Stomatitis differential diagnosis: Difference between revisions
Usama Talib (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Usama Talib (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 85: | Line 85: | ||
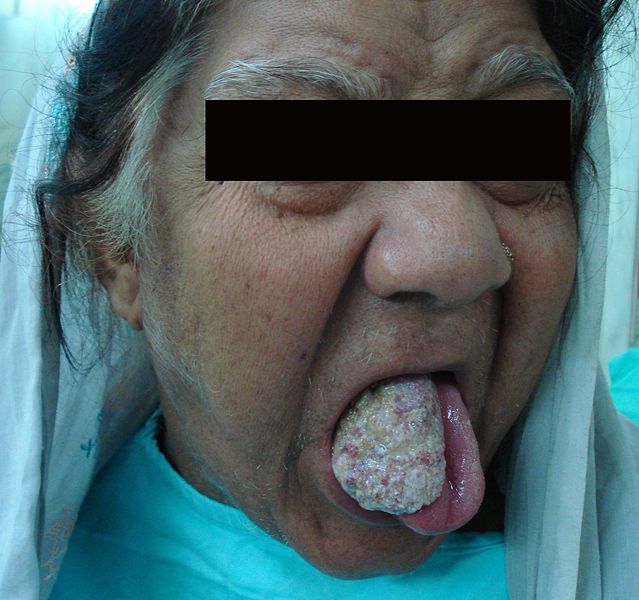
|[[Squamous cell carcinoma]] | |[[Squamous cell carcinoma]] | ||
| | | | ||
*Non healing ulcer, nodule, indurated plaque or mass | *Non healing [[ulcer]], [[nodule]], indurated plaque or mass | ||
*May involve skin, lips, inside the mouth, throat or esophagus | *May involve [[skin]], [[lips]], inside the [[mouth]], [[throat]] or [[esophagus]] | ||
| | | | ||
* Chronic sun or UV exposure | * Chronic sun or [[UV exposure]] | ||
* Fair skin | * Fair [[skin]] | ||
* Elderly age (>45 yrs) | * [[Elderly]] age (>45 yrs) | ||
* Male sex | * [[Male sex]] | ||
* Smoking | * [[Smoking]] | ||
| | | | ||
*Physical exam | *[[Physical exam]] | ||
*Biopsy | *[[Biopsy]] | ||
| | | | ||
*Oral Cavity | *[[Oral Cavity]] | ||
**Floor of mouth | **Floor of [[mouth]] | ||
**Lateral tongue | **Lateral [[tongue]] | ||
*Throat | *[[Throat]] | ||
*Esophagus | *[[Esophagus]] | ||
| | | | ||
*Malignant | *[[Malignant]] | ||
*Can spread to [[TMJ]] | *Can spread to [[TMJ]] | ||
*Some times associated with [[leukoplakia]] | *Some times associated with [[leukoplakia]] | ||
| Line 110: | Line 110: | ||
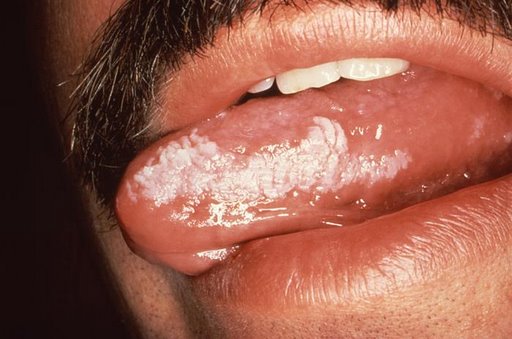
|[[Leukoplakia]] | |[[Leukoplakia]] | ||
| | | | ||
*White leathery spots on the mucous membranes of the tongue and inside of the mouth | *White leathery spots on the mucous membranes of the [[tongue]] and inside of the [[mouth]] | ||
*Lateral borders of tongue | *Lateral borders of [[tongue]] | ||
| | | | ||
*Atypical [[Tobacco]] use | *Atypical [[Tobacco]] use | ||
*Chronic irritation | *Chronic [[irritation]] | ||
*Immunodeficiency | *[[Immunodeficiency]] | ||
*Bloodroot (sanguinaria) | *[[Bloodroot]] (sanguinaria) | ||
| | | | ||
*Physical exam | *[[Physical exam]] | ||
*Diagnosis of exclusion | *Diagnosis of exclusion | ||
*Biopsy | *[[Biopsy]] | ||
| | | | ||
*Vulvar lesions occur independent of oral lesions | *Vulvar lesions occur independent of oral lesions | ||
| Line 126: | Line 126: | ||
*Associated with [[HIV]] | *Associated with [[HIV]] | ||
*Persistant white spots | *Persistant white spots | ||
*Benign but can progress to carcinoma after almost 10 years | *[[Benign]] but can progress to [[carcinoma]] after almost 10 years | ||
*Oral proliferative verrucous leukoplakia is an aggressive sub type with multiple lesions and higher conversion to warts or carcinoma<ref>{{Cite journal | *Oral proliferative [[verrucous leukoplakia]] is an aggressive sub type with multiple lesions and higher conversion to [[warts]] or [[carcinoma]]<ref>{{Cite journal | ||
| author = [[Ann M. Gillenwater]], [[Nadarajah Vigneswaran]], [[Hanadi Fatani]], [[Pierre Saintigny]] & [[Adel K. El-Naggar]] | | author = [[Ann M. Gillenwater]], [[Nadarajah Vigneswaran]], [[Hanadi Fatani]], [[Pierre Saintigny]] & [[Adel K. El-Naggar]] | ||
| title = Proliferative verrucous leukoplakia (PVL): a review of an elusive pathologic entity! | | title = Proliferative verrucous leukoplakia (PVL): a review of an elusive pathologic entity! | ||
| Line 143: | Line 143: | ||
|[[Melanoma]] | |[[Melanoma]] | ||
| | | | ||
