Brucellosis pathophysiology
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Danitza LukacVishal Devarkonda, M.B.B.S[2]
|
Brucellosis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Brucellosis pathophysiology On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Brucellosis pathophysiology |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Brucellosis pathophysiology |
Overview
Brucellosis is a zoonotic disease, humans could be infected by eating undercook meat or raw dairy products, inhalation of the bacteria and direct contact of bacteria with skin wounds or mucous membranes. Following transmission, white blood cells phagocyte the pathogen and transports it via hematologic or lymphatic route to different organs, specially to those of the reticuloendothelial system.
Pathophysiology
Brucellosis is a zoonotic disease, humans could be infected by eating undercook meat or raw dairy products, inhalation of the bacteria and direct contact of bacteria with skin wounds or mucous membranes. Following transmission, white blood cells phagocyte the pathogen and transports it via hematologic or lymphatic route to different organs specially to those of the reticuloendothelial system. Endotoxic lipopolysaccharide LPS, plays an important role in: survival of bacteria inside monocytic cell, supressing phagosome-lysosome fusion and internalizing bacteria into endoplasmic reticulum. The pathophysiology of Brucellosis can be described in the following steps:[1][2][3][4][5][6][7][8][9][10][11][12][13]
Transmission
According to CDC, humans are generally infected with Brucellosis in one of the following three ways:[1][14]
| ROUTE OF TRANSMISSION | |
|---|---|
| Gastrointestinal |
Eating undercooked meat or consuming unpasteurized/raw dairy products |
| Inhalation |
Breathing in the bacteria that cause brucellosis (inhalation) |
| Cutaneous |
Bacteria entering the body through skin wounds or mucous membranes |
| Other modes of transmission |
|
Incubation
Incubation period of brucellosis varies from one to four weeks. But occasionally, it may be as long as several months.
Dissemination
Following transmission, brucellae is ingested by macrophages and polymorphonuclear cells. On ingestion, they replicate intracellularly inside the lysed cells and disseminate systemically.
Seeding
- On transmission, bacteria is actively phagocytosed by neurophilic granulocytes and monocytes.
- On entry into the body, brucellae multiply in the neutrophilic granulocytes and monocytes, initially in lymph nodes, which is followed by systemic hematogenous spread resulting in multiple localizing infection
Immune response
Brucellosis elicits both humoral and cell-mediated immune responses:[1][2][3][4][5][6][7][8][9][15][16]
Humoral immune response
- Humoral response has a limited role in protecting host from Brucellae.
- On activation, B-cell produce IgM class antibody, which is followed by IgG antibodies .
- Antibodies promote clearance of extracellular bacteria and facilitate phagocytosis of the Brucellae.
Cell mediates immune response
- Tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) produces on activation of cell mediated immunity, stimulates T lymphocytes and macrophages, which help in eliminating intracellular brucellae. Virulent brucellae tend to suppress the activity of tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) and IFN-gamma.
- Cytokines such as interleukin (IL) 12 promote production of Interferon γ (IFN-γ) responses. IFN-γ, which drives TH1-type responses and stimulates macrophage activation. Cytokines, which include , IL-6, IL-4and IL-10, down-regulate the protective response.
Pathogenesis
The pathogenesis of brucellosis is complex and not fully understood:[1][2][3][4][5][6][7][8][9][17][18][19]
By avoiding innate immunity, brucella survive with in monocytic cells.
- Endotoxic lipopolysaccharide (LPS), plays a key role in survival of bacteria inside monocytic cell.
- LPS helps in survival of the bacteria inside the monocytic cell, by suppressing phagosome–lysosome fusion, internalizing bacteria into endoplasmic reticulum and inhibiting apoptosis of infected cell.
- Type IV secretion system (VirB) and type III secretion system, that regulates intracellular survival and trafficking has been identified, although type 3 not yet confirmed. Secretion system plays an important role in intracellular transport of the bacteria acid-stable proteins produced by brucella, facilitates the survival in phagosomes
- Cu-Zn superoxide dismutase, produced by brucellae, gives them resistance from reactive oxygen intermediates.
- Two component BvrS/BvrR system, codes for histidine kinase sensor. Histidine kinase sensor plays an important role in controlling the expression of molecular determinants which are necessary for cell invasion.[20]
- Hemolysins help the bacteria to be realeased from a cell and induce cell necrosis.
Genetics
There is no known genetic association to Brucellosis.
