Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma diagnostic study of choice
|
Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma Microchapters |
|
Differentiating Lymphoplasmacytic Lymphoma from other Diseases |
|---|
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma diagnostic study of choice On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma diagnostic study of choice |
|
FDA on Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma diagnostic study of choice |
|
CDC on Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma diagnostic study of choice |
|
Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma diagnostic study of choice in the news |
|
Blogs on Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma diagnostic study of choice |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma diagnostic study of choice |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Sara Mohsin, M.D.[2]
Overview
The diagnosis of lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma is based on bone marrow aspiration and biopsy and serum protein analysis studies such as immunohistochemistry, flow cytometry and cytogenetics to distinguish LPL from other types of B-cell lymphomas. CSF flow cytometry, protein electrophoresis and immunofixation is done for the diagnosis of Bing-Neel syndrome (a late, but severe, rare complication).
Diagnostic Study of Choice
- There is no single diagnostic study of choice for the diagnosis of lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma (LPL), but bone marrow aspiration and biopsy is considered to be mandatory for the assessment of patients with LPL and further supported by monoclonal protein/immunophenotypic studies such as immunohistochemistry, flow cytometry and cytogenetics to distinguish LPL from other types of B-cell lymphomas.[1][2]
- Not all the diagnostic tests mentioned are performed in a patient with lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma. A doctor takes into account the following factors before choosing diagnostic tests in a particular patient:
Diagnostic Criteria:
Diagnostic criteria presented in second International Workshop, Greece, 2002
- In September 26-30, 2002, in Athens, Greece,the Second International Workshop was held in which a diagnostic criteria for Waldenstrom's Macroglobulinemia was proposed. According to this criteria, the following findings on performing bone marrow biopsy and serum protein analysis are confirmatory of Waldenström macroglobulinemia and exclude other small B cell lymphoid neoplasms with plasmacytic differentiation:[1][3]
mSMART guidelines for diagnosis of Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia and associated disorders
- Mayo Stratification of Macroglobulinemia and Risk-Adapted Therapy (mSMART) Guidelines 2016 for diagnosis of Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia and associated disorders are as follows:[4]
Definitive Diagnostic Tests
- Genetic Testing:
- ARIDA
- IG gene rearrangement
- CXCR4 5338X
- MYD88 L265P
- Immunophenotyping
- Serum paraprotein
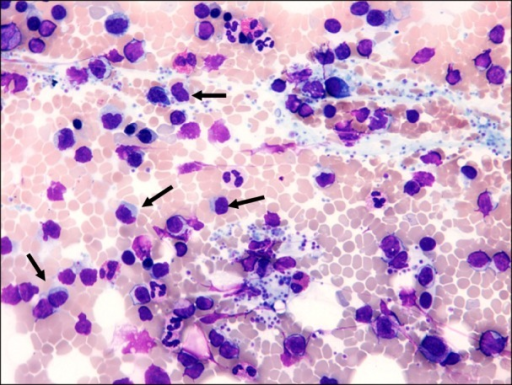
Bone Marrow Aspirate:
- A bone marrow aspirate is essential in the diagnosis of lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma
- Findings suggestive of lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma include:[5]
- Hypercellular bone marrow aspirate
- Lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate with characteristic immunophenotype
 |
Bone Marrow Biopsy:
- A bone marrow biopsy may be helpful in the diagnosis of lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma [5]
- Findings on the biopsy suggestive of lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma include:[5]
- Hypercellular and infiltrated with lymphoid and plasmacytoid cells
- Dutcher bodies (PAS positive intra-nuclear vacuoles containing IgM monoclonal protein)
- Three patterns of marrow involvement are described, as follows:
- Lymphoplasmacytoid cells (lymphoplasmacytic and small lymphocytes) in a nodular pattern
- Lymphoplasmacytic cells (small lymphocytes, mature plasma cells, mast cells) in an interstitial/nodular pattern
- A polymorphous infiltrate (small lymphocytes, plasma cells, plasmacytoid cells, immunoblasts with mitotic figures)
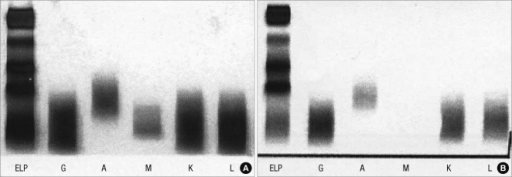
