Distal convoluted tubule
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
The distal convoluted tubule (DCT) is a portion of kidney nephron between the loop of Henle and the collecting duct system.
Physiology
It is partly responsible for the regulation of potassium, sodium, calcium, and pH.
- It regulates pH by absorbing bicarbonate and secreting protons (H+) into the filtrate.
- Sodium and potassium levels are controlled by secreting K+ and absorbing Na+. Sodium absorption by the distal tubule is mediated by the hormone aldosterone. Aldosterone increases sodium reabsorption. Sodium and chlorine (salt) reabsorption is also mediated by a group of kinases called WNK kinases. There are 4 different WNK kinases, WNK1, WNK2, WNK3, and WNK4.
- It also participates in calcium regulation by absorbing Ca2+ in response to parathyroid hormone.[1]
- Arginine vasopressin receptor 2 is also expressed in the DCT.
Clinical significance
Thiazide diuretics inhibit Na+/Cl- reabsorption from the DCT by blocking the thiazide-sensitive Na-Cl cotransporter.
Histology
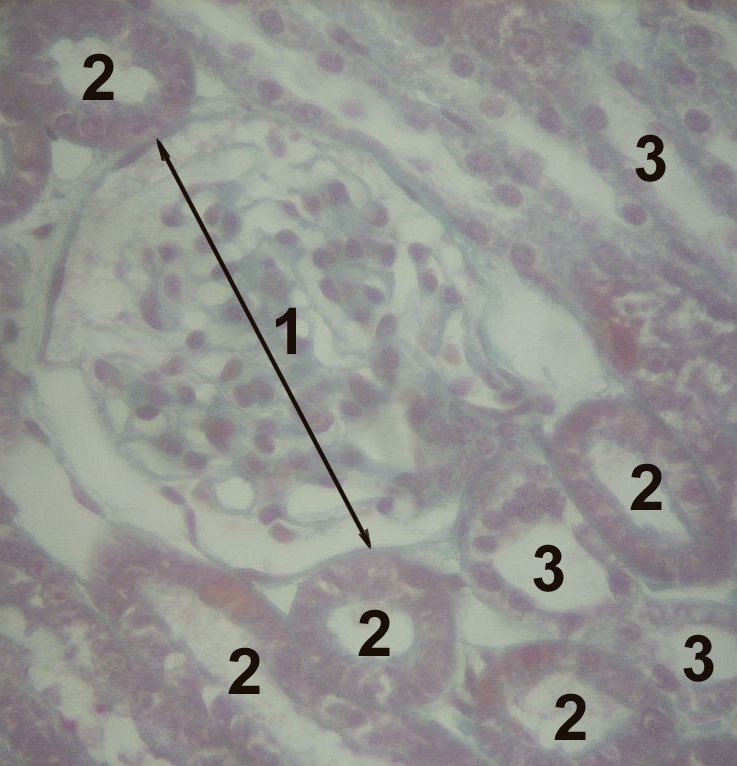
The distal convoluted tubule (DCT)is the final segment of the nephron. It is lined with simple cuboidal cells that are shorter then those of the PCT. The lumen appears larger in DCT than the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) lumen because the PCT has a brush border (microvilli). DCT can be recognized by its numerous mitochondria, basal infoldings and lateral membrane interdigitations with neighboring cells.
The point where DCT contacts afferent arteriole of renal corpuscle is called macula densa. It has tightly packed columnar cells which display reversed polarity and may monitor the osmolarity of blood.
Histologically, cells of the DCT can be differentiated from cells of the proximal convoluted tubule:
| Characteristic | PCT | DCT |
| apical brush border? | usually have | do not have |
| eosinophilicity? | more | less |
| cytoplasm? | more | less |
| have visible nuclei? | less likely | more likely |
Additional images
-
1 Glomerulus, 2 proximal tubule, 3 distal tubule
-
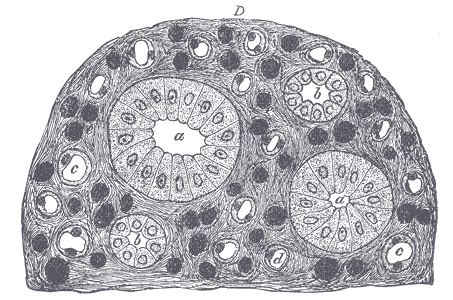
Transverse section of pyramidal substance of kidney of pig, the bloodvessels of which are injected.
References
External links
- Template:UCDavisOrganology - "Mammal, kidney cortex (LM, Medium)"
- Template:OklahomaHistology
- Essentials of Human Physiology by Thomas M. Nosek. Section 7/7ch03/7ch03p18.
- Essentials of Human Physiology by Thomas M. Nosek. Section 7/7ch07/7ch07p14.
- Histology image: 16004loa – Histology Learning System at Boston University
- Histology image: 16007loa – Histology Learning System at Boston University