*A lesion with ABCD | *A lesion with [[ABCD]] | ||
**Asymmetry | **[[Asymmetry]] | ||
**Border irregularity | **Border irregularity | ||
**Color variation | **Color variation | ||
** | **[[Diamete]]r changes | ||
*Bleeding from the lesion | *[[Bleeding]] from the lesion | ||
| | | | ||
*UV radiations | *[[UV radiations]] | ||
*[[Genetic predisposition]] | *[[Genetic predisposition]] | ||
*Old age | *[[Old age]] | ||
*Male gender | *[[Male gender]] | ||
*Family or personal history of [[melanoma]] | *Family or personal history of [[melanoma]] | ||
*Multiple benign or atypical [[Nevus|nevi]] | *Multiple benign or atypical [[Nevus|nevi]] | ||
| | | | ||
*ABCD characteristics | *[[ABCD]] characteristics | ||
*[[Bleeding]] or [[ulceration]] may show [[malignancy]] | *[[Bleeding]] or [[ulceration]] may show [[malignancy]] | ||
*Serum [[LDH]] may be elevated in case of [[malignancy]] | *Serum [[LDH]] may be elevated in case of [[malignancy]] | ||
*Biopsy | *[[Biopsy]] | ||
| | | | ||
*Can metastasize | *Can [[metastasize]] | ||
*All UV radiation or sun exposed areas can be effected independently | *All [[UV radiation]] or sun exposed areas can be effected independently | ||
*1-2 to hundreds of granules | *1-2 to hundreds of [[granules]] | ||
| | | | ||
*Neural crest cell derivative | *[[Neural crest cell derivative]] | ||
* | *Development begins with disruption of nevus growth control | ||
*Progression involves [[MAPK/ERK pathway]] | *Progression involves [[MAPK/ERK pathway]] | ||
*[[N-RAS]] or [[BRAF]] oncogene also involved | *[[N-RAS]] or [[BRAF]] oncogene also involved | ||
| Line 174: | Line 174: | ||
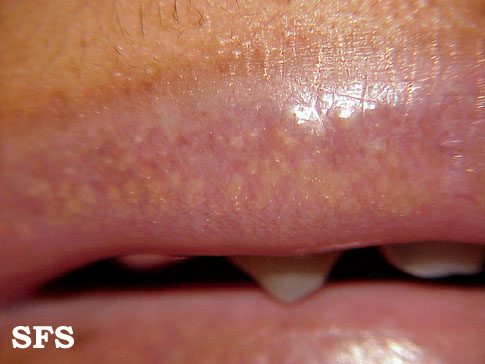
|[[Fordyce spots]] | |[[Fordyce spots]] | ||
| | | | ||
*Rice-like granules or spots | *Rice-like [[granules]] or [[spots]] | ||
*Small, painless, raised, pale, red or white | *Small, [[painless]], [[raised]], [[pale]], red or white | ||
*1 to 3 mm in diameter | *1 to 3 mm in [[diameter]] | ||
| | | | ||
*Greasy skin types | *Greasy skin types | ||
*Some [[rheumatic disorders]] | *Some [[rheumatic disorders]] | ||
*[[Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer]] | *[[Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer]] | ||
**Lower gingiva (gums) | **Lower [[gingiva]] (gums) | ||
**Vestibular mucosa | **[[Vestibular mucosa]] | ||
| | | | ||
*Physical exam | *[[Physical exam]] | ||
*Small keratin-filled pseudocysts | *Small [[keratin]]-filled [[pseudocysts]] | ||
*May be seen on incidental mucosal biopsy | *May be seen on [[incidental]] mucosal [[biopsy]] | ||
**Biopsy not done for them primarily | **[[Biopsy]] not done for them primarily | ||
| | | | ||
*Oral cavity | *[[Oral cavity]] | ||
**Vermilion border of the lips | **Vermilion border of the lips | ||
** Oral mucosa of the upper lip | **[[Oral mucosa]] of the upper lip | ||
*Buccal mucosa in the commissural region often bilaterally | *[[Buccal mucosa]] in the commissural region often bilaterally | ||
*Genitals | *[[Genitals]] | ||
| | | | ||
*Benign neoplasms with sebaceous features | *[[Benign neoplasms]] with [[sebaceous]] features | ||
*Visible sebaceous glands | *Visible [[sebaceous glands]] | ||
*No surrounding mucosal change | *No surrounding mucosal change | ||
*Several adjacent glands may coalesce into a larger cauliflower-like cluster | *Several adjacent [[glands]] may coalesce into a larger cauliflower-like cluster | ||
