Brain abscess differential diagnosis
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Farwa Haideri [2]

Overview
Brain abscess must be differentiated from metastatic tumors, necrotic tumors, and lymphomas.[1][2]
Differential Diagnosis
Brain abscess must be differentiated from:
- Metastatic tumors
- Necrotic tumors
- Lymphomas
Metastatic Tumor
- The big differential is that the abscess is often located in watershed regions, and tumors often enhance diffusely with contrast.
Necrotic Tumor
- Diagnosis of brain abscesses and necrotic tumors is often impossible without conventional MR imaging.[1]
- Several studies demonstrate the utility of Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) to differentiate between necrotic or cystic lesions and brain abscesses.[3]
- DWI has a sensitivity and specificity of over 90% for distinguishing abscess (low ADC) from necrotic tumors (high ADC).
Lymphoma
- Some studies suggest that indium scans can help differentiate abscess from CA, and thallium SPECT scans can distinguish CNS toxoplasmosis from lymphoma.[2]
Despite these differences, the true diagnosis is sometimes not made until biopsy.
| Diseases | Diagnostic tests | Physical Examination | Symptoms | Past medical history | Other Findings | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na+, K+, Ca2+ | CT /MRI | CSF Findings | Gold standard test | Neck stiffness | Motor or Sensory deficit | Papilledema | Bulging fontanelle | Cranial nerves | Headache | Fever | Altered mental status | |||
