Bursitis overview
|
Bursitis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Bursitis overview On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Bursitis overview |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Sara Mehrsefat, M.D. [2]
Overview
Bursitis is characterized by the inflammation of a bursa and the buildup of the fluid in the bursal sac. A bursa is a small, fluid-filled sac that acts as a cushion between a bone and other moving parts: muscles, tendons, or skin. Over 160 bursa are found throughout the body but relatively few of them can cause bursitis. Based on the nature of the inflammation, bursitis may be classified into 2 subtypes: septic and aseptic. The most common bursitis subtypes include subacromial, olecranon, trochanteric, prepatellar, and retrocalcaneal. Aseptic bursitis can be caused by overuse or repetitive injury to the joint, abnormal and bony structure, and/or crystal deposit in the bursa. Additionally, septic bursitis can be caused by bacterial infection of the bursa through a skin injury following repetitive trauma. Common causes of septic bursitis include Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, and Streptococcus spp. Bursitis must be differentiated from tendonitis, cellulitis, osteoarthritis, ligamentous injuries, and septic arthritis. The symptoms of bursitis differ based on the location of the inflammation. Focal swelling, pain, and redness are symptoms common to all forms of bursitis. The diagnosis of bursitis is usually made clinically. There are no diagnostic lab findings associated with bursitis. However, patients with septic bursitis may have elevated ESR, CRP, and white blood cell count. Ultrasonography may be a useful tool for confirming the diagnosis of bursitis, while the aspiration of bursal fluids is usually reserved for the diagnosis of septic bursitis.