Microscopic Pathology

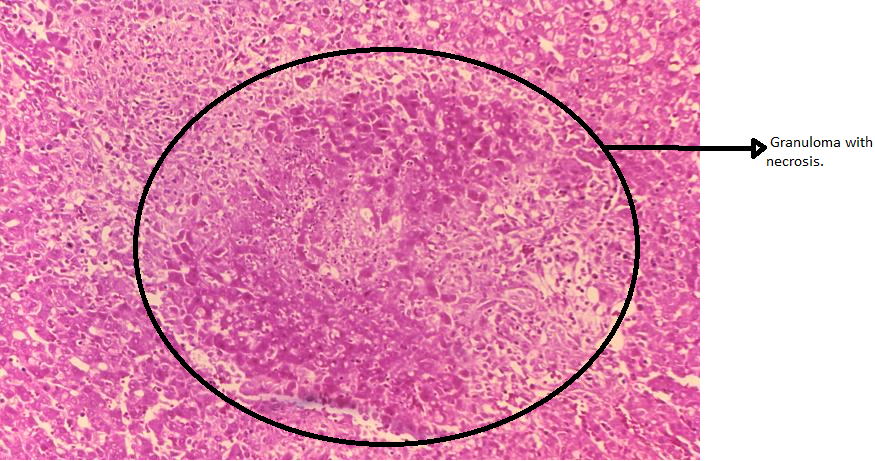
Reference
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Pappas G, Akritidis N, Bosilkovski M, Tsianos E (2005). "Brucellosis". N Engl J Med. 352 (22): 2325–36. doi:10.1056/NEJMra050570. PMID 15930423.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "CDC".
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Zhan Y, Liu Z, Cheers C (1996). "Tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-12 contribute to resistance to the intracellular bacterium Brucella abortus by different mechanisms". Infect Immun. 64 (7): 2782–6. PMC 174139. PMID 8698508.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Larralde de Luna M, Raspa ML, Ibargoyen J (1992). "Oral-facial-digital type 1 syndrome of Papillon-Léage and Psaume". Pediatr Dermatol. 9 (1): 52–6. PMID 1574477.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Gazapo E, Gonzalez Lahoz J, Subiza JL, Baquero M, Gil J, de la Concha EG (1989). "Changes in IgM and IgG antibody concentrations in brucellosis over time: importance for diagnosis and follow-up". J Infect Dis. 159 (2): 219–25. PMID 2915152.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Arenas GN, Staskevich AS, Aballay A, Mayorga LS (2000). "Intracellular trafficking of Brucella abortus in J774 macrophages". Infect Immun. 68 (7): 4255–63. PMC 101738. PMID 10858243.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Boschiroli ML, Ouahrani-Bettache S, Foulongne V, Michaux-Charachon S, Bourg G, Allardet-Servent A; et al. (2002). "Type IV secretion and Brucella virulence". Vet Microbiol. 90 (1–4): 341–8. PMID 12414154.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Lapaque N, Moriyon I, Moreno E, Gorvel JP (2005). "Brucella lipopolysaccharide acts as a virulence factor". Curr Opin Microbiol. 8 (1): 60–6. doi:10.1016/j.mib.2004.12.003. PMID 15694858.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 DelVecchio VG, Kapatral V, Elzer P, Patra G, Mujer CV (2002). "The genome of Brucella melitensis". Vet Microbiol. 90 (1–4): 587–92. PMID 12414174.
- ↑ Moreno E, Moriyon I (2002). "Brucella melitensis: a nasty bug with hidden credentials for virulence". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 99 (1): 1–3. doi:10.1073/pnas.022622699. PMC 117501. PMID 11782541.
- ↑ Gorvel JP, Moreno E (2002). "Brucella intracellular life: from invasion to intracellular replication". Vet Microbiol. 90 (1–4): 281–97. PMID 12414149.
- ↑ Ko J, Splitter GA (2003). "Molecular host-pathogen interaction in brucellosis: current understanding and future approaches to vaccine development for mice and humans". Clin Microbiol Rev. 16 (1): 65–78. PMC 145300. PMID 12525425.
- ↑ Dornand J, Gross A, Lafont V, Liautard J, Oliaro J, Liautard JP (2002). "The innate immune response against Brucella in humans". Vet Microbiol. 90 (1–4): 383–94. PMID 12414158.
- ↑ [CDC "https://www.cdc.gov/brucellosis/transmission/index.html"] Check
|url=value (help). External link in|title=(help) - ↑ Khan M, Harms JS, Marim FM, Armon L, Hall CL, Liu YP; et al. (2016). "The Bacterial Second Messenger Cyclic di-GMP Regulates Brucella Pathogenesis and Leads to Altered Host Immune Response" Check
|url=value (help). Infect Immun. 84 (12): 3458–3470. doi:10.1128/IAI.00531-16. PMC 5116723. PMID 27672085. - ↑ Pappas G, Akritidis N, Bosilkovski M, Tsianos E (2005). "Brucellosis". N Engl J Med. 352 (22): 2325–36. doi:10.1056/NEJMra050570. PMID 15930423.
- ↑ Barquero-Calvo E, Chaves-Olarte E, Weiss DS, et al. Brucella abortus uses a stealthy strategy to avoid activation of the innate immune system during the onset of infection. PLoS One 2007; 2:e631.
- ↑ Gorvel JP, Moreno E. Brucella intracellular life: from invasion to intracellular replication. Vet Microbiol 2002; 90:281.
- ↑ Pappas G, Akritidis N, Bosilkovski M, Tsianos E (2005). "Brucellosis". N Engl J Med. 352 (22): 2325–36. doi:10.1056/NEJMra050570. PMID 15930423.
- ↑ Pappas G, Akritidis N, Bosilkovski M, Tsianos E (2005). "Brucellosis" Check
|url=value (help). N Engl J Med. 352 (22): 2325–36. doi:10.1056/NEJMra050570. PMID 15930423.