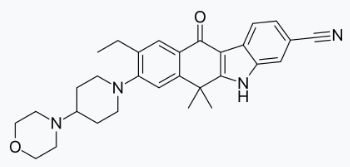
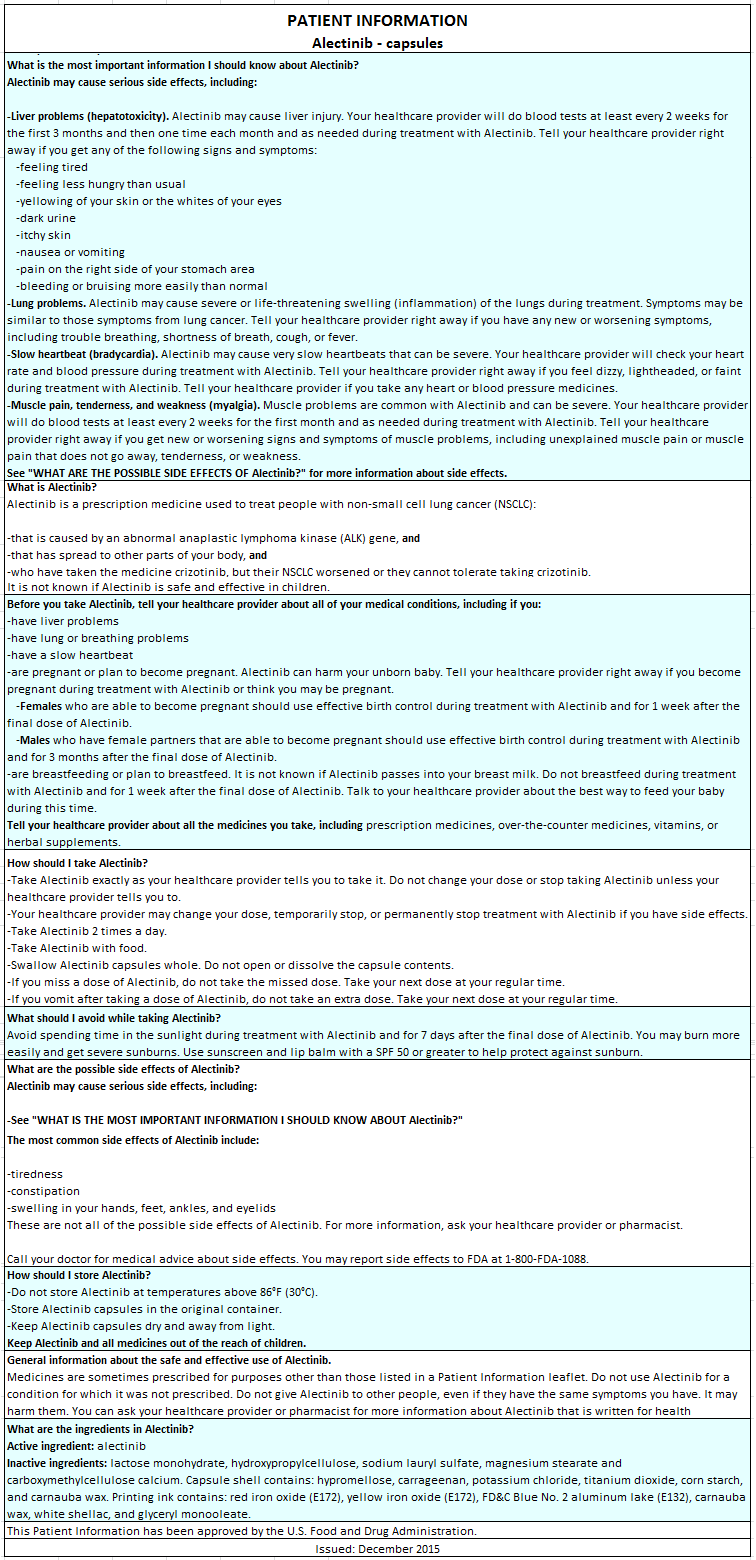
Alectinib
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Martin Nino [2]
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Alectinib is a kinase inhibitor that is FDA approved for the treatment of patients with anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-positive, metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who have progressed on or are intolerant to crizotinib. Common adverse reactions include fatigue, constipation, edema and myalgia (≥20%).
