Oral candidiasis pathophysiology
|
Oral candidiasis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Oral candidiasis pathophysiology On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Oral candidiasis pathophysiology |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Oral candidiasis pathophysiology |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Please help WikiDoc by adding more content here. It's easy! Click here to learn about editing.
Overview
Candida is a normal commensal of the skin and mucous membranes. The balance between the virulence of the fungus and the host immune defense is responsible avoiding opportunistic infection of candida. Deficiency of cell-mediated immunity or poor general status are the main risk factors for having opportunistic candidiasis. Candidiasis is usually localized to skin and mucous membranes. In rare cases, candidiasis can spread causing candidaemia and distant infection. These cases are usually associated with deficient immunity C. albicans is the main species causing infection in humans more than any other candida species.
Pathophysiology
Pathogenesis
Candida is a normal commensal of skin and mucous membranes. A competent immune system and an intact regenerating healthy skin prevent the virulence of Candida.
Candida Virulence factors
The main virulence factors that mediate the infection:[1]
- Secreting molecules that mediate adherence into host cells
- Production of hydrolases which has a lytic effect on tissues and facilitate the invasion by the fungus.
- Polymorphism: Candida has the ability to grow either as pseudohyphae (elongated ellipsoid form) or in a yeast form (rounded to oval budding form. While the role of polymorphism is not clearly understood in the virulence of Candida, it’s noted that the species that are capable of producing the most severe form of the disease has this ability.
- Biofilm production: which means the ability to form a thick layer of the organism on the mucosal surfaces or even on catheters and dentures.
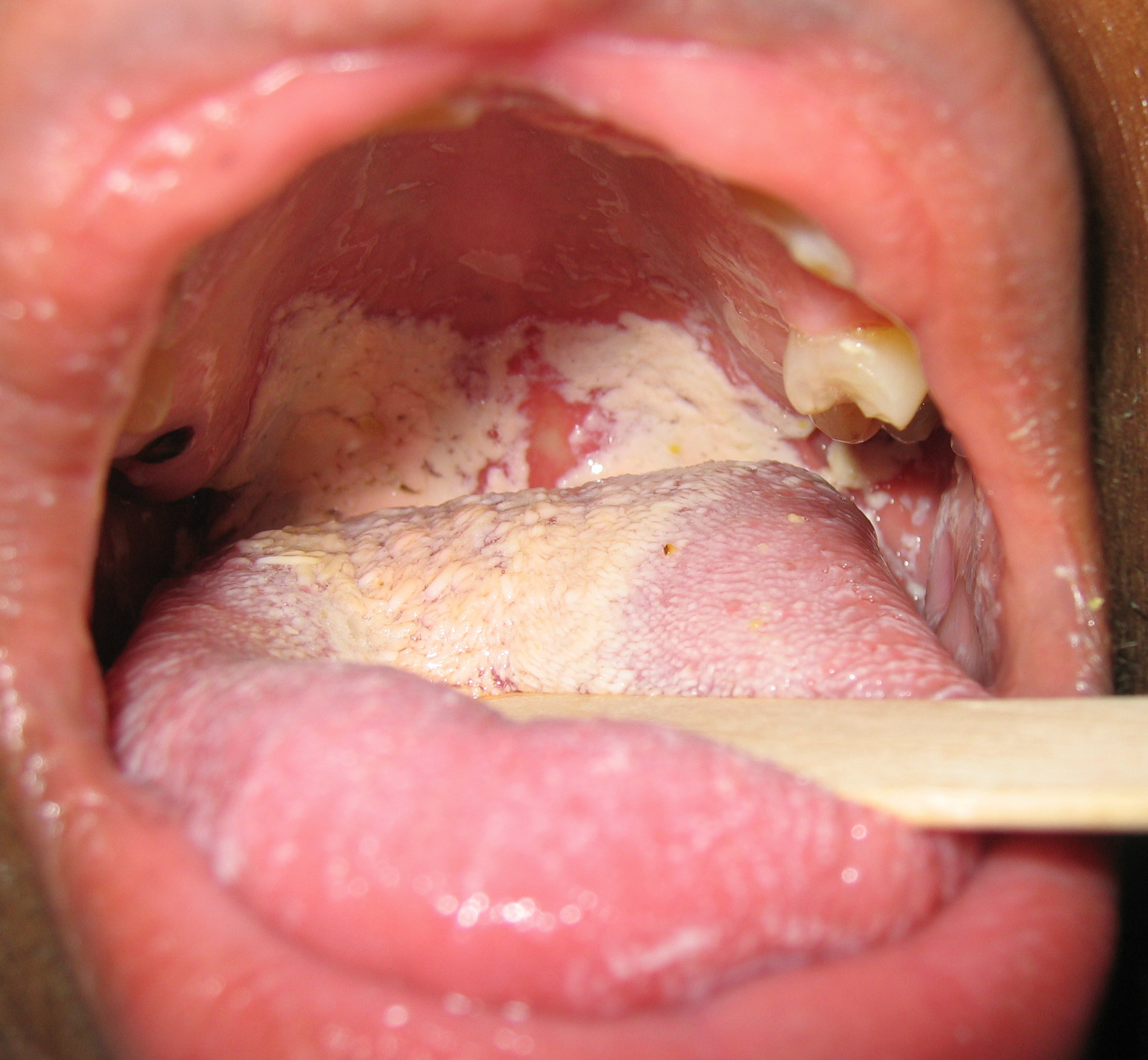
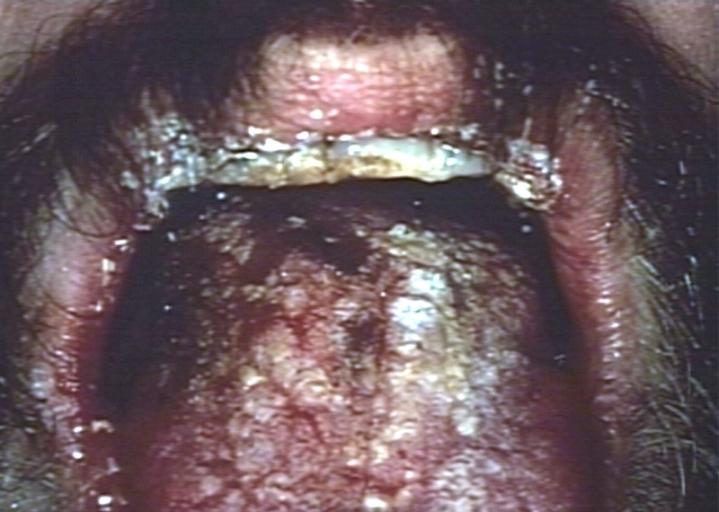
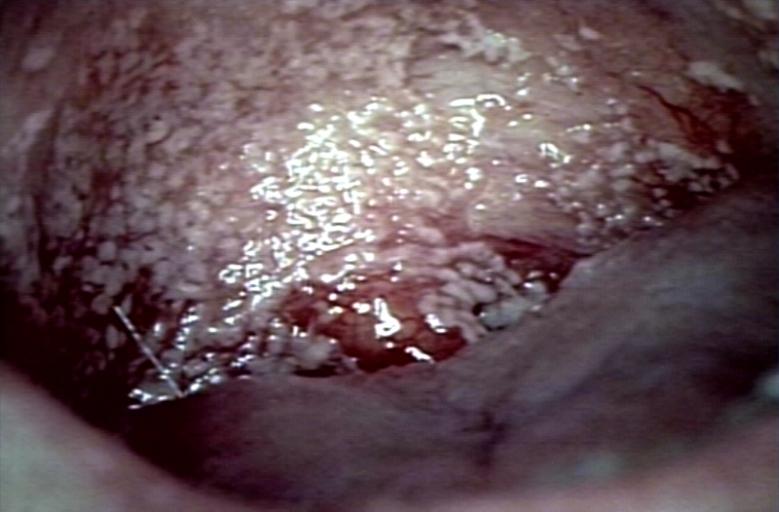
Gross Pathology
-
Oral manifestations of HIV infection and AIDS. Chronic oral candidiasis in patient with AIDS. Image courtesy of Professor Peter Anderson DVM PhD and published with permission. © PEIR, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Department of Pathology
-
Soft palate showing extensive oral candidiasis in patient with AIDS. Image courtesy of Professor Peter Anderson DVM PhD and published with permission. © PEIR, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Department of Pathology
Videos
{{#ev:youtube|Qqb6vZtXxu8}}
References
- ↑ Mayer FL, Wilson D, Hube B (2013). "Candida albicans pathogenicity mechanisms". Virulence. 4 (2): 119–28. doi:10.4161/viru.22913. PMC 3654610. PMID 23302789.