Coronary artery bypass surgery conduits used for bypass: Difference between revisions
Hardik Patel (talk | contribs) (/* 2011 ACCF/AHA Guideline for Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery (DO NOT EDIT){{cite journal| author=Hillis LD, Smith PK, Anderson JL, Bittl JA, Bridges CR, Byrne JG et al.| title=2011 ACCF/AHA Guideline for Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery...) |
|||
| (37 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
{{Coronary artery bypass surgery}} | {{Coronary artery bypass surgery}} | ||
{{CMG}}; '''Associate Editors-in-Chief:''' {{CZ}}, [[User:Mohammed Sbeih|Mohammed A. Sbeih, M.D.]] | {{CMG}}; '''Associate Editors-in-Chief:''' {{CZ}}, [[User:Mohammed Sbeih|Mohammed A. Sbeih, M.D.]] {{Anahita}} | ||
==Overview== | |||
The choice of conduits ([[artery|arteries]] and/or [[veins]] from elsewhere in the body) to [[bypass]] the blockages is highly [[surgery|surgeon]] and institution dependent. To choose the proper conduits for [[CABG]] both clinical and technical factors such as [[life expectancy]], presence of [[diabetes]], chronic renal failure, and degree of the target [[stenosis]] must be considered. [[Saphenous vein]], [[internal thoracic artery]], and [[radial artery]] are the most used [[vessels]] to harvest for [[grafting]]. The [[saphenous vein]] can be harvested by either direct visualization or via an [[endoscopy|endoscopic approach]]. Among these two methods the [[endoscopy|endoscopic approach]] has been associated with lower rates of [[wound]] [[infection]], greater [[patient]] satisfaction, and earlier mobilization. However, non-[[randomized]] data from a much larger multicenter study does suggest that [[endoscopyendoscopic harvesting]] may be associated with a higher rate of failure and adverse events such as death and [[MI]]. [[Veins]] that are used either have their valves removed or are turned around so that the [[valves]] in them do not occlude [[blood flow]] in the [[graft]]. On the other hand, numerous studies support the use of the [[Internal thoracic artery|left internal thoracic artery]] ([[Internal thoracic artery|LITA]]) (also known as the [[Internal thoracic artery|left internal mammary artery]] ([[Internal thoracic artery|LIMA]])) to [[graft]] the [[LAD]] in order to improve survival unless [[contraindications|contraindicated]]. Evidence shows that the right [[IMA]] can be used to [[graft]] the [[LAD]] if the [[LIMA]] is impractical and unusable. Furthermore, the right [[IMA]] can be used in conjunction with the [[LIMA]] which is called bilateral [[internal mammary artery]] (BIMA) [[grafting]]. The latter method showed a better outcome based on multiple studies. In multiple [[artery|arterial]] [[revascularization]] during [[Coronary artery bypass surgery]], the [[Internal thoracic artery|right internal thoracic artery]] ([[Internal thoracic artery|RITA]]) has been proofed to be a better choice as a conduit than the [[radial artery]]. On the other hand, numerous [[clinical trials]] have demonstrated better patency rates (in mid- and long-term) when the [[radial artery]] is used in comparison with the [[saphenous vein]]. | |||
==Conduits used for bypass== | ==Conduits used for bypass== | ||
The choice of conduits (arteries and/or veins from elsewhere in the body) to bypass the blockages is highly surgeon and institution dependent. Typically, the left [[internal thoracic artery]] (LITA) (also referred to as the ''[[left internal mammary artery]]'' or ''[[LIMA]]'') is grafted to the [[Left Anterior Descending]] artery and a combination of other arteries and veins is used for other coronary arteries. | *The choice of conduits ([[artery|arteries]] and/or [[veins]] from elsewhere in the body) to [[bypass]] the blockages is highly [[surgery|surgeon]] and institution dependent. | ||
*To choose the proper conduits for [[CABG]] both clinical and technical factors such as [[life expectancy]], presence of [[diabetes]], chronic renal failure, and degree of the target [[stenosis]] must be considered.<ref name="pmid34895950">{{cite journal| author=Writing Committee Members. Lawton JS, Tamis-Holland JE, Bangalore S, Bates ER, Beckie TM | display-authors=etal| title=2021 ACC/AHA/SCAI Guideline for Coronary Artery Revascularization: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. | journal=J Am Coll Cardiol | year= 2022 | volume= 79 | issue= 2 | pages= e21-e129 | pmid=34895950 | doi=10.1016/j.jacc.2021.09.006 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=34895950 }} </ref> | |||
*The following table published by 2021 ACA Revascularization Guideline presents the best practices for the Use of [[bypass]] [[conduits]] in [[CABG]]:<ref name="pmid34895950">{{cite journal| author=Writing Committee Members. Lawton JS, Tamis-Holland JE, Bangalore S, Bates ER, Beckie TM | display-authors=etal| title=2021 ACC/AHA/SCAI Guideline for Coronary Artery Revascularization: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. | journal=J Am Coll Cardiol | year= 2022 | volume= 79 | issue= 2 | pages= e21-e129 | pmid=34895950 | doi=10.1016/j.jacc.2021.09.006 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=34895950 }} </ref> | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|- | |||
| Assessing [[Anatomical terms of location|palmar arch]] completeness and [[ulna|ulnar]] compensation before harvesting the [[radial artery]]. If [[radial artery]] harvesting is considered it is recommended to use the [[arm]] with the best [[ulna|ulnar compensation]]. | |||
|- | |||
