Tuberculosis differential diagnosis
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Mashal Awais, M.D.[2]; Alejandro Lemor, M.D. [3]
Overview
Pulmonary tuberculosis should be distinguished from other diseases that cause cough, hemoptysis, fever, night sweat, and weight loss such as: bacterial pneumonia, atypical pneumonia, brucellosis, bronchogenic carcinoma, sarcoidosis, and Hodgkin lymphoma.
Differential Diagnosis
Pulmonary Tuberculosis
| Disease | Findings |
|---|---|
| Bacterial pneumonia | Sudden onset of symptoms, such as high fever, cough, purulent sputum, chest pain, leukocytosis, chest X-ray shows consolidation. |
| Bronchogenic carcinoma | may be asymptomatic, usually at older ages (> 50 years old), cough, hemoptysis, weight loss |
| Brucellosis | Fever, anorexia, night sweats, malaise,back pain , headache, and depression. History of exposure to infected animal |
| Hodgkin lymphoma | Fever, night sweats, pruritus, painless adenopathy, mediastinal mass |
| Mycoplasmal pneumonia | Gradual onset of dry cough, headache, malaise, sore throat. Diffuse bilateral infiltrates on chest X-ray. |
| Sarcoidosis | Non-caseating granulomas in lungs and other organs, bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy, mostly in African American females. |
