Pancreatitis: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Rohit reddy (talk | contribs) |
||
| (39 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ | __NOTOC__ | ||
{{Infobox_Disease | |||
| Name = Pancreatitis | |||
| Image = Blausen 0699 PancreasAnatomy2.png | |||
| Caption = Pancreas<ref><https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pancreas#/media/File:Blausen_0699_PancreasAnatomy2.png></ref> | |||
}} | }} | ||
{{ | {{Pancreatitis}} | ||
'''For patient information, click [[Acute pancreatitis (patient information)|here]]''' | |||
{{CMG}}, {{AE}}; {{IQ}} | |||
== | == Overview == | ||
Pancreatitis is an [[inflammatory]] disease of the [[pancreas]] characterized by reversible or irreversible changes in [[pancreatic]] structure and function leading to [[inflammation]] and [[fibrosis]]. The concept of [[pancreas]] and [[pancreatic duct]] was first described by Johannes Wirsung of Padua in 1642. [[Pancreatitis]] may be classified as [[acute pancreatitis]], [[chronic pancreatitis]], [[autoimmune pancreatitis]], and [[hereditary pancreatitis]]. Common causes of pancreatitis may include [[gallstones]], [[Hyperlipoproteinemia|hypertriglyceridemia]], alcohol, drugs, genetic, autoimmune, iatrogenic, trauma, infection, surgical causes, and obstruction. Acute pancreatitis usually presents with [[fever]], sharp [[abdominal pain]], nausea and vomiting. Patients with chronic pancreatitis present with dull abdominal pain, [[steatorrhea]], pancreatic [[diabetes]], [[nausea]], [[weight loss]], [[pseudocyst]] and [[pancreatic cancer]]. | |||
=== | == Causes == | ||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
[[ | ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Type of pancreatitis | ||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Causes | |||
|- | |||
|[[Acute pancreatitis]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Gallstone disease|Gallstones]] | |||
* [[Hypertriglyceridemia (patient information)|Hypertriglyceridemia]] | |||
* [[Alcohol]] | |||
* Drugs | |||
* Genetic | |||
* [[Autoimmune]] | |||
* Iatrogenic | |||
* Trauma | |||
* [[Infection]] | |||
* Surgical | |||
* Obstruction | |||
|- | |||
|[[Chronic pancreatitis]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Alcoholic]] | |||
* Tobacco smoking | |||
* [[Hypercalcemia]] | |||
* [[Hyperlipidemia]] | |||
* [[Chronic renal failure]] | |||
* [[Medications]]—phenacetin abuse | |||
* [[Toxins]]—[[Organotin compound|organotin compounds]] (e.g. dibutylin dichloride, DBTC) | |||
* Idiopathic | |||
* Tropical | |||
* [[Genetic]] | |||
* [[Autoimmune]] | |||
* Radiation | |||
* Obstruction | |||
|- | |||
|[[Autoimmune pancreatitis]] | |||
| | |||
* Idiopathic | |||
* Systemic [[autoimmune]] conditions | |||
|- | |||
|[[Hereditary pancreatitis]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Genetic mutations]] | |||
|} | |||
[[Acute pancreatitis]] | == Classification == | ||
[[Pancreatitis]] may be classified as: | |||
* [[Acute pancreatitis]] | |||
* [[Chronic pancreatitis]] | |||
* [[Autoimmune pancreatitis]] | |||
* [[Hereditary pancreatitis]] | |||
== | {{familytree/start}} | ||
{{ | {{familytree | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | B02 | |B01=Upper UTI | B02 = [[Pancreatitis]]}} | ||
[[ | {{familytree | | | | | | | | | |,|-|-|-|-|-|-|-|-|-|v|-|-|^|-|-|v|-|-|-|-|-|-|-|.| }} | ||
{{familytree | | | | | | | | | |!| | | | | | | | | |!| | | | | |!| | | | | | | |!| | | | | | | | | | }} | |||
{{familytree | | | | | | | | | C02 | | | | | | | | C03 | | | | C04 | | | | | | C05 | | C02 = [[Acute pancreatitis]] | C03 = [[Chronic pancreatitis]] | C04 = [[Autoimmune pancreatitis]] | C05 = [[Hereditary pancreatitis]]}} | |||
{{familytree/end}} | |||
== Differential Diagnosis == | |||
== | ===== Differentiating pancreatitis from other diseases on the basis of abdominal pain and weight loss: ===== | ||
Pancreatitis presents most commonly with abdominal pain. Pancreatitis must be differentiated from various disease which present with abdominal pain and weight loss such as [[Peptic Ulcer Disease|peptic ulcer disease]], [[pancreatic carcinoma]], [[gastritis]], and [[inflammatory bowel disease]]. | |||
<span style="font-size:85%">'''Abbreviations:''' | |||
'''[[RUQ]]'''= Right upper quadrant of the abdomen, '''LUQ'''= Left upper quadrant, '''LLQ'''= Left lower quadrant, '''RLQ'''= Right lower quadrant, '''LFT'''= Liver function test, SIRS= [[Systemic inflammatory response syndrome]], '''[[ERCP]]'''= [[Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography]], '''IV'''= Intravenous, '''N'''= Normal, '''AMA'''= Anti mitochondrial antibodies, '''[[LDH]]'''= [[Lactate dehydrogenase]], '''GI'''= Gastrointestinal, '''CXR'''= Chest X ray, '''IgA'''= [[Immunoglobulin A]], '''IgG'''= [[Immunoglobulin G]], '''IgM'''= [[Immunoglobulin M]], '''CT'''= [[Computed tomography]], '''[[PMN]]'''= Polymorphonuclear cells, '''[[ESR]]'''= [[Erythrocyte sedimentation rate]], '''[[CRP]]'''= [[C-reactive protein]], TS= [[Transferrin saturation]], SF= Serum [[Ferritin]], SMA= [[Superior mesenteric artery]], SMV= [[Superior mesenteric vein]], ECG= [[Electrocardiogram]]</span> | |||
