Cystitis echocardiography and ultrasound: Difference between revisions
m (Anmol Pitliya moved page Cystitis USG to Cystitis echocardiography and ultrasound without leaving a redirect) |
|||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
[[Ultrasonography]] is not done routinely to diagnose cystitis. [[Ultrasonography]] is sometimes done to diagnose the suspicion of emphysematous cystitis and for detecting the presence of tutors or stones.<ref name="pmid26985484">{{cite journal| author=Wegner J| title=[Cystitis. Ultrasound only in complicated anamnesis]. | journal=MMW Fortschr Med | year= 2015 | volume= 157 | issue= 18 | pages= 17 | pmid=26985484 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=26985484 }} </ref>Imaging findings for chronic hemorrhagic cystitis due to radiation or [[chemotherapy]] include a small fibrosed bladder with a thick wall and resultant [[hydronephrosis]]. [[Calcification]] is only rarely seen.<ref name=rrr> Radiation and Chemotherapy cystitis. Radiopaedia.http://radiopaedia.org/articles/radiation-and-chemotherapy-induced-cystitis Accessed on February 23, 2016</ref> | There are no echocardiography findings associated with cystitis. [[Ultrasonography]] is not done routinely to diagnose cystitis. [[Ultrasonography]] is sometimes done to diagnose the suspicion of emphysematous cystitis and for detecting the presence of tutors or stones.<ref name="pmid26985484">{{cite journal| author=Wegner J| title=[Cystitis. Ultrasound only in complicated anamnesis]. | journal=MMW Fortschr Med | year= 2015 | volume= 157 | issue= 18 | pages= 17 | pmid=26985484 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=26985484 }} </ref>Imaging findings for chronic hemorrhagic cystitis due to radiation or [[chemotherapy]] include a small fibrosed bladder with a thick wall and resultant [[hydronephrosis]]. [[Calcification]] is only rarely seen.<ref name="rrr">Radiation and Chemotherapy cystitis. Radiopaedia.http://radiopaedia.org/articles/radiation-and-chemotherapy-induced-cystitis Accessed on February 23, 2016</ref> | ||
==Ultrasonography | ==Echocardiography== | ||
[[Ultrasonography]] of the [[urinary bladder]] can show presence of a gas in the bladder wall. It can also help to detect the presence of a tumour or a stone. [[Ultrasonography]] is sometimes used to differentiate various aetiologies of lower abdominal pain including emphysematous cystitis, ruptured ectopic pregnancy or [[appendicitis]].<ref | There are no echocardiography findings associated with cystitis. | ||
[[Image:Emphysematous-cystitis-4.jpg | |||
[[Image:Emphysematous Cystitis.gif | == Ultrasonography == | ||
[[Ultrasonography]] of the [[urinary bladder]] can show presence of a gas in the bladder wall. It can also help to detect the presence of a tumour or a stone. [[Ultrasonography]] is sometimes used to differentiate various aetiologies of lower abdominal pain including emphysematous cystitis, ruptured ectopic pregnancy or [[appendicitis]].<ref>Radiopaedia.org</a>. From the case <a href="https://radiopaedia.org/cases/17035">rID: 17035</ref> | |||
[[Image:Emphysematous-cystitis-4.jpg|Source: Radiopedia<ref>Radiopaedia.org</a>. From the case <a href="https://radiopaedia.org/cases/17035">rID: 17035</ref>|500px|thumb|left]] | |||
[[Image:Emphysematous Cystitis.gif|Source: Radiopedia<ref>Radiopaedia.org</a>. From the case <a href="https://radiopaedia.org/cases/17035">rID: 17035</ref>|500px|thumb|left]] | |||
<br style="clear:both" /> | <br style="clear:both" /> | ||
| Line 15: | Line 18: | ||
{{Reflist|2}} | {{Reflist|2}} | ||
{{WH}} | {{WH}} | ||
{{WS}}[[Category:Emergency medicine]] | {{WS}} | ||
[[Category:Emergency medicine]] | |||
[[Category:Disease]] | [[Category:Disease]] | ||
[[Category:Primary care]] | [[Category:Primary care]] | ||
Revision as of 21:13, 13 June 2018
|
Cystitis Microchapters | |
|
Diagnosis | |
|
Treatment | |
|
Case Studies | |
|
Cystitis echocardiography and ultrasound On the Web | |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Cystitis echocardiography and ultrasound | |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Cystitis echocardiography and ultrasound | |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Usama Talib, BSc, MD [2]
Overview
There are no echocardiography findings associated with cystitis. Ultrasonography is not done routinely to diagnose cystitis. Ultrasonography is sometimes done to diagnose the suspicion of emphysematous cystitis and for detecting the presence of tutors or stones.[1]Imaging findings for chronic hemorrhagic cystitis due to radiation or chemotherapy include a small fibrosed bladder with a thick wall and resultant hydronephrosis. Calcification is only rarely seen.[2]
Echocardiography
There are no echocardiography findings associated with cystitis.