| Adapted from Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's principles and practice of infectious diseases 2010 [1] | |
Extra-Pulmonary Tuberculosis
| Extra-Pulmonary Location | Differential Diagnosis |
|---|---|
| Tuberculous Lymphadenitis | Lymphoma, squamous cell carcinoma, papillary thyroid cancer, pyogenic infection |
| Skeletal Tuberculosis | Multiple myeloma, bone metastasis, spinal cord abscess, osteoporosis |
| Tuberculous Arthrits | Bacterial septic arthritis, pseudogout |
| Central Nervous System Tuberculosis | Bacterial meningitis, viral meningitis, encephalitis |
| Tuberculosis Peritonitis | Bacterial peritonitis, chronic peritoneal dialysis |
| Adapted from Asian Spine J. Feb 2014; 8(1): 97–111[2]; Handbook of Clinical Neurology[3]; Circulation Dec 2005 vol.112 no.23 3608-3616[4]; Am J Trop Med Hyg 2013 vol. 88 no. 1 54-64[5] Clin Infect Dis.(2011)53(6):555-562.[6] | |
| Causes of
lung cavities |
Differentiating Features | Differentiating radiological findings | Diagnosis
confirmation |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
||
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| Disease | Prominent clinical features | Lab findings | Radiological findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neurocysticercosis |
|
|
|
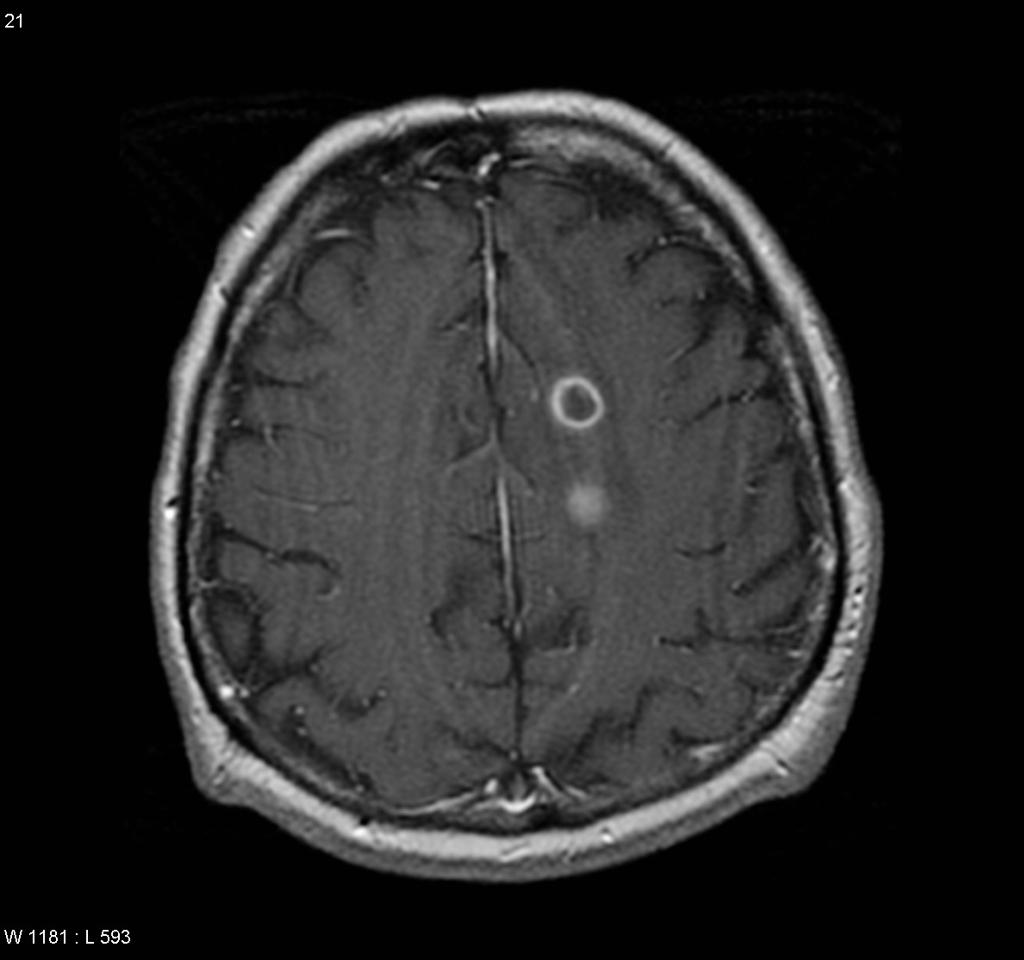
| Brain abscess |
|
|
|
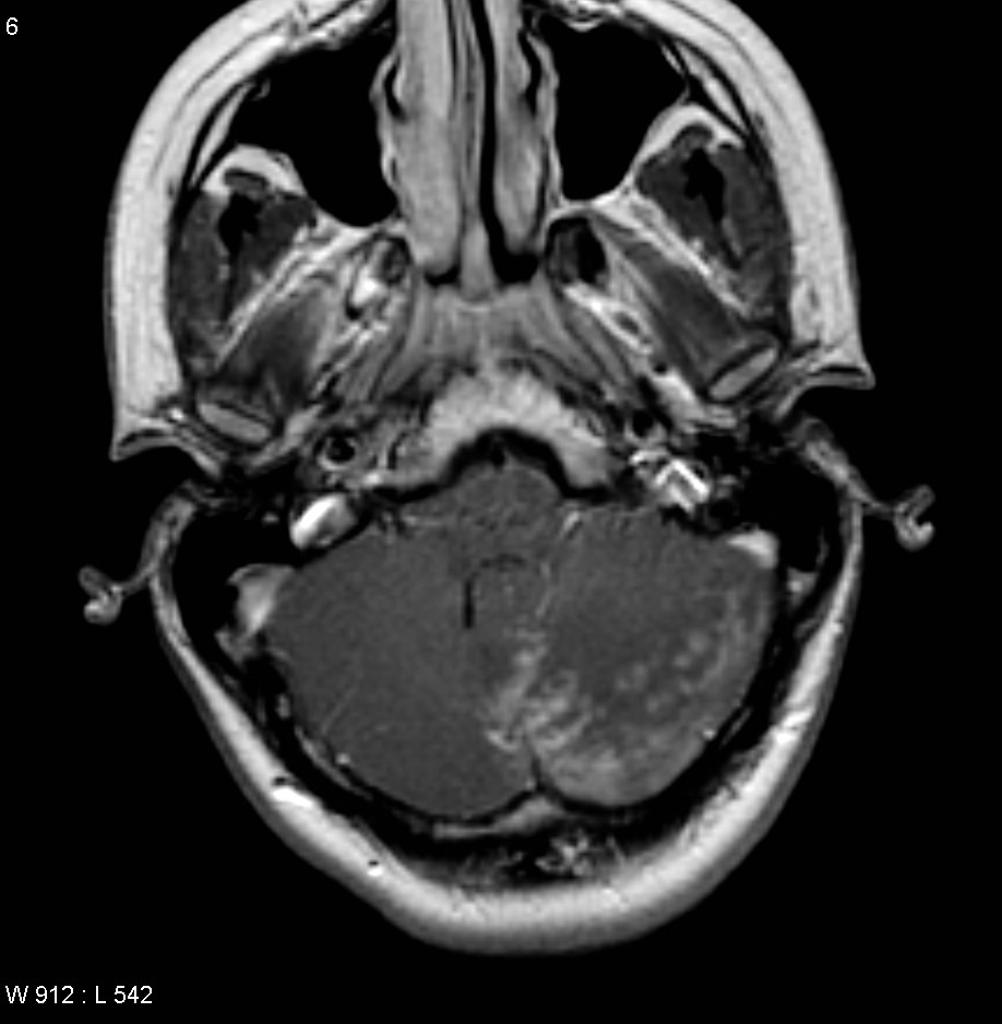
| Brain tumors |
|
| |
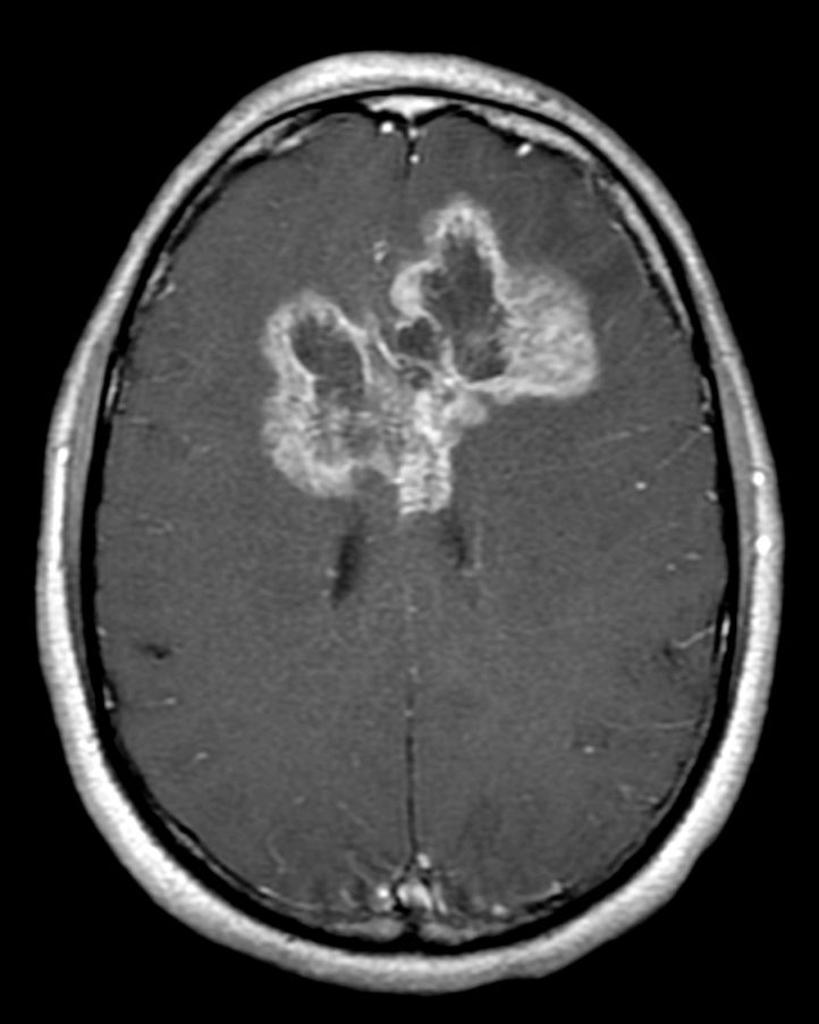
| Brain tuberculoma |
|
|
|
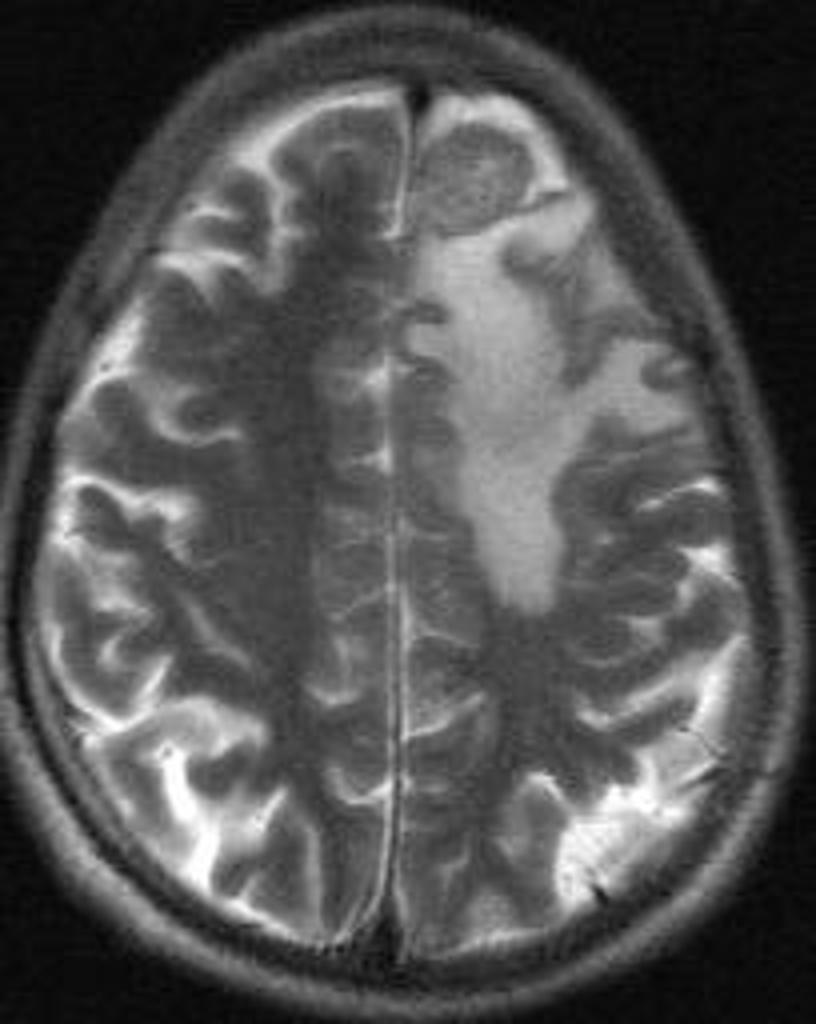
| Neurosarcoidosis |
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|---|
Pulmonary tuberculosis must be distinguished from other cavitary lung lesions.
Differential Diagnosis
Pulmonary tuberculosis must be distinguished from other cavitary lung lesions.
| Causes of
lung cavities |
Differentiating Features | Differentiating radiological findings | Diagnosis
confirmation |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
| |
|
|
||
|
|
| |
|
References
- ↑ Mandell, Gerald (2010). Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's principles and practice of infectious diseases. Philadelphia, PA: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier. ISBN 0443068399.
- ↑ Moon, Myung-Sang (2014). "Tuberculosis of Spine: Current Views in Diagnosis and Management". Asian Spine Journal. 8 (1): 97. doi:10.4184/asj.2014.8.1.97. ISSN 1976-1902.