| Brain tumour[4][5] | ✔ | Cancer cells[6] | MRI | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | Cachexia, gradual progression of symptoms | ||||
| Delirium tremens | ✔ | Clinical diagnosis | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | Alcohol intake, sudden witdrawl or reduction in consumption | Tachycardia, diaphoresis, hypertension, tremors, mydriasis, positional nystagmus, | ||||
| Subarachnoid hemorrhage[7] | ✔ | Xanthochromia[8] | CT scan without contrast[9][10] | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | Trauma/fall | Confusion, dizziness, nausea, vomiting | |
| Stroke | ✔ | Normal | CT scan without contrast | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | TIAs, hypertension, diabetes mellitus | Speech difficulty, gait abnormality | ||||
| Neurosyphilis[11][12] | ✔ | ↑ Leukocytes and protein | CSF VDRL-specifc
CSF FTA-Ab -sensitive[13] |
✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | Unprotected sexual intercourse, STIs | Blindness, confusion, depression,
Abnormal gait | |||
| Viral encephalitis | ✔ | Increased RBCS or xanthochromia, mononuclear lymphocytosis, high protein content, normal glucose | Clinical assesment | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | Tick bite/mosquito bite/ viral prodome for several days | Extreme lethargy, rash hepatosplenomegaly, lymphadenopathy, behavioural changes | ||
| Herpes simplex encephalitis | ✔ | Clinical assesment | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | History of hypertension | Delirium, cortical blindness, cerebral edema, seizure | |||||