<small><small> | |||
{| align="center" | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
{| style="border: 0px; font-size: 90%; margin: 3px;" align="center" | |||
! rowspan="3" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Disease | |||
| colspan="13" rowspan="1" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |'''Clinical manifestations''' | |||
! colspan="2" rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Diagnosis | |||
! rowspan="3" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Comments | |||
|- | |||
| colspan="9" rowspan="1" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |'''Symptoms''' | |||
! colspan="4" rowspan="1" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" | Signs | |||
|- | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Abdominal Pain | |||
! colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" | Fever | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Rigors and chills | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Nausea or vomiting | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Jaundice | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Constipation | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Diarrhea | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Weight loss | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |GI bleeding | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Hypo- | |||
tension | |||
! colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" | Guarding | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Rebound Tenderness | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Bowel sounds | |||
! colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" | Lab Findings | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Imaging | |||
|- | |||
| colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Chronic pancreatitis]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |[[Epigastric]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | ± | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | ± | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |− | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |N | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* Increased [[amylase]] / [[lipase]] | |||
* Increased stool fat content | |||
* Pancreatic function test | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |CT scan | |||
* Calcification | |||
* Pseudocyst | |||
* Dilation of main pancreatic duct | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* Predisposes to pancreatic cancer | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Pancreatic carcinoma]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |[[Epigastric]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |− | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" | N | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* ↑ [[Alkaline phosphatase]] | |||
* ↑ [[Bilirubin|serum bilirubin]] | |||
* ↑ [[gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase]] | |||
* ↑ [[CA 19-9]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* [[Computed tomography|MDCT]] with [[Positron emission tomography|PET]]/[[Computed tomography|CT]] | |||
* MRI | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
[[Skin]] manifestations may include: | |||
* [[Bullous pemphigoid]] | |||
* [[Mucous membrane pemphigoid|Cicatricial pemphigoid]] | |||
* [[Thrombophlebitis|Migratory superficial thrombophlebitis]] (classic [[Trousseau's syndrome]]) | |||
* [[Panniculitis|Pancreatic panniculitis]] | |||
|- | |||
| colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" | [[Peptic Ulcer Disease|Peptic ulcer disease]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Diffuse | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | ± | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | <nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | <nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | | |||
* Gastric ulcer- [[melena]] and [[hematemesis]] | |||
* Duodenal ulcer- [[melena]] and [[hematochezia]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Positive if perforated | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Positive if perforated | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Positive if perforated | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | N | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* Ascitic fluid | |||
** [[LDH]] > serum [[LDH]] | |||
** Glucose < 50mg/dl | |||
** Total protein > 1g/dl | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* Air under [[diaphragm]] in upright [[CXR]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* Upper GI [[endoscopy]] for diagnosis | |||
|- | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Disease | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Abdominal Pain | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Fever | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Rigors and chills | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Nausea or vomiting | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Jaundice | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Constipation | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Diarrhea | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Weight loss | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |GI bleeding | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Hypo- | |||