Ultrasonography
Ultrasonography of the urinary bladder can show presence of a gas in the bladder wall. It can also help to detect the presence of a tumour or a stone. Ultrasonography is sometimes used to differentiate various aetiologies of lower abdominal pain including emphysematous cystitis, ruptured ectopic pregnancy or appendicitis.[3]

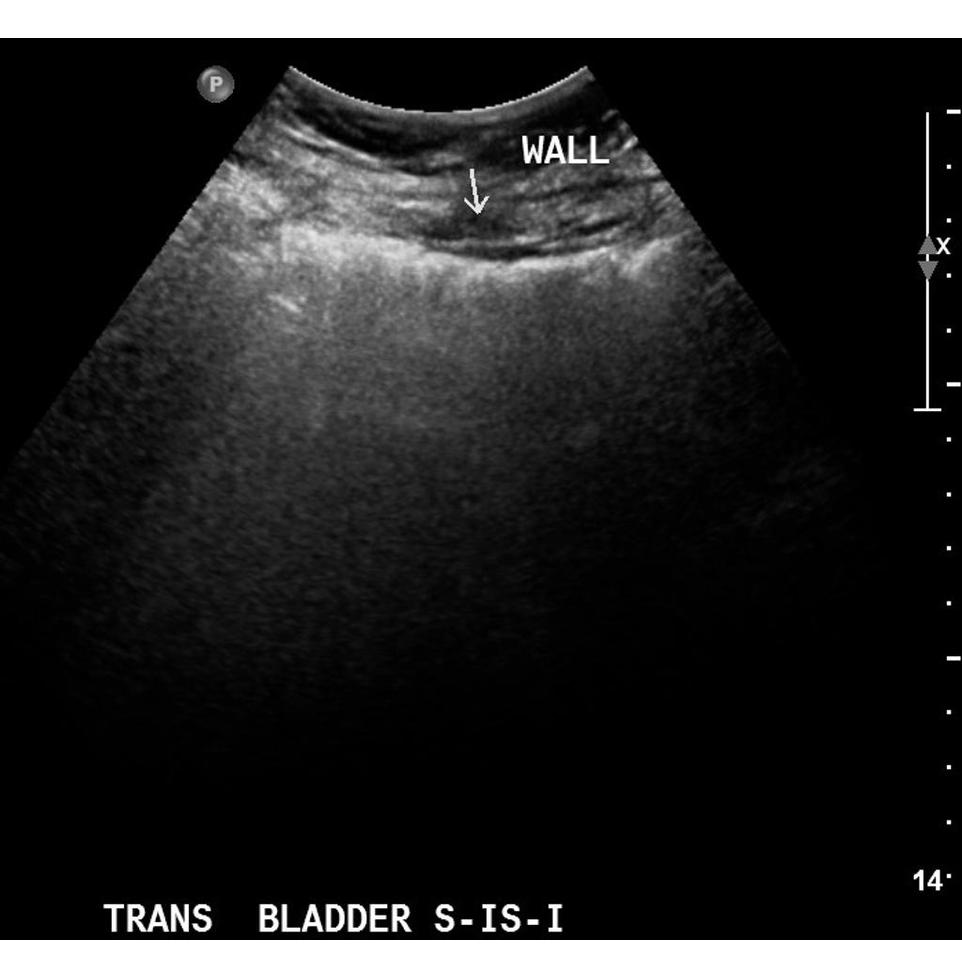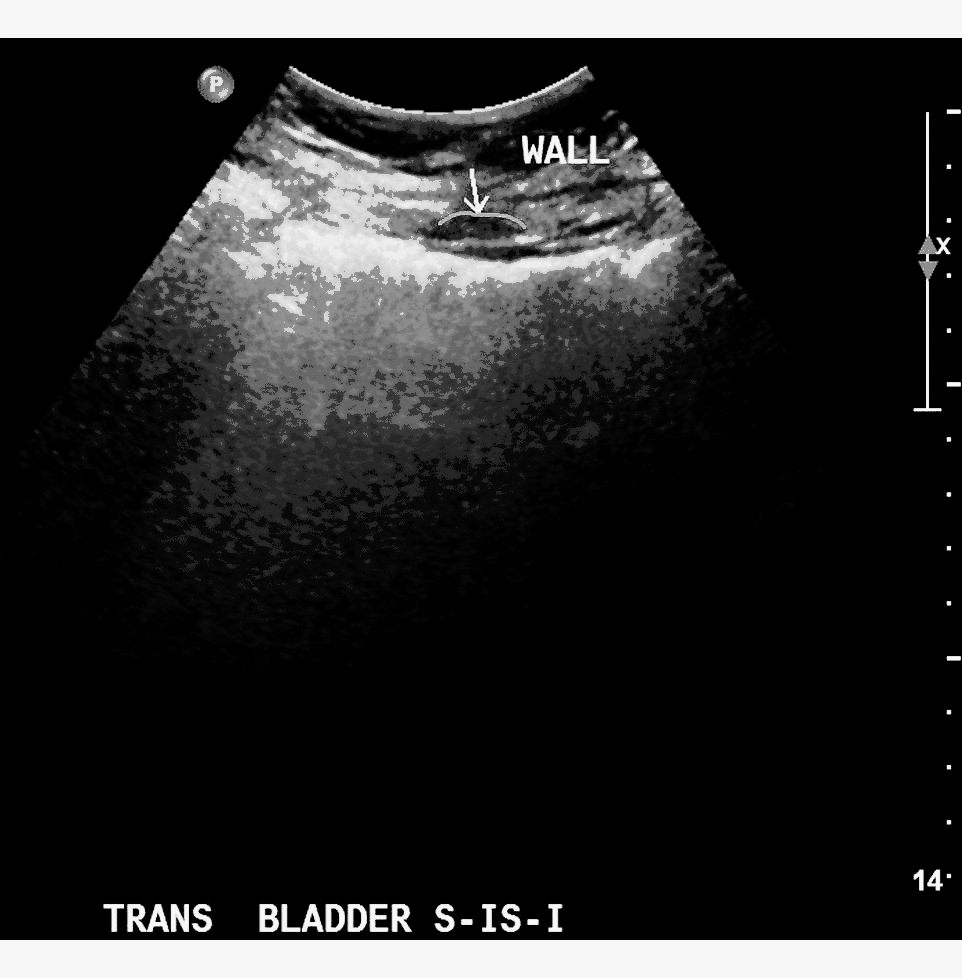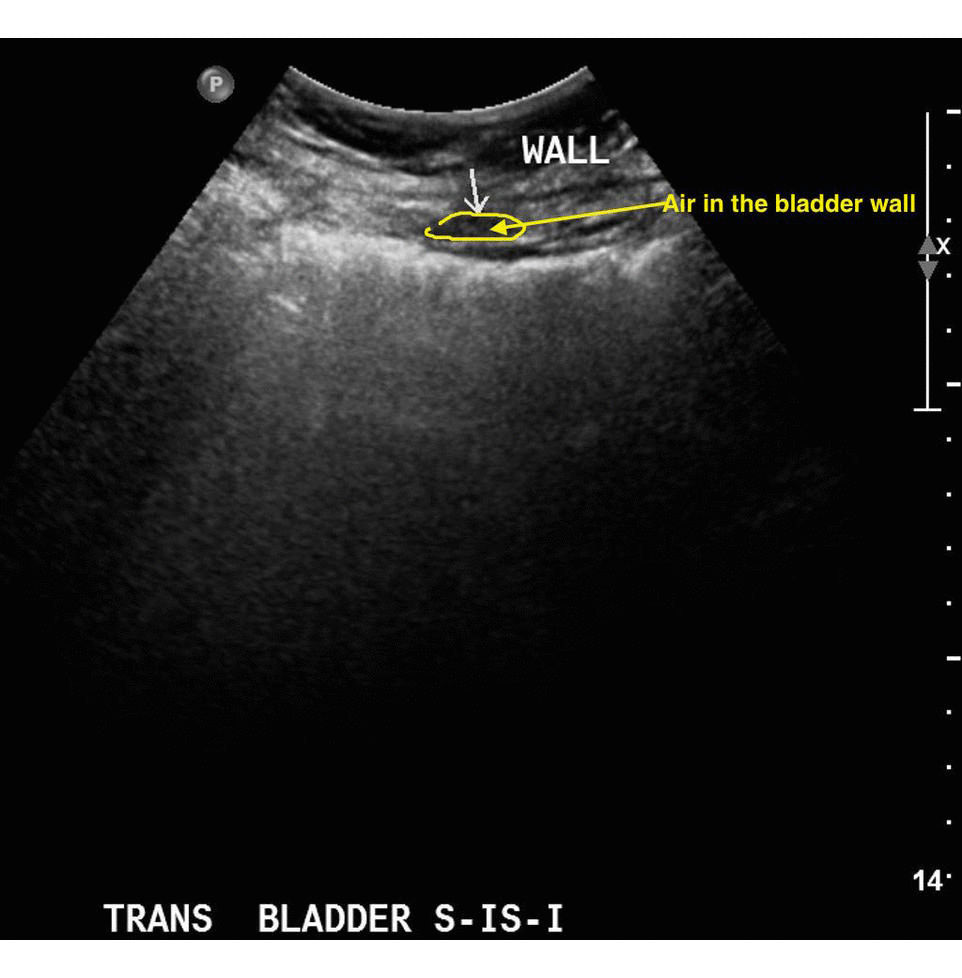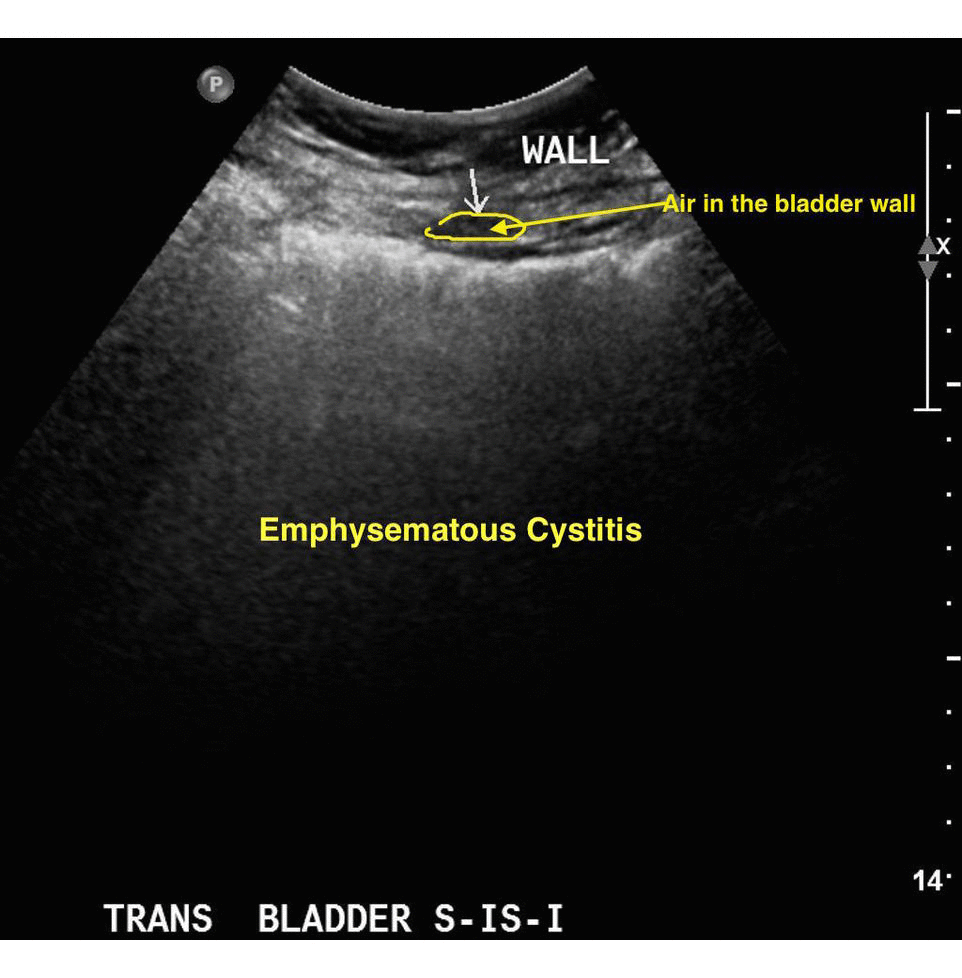
References
- ↑ Wegner J (2015). "[Cystitis. Ultrasound only in complicated anamnesis]". MMW Fortschr Med. 157 (18): 17. PMID 26985484.
- ↑ Radiation and Chemotherapy cystitis. Radiopaedia.http://radiopaedia.org/articles/radiation-and-chemotherapy-induced-cystitis Accessed on February 23, 2016
- ↑ Radiopaedia.org</a>. From the case <a href="https://radiopaedia.org/cases/17035">rID: 17035
- ↑ Radiopaedia.org</a>. From the case <a href="https://radiopaedia.org/cases/17035">rID: 17035
- ↑ Radiopaedia.org</a>. From the case <a href="https://radiopaedia.org/cases/17035">rID: 17035