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Indications
Alectinib is indicated for the treatment of patients with anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-positive, metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who have progressed on or are intolerant to crizotinib.
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on tumor response rate and duration of response. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial.
Dosage
- Dosing and Administration
- The recommended dose of Alectinib is 600 mg orally twice daily with food. Administer Alectinib until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
- Do not open or dissolve the contents of the capsule.
- If a dose of Alectinib is missed or vomiting occurs after taking a dose of Alectinib, take the next dose at the scheduled time.
- Dose Modifications for Adverse Reactions
- The dose reduction schedule for Alectinib is provided in TABLE 1.
- Table 1. Alectinib Dose Reduction Schedule
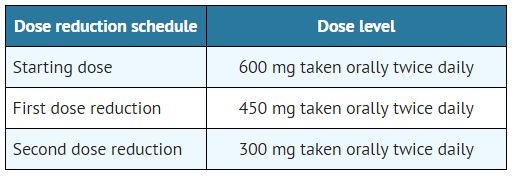
- Discontinue if patients are unable to tolerate the 300 mg twice daily dose.
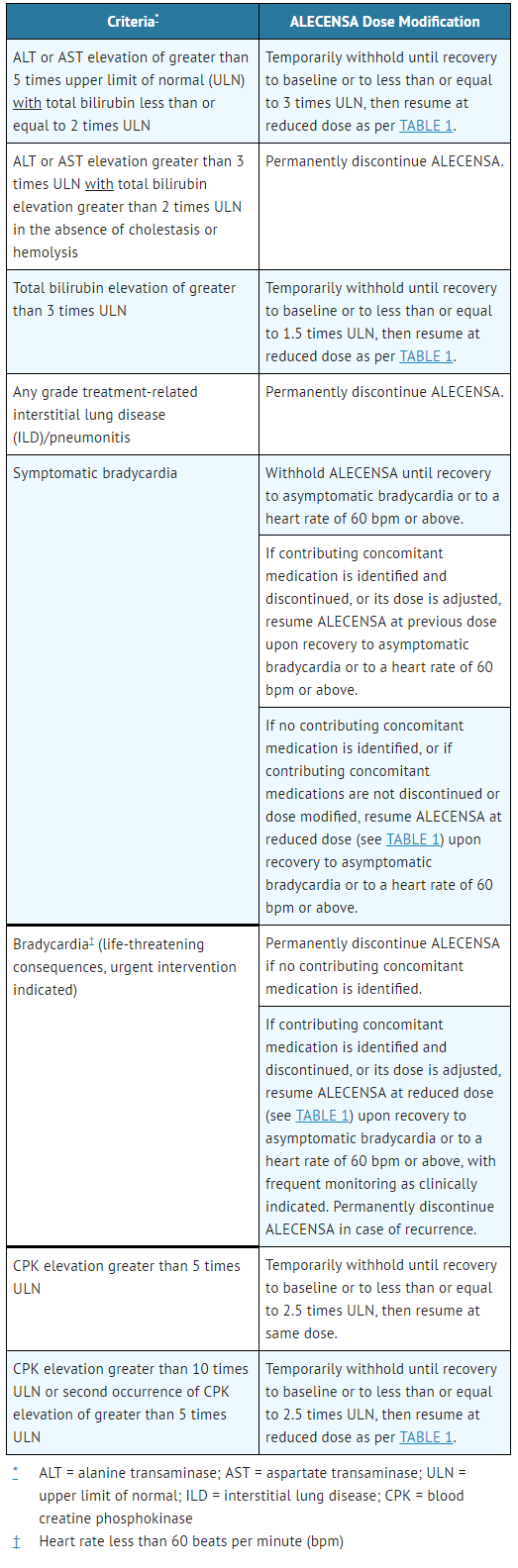
- Recommendations for dose modifications of Alectinib in case of adverse reactions are provided in TABLE 2.