|[[File:Fordyce spots 02.jpeg|Fordyce spots|400x400px]] | |[[File:Fordyce spots 02.jpeg|Fordyce spots|400x400px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 205: | Line 205: | ||
*[[Burning]] or [[tingling]] on the [[lips]], [[tongue]], or entire [[mouth]] | *[[Burning]] or [[tingling]] on the [[lips]], [[tongue]], or entire [[mouth]] | ||
| | | | ||
*Nutritional deficiencies | *[[Nutritional deficiencies]] | ||
*Chronic [[anxiety]] or [[depression] | *Chronic [[anxiety]] or [[depression] | ||
* | *[[Diabetes type 2]] | ||
*Menopause | *[[Menopause]] | ||
*Oral thrush or dry mouth, or damaged taste | *[[Oral thrush]] or [[dry mouth]], or damaged [[nerves]] transmitting taste | ||
*Female gender | *[[Female gender ]] | ||
*Menopause | *[[Menopause]] | ||
| | | | ||
*Presentation | *[[Presentation]] | ||
*Physical exam | *[[Physical exam]] | ||
| | | | ||
*Oral cavity | *[[Oral cavity]] | ||
| | | | ||
*Pain typically is low in the morning and builds up over the day | *Pain typically is low in the morning and builds up over the day | ||
| Line 224: | Line 224: | ||
|[[Torus palatinus]] | |[[Torus palatinus]] | ||
| | | | ||
*Bony growth on midline of the hard palate | *Bony growth on midline of the [[hard palate]] | ||
*Nodular mass covered with normal mucosa | *[[Nodular]] mass covered with normal [[mucosa]] | ||
| | | | ||
*Genetic predisposition | *[[Genetic predisposition]] | ||
**Autosomal | **[[Autosomal dominant]] | ||
| | | | ||
*Physical exam | *[[Physical exam]] | ||
*Types | *Types | ||
**Flat tori | **Flat tori | ||
| Line 237: | Line 237: | ||
**Lobular tori | **Lobular tori | ||
| | | | ||
*Hard palate | *[[Hard palate]] | ||
| | | | ||
*More common in Asian and Inuit populations | *More common in [[Asian]] and Inuit populations | ||
*Twice more common in females | *Twice more common in [[females]] | ||
*Repeated trauma can cause bleeding | *Repeated [[trauma]] can cause [[bleeding]] | ||
*Surgery may be required in symptomatic | *[[Surgery]] may be required in symptomatic | ||
|[[File:06-06-06palataltori.jpg|Torus palatinus|400x400px]] | |[[File:06-06-06palataltori.jpg|Torus palatinus|400x400px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 252: | Line 252: | ||
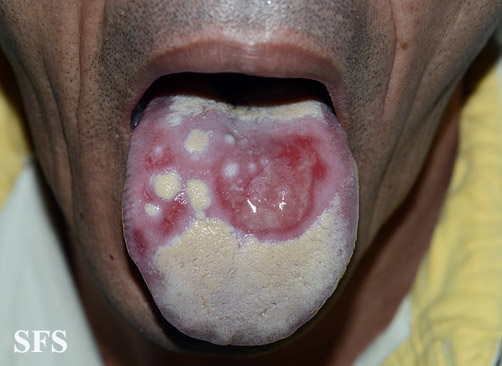
|[[Behçet's disease|Behcet's disease]] | |[[Behçet's disease|Behcet's disease]] | ||
| | | | ||
*Painful mouth sores | *Painful [[mouth sores]] | ||
*Acne like skin lesions | *[[Acne]] like skin lesions | ||
*Headache, [[fever]], poor balance, disorientation | *Headache, [[fever]], poor [[balance]], [[disorientation]] | ||
*Abdominal pain, diarrhea or bleeding | *[[Abdominal pain]], [[diarrhea]] or [[bleeding]] | ||
*Uveitis | *[[Uveitis]] | ||
*Joint swelling and joint pain | *Joint [[swelling]] and joint [[pain]] | ||
*Genital sores wit pain and scaring | *Genital [[sores]] wit [[pain]] and [[scaring]] | ||
*Aneurysms | *[[Aneurysms]] | ||
| | | | ||
*Over active immune system | *Over active [[immune system]] | ||
| | | | ||
*Physical examination | *[[Physical examination]] | ||
| | | | ||
*Mouth | *[[Mouth]] | ||
*Genitals | *[[Genitals]] | ||
*GIT | *[[GIT]] | ||
*Eye | *[[Eye]] | ||
*Joints | *[[Joints] | ||
*Skin | *[[Skin]] | ||
*Vascular system | *[[Vascular system]] | ||
