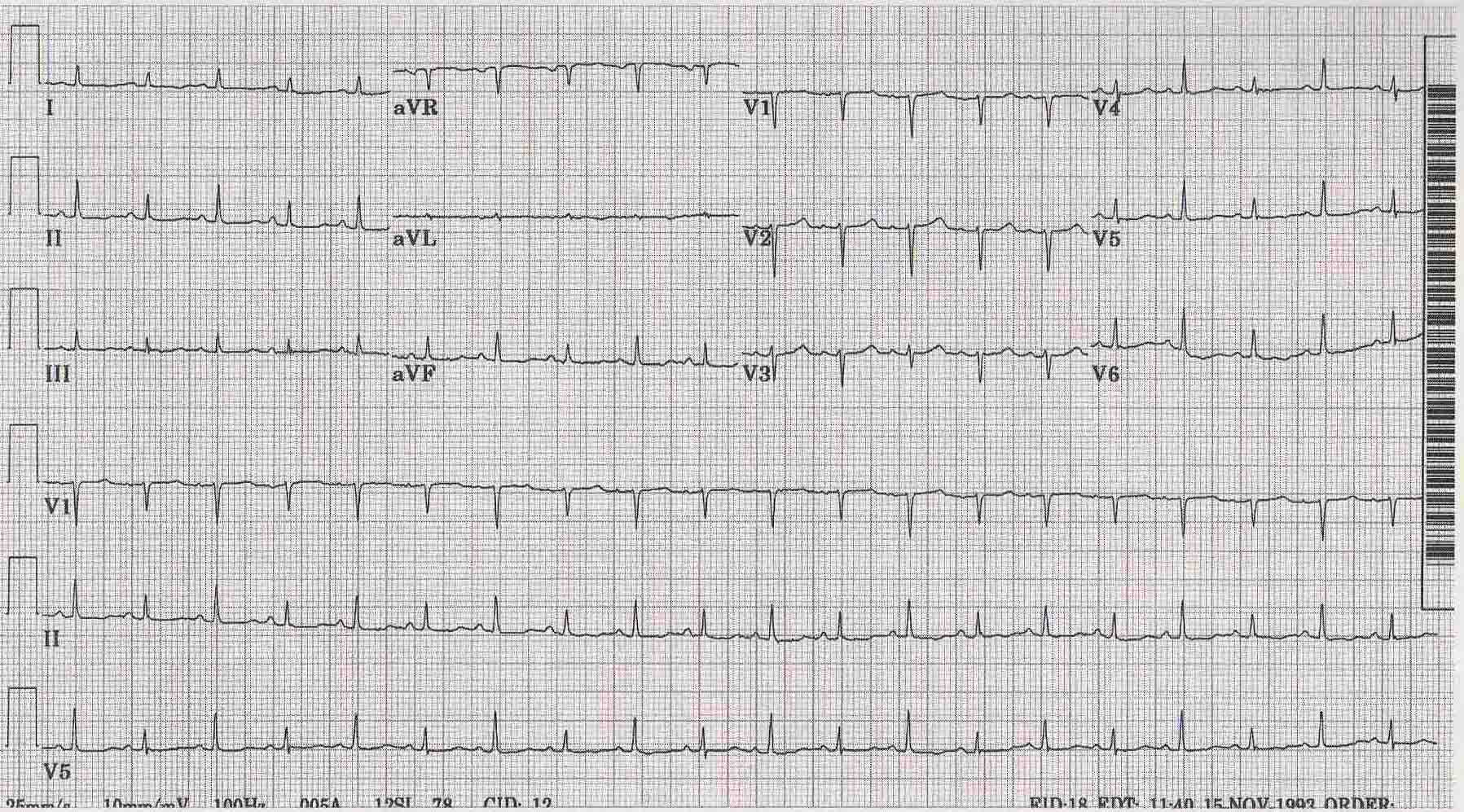
Copyleft image obtained courtesy of ECGpedia,http://en.ecgpedia.org/wiki/Main_Page
2015 ESC Guidelines on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pericarditis (DO NOT EDIT)[3]
Recommendations for the general diagnostic work-up of pericardial diseases
| Class I |
| 1. In all cases of suspected pericardial disease a first diagnostic evaluation is recommended with:
– ECG – transthoracic echocardiography – routine blood tests, including markers of inflammation (i.e., CRP and/or ESR), white blood cell count with differential count, renal function and liver tests and myocardial lesion tests (CK, troponins). 2. CT and/or CMR are recommended as second-level testing for diagnostic workup in pericarditis. 3. Pericardiocentesis or surgical drainage are indicated for cardiac tamponade or suspected bacterial and neoplastic pericarditis. 4. Further testing is indicated in high-risk patients (defined as above) according to the clinical conditions. (Level of Evidence: C)
|
Recommendations for diagnosis of acute pericarditis
| Class I |
| 1. ECG is recommended in all patients with suspected acute pericarditis.
2. Transthoracic echocardiography is recommended in all patients with suspected acute pericarditis. 3. Chest X-ray is recommended in all patients with suspected acute pericarditis. 4. Assessment of markers of inflammation (i.e. CRP) and myocardial injury (i.e. CK, troponin) is recommended in patients with suspected acute pericarditis. (Level of Evidence: C)
|
References
- ↑ Troughton RW, Asher CR, Klein AL (2004). "Pericarditis". Lancet. 363 (9410): 717–27. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(04)15648-1. PMID 15001332.
- ↑ Spodick DH (2003). "Acute pericarditis: current concepts and practice". JAMA. 289 (9): 1150–3. doi:10.1001/jama.289.9.1150. PMID 12622586.
- ↑ Adler, Yehuda; Charron, Philippe; Imazio, Massimo; Badano, Luigi; Barón-Esquivias, Gonzalo; Bogaert, Jan; Brucato, Antonio; Gueret, Pascal; Klingel, Karin; Lionis, Christos; Maisch, Bernhard; Mayosi, Bongani; Pavie, Alain; Ristić, Arsen D.; Sabaté Tenas, Manel; Seferovic, Petar; Swedberg, Karl; Tomkowski, Witold (2015). "2015 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of pericardial diseases". European Heart Journal. 36 (42): 2921–2964. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehv318. ISSN 0195-668X.