- Table 2. Alectinib Dose Modifications for Adverse Reactions
ALECENSA: Alectinib's Brand name
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Alectinib in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Alectinib in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
The safety and effectiveness of Alectinib in pediatric patients have not been established.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Alectinib in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Alectinib in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
None
Warnings
Elevations of AST greater than 5 times the upper limit of normal (ULN) occurred in 3.6% of patients, and elevations of ALT greater than 5 times the ULN occurred in 4.8% of patients. Elevations of bilirubin greater than 3 times the ULN occurred in 2.8% of patients in Studies 1 and 2. The majority (76% of the patients with hepatic transaminase elevations and 68% of the patients with bilirubin elevations) of these events occurred during the first 3 months of treatment. Four patients discontinued Alectinib for Grade 3-4 AST and/or ALT elevations, and 3 patients discontinued Alectinib for Grade 3 bilirubin elevations. In Studies 1 and 2, two patients with Grade 3-4 AST/ALT elevations had documented drug induced liver injury by liver biopsy. Concurrent elevations in ALT or AST greater than or equal to three times the ULN and total bilirubin greater than or equal to two times the ULN, with normal alkaline phosphatase, occurred in less than 1% of patients treated with Alectinib across clinical trials.
Monitor liver function tests including ALT, AST, and total bilirubin every 2 weeks during the first 3 months of treatment, then once a month and as clinically indicated, with more frequent testing in patients who develop transaminase and bilirubin elevations. Based on the severity of the adverse drug reaction, withhold Alectinib and resume at a reduced dose, or permanently discontinue Alectinib as described in Table 2.
Severe ILD (Grade 3) occurred in one (0.4%) of 253 patients exposed to Alectinib in Studies 1 and 2.
Promptly investigate for ILD/pneumonitis in any patient who presents with worsening of respiratory symptoms indicative of ILD/pneumonitis (e.g., dyspnea, cough and fever).
Immediately withhold Alectinib treatment in patients diagnosed with ILD/pneumonitis and permanently discontinue Alectinib if no other potential causes of ILD/pneumonitis have been identified.
Symptomatic bradycardia can occur with Alectinib. Cases of bradycardia (7.5%) have been reported in patients treated with Alectinib. Twenty percent of 221 patients treated with Alectinib for whom serial ECGs were available had heart rates of less than 50 beats per minute (bpm).
Monitor heart rate and blood pressure regularly. Dose modification is not required in cases of asymptomatic bradycardia. In cases of symptomatic bradycardia that is not life-threatening, withhold Alectinib until recovery to asymptomatic bradycardia or to a heart rate of 60 bpm or above and evaluate concomitant medications known to cause bradycardia, as well as anti-hypertensive medications. If attributable to a concomitant medication, resume Alectinib at a reduced dose (see TABLE 1) upon recovery to asymptomatic bradycardia or to a heart rate of 60 bpm or above, with frequent monitoring as clinically indicated. Permanently discontinue Alectinib in case of recurrence. Permanently discontinue Alectinib in cases of life-threatening bradycardia if no contributing concomitant medication is identified.
Severe Myalgia and Creatine Phosphokinase (CPK) Elevation
Myalgia or musculoskeletal pain occurred in 29% of patients in Studies 1 and 2. The incidence of Grade 3 myalgia/musculoskeletal pain was 1.2%. Dose modifications for myalgia/musculoskeletal pain were required in 0.8% of patients.
Elevations of CPK occurred in 43% of 218 patients with CPK laboratory data available in Study 1 and Study 2. The incidence of Grade 3 elevations of CPK was 4.6%. Median time to Grade 3 CPK elevation was 14 days (interquartile range 13-14 days). Dose modifications for elevation of CPK occurred in 5.0% of patients.
Advise patients to report any unexplained muscle pain, tenderness, or weakness. Assess CPK levels every two weeks for the first month of treatment and as clinically indicated in patients reporting symptoms. Based on the severity of the CPK elevation, withhold Alectinib, then resume or reduce dose [see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION (2.2)].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on findings from animal studies and its mechanism of action, Alectinib can cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women. Administration of alectinib to pregnant rats and rabbits during the period of organogenesis resulted in embryo-fetal toxicity and abortion at maternally toxic doses with exposures approximately 2.7-times those observed in humans with alectinib 600 mg twice daily. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with Alectinib and for 1 week following the final dose.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the label:
- Hepatotoxicity
- Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)/Pneumonitis
- Bradycardia
- Severe Myalgia and Creatine Phosphokinase (CPK) Elevation
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of Alectinib was evaluated in 253 patients with ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treated with Alectinib 600 mg orally twice daily in two clinical trials, Studies 1 and 2. The median duration of exposure to Alectinib was 9.3 months. One hundred sixty-nine patients (67%) were exposed to Alectinib for more than 6 months, and 100 patients (40%) for more than one year. The population characteristics were: median age 53 years, age less than 65 (86%), female (55%), White (74%), Asian (18%), NSCLC adenocarcinoma histology (96%), never or former smoker (98%), ECOG Performance Status (PS) 0 or 1 (91%), and prior chemotherapy treatment (78%).
