Luteinizing hormone
| Chorionic gonadotropin alpha | |
|---|---|
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | CGA |
| Alt. symbols | HCG, GPHa, GPHA1 |
| Entrez | 1081 |
| HUGO | 1885 |
| OMIM | 118850 |
| RefSeq | NM_000735 |
| UniProt | P01215 |
| Other data | |
| Locus | Chr. 6 q14-q21 |
| Luteinizing hormone beta polypeptide | |
|---|---|
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | LHB |
| Entrez | 3972 |
| HUGO | 6584 |
| OMIM | 152780 |
| RefSeq | NM_000894 |
| UniProt | P01229 |
| Other data | |
| Locus | Chr. 19 q13.3 |
Luteinizing hormone (LH, also known as lutropin and sometimes lutrophin[1]) is a hormone produced by gonadotropic cells in the anterior pituitary gland. In females, an acute rise of LH ("LH surge") triggers ovulation[2] and development of the corpus luteum. In males, where LH had also been called interstitial cell–stimulating hormone (ICSH),[3] it stimulates Leydig cell production of testosterone.[2] It acts synergistically with FSH.
Structure
LH is a heterodimeric glycoprotein. Each monomeric unit is a glycoprotein molecule; one alpha and one beta subunit make the full, functional protein.
Its structure is similar to that of the other glycoprotein hormones, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). The protein dimer contains 2 glycopeptidic subunits, labeled alpha and beta subunits, that are non-covalently associated (i.e., without any disulfide bridge linking them):[4]
- The alpha subunits of LH, FSH, TSH, and hCG are identical, and contain 92 amino acids in human but 96 amino acids in almost all other vertebrate species (glycoprotein hormones do not exist in invertebrates).
- The beta subunits vary. LH has a beta subunit of 120 amino acids (LHB) that confers its specific biologic action and is responsible for the specificity of the interaction with the LH receptor. This beta subunit contains an amino acid sequence that exhibits large homologies with that of the beta subunit of hCG and both stimulate the same receptor. However, the hCG beta subunit contains an additional 24 amino acids, and the two hormones differ in the composition of their sugar moieties.
The different composition of these oligosaccharides affects bioactivity and speed of degradation. The biologic half-life of LH is 20 minutes, shorter than that of FSH (3–4 hours) and hCG (24 hours).[citation needed]
Genes
The gene for the alpha subunit is located on chromosome 6q12.21.
The luteinizing hormone beta subunit gene is localized in the LHB/CGB gene cluster on chromosome 19q13.32. In contrast to the alpha gene activity, beta LH subunit gene activity is restricted to the pituitary gonadotropic cells. It is regulated by the gonadotropin-releasing hormone from the hypothalamus. Inhibin, activin, and sex hormones do not affect genetic activity for the beta subunit production of LH.
Function
In females: ovulation, maintaining of corpus luteum and secretion of progesterone.
In males: testosterone secretion.
Effects in females
LH supports theca cells in the ovaries that provide androgens and hormonal precursors for estradiol production. At the time of menstruation, FSH initiates follicular growth, specifically affecting granulosa cells.[5] With the rise in estrogens, LH receptors are also expressed on the maturing follicle, which causes it to produce more estradiol. Eventually, when the follicle has fully matured, a spike in 17α-hydroxyprogesterone production by the follicle inhibits the production of estrogens, leading to a decrease in estrogen-mediated negative feedback of GnRH in the hypothalamus, which then stimulates the release of LH from the anterior pituitary.[6] However another theory of the LH peak is a positive feedback mechanism from estradiol. The levels keep rising through the follicular phase and when they reach an unknown threshold, this results in the peak of the LH.[7] This effect is opposite from the usual negative feedback mechanism presented at lower levels. In other words, the mechanism(s) are not yet clear. The increase in LH production only lasts for 24 to 48 hours. This "LH surge" triggers ovulation, thereby not only releasing the egg from the follicle, but also initiating the conversion of the residual follicle into a corpus luteum that, in turn, produces progesterone to prepare the endometrium for a possible implantation. LH is necessary to maintain luteal function for the second two weeks of the menstrual cycle. If pregnancy occurs, LH levels will decrease, and luteal function will instead be maintained by the action of hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin), a hormone very similar to LH but secreted from the new placenta.