[1][2] Medical therapy for non-septic bursitis depends on the involved bursa and includes the RICE regimen (rest, ice, compression, elevation), NSAIDs, and/or corticosteroid injections. Restriction of activity is encouraged to prevent further injury and promote healing. Antimicrobials are the mainstay of therapy for septic bursitis. Surgical management is often reserved for non-responders.[3][4][5]
Classification
Based on the nature of the inflammation, bursitis may classified into 2 subtypes: septic and aseptic. Common anatomic locations of bursitis include the shoulder, elbow, hip, knee, and ankle. The most common bursitis subtypes include:[6][7][8][9]
- Subacromial bursitis
- Olecranon bursitis
- Trochanteric bursitis
- Prepatellar bursitis
- Retrocalcaneal bursitis
Pathophysiology
Bursitis is characterized by acute or chronic inflammation of a bursa and buildup of fluid in the bursa sac. A bursa is a small, fluid-filled sac that acts as a cushion between a bone and other moving parts: muscles, tendons, or skin. Over 160 bursa are found throughout the body and only few of them can cause bursitis. Aseptic bursitis can be caused by overuse and repetitive injuries to the joint, abnormal bony structure and crystal deposit in the bursa. It commonly affects the knee or elbow as a result of kneeling or leaning on the elbows longer than usual. Moreover, septic bursitis can be caused by bacterial infection of the bursa through the skin injury following repetitive trauma.[7][10][11]
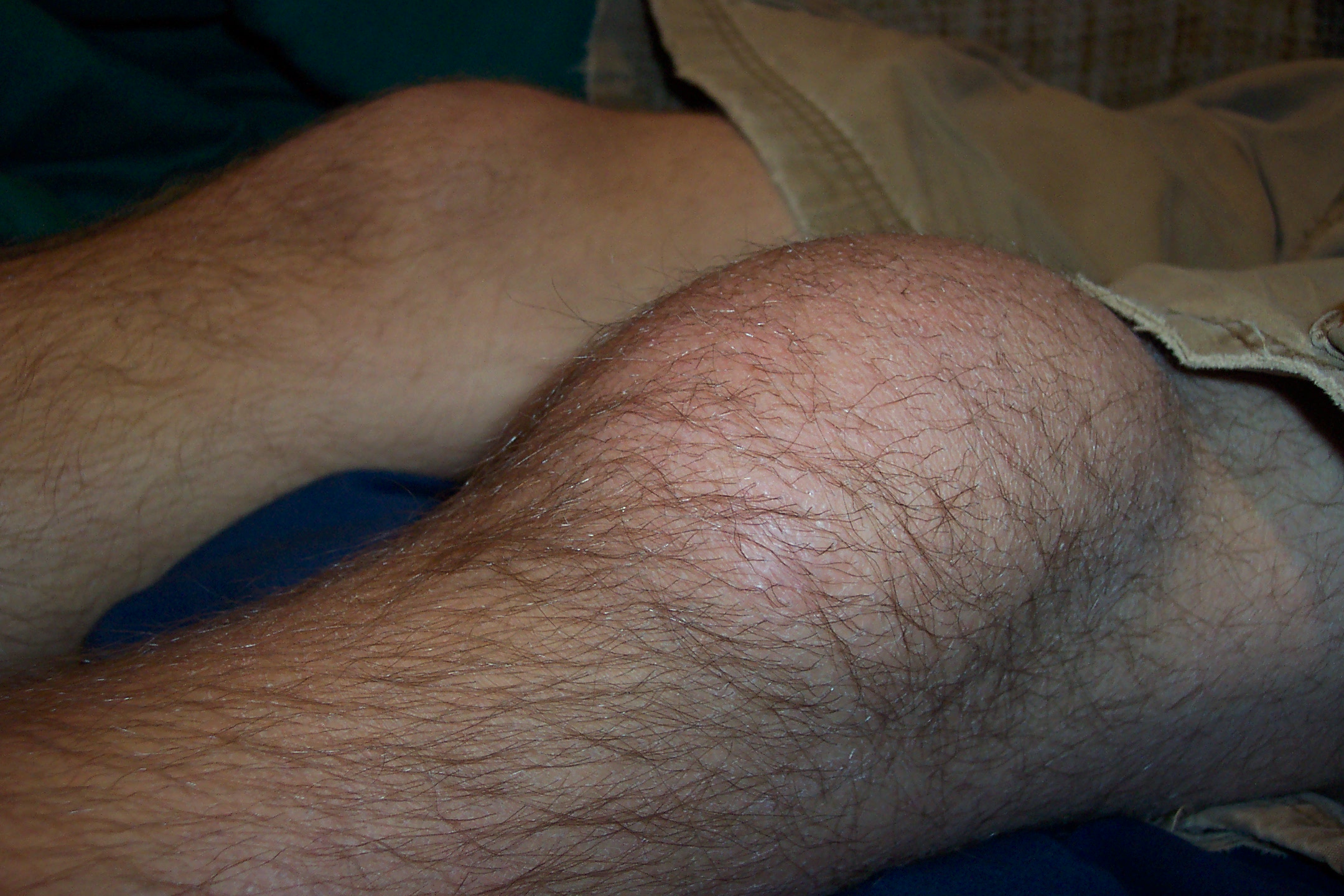
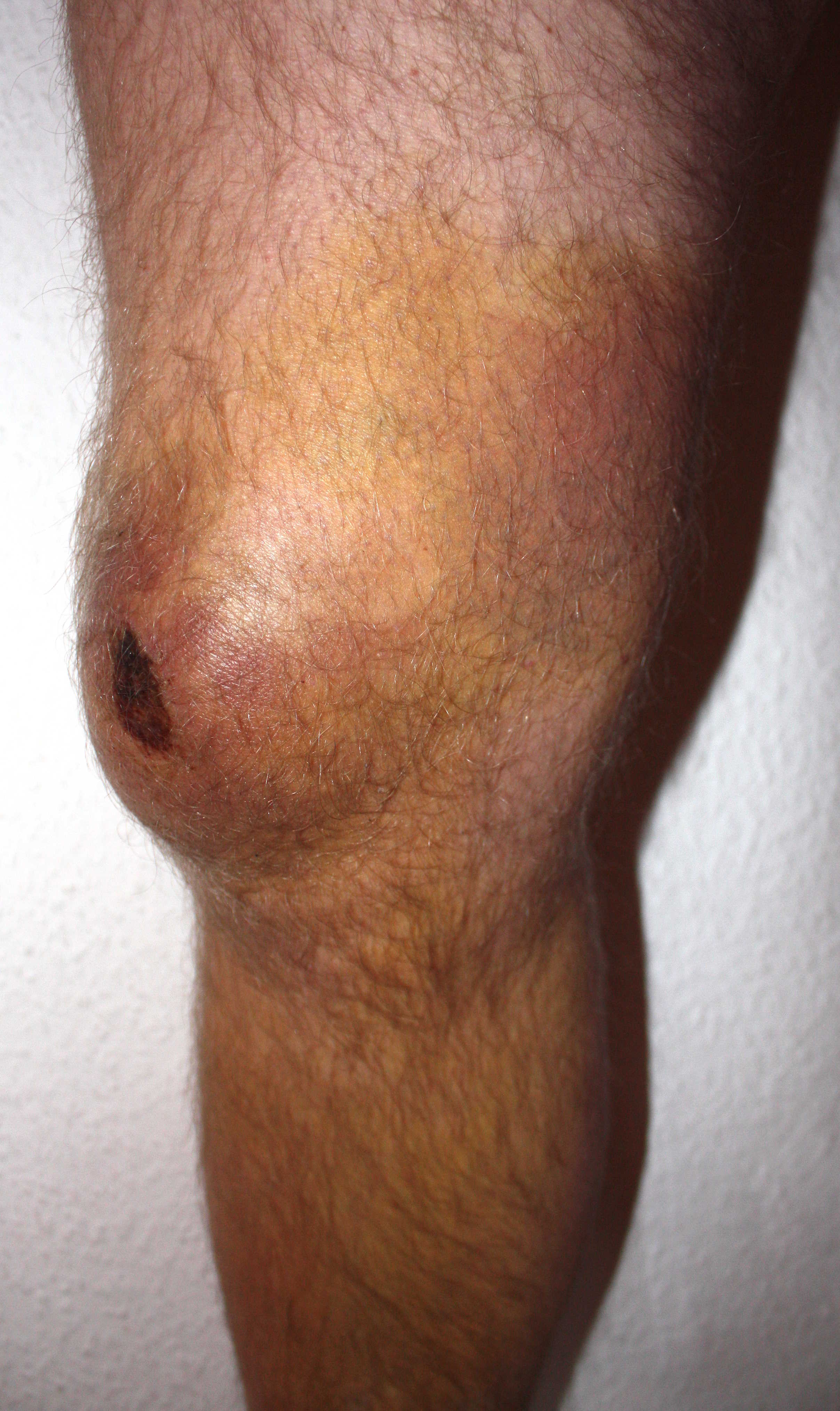
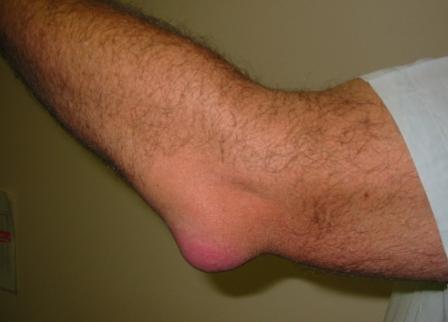
Images
The following images depict different cases of bursitis:[12]
-
Prepatellar bursitis
-
Prepatellar bursitis
-
Olecranon bursitis
-
Olecranon bursitis
Causes
Common causes of bursitis include:
Aseptic bursitis:
- Prolonged pressure, overuse, or strenuous activity
- Other inflammatory conditions (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis and spondyloarthritis)
- Gout and pseudogout
Septic bursitis:[1][8][13][14][15]
Differential Diagnosis
Bursitis symptoms and signs are relatively non-specific. Even after detailed history and physical examination, imaging studies are often necessary to rule out other musculoskeletal conditions. Bursitis must be differentiated from tendonitis, cellulitis, osteoarthritis, ligamentous injuries, and septic arthritis.[7][8][9]
Epidemiology and Demographics
Bursitis accounts for 400 visits per 100,000 visits to primary care clinic. The exact prevalence and incidence of bursitis are unknown.[15]
Risk Factors
Common risk factors in the development of bursitis include rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, gout, pseudogout cellulitis, diabetes mellitus, use of systemic glucocorticoids, alcoholism, malignancy, and leukopenia. Additionally, having a hobby or job that involves repetitive motions such as bicycling, playing baseball, gardening, or setting tiles may lead to bursitis.[15]
Screening
Screening for bursitis is not recommended.[16]
Natural History, Complications, and Prognosis
Bursitis is often caused by overused and repetitive injuries to the join. Symptoms of bursitis may develop rapidly within 2 to 3 days in an acute form. It usually presents with edema, erythema, and tenderness over the involved joint. In most cases after adjustment of activities, bursitis will gradually clear within few days to weeks without any long-term consequences. If left untreated, acute bursitis may lead to chronic bursitis which may result in cicatricial adhesions, reduced mobility, and progressive pain. With treatment and activities adjustment, septic and aseptic bursitis are associated with excellent prognosis.