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 19% of patients; the most frequently reported serious adverse reactions were pulmonary embolism (1.2%), dyspnea (1.2%), and hyperbilirubinemia (1.2%). Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 2.8% of patients and included hemorrhage (0.8%), intestinal perforation (0.4%), dyspnea (0.4%), pulmonary embolism (0.4%), and endocarditis (0.4%). Permanent discontinuation of Alectinib for adverse reactions occurred in 6% of patients. The most frequent adverse reactions that led to permanent discontinuation were hyperbilirubinemia (1.6%), increased ALT levels (1.6%), and increased AST levels (1.2%). Overall, 23% of patients initiating treatment at the recommended dose required at least one dose reduction. The median time to first dose reduction was 48 days. The most frequent adverse reactions that led to dose reductions or interruptions were elevations in bilirubin (6%), CPK (4.3%), ALT (4.0%), and AST (2.8%), and vomiting (2.8%).
TABLE 3 summarizes adverse reactions in Studies 1 and 2.
- Table 3. Adverse Reactions in ≥ 10% (All Grades) or ≥ 2% (Grade 3-4) of Patients in Studies 1 and 2
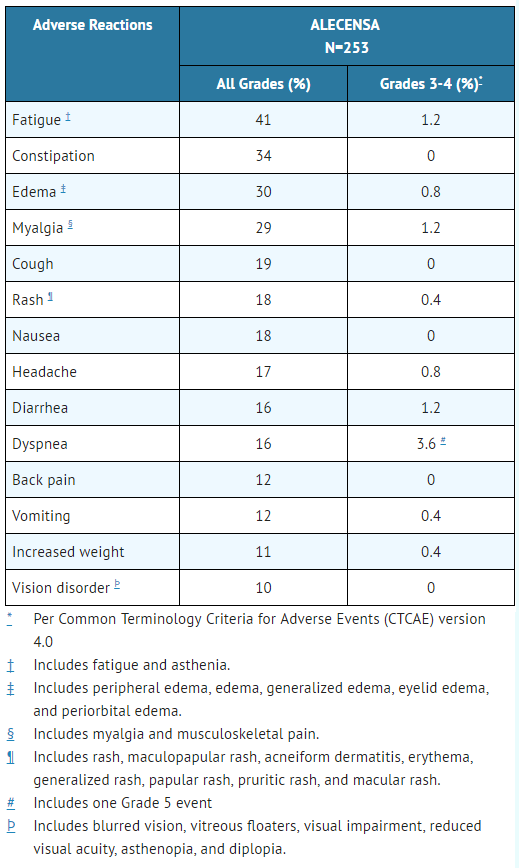
ALECENSA: Alectinib's Brand name
- Additional safety information from clinical trial experience
- Photosensitivity occurred in 9.9% of patients exposed to Alectinib in Studies 1 and 2. Patients were advised to avoid sun exposure and to use broad-spectrum sunscreen. The incidence of Grade 2 photosensitivity was 0.4%; the remaining events were Grade 1 in severity.
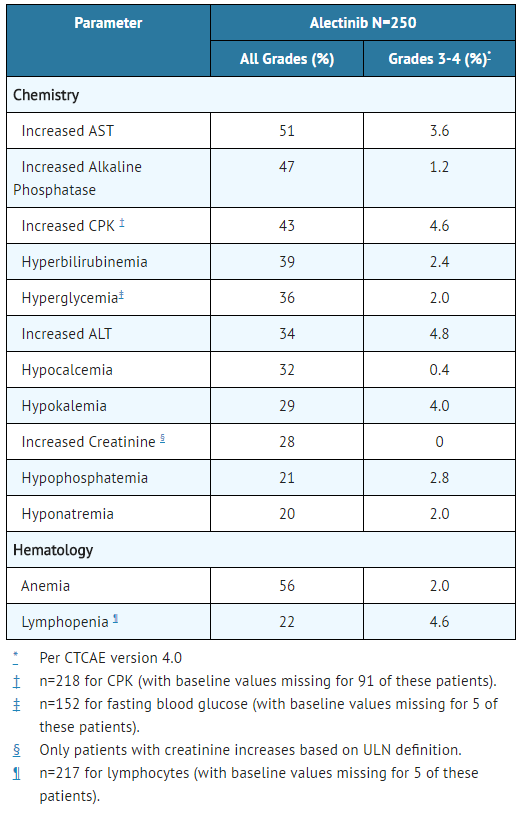
- TABLE 4 summarizes laboratory abnormalities of Alectinib in Studies 1 and 2.