Gonadal steroids (estrogens and androgens) generally have negative feedback effects on GnRH-1 release at the level of the hypothalamus and at the gonadotropes, reducing their sensitivity to GnRH. Positive feedback by estrogens also occurs in the gonadal axis of female mammals and is responsible for the midcycle surge of LH that stimulates ovulation. Although estrogens inhibit kisspeptin (Kp) release from kiss1 neurons in the ARC, estrogens stimulate Kp release from the Kp neurons in the AVPV. As estrogens' levels gradually increase the positive effect predominates, leading to the LH surge. GABA-secreting neurons that innervate GnRH-1 neurons also can stimulate GnRH-1 release. These GABA neurons also possess ERs and may be responsible for the GnRH-1 surge. Part of the inhibitory action of endorphins on GnRH-1 release is through inhibition of these GABA neurons. Rupture of the ovarian follicle at ovulation causes a drastic reduction in estrogen synthesis and a marked increase in secretion of progesterone by the corpus luteum in the ovary, reinstating a predominantly negative feedback on hypothalamic secretion of GnRH-1.[8]
Effects in males
LH acts upon the Leydig cells of the testis and is regulated by gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH).[9] The Leydig cells produce testosterone (T) under the control of LH, which regulates the expression of the enzyme 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase that is used to convert androstenedione, the hormone produced by the testes, to testosterone,[10] an androgen that exerts both endocrine activity and intratesticular activity on spermatogenesis.
LH is released from the pituitary gland, and is controlled by pulses of gonadotropin-releasing hormone. When T levels are low, GnRH is released by the hypothalamus, stimulating the pituitary gland to release LH.[9] As the levels of T increase, it will act on the hypothalamus and pituitary through a negative feedback loop and inhibit the release of GnRH and LH consequently.[10] Androgens (T, DHT) inhibit monoamine oxidase (MAO) in pineal, leading to increased melatonin and reduced LH and FSH by melatonin-induced increase of Gonadotropin-Inhibitory Hormone (GnIH)[11] synthesis and secretion. T can also be aromatized into estradiol (E2) to inhibit LH. E2 decreases pulse amplitude and responsiveness to GnRH from the hypothalamus onto the pituitary.[12]
Changes in LH and testosterone (T) blood levels and pulse secretions are induced by changes in sexual arousal in human males.[13]
Normal levels
- The ranges denoted By biological stage may be used in closely monitored menstrual cycles in regard to other markers of its biological progression, with the time scale being compressed or stretched to how much faster or slower, respectively, the cycle progresses compared to an average cycle.
- The ranges denoted Inter-cycle variability are more appropriate to use in non-monitored cycles with only the beginning of menstruation known, but where the woman accurately knows her average cycle lengths and time of ovulation, and that they are somewhat averagely regular, with the time scale being compressed or stretched to how much a woman's average cycle length is shorter or longer, respectively, than the average of the population.
- The ranges denoted Inter-woman variability are more appropriate to use when the average cycle lengths and time of ovulation are unknown, but only the beginning of menstruation is given.
LH levels are normally low during childhood and, in women, high after menopause. As LH is secreted as pulses, it is necessary to follow its concentration over a sufficient period of time to get proper information about its blood level.
During the reproductive years, typical levels are between 1–20 IU/L. Physiologic high LH levels are seen during the LH surge (v.s.); typically they last 48 hours.