| Wernicke’s encephalopathy | Normal | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | History of alcohal abuse | Ophthalmoplegia, confusion | ||||||||
| CNS abscess | ✔ | ↑ leukocytes >100,000/ul, ↓ glucose and ↑ protien, ↑ red blood cells, lactic acid >500mg | Contrast enhanced MRI is more sensitive and specific,
Histopathological examination of brain tissue |
✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | History of drug abuse, endocarditis, ↓ immune status | High grade fever, fatigue,nausea, vomiting | ||
| Drug toxicity | ✔ | ✔ | Lithium, Sedatives, phenytoin, carbamazepine | |||||||||||
| Conversion disorder | Diagnosis of exclusion | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | Tremors, blindness, difficulty swallowing | |||||||
| Electrolyte disturbance | ↓ or ↑ | Depends on the cause | ✔ | ✔ | Confusion, seizures | |||||||||
| Febrile convulsion | Not performed in first simple febrile seizures | Clinical diagnosis and EEG | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | Family history of febrile seizures, viral illness or gastroenteritis | Age > 1 month, | ||||||
| Subdural empyema | ✔ | Clinical assesment and MRI | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | History of relapses and remissions | Blurry vision, urinary incontinence, fatigue | ||||
| Hypoglycemia | ↓ or ↑ | Serum blood glucose | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | History of diabetes | Palpitations, sweating, dizziness, low serum, glucose | |||||||