- Table 4. Laboratory Abnormalities Occurring in >20% of Patients in Studies 1 and 2
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Alectinib Postmarketing Experience in the drug label.
Drug Interactions
No pharmacokinetic interactions with alectinib requiring dosage adjustment have been identified.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Risk Summary
- Based on animal studies and its mechanism of action, Alectinib can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. There are no available data on Alectinib use in pregnant women.
- Administration of alectinib to pregnant rats and rabbits by oral gavage during the period of organogenesis resulted in embryo-fetal toxicity and abortion at maternally toxic doses with exposures approximately 2.7-times those observed in humans treated with alectinib at 600 mg twice daily. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
- In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically-recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
- Data
- Animal Data
- In a preliminary rabbit embryo-fetal study, administration of alectinib by oral gavage during the period of organogenesis resulted in abortion or complete embryo-fetal mortality at a maternally toxic dose of 27 mg/kg/day (approximately 2.9-fold the estimated area under the curve (AUC(0-24h,ss)) in humans treated with alectinib 600 mg BID) in three of six pregnant rabbits. The remaining three pregnant rabbits in this group had few live fetuses, decreased fetal and placental weights, and retroesophageal subclavian artery. In a rat preliminary embryo-fetal development study, administration of alectinib during organogenesis resulted in complete litter loss in all pregnant rats at 27 mg/kg/day (approximately 4.5-fold the estimated AUC(0-24h,ss) in humans treated with alectinib 600 mg BID). Doses greater than or equal to 9 mg/kg/day (approximately 2.7-fold the estimated human AUC(0-24h,ss) in humans treated with alectinib 600 mg BID), resulted in maternal toxicity as well as developmental toxicities including decreased fetal weight, dilated ureter, thymic cord, small ventricle and thin ventricle wall, and reduced number of sacral and caudal vertebrae.
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Alectinib in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Alectinib during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
There are no data on the presence of alectinib or its metabolites in human milk, the effects of alectinib on the breast-fed infant, or its effects on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breast-fed infants from alectinib, advise a lactating woman not to breastfeed during treatment with Alectinib and for 1 week after the final dose.
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of Alectinib in pediatric patients have not been established.
- Animal Data
- Juvenile animal studies have not been conducted using alectinib. In general toxicology studies, treatment of rats with doses of alectinib resulting in exposures greater than or equal to approximately 4.5 times those in humans treated with alectinib at 600 mg twice daily resulted in changes in the growing teeth and bones. Findings in teeth included discoloration and changes in tooth size along with histopathological disarrangement of the ameloblast and odontoblast layers. There were also decreases in the trabecular bone and increased osteoclast activity in the femur and sternum.
Geriatic Use
Clinical studies of Alectinib did not include sufficient number of subjects aged 65 and older to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Alectinib with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Alectinib with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment is recommended for patients with mild or moderate renal impairment. The safety of Alectinib in patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/min) or end-stage renal disease has not been studied.
Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment is recommended for patients with mild hepatic impairment (total bilirubin less than or equal to upper limit of normal (ULN) and aspartate transaminase (AST) greater than ULN or total bilirubin greater than 1.0 to 1.5 times ULN and any AST). The safety of Alectinib in patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment has not been studied.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
- Females
- Alectinib can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with Alectinib and for 1 week after the final dose.
- Males
- Based on genotoxicity findings, advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with Alectinib and for 3 months following the final dose.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Alectinib in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
There is limited information regarding Alectinib Administration in the drug label.
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Alectinib Monitoring in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding the compatibility of Alectinib and IV administrations.
Overdosage
No experience with overdose is available. There is no specific antidote for overdose with Alectinib. Alectinib and its major active metabolite M4 are > 99% bound to plasma proteins; therefore, hemodialysis is likely to be ineffective in the treatment of overdose.
