Urokinase
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| DrugBank | |
| E number | {{#property:P628}} |
| ECHA InfoCard | {{#property:P2566}}Lua error in Module:EditAtWikidata at line 36: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C1376H2145N383O406S18 |
| Molar mass | 31126.5 g/mol |
| plasminogen activator, urokinase | |
|---|---|
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | PLAU |
| Entrez | 5328 |
| HUGO | 9052 |
| OMIM | 191840 |
| RefSeq | NM_002658 |
| UniProt | P00749 |
| Other data | |
| EC number | 3.4.21.31 |
| Locus | Chr. 10 q24 |
|
WikiDoc Resources for Urokinase |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Urokinase |
|
Media |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Urokinase at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Urokinase at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Urokinase
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Urokinase Discussion groups on Urokinase Directions to Hospitals Treating Urokinase Risk calculators and risk factors for Urokinase
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Urokinase |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
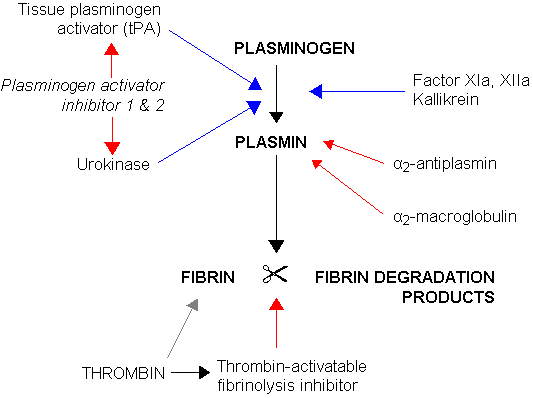
Urokinase (Abbokinase), also called urokinase-type Plasminogen Activator (uPA), is a serine protease (EC 3.4.21.73). Urokinase was originally isolated from human urine, but is present in several physiological locations, such as blood stream and the extracellular matrix. The primary physiological substrate is plasminogen, which is an inactive zymogen form of the serine protease plasmin. Activation of plasmin triggers a proteolysis cascade which, depending on the physiological environment participate in thrombolysis or extracellular matrix degradation. This links urokinase to vascular diseases and cancer.
Molecular characteristics
Urokinase is a 411 residue protein, consisting of three domains: the serine protease domain, the kringle domain and the growth factor domain. Urokinase is synthesized as a zymogen form (prourokinase or single chain urokinase), and is activated by proteolytic cleavage between L158 and I159. The two resulting chains are kept together by a disulfide bond.
Interaction partners
The most important inhibitors of urokinase are the serpins plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) and plasminogen activator inhibitor-2 (PAI-2), which inhibits the protease activity irreversibly. In the extracellular matrix urokinase is tethered to the cell membrane by its interaction to the urokinase receptor.
-
Fibrinolysis (simplified). Blue arrows denote stimulation, and red arrows inhibition.
Urokinase and cancer
Elevated expression levels of urokinase and several other components of the plasminogen activation system are found to be correlated with tumor malignancy. It is believed that the tissue degradation following plasminogen activation, facilitates tissue invasion and thus contributes to metastasis. This makes urokinase an attractive drug target and inhibitors have been sought to be used as anticancer agents. However incompatibilities between the human and murine system hampers clinical evaluation of these agents. Through its interaction with the urokinase receptor, urokinase affects several other aspects of cancer biology such as cells adhesion, migration and cellular mitotic pathways.
Clinical applications
Urokinase is used clinically as a thrombolytic agent in the treatment of severe or massive deep venous thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, myocardial infarction, and occluded intravenous or dialysis cannulas. Recently, Alteplase has replaced urokinase as a thrombolytic drug in acute infarction.
- Pages with script errors
- E number from Wikidata
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Chemical articles with unknown parameter in Infobox drug
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without InChI source
- Articles without UNII source
- Drugs with no legal status
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Protein pages needing a picture
- Genes on human chromosome 10
- Hematology
- Drugs
- EC 3.4.21
- Cardiology