tension | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Guarding | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Rebound Tenderness | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Bowel sounds | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Lab Findings | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Imaging | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Comments | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Gastritis|Gastritis]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |[[Epigastric]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | ± | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | <nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Positive in chronic gastritis | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |N | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* [[H.pylori infection diagnostic tests]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* [[Endoscopy]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* [[H.pylori gastritis guideline recommendation]] | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Gastric outlet obstruction|Gastric outlet obstruction]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |[[Epigastric]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | ± | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | <nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Hyperactive | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* [[Complete blood count]] | |||
* [[Basic metabolic panel]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* [[Abdominal x-ray]]- air fluid level | |||
* Barium upper GI studies- narrowed pylorus | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* Succussion splash | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" |Gastroparesis | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Epigastric | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |− | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | ± | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Hyperactive/hypoactive | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
*Hemoglobin | |||
*Fasting plasma glucose | |||
*Serum total protein, albumin, thyrotropin (TSH), and an antinuclear antibody (ANA) titer | |||
*HbA1c | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
*Scintigraphic gastric emptying | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
*Succussion splash | |||
*Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) | |||
*Full thickness gastric and small intestinal biopsy | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Dumping syndrome]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Lower and then diffuse | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |− | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |− | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Hyperactive | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* Glucose challenge test | |||
* Hydrogen breath test | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* Upper GI series | |||
* Gastric emptying study | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* Postgastrectomy | |||
|- | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Disease | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Abdominal Pain | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Fever | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Rigors and chills | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Nausea or vomiting | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Jaundice | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Constipation | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Diarrhea | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Weight loss | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |GI bleeding | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Hypo- | |||
tension | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Guarding | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Rebound Tenderness | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Bowel sounds | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Lab Findings | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Imaging | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Comments | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Inflammatory bowel disease]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Diffuse | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | ± | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | ± | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Normal or hyperactive | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* [[Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody]] ([[P-ANCA]]) in [[Ulcerative colitis]] | |||