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Alectinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor that targets ALK and RET. In nonclinical studies, alectinib inhibited ALK phosphorylation and ALK-mediated activation of the downstream signaling proteins STAT3 and AKT, and decreased tumor cell viability in multiple cell lines harboring ALK fusions, amplifications, or activating mutations. The major active metabolite of alectinib, M4, showed similar in vitro potency and activity.
Alectinib and M4 demonstrated in vitro and in vivo activity against multiple mutant forms of the ALK enzyme, including some mutations identified in NSCLC tumors in patients who have progressed on crizotinib.
In mouse models implanted with tumors carrying ALK fusions, administration of alectinib resulted in antitumor activity and prolonged survival, including in mouse models implanted intracranially with ALK-driven tumor cell lines.
Structure
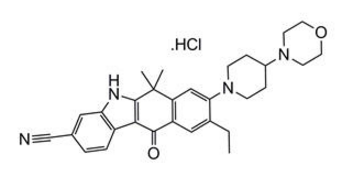
Alectinib is a kinase inhibitor for oral administration. The molecular formula for alectinib is C30H34N4O2 ∙ HCl. The molecular weight is 482.62 g/mol (free base form) and 519.08 g/mol (hydrochloride salt). Alectinib is described chemically as 9-ethyl-6, 6-dimethyl-8-[4-(morpholin-4-yl)piperidin-1-yl]-11-oxo-6, 11-dihydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile hydrochloride. The chemical structure of alectinib is shown below:
Alectinib HCl is a white to yellow white powder or powder with lumps with a pKa of 7.05 (base).
Alectinib is supplied as hard capsules containing 150 mg of alectinib (equivalent to 161.33 mg alectinib HCl) and the following inactive ingredients: lactose monohydrate, hydroxypropylcellulose, sodium lauryl sulfate, magnesium stearate, and carboxymethylcellulose calcium. The capsule shell contains hypromellose, carrageenan, potassium chloride, titanium dioxide, corn starch, and carnauba wax. The printing ink contains red iron oxide (E172), yellow iron oxide (E172), FD&C Blue No. 2 aluminum lake (E132), carnauba wax, white shellac, and glyceryl monooleate.
Pharmacodynamics
- Cardiac Electrophysiology
- The ability of alectinib to prolong the QT interval was assessed in 221 patients administered Alectinib 600 mg twice daily in clinical studies. Alectinib did not prolong the QTc (QT corrected for heart rate) interval to any clinically relevant extent. One patient had a maximum post-baseline QTcF value of greater than 500 msec and one patient had a maximum QTcF change from baseline of greater than 60 msec.
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of alectinib and its major active metabolite M4 have been characterized in patients with ALK-positive NSCLC and healthy subjects.
In patients with ALK-positive NSCLC, the geometric mean (coefficient of variation %) steady-state maximal concentration (Cmax,ss) for alectinib was 665 ng/mL (44%) and for M4 was 246 ng/mL (45%) with peak to trough concentration ratio of 1.2. The geometric mean steady-state area under the curve from 0 to 12 hours (AUC(0-12h,ss)) for alectinib was 7,430 ng*h/mL (46%) and for M4 was 2,810 ng*h/mL (46%). Alectinib exposure is dose proportional across the dose range of 460 mg to 900 mg (i.e., 0.75 to 1.5 times the approved recommended dosage) under fed conditions. Alectinib and M4 reached steady-state concentrations by day 7. The geometric mean accumulation was approximately 6-fold for both alectinib and M4.
- The absolute bioavailability of alectinib was 37% (90% CI: 34%, 40%) under fed conditions.
- A high-fat, high-calorie meal increased the combined exposure (AUC(0-inf)) of alectinib plus M4 by 3.1-fold (90% CI: 2.7, 3.6) following oral administration of a single 600 mg dose of Alectinib.
- The apparent volume of distribution is 4,016 L for alectinib and 10,093 L for M4.
- Alectinib and M4 are bound to human plasma proteins greater than 99%, independent of drug concentration.
- Alectinib concentrations in the cerebrospinal fluid in patients with ALK-positive NSCLC approximate estimated alectinib free concentrations in the plasma.