Electrophoresis and Immunofixation
- Serum protein electrophoresis is important for the diagnosis of lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma
- Findings on an electrophoresis diagnostic of lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma include:[6]
- Sharp, narrow spike of monoclonal IgM protein
- Dense band of monoclonal IgM protein
- The paraprotein can be of any size
- Serum immunofixation is important for the diagnosis of lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma. It helps in confirming the presence of a monoclonal protein, in addition to determining its type[6]
 |
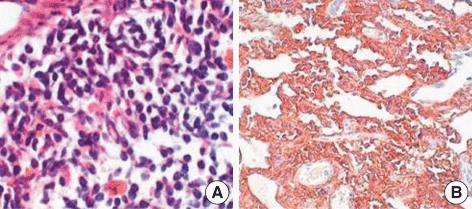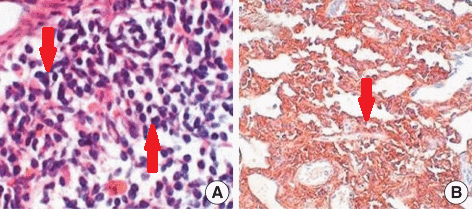
CSF flow cytometry, protein electrophoresis and immunofixation for diagnosis of Bing-Neel syndrome:
- For diagnosing Bing-Neel syndrome, after lumbar puncture, CSF flow cytometry is done which shows a lambda light chain-restricted population of B-cells consistent with a CD5+ CD10+ B-cell lymphoma
- Furthermore, protein electrophoresis and immunofixation should be done for the detection and classification of a monoclonal protein as well as molecular diagnostic testing for immunoglobulin gene rearrangement and mutated MYD88[7][8][9]
 |
 |
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Dimopoulos MA, Kyle RA, Anagnostopoulos A, Treon SP (2005). "Diagnosis and management of Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia". J Clin Oncol. 23 (7): 1564–77. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.03.144. PMID 15735132.
- ↑ Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Pileri SA, Harris NL, Stein H, Siebert R; et al. (2016). "The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms". Blood. 127 (20): 2375–90. doi:10.1182/blood-2016-01-643569. PMC 4874220. PMID 26980727.
- ↑ Owen RG, Treon SP, Al-Katib A, Fonseca R, Greipp PR, McMaster ML; et al. (2003). "Clinicopathological definition of Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia: consensus panel recommendations from the Second International Workshop on Waldenstrom's Macroglobulinemia". Semin Oncol. 30 (2): 110–5. doi:10.1053/sonc.2003.50082. PMID 12720118.
- ↑ Ansell, Stephen M.; Kyle, Robert A.; Reeder, Craig B.; Fonseca, Rafael; Mikhael, Joseph R.; Morice, William G.; Bergsagel, P. Leif; Buadi, Francis K.; Colgan, Joseph P.; Dingli, David; Dispenzieri, Angela; Greipp, Philip R.; Habermann, Thomas M.; Hayman, Suzanne R.; Inwards, David J.; Johnston, Patrick B.; Kumar, Shaji K.; Lacy, Martha Q.; Lust, John A.; Markovic, Svetomir N.; Micallef, Ivana N.M.; Nowakowski, Grzegorz S.; Porrata, Luis F.; Roy, Vivek; Russell, Stephen J.; Short, Kristen E. Detweiler; Stewart, A. Keith; Thompson, Carrie A.; Witzig, Thomas E.; Zeldenrust, Steven R.; Dalton, Robert J.; Rajkumar, S. Vincent; Gertz, Morie A. (2010). "Diagnosis and Management of Waldenström Macroglobulinemia: Mayo Stratification of Macroglobulinemia and Risk-Adapted Therapy (mSMART) Guidelines". Mayo Clinic Proceedings. 85 (9): 824–833. doi:10.4065/mcp.2010.0304. ISSN 0025-6196.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Leleu X, Roccaro AM, Moreau AS, Dupire S, Robu D, Gay J; et al. (2008). "Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia". Cancer Lett. 270 (1): 95–107. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2008.04.040. PMC 3133633. PMID 18555588.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Riches PG, Sheldon J, Smith AM, Hobbs JR (1991). "Overestimation of monoclonal immunoglobulin by immunochemical methods". Ann Clin Biochem. 28 ( Pt 3): 253–9. doi:10.1177/000456329102800310. PMID 1872571.
- ↑ O'Neil DS, Francescone MA, Khan K, Bachir A, O'Connor OA, Sawas A (2018). "A Case of Bing-Neel Syndrome Successfully Treated with Ibrutinib". Case Rep Hematol. 2018: 8573105. doi:10.1155/2018/8573105. PMC 6136466. PMID 30228918.
- ↑ Minnema MC, Kimby E, D'Sa S, Fornecker LM, Poulain S, Snijders TJ; et al. (2017). "Guideline for the diagnosis, treatment and response criteria for Bing-Neel syndrome". Haematologica. 102 (1): 43–51. doi:10.3324/haematol.2016.147728. PMC 5210231. PMID 27758817.
- ↑ Tallant A, Selig D, Wanko SO, Roswarski J (2018). "First-line ibrutinib for Bing-Neel syndrome". BMJ Case Rep. 2018. doi:10.1136/bcr-2018-226102. PMID 30279255.