* [[Anti saccharomyces cerevisiae antibodies]] (ASCA) in [[Crohn's disease]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* [[String sign]] on [[abdominal x-ray]] in [[Crohn's disease]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
Extra intestinal findings: | |||
* [[Uveitis]] | |||
* [[Arthritis]] | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Irritable bowel syndrome]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Diffuse | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | ± | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | ± | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |N | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Normal | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Normal | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Symptomatic treatment | |||
* High [[dietary fiber]] | |||
* [[Osmotic]] [[laxatives]] | |||
* [[Antispasmodic]] drugs | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Whipple's disease]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Diffuse | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | ± | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | ± | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | ± | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |N | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* [[Thrombocytopenia]] | |||
* [[Hypoalbuminemia]] | |||
* [[Small intestinal]] [[biopsy]] for [[Tropheryma whipplei]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |[[Whipple's disease other diagnostic studies|Endoscopy]] is used to confirm diagnosis. | |||
Images used to find complications | |||
*[[Whipple's disease x ray|Chest and joint x-ray]] | |||
*[[Whipple's disease CT|CT]] | |||
*[[Whipple's disease MRI|MRI]] | |||
*[[Whipple's disease ultrasound|Echocardiography]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Extra intestinal findings: | |||
* [[Uveitis]] | |||
* [[Endocarditis]] | |||
* [[Encephalitis]] | |||
* [[Dementia]] | |||
* [[Hepatosplenomegaly]] | |||
* [[Arthritis]] | |||
* [[Ascites]] | |||
|- | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Disease | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Abdominal Pain | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Fever | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Rigors and chills | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Nausea or vomiting | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Jaundice | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Constipation | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Diarrhea | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Weight loss | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |GI bleeding | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Hypo- | |||
tension | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Guarding | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Rebound Tenderness | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Bowel sounds | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Lab Findings | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Imaging | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Comments | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Tropical sprue]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Diffuse | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |N | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* Fat soluble vitamin deficiency | |||
* [[Hypoalbuminemia]] | |||
* Fecal stool test | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Barium studies: | |||
* Dilation and edema of mucosal folds | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* [[Steatorrhea]]- 10-40 g/day (Normal=5 g/day) | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Celiac disease]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Diffuse | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Hyperactive | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* [[IgA]] endomysial antibody | |||
* [[IgA]] [[tissue transglutaminase]] antibody | |||
* [[Anti-gliadin antibodies|Anti-gliadin antibody]] | |||
* Small bowel biopsy | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |US: | |||
* Bull’s eye or target pattern | |||
* Pseudokidney sign | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* Gluten allergy | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" |Colon carcinoma | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Diffuse/localized | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | ± | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | ± | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | ± | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* Normal or hyperactive if obstruction present | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* CBC | |||
* Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* Colonoscopy | |||
* Flexible sigmoidoscopy | |||
* Barium enema | |||