- In vitro studies suggest that alectinib is not a substrate of P-glycoprotein (P-gp), but M4 is a substrate of P-gp. Alectinib and M4 are not substrates of breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP), organic anion-transporting polypeptide (OATP) 1B1, or OATP1B3.
- Elimination
- Alectinib is metabolized by CYP3A4 to its major active metabolite M4. The geometric mean metabolite/parent exposure ratio at steady-state is 0.40. M4 is subsequently metabolized by CYP3A4. Alectinib and M4 were the main circulating moieties in plasma, constituting 76% of the total radioactivity.
- Ninety-eight percent of the radioactivity was excreted in feces following oral administration of a single radiolabeled dose of alectinib under fed conditions. Eighty-four percent of the dose was excreted in the feces as unchanged alectinib and 6% of the dose was excreted as M4. Excretion of radioactivity in urine was less than 0.5% of administered radiolabeled dose of alectinib.
- Specific Populations
- Age, body weight, mild hepatic impairment, mild to moderate renal impairment (creatinine clearance 30 to 89 mL/min), race (White, Asian, and Other), and sex had no clinically meaningful effect on the systemic exposure of alectinib and M4. The pharmacokinetics of alectinib has not been studied in patients with severe renal impairment, end-stage renal disease or moderate to severe hepatic impairment.
- Drug Interactions
- Effect of Other Drugs on Alectinib
- No clinically meaningful effect on the combined exposure of alectinib plus M4 was observed in clinical studies following co-administration of Alectinib with a strong CYP3A inhibitor (posaconazole), a strong CYP3A inducer (rifampin), or an acid-reducing agent (esomeprazole).
- Effect of Alectinib on Other Drugs
- No clinically meaningful effect on the exposure of midazolam (sensitive CYP3A substrate) or repaglinide (sensitive CYP2C8 substrate) is expected following co-administration with Alectinib.
- In vitro studies suggest that alectinib and M4 do not inhibit CYP1A2, 2B6, 2C9, 2C19 or 2D6.
Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies with alectinib have not been conducted.
Alectinib was not mutagenic in vitro in the bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assay, but was positive with an increased number of micronuclei in a rat bone marrow micronucleus test. The mechanism of micronucleus induction was abnormal chromosome segregation (aneugenicity) and not a clastogenic effect on chromosomes.
No studies in animals have been performed to evaluate the effect of alectinib on fertility. No adverse effects on male and female reproductive organs were observed in general toxicology studies conducted in rats and monkeys.
Clinical Studies
The safety and efficacy of Alectinib were established in two single-arm, multicenter clinical trials (Studies 1 and 2). Patients with locally advanced or metastatic ALK-positive NSCLC, who have progressed on crizotinib, with documented ALK positive NSCLC based on an FDA-approved test, and ECOG PS of 0-2 were enrolled in both studies. Eligibility criteria permitted enrollment of patients with prior chemotherapy and prior CNS radiotherapy provided that CNS metastases were stable for at least two weeks. All patients received Alectinib 600 mg orally twice daily. The major efficacy outcome measure in both studies was objective response rate (ORR) according to Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumours (RECIST v1.1) as evaluated per Independent Review Committee (IRC). Additional outcome measures as evaluated by the IRC included duration of response (DOR), CNS ORR, and CNS DOR.
Study 1 was conducted in North America and enrolled 87 patients. Baseline demographic and disease characteristics in Study 1 were median age 54 years old (range 29 to 79, 18% 65 and over), 84% White and 8% Asian, 55% female, 35% ECOG PS 0 and 55% ECOG PS 1, 100% never or former smokers, 99% Stage IV, 94% adenocarcinoma, and 74% prior chemotherapy. The most common sites of extra-thoracic metastasis included 60% CNS (of whom 65% had received CNS radiation), 43% lymph nodes, 36% bone, and 34% liver.
Study 2 was conducted internationally and enrolled 138 patients. Baseline demographic and disease characteristics in Study 2 were median age 52 years old (range 22 to 79, 10% 65 and over), 67% White and 26% Asian, 56% female, 32% ECOG PS 0 and 59% ECOG PS 1, 98% never or former smokers, 99% Stage IV, 96% adenocarcinoma, and 80% prior chemotherapy. The most common sites of extra-thoracic metastasis included 61% CNS (of whom 73% had received CNS radiation), 51% bone, 38% lymph nodes, and 30% liver.