*Brain | *[[Brain]] | ||
| | | | ||
*Outbreaks of exaggerated inflammation | *[[Outbreaks]] of exaggerated [[inflammation]] | ||
*Affects smaller blood vessels | *Affects smaller [[blood vessels]] | ||
|[[File:Behcet's syndrome 11.jpeg|Behcet's disease|400x400px]] | |[[File:Behcet's syndrome 11.jpeg|Behcet's disease|400x400px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[Crohn's disease]] | |[[Crohn's disease]] | ||
| | | | ||
*Chronic, episodic diarrhea or constipation | *Chronic, [[episodic diarrhea]] or [[constipation]] | ||
*Abdominal pain | *[[Abdominal pain]] | ||
*Vomiting | *[[Vomiting]] | ||
*Weight loss or weight gain | *[[Weight loss]] or [[weight gain]] | ||
| | | | ||
*Smoking | *[[Smoking]] | ||
*Whites and European Jews | *[[Whites]] and [[European]] [[Jews]] | ||
*Hormonal contraception | *[[Hormonal contraception]] | ||
*Diets high in microparticles, sweet, fatty or refined foods | *Diets high in microparticles, sweet, fatty or refined foods | ||
*Industrialized country | *Industrialized country | ||
| | | | ||
*Typical history and symptoms | *Typical [[history]] and [[symptoms]] | ||
*Skip lesions on biopsy | *[[Skip lesions]] on [[biopsy]] | ||
*Anti-[[Saccharomyces cerevisiae antibodies]] (ASCA) | *Anti-[[Saccharomyces cerevisiae antibodies]] ([[ASCA]]) | ||
*Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA) | *[[Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies]] ([[ANCA]]) | ||
| | | | ||
*Eyes | *[[Eyes]] | ||
*Joints | *[[Joints]] | ||
*Skin | *[[Skin]] | ||
| | | | ||
*May lead to | *May lead to | ||
** | **[[Obstruction]]s | ||
** | **[[Abscess]]es | ||
**Free perforation | **Free [[perforation]] | ||
**Hemorrhage | **[[Hemorrhage]] | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 319: | Line 319: | ||
*[[Medications]]<ref name="PMID17142169">{{cite journal |author=Andrès E, Zimmer J, Affenberger S, Federici L, Alt M, Maloisel F. |title=Idiosyncratic drug-induced agranulocytosis: Update of an old disorder. |journal=Eur J Intern Med. |volume=17|issue=8 |pages=529-35 |year=2006|pmid 17142169|doi=|url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17142169}}</ref> | *[[Medications]]<ref name="PMID17142169">{{cite journal |author=Andrès E, Zimmer J, Affenberger S, Federici L, Alt M, Maloisel F. |title=Idiosyncratic drug-induced agranulocytosis: Update of an old disorder. |journal=Eur J Intern Med. |volume=17|issue=8 |pages=529-35 |year=2006|pmid 17142169|doi=|url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17142169}}</ref> | ||
*[[List of chemotherapeutic agents#Cytotoxic Chemotherapy|Cytotoxic chemotherapy]] | *[[List of chemotherapeutic agents#Cytotoxic Chemotherapy|Cytotoxic chemotherapy]] | ||
*Hematologic malignancies | *[[Hematologic malignancies]] | ||
*[[Autoimmune disorders]] | *[[Autoimmune disorders]] | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 326: | Line 326: | ||
*[[Basopenia]] | *[[Basopenia]] | ||
| | | | ||
*Oral cavity | *[[Oral cavity]] | ||
*Skin | *[[Skin]] | ||
*GIT | *[[GIT]] | ||
*Urinary system | *[[Urinary system]] | ||
*Conjunctiva | *[[Conjunctiva]] | ||
| | | | ||
*[[Immunocompromization]] | *[[Immunocompromization]] | ||
*Types | *Types | ||