* CT colonography | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* PILLCAM 2: A colon capsule for CRC screening may be used in patients with an incomplete colonoscopy who lacks obstruction | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Hepatitis|Viral hepatitis]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |[[RUQ]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Positive in Hep A and E | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Positive in fulminant hepatitis | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Positive in acute | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |N | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* Abnormal LFTs | |||
* Viral serology | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* US | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* Hep A and E have fecal-oral route of transmission | |||
* Hep B and C transmits via blood transfusion and sexual contact. | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Liver abscess]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |RUQ | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | ± | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | ± | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Normal or hypoactive | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* CBC | |||
* Blood cultures | |||
* Abnormal [[Liver function test|liver function tests]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* US | |||
* CT | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Hepatocellular carcinoma]]/Metastasis | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |RUQ | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* Normal | |||
* Hyperactive if obstruction present | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* High levels of [[Alpha-fetoprotein|AFP]] in serum | |||
* Abnormal [[Liver function test|liver function tests]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* US | |||
* CT | |||
* Liver biopsy | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
Other symptoms: | |||
* [[Splenomegaly]] | |||
* [[Variceal bleeding]] | |||
* [[Ascites]] | |||
* [[Spider nevi]] | |||
* [[Asterixis]] | |||
|- | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Disease | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Abdominal Pain | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Fever | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Rigors and chills | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Nausea or vomiting | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Jaundice | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Constipation | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Diarrhea | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Weight loss | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |GI bleeding | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Hypo- | |||
tension | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Guarding | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Rebound Tenderness | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Bowel sounds | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Lab Findings | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Imaging | |||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Comments | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Cirrhosis|Cirrhosis]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |[[RUQ]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |N | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* [[Hypoalbuminemia]] | |||
* Prolonged PT | |||
* Abnormal LFTs | |||
* [[Hyponatremia]] | |||
* [[Thrombocytopenia]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |US | |||
* Nodular, shrunken liver | |||
* [[Ascites]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* Stigmata of liver disease | |||
* Cruveilhier- Baumgarten murmur | |||
|- | |||
| colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" |Small bowel obstruction | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Diffuse | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | ± | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Hyperactive then absent | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* [[Leukocytosis]] with left shift indicates complications | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |[[Abdominal X-ray|Abdominal X ray]] | |||
* Dilated loops of bowel with air fluid levels | |||
* Gasless abdomen | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* "Target sign"– , indicative of intussusception | |||
* Venous cut-off sign" – suggests thrombosis | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Mesenteric ischemia]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Periumbilical | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Positive if bowel becomes gangrenous | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Positive if bowel becomes gangrenous | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Positive if bowel becomes gangrenous | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Hyperactive to absent | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* [[Leukocytosis]] and [[lactic acidosis]] | |||
* [[Amylase]] levels | |||
* [[D-dimer]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |CT angiography | |||