Differentiating brain abscess in immunocompromised host
Brain abscess is common among immunocompromised patients who are at high risk for other fungal, bacterial, and viral infections. It should be differentiated from the following diseases:
| Disease | Differentiating signs and symptoms | Differentiating tests |
|---|---|---|
| CNS lymphoma[14] |
|
|
| Disseminated tuberculosis[15] |
|
|
| Aspergillosis[16] |
|
|
| Cryptococcosis |
|
|
| Chagas disease[17] |
|
|
| CMV infection[18] |
|
|
| HSV infection[19] |
|
|
| Varicella Zoster infection[20] |
|
|
| Brain abscess[21][22] |
|
|
| Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy[23] |
|
| Disease | Prominent clinical features | Lab findings | Radiological findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neurocysticercosis |
|
|
|
| Brain abscess |
|
|
|
| Brain tumors |
|
| |
| Brain tuberculoma |
|
|
|
| Neurosarcoidosis |
|
|
|
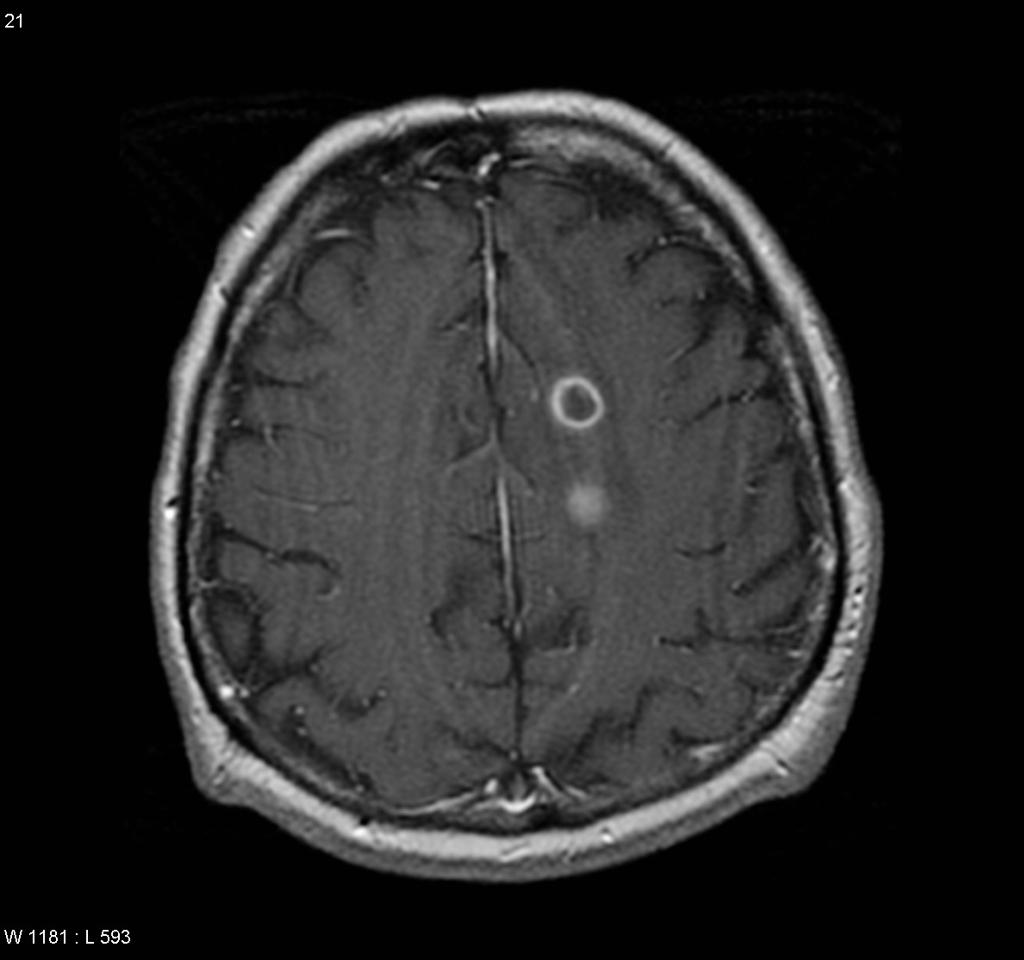 |
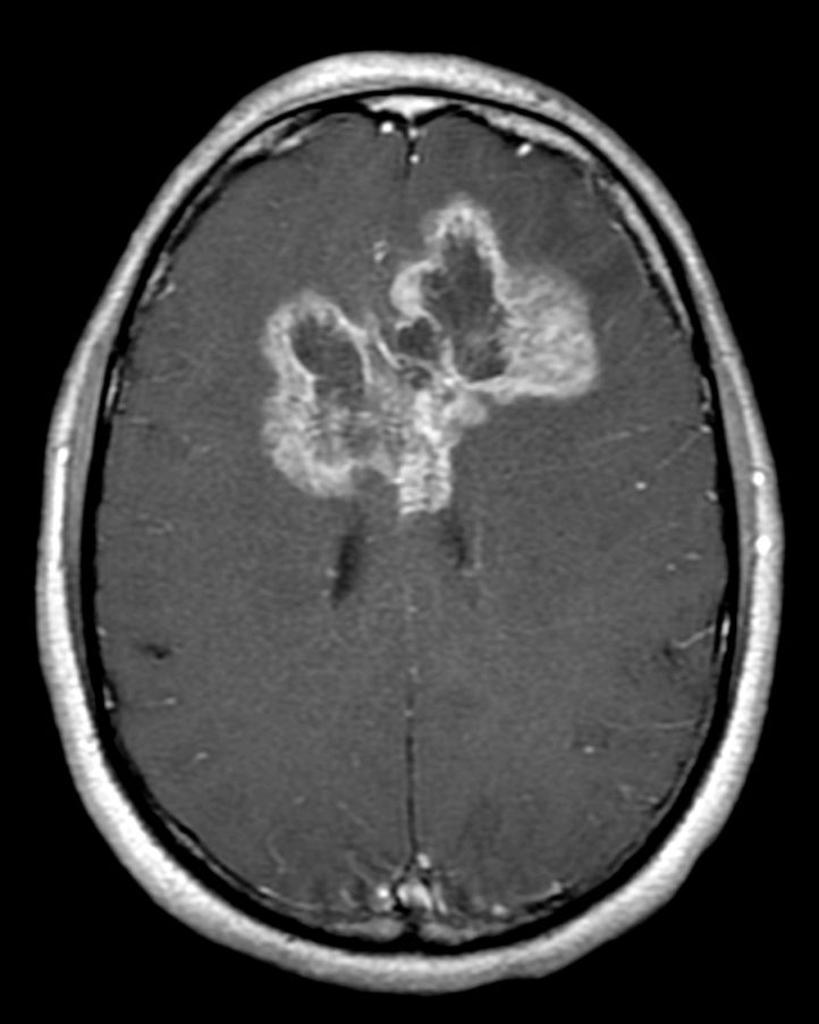 |
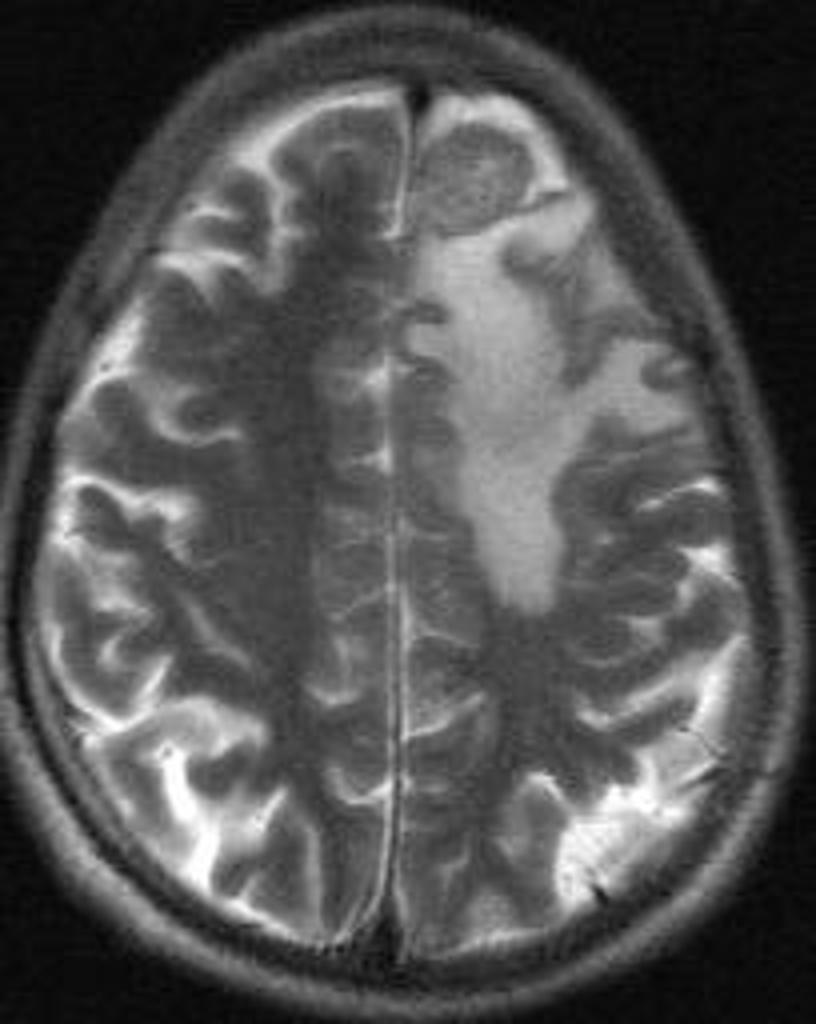 |
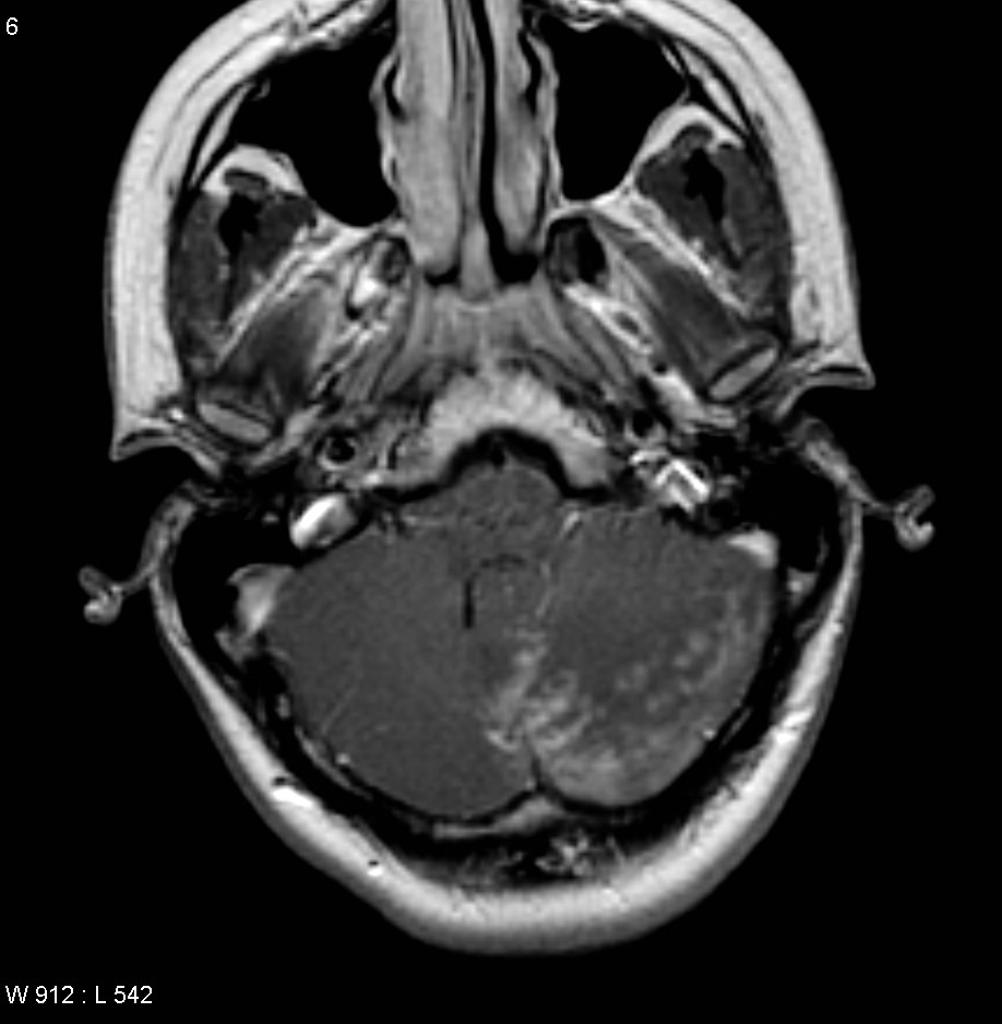 |
|---|
References
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 Desprechins B, Stadnik T, Koerts G, Shabana W, Breucq C, Osteaux M (1999). "Use of diffusion-weighted MR imaging in differential diagnosis between intracerebral necrotic tumors and cerebral abscesses". AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 20 (7): 1252–7. PMID 10472982.