**Drug-induced | **[[Drug-induced]] | ||
**Malignant | **[[Malignant]] | ||
**Autoimmune | **[[Autoimmune]] | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[Syphilis]]<ref> title="By Internet Archive Book Images [No restrictions], via Wikimedia Commons" href="https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3AA_manual_of_syphilis_and_the_venereal_diseases%2C_(1900)_(14595882378).jpg"</ref> | |[[Syphilis]]<ref> title="By Internet Archive Book Images [No restrictions], via Wikimedia Commons" href="https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3AA_manual_of_syphilis_and_the_venereal_diseases%2C_(1900)_(14595882378).jpg"</ref> | ||
| | | | ||
*Chancre | *[[Chancre]] | ||
*Regional lymphadenopathy | *Regional [[lymphadenopathy]] | ||
| | | | ||
*Multiple sexual partners | *[[Multiple sexual partners]] | ||
*Illicit drug use | *Illicit [[drug use]] | ||
*Unprotected sex | *[[Unprotected sex]] | ||
*Men who have sex with men | *[[Men who have sex with men]] | ||
*Residence in highly prevalent areas | *Residence in highly prevalent areas | ||
*[[Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)|HIV]] infection | *[[Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)|HIV]] infection | ||
*Presence of other [[STI]]s | *Presence of other [[STI]]s | ||
*Previous history of STIs | *Previous history of STIs | ||
*Intravenous drug use | *[[Intravenous drug use]] | ||
| | | | ||
*Darkfield microscopy | *[[Darkfield microscopy]] | ||
*Nontreponemal tests like [[VDRL]] and [[RPR test]]) | *[[Nontreponemal tests]] like [[VDRL]] and [[RPR test]]) | ||
*Treponemal tests [[FTA-ABS tests]], (TP-PA) assay, [[Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)|enzyme immunoassays]], and [[Chemiluminescence|chemiluminescence immunoassays]]) | *[[Treponemal tests[[ [[FTA-ABS tests]], (TP-PA) assay, [[Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)|enzyme immunoassays]], and [[Chemiluminescence|chemiluminescence immunoassays]]) | ||
| | | | ||
*Penis | *[[Oral cavity]] | ||
*Cervix | *[[Penis]] | ||
*Labia | *[[Cervix]] | ||
*Anal canal | *[[Labia]] | ||
*Rectum | *[[Anal canal]] | ||
* | *[[Rectum ]] | ||
*[[CNS]] | |||
*CVS | *[[CVS]] | ||
| | | | ||
*Primary syphilis | *[[Primary syphilis]] | ||
**Chancre | **[[Chancre]] | ||
*Secondary syphilis | *[[Secondary syphilis]] | ||
**Condylomata lata | **[[Condylomata lata]] | ||
*Latent syphilis | *[[Latent syphilis]] | ||
**Asymptomatic | **[[Asymptomatic]] | ||
*Tertiary syphilis | *[[Tertiary syphilis]] | ||
**Gummas | **[[Gummas]] | ||
**Neurosyphilis | **[[Neurosyphilis]] | ||
|[[File:Syphilis oral.jpg|oral syphilis|400x400px]] | |[[File:Syphilis oral.jpg|oral syphilis|400x400px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 381: | Line 381: | ||
| | | | ||
*[[Fever]] | *[[Fever]] | ||
*Sores in the mouth | *[[Sores]] in the [[mouth]] | ||
*Rash with blisters | *[[Rash]] with [[blisters]] | ||
*Aches | *[[Aches]] | ||
| | | | ||
*[[Pregnancy]] | *[[Pregnancy]] | ||
*[[immunodeficiency]] | *[[immunodeficiency]] | ||
| | | | ||
*History and Physical exam | *[[History]] and [[Physical exam]] | ||
*Throat swabs | *[[Throat swabs]] | ||
*Swabs from the lesion | *Swabs from the lesion | ||
*Tzanck test | *[[Tzanck test]] | ||
| | | | ||
*Oral cavity | *[[Oral cavity]] | ||
*Skin | *[[Skin]] | ||
| | | | ||
*Symptomatic treatment | *Symptomatic treatment | ||
| Line 401: | Line 401: | ||