In males over 18 years of age, reference ranges have been estimated to be 1.8–8.6 IU/L.[15]
LH is measured in international units (IU). When quantifying the amount of LH in a sample in IUs, it is important to know which international standard your lot of LH was calibrated against, as they can vary broadly from year to year. For human urinary LH, one IU is most recently defined as 1/189th of an ampule denoted 96/602 and distributed by the NIBSC, corresponding to approximately 0.04656µg of LH protein for a single IU, but older standard versions are still widely in use.[16][17]
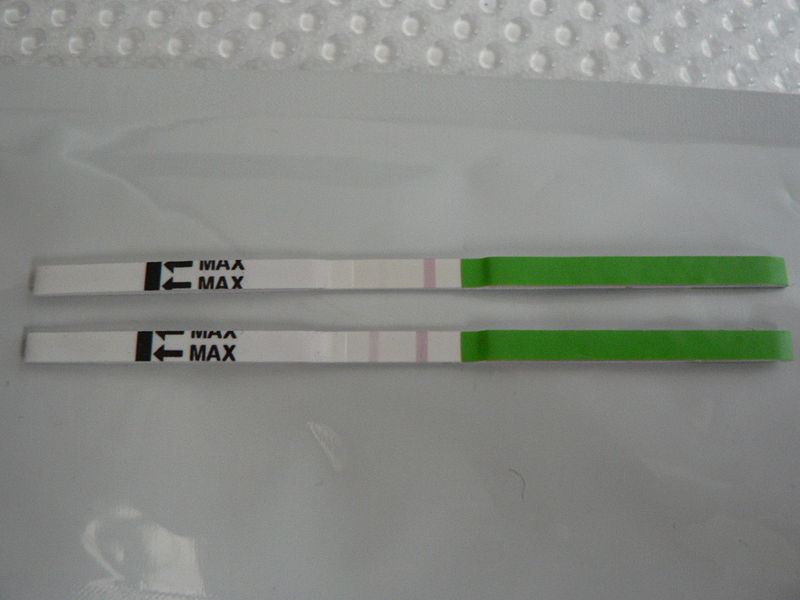
Predicting ovulation
The detection of a surge in release of luteinizing hormone indicates impending ovulation. LH can be detected by urinary ovulation predictor kits (OPK, also LH-kit) that are performed, typically daily, around the time ovulation may be expected.[19] A conversion from a negative to a positive reading would suggest that ovulation is about to occur within 24–48 hours, giving women two days to engage in sexual intercourse or artificial insemination with the intention of conceiving.[20]
The recommended testing frequency differs between manufacturers. For example, the Clearblue test is taken daily, and an increased frequency does not decrease the risk of missing an LH surge.[21] On the other hand, the Chinese company Nantong Egens Biotechnology recommends using their test twice per day.[22] If testing once per day, no significant difference has been found between testing LH in the morning versus in the evening, in relation to conception rates,[23] and recommendations of what time in the day to take the test varies between manufacturers and healthcare workers.[24] Tests may be read manually using a colour-change paper strip, or digitally with the assistance of reading electronics.
Tests for luteinising hormone may be combined with testing for estradiol in tests such as the Clearblue fertility monitor.[medical citation needed]
The sensitivity of LH tests are measured in milli international unit, with tests commonly available in the range 10–40 m.i.u. (the lower the number, the higher the sensitivity).[citation needed]
As sperm can stay viable in the woman for several days, LH tests are not recommended for contraceptive practices, as the LH surge typically occurs after the beginning of the fertile window.
Disease states
Excess
In children with precocious puberty of pituitary or central origin, LH and FSH levels may be in the reproductive range instead of the low levels typical for their age.
During the reproductive years, relatively elevated LH is frequently seen in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome; however, it would be unusual for them to have LH levels outside of the normal reproductive range.
Persistently high LH levels are indicative of situations where the normal restricting feedback from the gonad is absent, leading to a pituitary production of both LH and FSH. While this is typical in menopause, it is abnormal in the reproductive years. There it may be a sign of:
- Premature menopause
- Gonadal dysgenesis, Turner syndrome
- Castration
- Swyer syndrome
- Polycystic ovary syndrome
- Certain forms of congenital adrenal hyperplasia
- Testicular failure
- Pregnancy - BetaHCG can mimic LH so tests may show elevated LH
Note: A medical drug for inhibiting luteinizing hormone secretion is Butinazocine.[25]
Deficiency
Diminished secretion of LH can result in failure of gonadal function (hypogonadism). This condition is typically manifest in males as failure in production of normal numbers of sperm. In females, amenorrhea is commonly observed. Conditions with very low LH secretions include:
- Pasqualini syndrome[26][27][28]
- Kallmann syndrome
- Hypothalamic suppression
- Hypopituitarism
- Eating disorder
- Female athlete triad
- Hyperprolactinemia
- Hypogonadism
- Gonadal suppression therapy
- GnRH antagonist
- GnRH agonist (inducing an initial stimulation (flare up) followed by permanent blockage of the GnRH pituitary receptor)
As a medication
LH is available mixed with FSH in the form of menotropin, and other forms of urinary gonadotropins. More purified forms of urinary gonadotropins may reduce the LH portion in relation to FSH. Recombinant LH is available as lutropin alfa (Luveris).[29] All these medications have to be given parenterally. They are commonly used in infertility therapy to stimulate follicular development, the notable one being in IVF therapy.