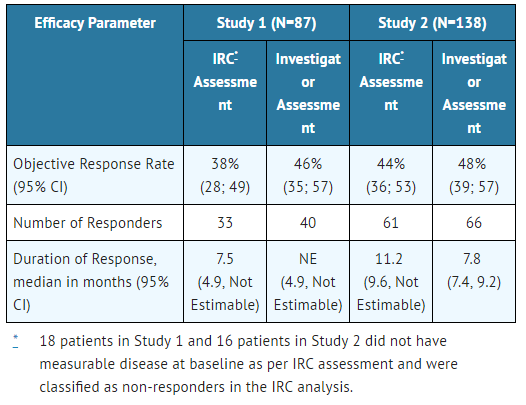
Efficacy results from Studies 1 and 2 in all treated patients are summarized in TABLE 5. The median duration of follow-up on Study 1 was 4.8 months for both IRC and Investigator assessments and on Study 2, 10.9 months for IRC assessment and 7.0 months for Investigator assessment. All responses were partial responses.
- Table 5: Efficacy Results in Studies 1 and 2
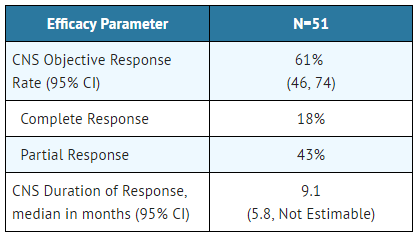
An assessment of ORR and duration of response for CNS metastases in the subgroup of 51 patients in Studies 1 and 2 with baseline measurable lesions in the CNS according to RECIST v1.1 are summarized in TABLE 6. Thirty-five (69%) patients with measurable CNS lesions had received prior brain radiation, including 25 (49%) who completed radiation treatment at least 6 months before starting treatment with Alectinib. Responses were observed irrespective of prior brain radiation status.
- Table 6: CNS Objective Response in Patients with Measurable CNS Lesions in Studies 1 and 2
How Supplied
Hard capsules, white 150 mg capsules with "ALE" printed in black ink on the cap and "150 mg" printed in black ink on the body, available in:
240 capsules per bottle: NDC 50242-130-01
Storage
Do not store above 30°C (86°F). Store in the original container to protect from light and moisture.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Alectinib |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Alectinib |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Inform patients of the following:
- Inform patients of the signs and symptoms of bilirubin and hepatic transaminase elevations. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider immediately for signs or symptoms of bilirubin and hepatic transaminase elevations.
- Inform patients of the risks of severe ILD/pneumonitis. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider immediately to report new or worsening respiratory symptoms.
- Inform patients that symptoms of bradycardia including dizziness, lightheadedness, and syncope can occur while taking Alectinib. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider to report these symptoms and to inform their healthcare provider about the use of any heart or blood pressure medications.
- Inform patients of signs and symptoms of myalgia, including unexplained and/or persistent muscle pain, tenderness, or weakness. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider immediately to report new or worsening symptoms of muscle pain or weakness.
Inform patients of the signs and symptoms of photosensitivity. Advise patients to avoid prolonged sun exposure while taking Alectinib and for at least 7 days after study drug discontinuation and to use proper protection from the sun. Advise patients to use a broad spectrum ultraviolet A (UVA)/ultraviolet B (UVB) sunscreen and lip balm (SPF ≥50) to help protect against potential sunburn.
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
- Alectinib can cause fetal harm if taken during pregnancy. Advise a pregnant woman of the potential risk to a fetus.
- Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with Alectinib and for at least 1 week after the last dose of Alectinib. Advise patients to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy.
- Advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with Alectinib and for 3 months after the last dose.
- Lactation
Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with Alectinib and for one week after the last dose.
- Administration
Instruct patients to take Alectinib twice a day. Advise patients to take Alectinib with food and to swallow Alectinib capsules whole.
- Missed Dose
Advise patients that if a dose of Alectinib is missed or if the patient vomits after taking a dose of Alectinib, patients should be advised not to take an extra dose, but to take the next dose at the regular time.
Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-Alectinib interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor regarding the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
ALECENSA®
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Alectinib Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "Alecensa (alectinib) Capsules, for Oral Use. Full Prescribing Information" (PDF). Genentech USA, Inc. Retrieved 8 February 2017.