Hydrochlorothiazide detailed information: Difference between revisions
m (Protected "Hydrochlorothiazide detailed information": Protecting pages from unwanted edits ([edit=sysop] (indefinite) [move=sysop] (indefinite))) |
m (Robot: Automated text replacement (-{{SIB}} + & -{{EH}} + & -{{EJ}} + & -{{Editor Help}} + & -{{Editor Join}} +)) |
||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
{{CMG}} | {{CMG}} | ||
==[[Hydrochlorothiazide (patient information)|For patient information, click here]]== | ==[[Hydrochlorothiazide (patient information)|For patient information, click here]]== | ||
Revision as of 16:06, 9 August 2012
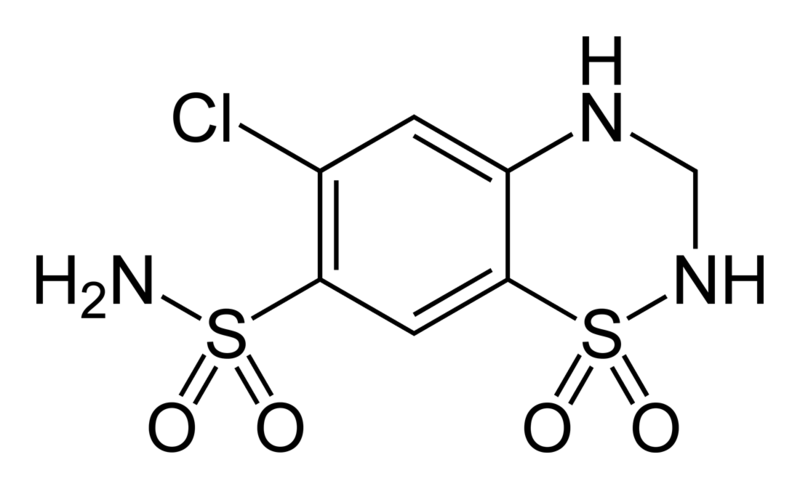 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral (capsules, tablets, oral solution) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Variably absorbed from GI tract |
| Elimination half-life | 5.6-14.8 hours |
| Excretion | Primarily excreted unchanged in urine |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| E number | {{#property:P628}} |
| ECHA InfoCard | {{#property:P2566}}Lua error in Module:EditAtWikidata at line 36: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C7H8ClN3O4S2 |
| Molar mass | 297.742 |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
For patient information, click here
Hydrochlorothiazide, sometimes abbreviated HCT, HCTZ, or HZT is a popular diuretic drug that acts by inhibiting the kidneys' ability to retain water. This reduces the volume of the blood, decreasing blood return to the heart and thus cardiac output and, by other mechanisms, is believed to lower peripheral vascular resistance. Hydrochlorothiazide is sold both as a generic drug and under a large number of brand names, including: Apo-Hydro, Aquazide H, Dichlotride, Hydrodiuril, HydroSaluric, Microzide, Oretic.
Activity
Hydrochlorothiazide belongs to the thiazide class of diuretics, acting on the kidneys to reduce sodium (Na) reabsorption in the distal convoluted tubule. This reduces the osmotic pressure in the kidneys, causing less water to be reabsorbed by the collecting ducts. This leads to increased urinary output.
Indications
HCT is often used in the treatment of hypertension, congestive heart failure, symptomatic edema and the prevention of kidney stones. It is effective for nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (paradoxical effect, which decreases urine formation) and is also sometimes used for hypercalciuria and Dent's Disease.
Hypokalemia, an occasional side-effect, can be usually prevented by potassium supplements or combining hydrochlorothiazide with a potassium-sparing diuretic.
Side effects
- Hypokalemia
- Hypomagnesemia
- Hyperuricemia and gout
- High blood sugar
- High cholesterol
- Headache
- Impotence
- Nausea/Vomiting
NOTE: This list needs references. The NIH link provided below does not agree with several items on this list.
External links
http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/druginfo/medmaster/a682571.html
de:Hydrochlorothiazid
hr:Hidroklorotiazid
hu:Hidroklorotiazid
no:Hydroklortiazid
nn:Hydroklortiazid
- Pages with script errors
- Drugs with non-standard legal status
- E number from Wikidata
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without InChI source
- Articles without UNII source
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Thiazides
- Drugs