Diagnosis
History
Complete history will help determine whether the bursitis is associated with any specific activities.[7][8][9]
Symptoms and Physical Examination
| Type of Bursitis | Symptoms | Physical examination |
|---|---|---|
| Subacromial bursitis[8] |
|
|
| Olecranon bursitis[17][18] |
|
|
| Trochanteric bursitis[19][20] |
|
|
| Prepatellar bursitis[9][21] |
|
|
| Retrocalcaneal bursitis[7][22] |
|
|
Laboratory Findings
The diagnosis of bursitis is usually made clinically. There are no diagnostic lab findings associated with bursitis. However, patients with septic bursitis may have elevated ESR, CRP, and white blood cells.[23][8][9]
X ray
X ray is not often required in patients with bursitis. X ray may be used as a diagnostic measure to support a clinical diagnosis of bursitis. Joint x ray is generally reserved for patients with history of significant trauma. A plain x ray may be helpful in the diagnosis of fracture or dislocation.[24][21][25]
CT
CT scan is not often required in patients with bursitis. It is usually reserved for the patients who are not responding to initial treatment. On CT scan, superficial bursitis may be characterized by fluid density at the subcutaneous tissue.[24][21]
MRI
MRI is not often required in patients with bursitis. Due to the cost and time, the use of MRI is limited compere to ultrasound. MRI is often reserved for patients who are highly suspicious of other medical conditions such as tumors, ligamentous injures, and tendon injuries. On MRI, bursitis is characterized by bursal fluid collection, subcutaneous edema, and joint effusion.[24][21]
Ultrasound
Ultrasonography may be a useful tool for confirming the diagnoses of bursitis. On ultrasound, bursitis may be characterized by bursal wall distention with presence of local hypoechoic or anechoic intra-bursal material, synovial proliferation, calcifications, and rheumatoid nodules.[26][27]
Other Diagnostic Studies
Other diagnostic study for bursitis include aspiration of the bursal fluid. Aspiration of bursal fluids is not recommended in the management of all types of bursitis. It is usually reserved for the diagnosis of septic bursitis.[1][2]
Treatment
Medical Therapy
Medical therapy for non-septic bursitis depends on the involved bursa and includes the RICE regimen (rest, ice, compression, elevation), NSAIDs, and/or corticosteroid injections. Restriction of activity is encouraged to prevent further injury and promote healing. Antimicrobials are the mainstay of therapy for septic bursitis. Surgical management is often reserved for non-responders.[3][4][5]
| Septic[3][4] | Aseptic |
|---|---|
|
|
Surgery
Surgical intervention is not recommended for the management of bursitis. However, surgical techniques include bursectomy or longitudinal band release are usually reserved for patients with chronic, recurrent, or septic bursitis.[28][29]
Primary Prevention
Effective measures for the primary prevention of bursitis include maintaining a healthy weight, taking breaks from repetitive tasks, using foam for kneeling and elbow pads, and practicing good posture and position.[30]
Secondary Prevention
There are no established method for secondary prevention of bursitis. However, activities adjustment and using foam for kneeling or elbow pads, and resting while doing repetitive tasks may be lead to the fast recovery.[30]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Stell IM, Gransden WR (1998). "Simple tests for septic bursitis: comparative study". BMJ. 316 (7148): 1877. PMC 28586. PMID 9632407.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Shell, Donald, Rob Perkins, and Andrew Cosgarea. "Septic olecranon bursitis: recognition and treatment." The Journal of the American Board of Family Practice 8.3 (1995): 217-220.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Reilly D, Kamineni S (2016). "Olecranon bursitis". J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 25 (1): 158–67. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2015.08.032. PMID 26577126.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Zimmermann B, Mikolich DJ, Ho G (1995). "Septic bursitis". Semin Arthritis Rheum. 24 (6): 391–410. PMID 7667644.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Aaron DL, Patel A, Kayiaros S, Calfee R (2011). "Four common types of bursitis: diagnosis and management". J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 19 (6): 359–67. PMID 21628647.
- ↑ Chatra PS (2012). "Bursae around the knee joints". Indian J Radiol Imaging. 22 (1): 27–30. doi:10.4103/0971-3026.95400. PMC 3354353. PMID 22623812.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 Fauci, Anthony S., and Carol Langford. Harrison's rheumatology. McGraw Hill Professional, 2010.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 8.5 Walker‐Bone, Karen, et al. "Prevalence and impact of musculoskeletal disorders of the upper limb in the general population.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 Aaron, Daniel L., et al. "Four common types of bursitis: diagnosis and management." Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons 19.6 (2011): 359-367.