Often, HCG medication is used as an LH substitute because it activates the same receptor. Medically used hCG is derived from urine of pregnant women, is less costly, and has a longer half-life than LH.
References
- ↑ Ujihara M, Yamamoto K, Nomura K, Toyoshima S, Demura H, Nakamura Y, Ohmura K, Osawa T (June 1992). "Subunit-specific sulphation of oligosaccharides relating to charge-heterogeneity in porcine lutrophin isoforms". Glycobiology. 2 (3): 225–31. doi:10.1093/glycob/2.3.225. PMID 1498420.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Essentials of Human Physiology by Thomas M. Nosek. Section 5/5ch9/s5ch9_5.
- ↑ Louvet JP, Harman SM, Ross GT (May 1975). "Effects of human chorionic gonadotropin, human interstitial cell stimulating hormone and human follicle-stimulating hormone on ovarian weights in estrogen-primed hypophysectomized immature female rats". Endocrinology. 96 (5): 1179–86. doi:10.1210/endo-96-5-1179. PMID 1122882.
- ↑ Jiang X, Dias JA, He X (January 2014). "Structural biology of glycoprotein hormones and their receptors: insights to signaling". Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology. 382 (1): 424–51. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2013.08.021. PMID 24001578.
- ↑ Bowen, R. (13 May 2004). "Gonadotropins: Luteinizing and Follicle Stimulating Hormones". Colorado State University. Retrieved 12 March 2012.
- ↑ Mahesh VB (January 2012). "Hirsutism, virilism, polycystic ovarian disease, and the steroid-gonadotropin-feedback system: a career retrospective". American Journal of Physiology. Endocrinology and Metabolism. 302 (1): E4–E18. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00488.2011. PMC 3328092. PMID 22028409.
- ↑ Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology 2006 page 1021
- ↑ Norris DO, Carr JA (2013). Vertebrate Endocrinology. Academic Press. p. 126. ISBN 978-0-12-396465-6.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 "Male Medical Fertility Treatment: HCG + LH + Recombinant FSH To Increase Sperm Count Through Spermatogenisis". Archived from the original on February 19, 2015. Retrieved 6 April 2015.[unreliable medical source?]
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 "The onset of puberty is controlled by two major hormones: FSH initiates spermatogenesis and LH signals the release of testosterone". Retrieved 6 April 2015.[unreliable medical source?]
- ↑ Ubuka T, Son YL, Tobari Y, Narihiro M, Bentley GE, Kriegsfeld LJ, Tsutsui K. "Central and Direct Regulation of Testicular Activity by Gonadotropin-Inhibitory Hormone and Its Receptor". Frontiers in Endocrinology. 5: 8. doi:10.3389/fendo.2014.00008. PMC 3902780. PMID 24478760.
- ↑ Pitteloud N, Dwyer AA, DeCruz S, Lee H, Boepple PA, Crowley WF, Hayes FJ (March 2008). "Inhibition of luteinizing hormone secretion by testosterone in men requires aromatization for its pituitary but not its hypothalamic effects: evidence from the tandem study of normal and gonadotropin-releasing hormone-deficient men". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 93 (3): 784–91. doi:10.1210/jc.2007-2156. PMC 2266963. PMID 18073301.
- ↑ Stoléru SG, Ennaji A, Cournot A, Spira A (1993). "LH pulsatile secretion and testosterone blood levels are influenced by sexual arousal in human males". Psychoneuroendocrinology. 18 (3): 205–18. doi:10.1016/0306-4530(93)90005-6. PMID 8516424.