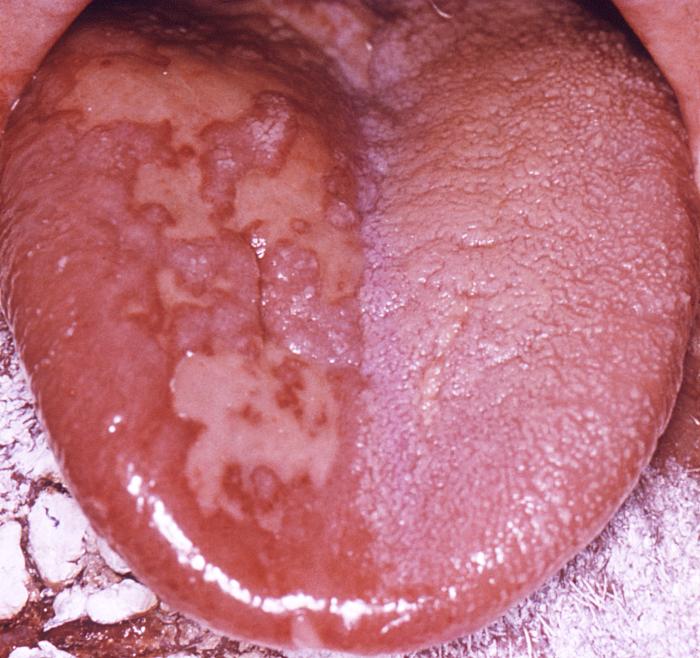
|[[Chickenpox|Chicken pox]] | |[[Chickenpox|Chicken pox]] | ||
| | | | ||
*Conjunctival symptoms | *[[Conjunctival symptoms]] | ||
*Catarrhal symptoms | *[[Catarrhal symptoms]] | ||
*Characteristic spots on the trunk appearing in two or three waves | *Characteristic [[spots]] on the trunk appearing in two or three waves | ||
*Itching | *[[Itching]] | ||
| | | | ||
*Pregnancy | *[[Pregnancy]] | ||
*Premature infants born to susceptible mothers | *[[Premature infants]] born to susceptible mothers | ||
*All infants born at less than 28 weeks gestation or who weigh ≤1000 grams | *All [[infants]] born at less than 28 weeks [[gestation]] or who weigh ≤1000 grams | ||
*Immunocompromised | *[[Immunocompromised]] | ||
| | | | ||
*History and physical exam | *[[History]] and [[physical exam]] | ||
*PCR to detect VZV in skin lesions (vesicles, scabs, maculopapular lesions) | *[[PCR]] to detect [[VZV]] in [[skin lesions]] ([[vesicles]], [[scabs]], [[maculopapular lesions]]) | ||
| | | | ||
*Oral cavity | *[[Oral cavity]] | ||
*Skin | *[[Skin]] | ||
| | | | ||
*Sodium bicarbonate in baths or antihistamines for itching | *[[Sodium bicarbonate]] in baths or [[antihistamines]] for [[itching]] | ||
*Paracetamol (acetaminophen) for fever | *[[Paracetamol]] ([[acetaminophen]]) for [[fever]] | ||
*[[Prednisolone]] is contraindicated | *[[Prednisolone]] is [[contraindicated]] | ||
|[[File:Chickenpox18.jpeg|Chickenpox|400x400px]] | |[[File:Chickenpox18.jpeg|Chickenpox|400x400px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
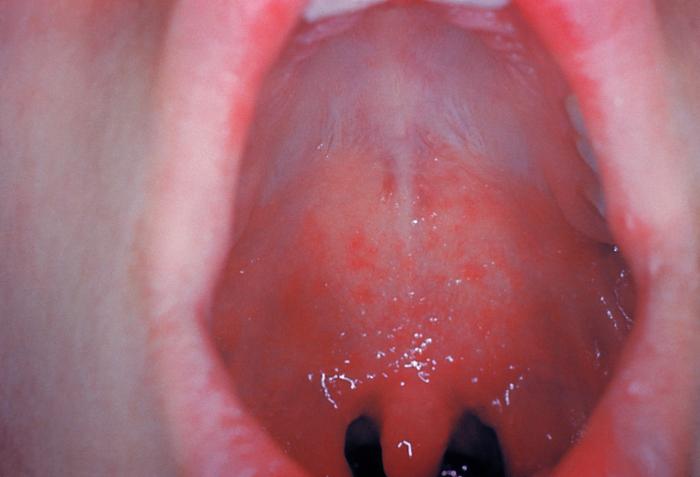
| Line 430: | Line 430: | ||
*[[Conjunctivitis]] (pink eye) | *[[Conjunctivitis]] (pink eye) | ||
*[[Malaise]] | *[[Malaise]] | ||
*Koplick spots in mouth | *[[Koplick spots]] in mouth | ||
| | | | ||
*Unvaccinated individuals<ref name="pmid11135778">{{cite journal| author=Feikin DR, Lezotte DC, Hamman RF, Salmon DA, Chen RT, Hoffman RE| title=Individual and community risks of measles and pertussis associated with personal exemptions to immunization. | journal=JAMA | year= 2000 | volume= 284 | issue= 24 | pages= 3145-50 | pmid=11135778 | doi= | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=11135778 }} </ref><ref name="pmid9009400">{{cite journal| author=Ratnam S, West R, Gadag V, Williams B, Oates E| title=Immunity against measles in school-aged children: implications for measles revaccination strategies. | journal=Can J Public Health | year= 1996 | volume= 87 | issue= 6 | pages= 407-10 | pmid=9009400 | doi= | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=9009400 }} </ref> | *[[Unvaccinated]] individuals<ref name="pmid11135778">{{cite journal| author=Feikin DR, Lezotte DC, Hamman RF, Salmon DA, Chen RT, Hoffman RE| title=Individual and community risks of measles and pertussis associated with personal exemptions to immunization. | journal=JAMA | year= 2000 | volume= 284 | issue= 24 | pages= 3145-50 | pmid=11135778 | doi= | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=11135778 }} </ref><ref name="pmid9009400">{{cite journal| author=Ratnam S, West R, Gadag V, Williams B, Oates E| title=Immunity against measles in school-aged children: implications for measles revaccination strategies. | journal=Can J Public Health | year= 1996 | volume= 87 | issue= 6 | pages= 407-10 | pmid=9009400 | doi= | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=9009400 }} </ref> | ||