- ↑ Garcia-Monco, Juan Carlos (2014). "Tuberculosis". 121: 1485–1499. doi:10.1016/B978-0-7020-4088-7.00100-0. ISSN 0072-9752.
- ↑ Mayosi, B. M. (2005). "Tuberculous Pericarditis". Circulation. 112 (23): 3608–3616. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.543066. ISSN 0009-7322.
- ↑ Daher, E. D. F.; da Silva Junior, G. B.; Barros, E. J. G. (2013). "Renal Tuberculosis in the Modern Era". American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene. 88 (1): 54–64. doi:10.4269/ajtmh.2013.12-0413. ISSN 0002-9637.
- ↑ Fontanilla, J.-M.; Barnes, A.; von Reyn, C. F. (2011). "Current Diagnosis and Management of Peripheral Tuberculous Lymphadenitis". Clinical Infectious Diseases. 53 (6): 555–562. doi:10.1093/cid/cir454. ISSN 1058-4838.
- ↑ Jump up to: 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 Chaudhuri MR (1973). "Primary pulmonary cavitating carcinomas". Thorax. 28 (3): 354–66. PMC 470041. PMID 4353362.
- ↑ Jump up to: 8.0 8.1 Mouroux J, Padovani B, Elkaïm D, Richelme H (1996). "Should cavitated bronchopulmonary cancers be considered a separate entity?". Ann. Thorac. Surg. 61 (2): 530–2. doi:10.1016/0003-4975(95)00973-6. PMID 8572761.