- ↑ Jump up to: 2.0 2.1 Ruiz A, Ganz WI, Post MJ, Camp A, Landy H, Mallin W; et al. (1994). "Use of thallium-201 brain SPECT to differentiate cerebral lymphoma from toxoplasma encephalitis in AIDS patients". AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 15 (10): 1885–94. PMID 7863938.
- ↑ Bavelloni A, Piazzi M, Raffini M, Faenza I, Blalock WL (2015). "Prohibitin 2: At a communications crossroads". IUBMB Life. 67 (4): 239–54. doi:10.1002/iub.1366. PMID 25904163.
- ↑ Soffer D (1976) Brain tumors simulating purulent meningitis. Eur Neurol 14 (3):192-7. PMID: 1278192
- ↑ Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedpmid3883130 - ↑ Weston CL, Glantz MJ, Connor JR (2011). "Detection of cancer cells in the cerebrospinal fluid: current methods and future directions". Fluids Barriers CNS. 8 (1): 14. doi:10.1186/2045-8118-8-14. PMC 3059292. PMID 21371327.
- ↑ Yeh ST, Lee WJ, Lin HJ, Chen CY, Te AL, Lin HJ (2003) Nonaneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage secondary to tuberculous meningitis: report of two cases. J Emerg Med 25 (3):265-70. PMID: 14585453
- ↑ Lee MC, Heaney LM, Jacobson RL, Klassen AC (1975). "Cerebrospinal fluid in cerebral hemorrhage and infarction". Stroke. 6 (6): 638–41. PMID 1198628.
- ↑ Birenbaum D, Bancroft LW, Felsberg GJ (2011). "Imaging in acute stroke". West J Emerg Med. 12 (1): 67–76. PMC 3088377. PMID 21694755.
- ↑ DeLaPaz RL, Wippold FJ, Cornelius RS, Amin-Hanjani S, Angtuaco EJ, Broderick DF; et al. (2011). "ACR Appropriateness Criteria® on cerebrovascular disease". J Am Coll Radiol. 8 (8): 532–8. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2011.05.010. PMID 21807345.