*Crowded and/or unsanitary conditions | *Crowded and/or [[unsanitary]] conditions | ||
*Traveling to less developed and developing countries | *Traveling to less developed and [[developing countries]] | ||
*Immunocompromized | *[[Immunocompromized]] | ||
*Winter and spring seasons | *[[Winter]] and [[spring]] seasons | ||
*Born after 1956 and never fully vaccinated | *Born after 1956 and never fully vaccinated | ||
*Health care workers | *Health care workers | ||
| | | | ||
*History and examination | *[[History]] and [[examination]] | ||
*PCR for Measles-specific IgM antibody | *[[PCR]] for [[Measles]]-specific [[IgM antibody]] | ||
*PCR for Measles RNA | *[[PCR]] for [[Measles]] [[RNA]] | ||
| | | | ||
*Oral cavity | *[[Oral cavity]] | ||
*Skin | *[[Skin]] | ||
*Respiratory tract | *[[Respiratory tract]] | ||
*Eyes | *[[Eyes]] | ||
*Throat | *[[Throat]] | ||
| | | | ||
*Caused by Morbillivirus | *Caused by [[Morbillivirus]] | ||
*Primary site of infection is the respiratory epithelium of the nasopharynx | *Primary site of infection is the [[respiratory epithelium]] of the [[nasopharynx]] | ||
*Transmitted in respiratory secretions, via aerosol droplets containing virus particles | *Transmitted in [[respiratory secretions]], via [[aerosol droplets]] containing [[virus particles]] | ||
|[[File:Koplikspot1.jpg|Koplick spots (Measles)|400x400px]] | |[[File:Koplikspot1.jpg|Koplick spots (Measles)|400x400px]] | ||
|}</small> | |}</small> | ||
Revision as of 20:55, 17 March 2017
|
Stomatitis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Stomatitis differential diagnosis On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Stomatitis differential diagnosis |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Stomatitis differential diagnosis |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Sara Mehrsefat, M.D. [2], Usama Talib, BSc, MD [3]
Overview
Stomatitis should be differentiated from various subtypes of stomatitis and from many other disease that can involve the oral cavity such as agranulocystosis, Behcet's disease, immunodeficiency and tutors of the oral cavity like leukoplakia etc.[1][2]
Differential diagnosis
Stomatitis must be differentiated from its different kinds and from various other disease that can mimic stomatitis or have accompanying features involving other organs. Stomatitis should be differentiated from other disease as well as from possible underlying conditions causing stomatitis including:[1][2]
- Tumors of the tongue
- Autoimmune diseases[7]
- Agranulocytosis
- Fordyce's spots
- Drug induced
- Burning mouth syndrome
- Syphilis
- Coxsackie virus accompanies involvement of the hands and the mouth
- HIV
- VZV or Chicken pox
| Disease | Presentation | Risk Factors | Diagnosis | Affected Organ Systems | Important features | Picture |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diseases predominantly affecting the oral cavity | ||||||
| Squamous cell carcinoma |
|
|
| |||
| Leukoplakia |
|
|
|
| ||
| Melanoma |
|
|
|
|

| |
| Fordyce spots |
|
|
|
|
| |
| Burning mouth syndrome |
|
|
||||
| Torus palatinus |
|
|

| |||
| Diseases involving oral cavity and other organ systems | ||||||
| Behcet's disease |
|
|
|
| ||
| Crohn's disease |