- ↑ Jump up to: 9.0 9.1 Onn A, Choe DH, Herbst RS, Correa AM, Munden RF, Truong MT, Vaporciyan AA, Isobe T, Gilcrease MZ, Marom EM (2005). "Tumor cavitation in stage I non-small cell lung cancer: epidermal growth factor receptor expression and prediction of poor outcome". Radiology. 237 (1): 342–7. doi:10.1148/radiol.2371041650. PMID 16183941.
- ↑ Jump up to: 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 Langford CA, Hoffman GS (1999). "Rare diseases.3: Wegener's granulomatosis". Thorax. 54 (7): 629–37. PMC 1745525. PMID 10377211.
- ↑ Jump up to: 11.0 11.1 Lee KS, Kim TS, Fujimoto K, Moriya H, Watanabe H, Tateishi U, Ashizawa K, Johkoh T, Kim EA, Kwon OJ (2003). "Thoracic manifestation of Wegener's granulomatosis: CT findings in 30 patients". Eur Radiol. 13 (1): 43–51. doi:10.1007/s00330-002-1422-2. PMID 12541109.
- ↑ Jump up to: 12.0 12.1 Baughman RP, Teirstein AS, Judson MA, Rossman MD, Yeager H, Bresnitz EA, DePalo L, Hunninghake G, Iannuzzi MC, Johns CJ, McLennan G, Moller DR, Newman LS, Rabin DL, Rose C, Rybicki B, Weinberger SE, Terrin ML, Knatterud GL, Cherniak R (2001). "Clinical characteristics of patients in a case control study of sarcoidosis". Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 164 (10 Pt 1): 1885–9. doi:10.1164/ajrccm.164.10.2104046. PMID 11734441.
- ↑ Jump up to: 13.0 13.1 Brauner MW, Grenier P, Mompoint D, Lenoir S, de Crémoux H (1989). "Pulmonary sarcoidosis: evaluation with high-resolution CT". Radiology. 172 (2): 467–71. doi:10.1148/radiology.172.2.2748828. PMID 2748828.
- ↑ Jump up to: 14.0 14.1 Murphy J, Schnyder P, Herold C, Flower C (1998). "Bronchiolitis obliterans organising pneumonia simulating bronchial carcinoma". Eur Radiol. 8 (7): 1165–9. doi:10.1007/s003300050527. PMID 9724431.
- ↑ Jump up to: 15.0 15.1 15.2 15.3 Al-Ghanem S, Al-Jahdali H, Bamefleh H, Khan AN (2008). "Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia: pathogenesis, clinical features, imaging and therapy review". Ann Thorac Med. 3 (2): 67–75. doi:10.4103/1817-1737.39641. PMC 2700454. PMID 19561910.
- ↑ Jump up to: 16.0 16.1 Cordier JF, Loire R, Brune J (1989). "Idiopathic bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia. Definition of characteristic clinical profiles in a series of 16 patients". Chest. 96 (5): 999–1004. PMID 2805873.
- ↑ Jump up to: 17.0 17.1 Lee KS, Kullnig P, Hartman TE, Müller NL (1994). "Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia: CT findings in 43 patients". AJR Am J Roentgenol. 162 (3): 543–6. doi:10.2214/ajr.162.3.8109493. PMID 8109493.
- ↑ Jump up to: 18.0 18.1 Suri HS, Yi ES, Nowakowski GS, Vassallo R (2012). "Pulmonary langerhans cell histiocytosis". Orphanet J Rare Dis. 7: 16. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-7-16. PMC 3342091. PMID 22429393.
- ↑ Jump up to: 19.0 19.1 Moore AD, Godwin JD, Müller NL, Naidich DP, Hammar SP, Buschman DL, Takasugi JE, de Carvalho CR (1989). "Pulmonary histiocytosis X: comparison of radiographic and CT findings". Radiology. 172 (1): 249–54. doi:10.1148/radiology.172.1.2787035. PMID 2787035.
- ↑ Brouwer MC, Tunkel AR, McKhann GM, van de Beek D (2014). "Brain abscess". N. Engl. J. Med. 371 (5): 447–56. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1301635. PMID 25075836.
- ↑ "Brain Abscess — NEJM".
- ↑ Jump up to: 22.0 22.1 "Primary Brain Tumors in Adults - American Family Physician".
- ↑ "The Journal of Association of Chest Physicians - Tuberculoma of the brain - A diagnostic dilemma: Magnetic resonance spectroscopy a new ray of hope : Download PDF".
- ↑ Jump up to: 24.0 24.1 "Neurosarcoidosis".