* SMA or SMV thrombosis | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* Also known as abdominal angina that worsens with eating | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Ischemic colitis|Acute ischemic colitis]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Diffuse | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | ± | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Hyperactive then absent | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* [[Leukocytosis]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |[[Abdominal x-ray]] | |||
* Distension and pneumatosis | |||
CT scan | |||
* Double halo appearance, thumbprinting | |||
* Thickening of bowel | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* May lead to shock | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Diffuse | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | ± | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |N | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* [[Fibrinogen]] | |||
* [[D-dimer]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* Focused Assessment with Sonography in Trauma (FAST) | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* Unstable hemodynamics | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Pleural empyema]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |[[RUQ]]/[[Epigastric]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | ± | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | − | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |N | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* [[Thoracentesis]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |[[Chest X-ray]] | |||
* Pleural opacity | |||
* Localization of effusion | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Physical examination | |||
* Crackles | |||
* [[Egophony]] | |||
* Increased [[tactile fremitus]] | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
|} | |||
<small></small> | |||
[[pl:Zapalenie trzustki]] | |||
{{WikiDoc Help Menu}} | |||
{{WikiDoc Sources}} | |||
<references /> | |||
{{ | |||
[[Category:Gastroenterology]] | [[Category:Gastroenterology]] | ||
| Line 254: | Line 745: | ||
[[Category:Abdominal pain]] | [[Category:Abdominal pain]] | ||
[[Category:Emergency medicine]] | [[Category:Emergency medicine]] | ||
Latest revision as of 19:32, 23 August 2021
| Pancreatitis | |
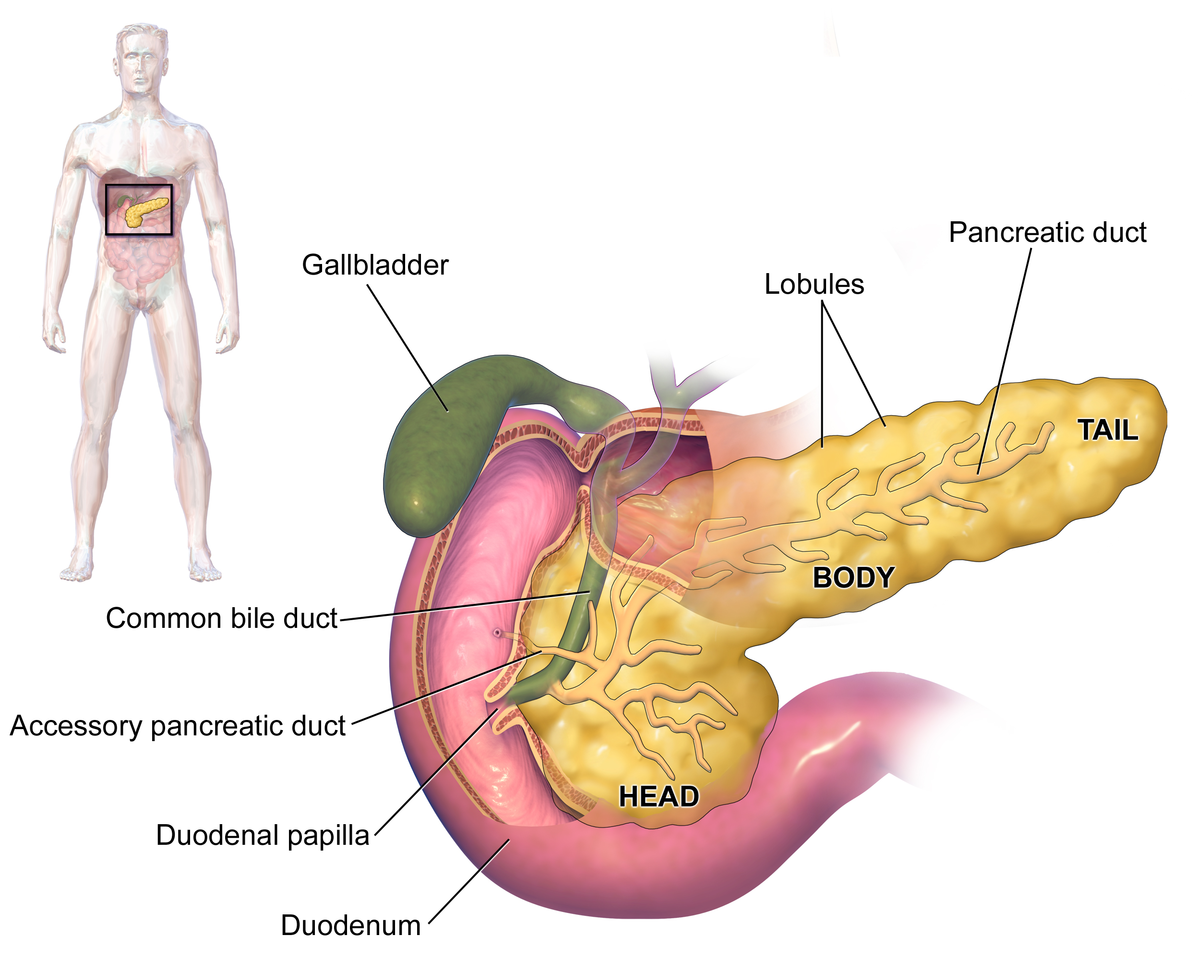 | |
|---|---|
| Pancreas[1] |
|
Pancreatitis Main Page |
For patient information, click here
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1], Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: ; Iqra Qamar M.D.[2]
Overview
Pancreatitis is an inflammatory disease of the pancreas characterized by reversible or irreversible changes in pancreatic structure and function leading to inflammation and fibrosis. The concept of pancreas and pancreatic duct was first described by Johannes Wirsung of Padua in 1642. Pancreatitis may be classified as acute pancreatitis, chronic pancreatitis, autoimmune pancreatitis, and hereditary pancreatitis. Common causes of pancreatitis may include gallstones, hypertriglyceridemia, alcohol, drugs, genetic, autoimmune, iatrogenic, trauma, infection, surgical causes, and obstruction. Acute pancreatitis usually presents with fever, sharp abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting. Patients with chronic pancreatitis present with dull abdominal pain, steatorrhea, pancreatic diabetes, nausea, weight loss, pseudocyst and pancreatic cancer.
Causes
| Type of pancreatitis | Causes |
|---|---|
| Acute pancreatitis |
|
| Chronic pancreatitis |
|
| Autoimmune pancreatitis |
|
| Hereditary pancreatitis |
Classification
Pancreatitis may be classified as:
| Pancreatitis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Acute pancreatitis | Chronic pancreatitis | Autoimmune pancreatitis | Hereditary pancreatitis | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Differential Diagnosis
Differentiating pancreatitis from other diseases on the basis of abdominal pain and weight loss:
Pancreatitis presents most commonly with abdominal pain. Pancreatitis must be differentiated from various disease which present with abdominal pain and weight loss such as peptic ulcer disease, pancreatic carcinoma, gastritis, and inflammatory bowel disease.
Abbreviations: RUQ= Right upper quadrant of the abdomen, LUQ= Left upper quadrant, LLQ= Left lower quadrant, RLQ= Right lower quadrant, LFT= Liver function test, SIRS= Systemic inflammatory response syndrome, ERCP= Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, IV= Intravenous, N= Normal, AMA= Anti mitochondrial antibodies, LDH= Lactate dehydrogenase, GI= Gastrointestinal, CXR= Chest X ray, IgA= Immunoglobulin A, IgG= Immunoglobulin G, IgM= Immunoglobulin M, CT= Computed tomography, PMN= Polymorphonuclear cells, ESR= Erythrocyte sedimentation rate, CRP= C-reactive protein, TS= Transferrin saturation, SF= Serum Ferritin, SMA= Superior mesenteric artery, SMV= Superior mesenteric vein, ECG= Electrocardiogram
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||