|
|
|
|
||
| Agranulocytosis |
|
|
||||
| Syphilis[11] |
|
|
|

| ||
| Coxsackie virus |
|
|

| |||
| Chicken pox |
|
|
|
|
| |
| Measles |
|
|
|
|
| |
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Mandell; Gouglas, Gordon; Bennett, John. Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. Harvard Medical School: WILEY MEDICAL. p. 383. ISBN 0-471-87643-7. Unknown parameter
|firs1t=ignored (help) - ↑ 2.0 2.1 Scully C (1999). "A review of common mucocutaneous disorders affecting the mouth and lips". Ann Acad Med Singapore. 28 (5): 704–7. PMID 10597357.
- ↑ R. Morgan, J. Tsang, N. Harrington & L. Fook (2001). "Survey of hospital doctors' attitudes and knowledge of oral conditions in older patients". Postgraduate medical journal. 77 (908): 392–394. PMID 11375454. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ D. Grady, J. Greene, T. E. Daniels, V. L. Ernster, P. B. Robertson, W. Hauck, D. Greenspan, J. Greenspan & S. Jr Silverman (1990). "Oral mucosal lesions found in smokeless tobacco users". Journal of the American Dental Association (1939). 121 (1): 117–123. PMID 2370378. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ P. DeMatos, D. S. Tyler & H. F. Seigler (1998). "Malignant melanoma of the mucous membranes: a review of 119 cases". Annals of surgical oncology. 5 (8): 733–742. PMID 9869521. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Barry Ladizinski & Kachiu C. Lee (2014). "A nodular protuberance on the hard palate". JAMA. 311 (15): 1558–1559. doi:10.1001/jama.2014.271. PMID 24737369. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Magliocca KR, Fitzpatrick SG (2017) Autoimmune Disease Manifestations in the Oral Cavity. Surg Pathol Clin 10 (1):57-88. DOI:10.1016/j.path.2016.11.001 PMID: 28153136
- ↑ Dalghous AM, Freysdottir J, Fortune F (2006). "Expression of cytokines, chemokines, and chemokine receptors in oral ulcers of patients with Behcet's disease (BD) and recurrent aphthous stomatitis is Th1-associated, although Th2-association is also observed in patients with BD". Scand J Rheumatol. 35 (6): 472–5. PMID 17343257.
- ↑ Ann M. Gillenwater, Nadarajah Vigneswaran, Hanadi Fatani, Pierre Saintigny & Adel K. El-Naggar (2013). "Proliferative verrucous leukoplakia (PVL): a review of an elusive pathologic entity!". Advances in anatomic pathology. 20 (6): 416–423. doi:10.1097/PAP.0b013e3182a92df1. PMID 24113312. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Andrès E, Zimmer J, Affenberger S, Federici L, Alt M, Maloisel F. (2006). "Idiosyncratic drug-induced agranulocytosis: Update of an old disorder". Eur J Intern Med. 17 (8): 529–35. Text "pmid 17142169" ignored (help)
- ↑ title="By Internet Archive Book Images [No restrictions], via Wikimedia Commons" href="https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3AA_manual_of_syphilis_and_the_venereal_diseases%2C_(1900)_(14595882378).jpg"
- ↑ Feikin DR, Lezotte DC, Hamman RF, Salmon DA, Chen RT, Hoffman RE (2000). "Individual and community risks of measles and pertussis associated with personal exemptions to immunization". JAMA. 284 (24): 3145–50. PMID 11135778.
- ↑ Ratnam S, West R, Gadag V, Williams B, Oates E (1996). "Immunity against measles in school-aged children: implications for measles revaccination strategies". Can J Public Health. 87 (6): 407–10. PMID 9009400.