- ↑ Hellmann DB, Imboden JB., Jr. Musculoskeletal and immunologic disorders. In: McPhee SJ, Papadakis MA, editors. Current Medical Diagnosis & Treatment. McGraw-Hill Lange; 2010. pp. 2056–2061.
- ↑ García-Porrúa C, González-Gay MA, Ibañez D, García-País MJ (1999). "The clinical spectrum of severe septic bursitis in northwestern Spain: a 10 year study". J Rheumatol. 26 (3): 663–7. PMID 10090179.
- ↑ Wikimedia Commons. Bursitis. (2012) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Category:Bursitis Accessed on August 31, 2016
- ↑ Wang JP, Granlund KF, Bozzette SA, Botte MJ, Fierer J (2000). "Bursal sporotrichosis: case report and review". Clin Infect Dis. 31 (2): 615–6. doi:10.1086/313983. PMID 10987734.
- ↑ National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin disease, Bursitis. http://www.niams.nih.gov/Health_Info/Bursitis/default.asp Accessed August 25, 2016
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 McAfee JH, Smith DL (1988). "Olecranon and prepatellar bursitis. Diagnosis and treatment". West J Med. 149 (5): 607–10. PMC 1026560. PMID 3074561.
- ↑ U.S. Preventive Services Task Force http://www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/BrowseRec/Search?s=bursitis Accessed on August 29, 2016
- ↑ Stell IM (1996). "Septic and non-septic olecranon bursitis in the accident and emergency department--an approach to management". J Accid Emerg Med. 13 (5): 351–3. PMC 1342774. PMID 8894865.
- ↑ Lockman L (2010). "Treating nonseptic olecranon bursitis: a 3-step technique". Can Fam Physician. 56 (11): 1157. PMC 2980436. PMID 21075998.
- ↑ Brinks A, van Rijn RM, Bohnen AM, Slee GL, Verhaar JA, Koes BW; et al. (2007). "Effect of corticosteroid injection for trochanter pain syndrome: design of a randomised clinical trial in general practice". BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 8: 95. doi:10.1186/1471-2474-8-95. PMC 2045096. PMID 17880718.
- ↑ Karpinski MR, Piggott H (1985). "Greater trochanteric pain syndrome. A report of 15 cases". J Bone Joint Surg Br. 67 (5): 762–3. PMID 4055877.
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 21.2 21.3 Huang, Yu-Chih, and Wen-Lin Yeh. "Endoscopic treatment of prepatellar bursitis." International orthopaedics 35.3 (2011): 355-358.
- ↑ Lyman, Jeffrey, Paul S. Weinhold, and Louis C. Almekinders. "Strain behavior of the distal Achilles tendon implications for insertional Achilles tendinopathy." The American Journal of Sports Medicine 32.2 (2004): 457-461.
- ↑ Approach to Articular and Musculoskeletal Disorders, Harrison's Internal Medicine, 2011
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 24.2 Radiopedia. Olecranon Bursitis. http://radiopaedia.org/articles/olecranon-bursitis Accessed on August 23, 2016
- ↑ Blankstein A, Cohen I, Diamant L, Heim M, Dudkiewicz I, Israeli A; et al. (2001). "Achilles tendon pain and related pathologies: diagnosis by ultrasonography". Isr Med Assoc J. 3 (8): 575–8. PMID 11519381.
- ↑ Blankstein A, Ganel A, Givon U, Mirovski Y, Chechick A. Ultrasonographic findings in patients with olecranon bursitis. Ultraschall Med 2006; 27: 568-571.
- ↑ Martinoli C, Bianchi S, Giovagnorio F, Pugliese F. Ultrasound of the elbow. Skeletal Radiol 2001; 30: 605-614
- ↑ Huang YC, Yeh WL (2011). "Endoscopic treatment of prepatellar bursitis". Int Orthop. 35 (3): 355–8. doi:10.1007/s00264-010-1033-5. PMC 3047636. PMID 20521045.
- ↑ Lustenberger DP, Ng VY, Best TM, Ellis TJ (2011). "Efficacy of treatment of trochanteric bursitis: a systematic review". Clin J Sport Med. 21 (5): 447–53. doi:10.1097/JSM.0b013e318221299c. PMC 3689218. PMID 21814140.
- ↑ 30.0 30.1 National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin disease. Bursitis. http://www.niams.nih.gov/Health_Info/Bursitis/default.asp Accessed August 25, 2016