- ↑ Liu LL, Zheng WH, Tong ML, Liu GL, Zhang HL, Fu ZG; et al. (2012). "Ischemic stroke as a primary symptom of neurosyphilis among HIV-negative emergency patients". J Neurol Sci. 317 (1–2): 35–9. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2012.03.003. PMID 22482824.
- ↑ Berger JR, Dean D (2014). "Neurosyphilis". Handb Clin Neurol. 121: 1461–72. doi:10.1016/B978-0-7020-4088-7.00098-5. PMID 24365430.
- ↑ Ho EL, Marra CM (2012). "Treponemal tests for neurosyphilis--less accurate than what we thought?". Sex Transm Dis. 39 (4): 298–9. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e31824ee574. PMC 3746559. PMID 22421697.
- ↑ Gerstner ER, Batchelor TT (2010). "Primary central nervous system lymphoma". Arch. Neurol. 67 (3): 291–7. doi:10.1001/archneurol.2010.3. PMID 20212226.
- ↑ von Reyn CF, Kimambo S, Mtei L, Arbeit RD, Maro I, Bakari M, Matee M, Lahey T, Adams LV, Black W, Mackenzie T, Lyimo J, Tvaroha S, Waddell R, Kreiswirth B, Horsburgh CR, Pallangyo K (2011). "Disseminated tuberculosis in human immunodeficiency virus infection: ineffective immunity, polyclonal disease and high mortality". Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 15 (8): 1087–92. doi:10.5588/ijtld.10.0517. PMID 21740673.
- ↑ Latgé JP (1999). "Aspergillus fumigatus and aspergillosis". Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 12 (2): 310–50. PMC 88920. PMID 10194462.
- ↑ Rassi A, Rassi A, Marin-Neto JA (2010). "Chagas disease". Lancet. 375 (9723): 1388–402. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60061-X. PMID 20399979.
- ↑ Emery VC (2001). "Investigation of CMV disease in immunocompromised patients". J. Clin. Pathol. 54 (2): 84–8. PMC 1731357. PMID 11215290.
- ↑ Bustamante CI, Wade JC (1991). "Herpes simplex virus infection in the immunocompromised cancer patient". J. Clin. Oncol. 9 (10): 1903–15. doi:10.1200/JCO.1991.9.10.1903. PMID 1919640.
- ↑ Hambleton S (2005). "Chickenpox". Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 18 (3): 235–40. PMID 15864101.
- ↑ Alvis Miranda H, Castellar-Leones SM, Elzain MA, Moscote-Salazar LR (2013). "Brain abscess: Current management". J Neurosci Rural Pract. 4 (Suppl 1): S67–81. doi:10.4103/0976-3147.116472. PMC 3808066. PMID 24174804.
- ↑ Patel K, Clifford DB (2014). "Bacterial brain abscess". Neurohospitalist. 4 (4): 196–204. doi:10.1177/1941874414540684. PMC 4212419. PMID 25360205.
- ↑ Tan CS, Koralnik IJ (2010). "Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy and other disorders caused by JC virus: clinical features and pathogenesis". Lancet Neurol. 9 (4): 425–37. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(10)70040-5. PMC 2880524. PMID 20298966.
- ↑ Brouwer MC, Tunkel AR, McKhann GM, van de Beek D (2014). "Brain abscess". N. Engl. J. Med. 371 (5): 447–56. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1301635. PMID 25075836.
- ↑ "Brain Abscess — NEJM".
- ↑ Jump up to: 26.0 26.1 "Primary Brain Tumors in Adults - American Family Physician".
- ↑ "The Journal of Association of Chest Physicians - Tuberculoma of the brain - A diagnostic dilemma: Magnetic resonance spectroscopy a new ray of hope : Download PDF".
- ↑ Jump up to: 28.0 28.1 "Neurosarcoidosis".