- ↑ Häggström, Mikael (2014). "Reference ranges for estradiol, progesterone, luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone during the menstrual cycle". WikiJournal of Medicine. 1 (1). doi:10.15347/wjm/2014.001. ISSN 2002-4436.
- ↑ Mayo Medical Laboratories - Test ID: LH, Luteinizing Hormone (LH), Serum, retrieved December 2012
- ↑ World Health Organization Proposed International Standard for Luteinizing Hormone. WHO Expert Committee on Biological Standardization. World Health Organization. Geneva. 2003.
- ↑ WHO International Standard, Luteinizing Hormone, Human, Recombinant. National Institute for Biological Standards and Control.
- ↑ Dunson, D.B.; Baird, D.D.; Wilcox, A.J.; Weinberg, C.R. (1999). "Day-specific probabilities of clinical pregnancy based on two studies with imperfect measures of ovulation". Human Reproduction. 14 (7): 1835–1839. doi:10.1093/humrep/14.7.1835. ISSN 1460-2350.
- ↑ Nielsen MS, Barton SD, Hatasaka HH, Stanford JB (August 2001). "Comparison of several one-step home urinary luteinizing hormone detection test kits to OvuQuick". Fertility and Sterility. 76 (2): 384–7. doi:10.1016/S0015-0282(01)01881-7. PMID 11476792.
- ↑ "Ovulation Predictor Kit Frequently Asked Questions". Fertility Plus. Archived from the original on March 12, 2012. Retrieved 12 March 2012.[unreliable medical source?]
- ↑ "Clear Blue Ovulation Test Instructions". Ovulation Guide. Retrieved 2018-01-19.
- ↑ "Advanced Ovulation Test" (PDF). Homehealth-UK. Retrieved 2018-01-19. Version 1.1 02/11/15
- ↑ Martinez AR, Bernardus RE, Vermeiden JP, Schoemaker J (1994). "Time schedules of intrauterine insemination after urinary luteinizing hormone surge detection and pregnancy results". Gynecol Endocrinol. 8 (1): 1–5. PMID 8059611.
- ↑ Page 67 in: Godwin I. Meniru (2001). Cambridge Guide to Infertility Management and Assisted Reproduction. Cambridge University Press.
- ↑ U.S. Patent 4,406,904
- ↑ Weiss J, Axelrod L, Whitcomb RW, Harris PE, Crowley WF, Jameson JL (January 1992). "Hypogonadism caused by a single amino acid substitution in the beta subunit of luteinizing hormone". The New England Journal of Medicine. 326 (3): 179–83. doi:10.1056/NEJM199201163260306. PMID 1727547.
- ↑ Valdes-Socin H, Salvi R, Daly AF, Gaillard RC, Quatresooz P, Tebeu PM, Pralong FP, Beckers A (December 2004). "Hypogonadism in a patient with a mutation in the luteinizing hormone beta-subunit gene". The New England Journal of Medicine. 351 (25): 2619–25. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa040326. PMID 15602022.
- ↑ Valdes-Socin H, Daly AF, Beckers A (2017). "Luteinizing Hormone Deficiency: Historical Views and Future Perspectives" (PDF). Austin Andrology. 2 (1): 1015.
- ↑ Luveris information[unreliable medical source?] Archived June 18, 2006, at the Wayback Machine.
External links
- Luteinizing+Hormone at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- All articles lacking reliable references
- Articles lacking reliable references from May 2015
- Articles with invalid date parameter in template
- Webarchive template wayback links
- Protein pages needing a picture
- Genes on human chromosome 6
- Genes on human chromosome 19
- All articles with unsourced statements
- Articles with unsourced statements from November 2008
- Pages with broken file links
- Articles with unsourced statements from June 2018
- Articles with unsourced statements from August 2009
- Recombinant proteins
- Glycoproteins
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone and gonadotropins
- Peptide hormones
- Sex hormones
- Human hormones
- Hormones of the hypothalamus-pituitary-gonad axis
- Anterior pituitary hormones