| It is recommended to use [[radial artery]] [[grafts]] to target [[vessels]] with [[stenosis|subocclusive stenosis]]. | |||
|- | |||
| It is recommended to avoid [[radial artery]] use after [[Radial artery catheterization|transradial catheterization]]. | |||
|- | |||
| It is recommended to avoid [[radial artery]] use in [[chronic kidney disease]] [[patients]] and in those with a high likelihood of rapid progression to [[hemodialysis]]. | |||
|- | |||
| It is recommended to avoid [[oral]] [[calcium channel blockers]] for the first [[surgery|postoperative]] year after [[radial artery]] [[grafting]]. | |||
|- | |||
| It is recommended to avoid bilateral [[percutaneous]] or [[surgery|surgical]] [[radial artery]] procedures in [[patients]] with [[coronary artery disease]] with a goal to preserve the [[artery]] for future use. | |||
|- | |||
| It is recommended to use the [[internal mammary artery]] (using the skeletonization technique) to reduce the risk of [[Sternum|sternal]] [[wound]] [[complications]]. | |||
|- | |||
| It is recommended to use an [[endoscopy|endoscopic]] [[saphenous vein]] harvest technique in [[patients]] at risk of [[wound]] [[complications]]. | |||
|- | |||
| For [[patients]] at low risk of [[wound]] [[complications]], it is recommended to use a no-touch [[saphenous vein]] harvest technique. | |||
|- | |||
| It is recommended to use the skeletonized [[right gastroepiploic artery]] to [[graft]] [[right coronary artery]] target [[vessels]] with subocclusive [[stenosis]] if the operator is experienced with the use of the [[artery]]. | |||
|} | |||
*Typically, the left [[internal thoracic artery]] ([[Internal thoracic artery|LITA]]) (also referred to as the ''[[left internal mammary artery]]'' or ''[[LIMA]]'') is grafted to the [[Left Anterior Descending]] [[artery]] and a combination of other [[artery|arteries]] and [[veins]] is used for other [[coronary arteries]]. | |||
*The right [[internal thoracic artery]] ([[Internal thoracic artery|RITA]]), the [[great saphenous vein]] from the [[leg]] and the [[radial artery]] from the forearm are frequently used. | |||
*The [[right gastroepiploic artery]] from the [[stomach]] is infrequently used given the difficult mobilization from the [[abdomen]]. | |||
==Saphenous vein== | ==Saphenous vein== | ||
===Saphenous vein anatomy=== | |||
The [[great saphenous vein]] ([[GSV]]) is frequently used as a conduit for CABG. It originates from where the dorsal vein of the [[first digit]] (the large [[toe]]) merges with the [[dorsal venous arch of the foot]]. | *The [[great saphenous vein]] ([[GSV]]) is frequently used as a conduit for [[CABG]]. It originates from where the dorsal [[vein]] of the [[first digit]] (the large [[toe]]) merges with the [[dorsal venous arch of the foot]]. | ||
*After passing [[Anatomical terms of location|anterior]] to the [[medial malleolus]] (where it often can be visualized and [[Palpation|palpated]]), it runs up the [[medial]] side of the [[leg]]. At [[knee]], it runs over the [[Anatomical terms of location|posterior border]] of the [[medial epicondyle]] of the [[femur]] bone. | |||
After passing anterior to the [[medial malleolus]] (where it often can be visualized and [[Palpation|palpated]]), it runs up the [[medial]] side of the leg. At | *The [[great saphenous vein]] then courses [[Anatomical terms of location|laterally]] to lie on the [[Anatomical terms of location|anterior surface]] of the [[thigh]] before entering an opening in the [[fascia lata]] called the [[saphenous opening]]. It joins with the [[femoral vein]] in the region of the [[femoral triangle]] at the saphenofemoral junction. | ||
*The '''small [[saphenous vein]]''' (also '''lesser [[saphenous vein]]''') originates where the [[Anatomical terms of location|dorsal]] [[vein]] from the [[fifth digit]] (smallest [[toe]]) merges with the [[dorsal [[venous]] arch of the [[foot]], which attaches to the [[great saphenous vein]]. It is considered a [[superficial vein]] and is [[subcutaneous]] (just under the [[skin]]). From its origin, it courses around the lateral aspect of the [[foot]] ([[Anatomical terms of location|inferior]] and [[Anatomical terms of location|posterior]] to the [[lateral malleolus]]) and runs along the [[Anatomical terms of location|posterior]] aspect of the [[leg]] (with the [[sural nerve]]), passes between the heads of the [[gastrocnemius muscle]], and drains into the [[popliteal vein]], approximately at or above the level of the [[knee]] [[joint]]. | |||
The [[great saphenous vein]] then courses laterally to lie on the anterior surface of the thigh before entering an opening in the [[fascia lata]] called the [[saphenous opening]]. It joins with the [[femoral vein]] in the region of the [[femoral triangle]] at the saphenofemoral junction. | |||
The '''small saphenous vein''' (also '''lesser saphenous vein''') originates where the dorsal vein from the [[fifth digit]] (smallest toe) merges with the [[dorsal venous arch of the foot]], which attaches to the [[great saphenous vein]]. It is considered a [[superficial vein]] and is [[subcutaneous]] (just under the skin). From its origin, it courses around the lateral aspect of the foot (inferior and posterior to the [[lateral malleolus]]) and runs along the posterior aspect of the leg (with the [[sural nerve]]), passes between the heads of the [[gastrocnemius muscle]], and drains into the [[popliteal vein]], approximately at or above the level of the [[knee]] joint. | |||
<gallery perRow="3"> | <gallery perRow="3"> | ||
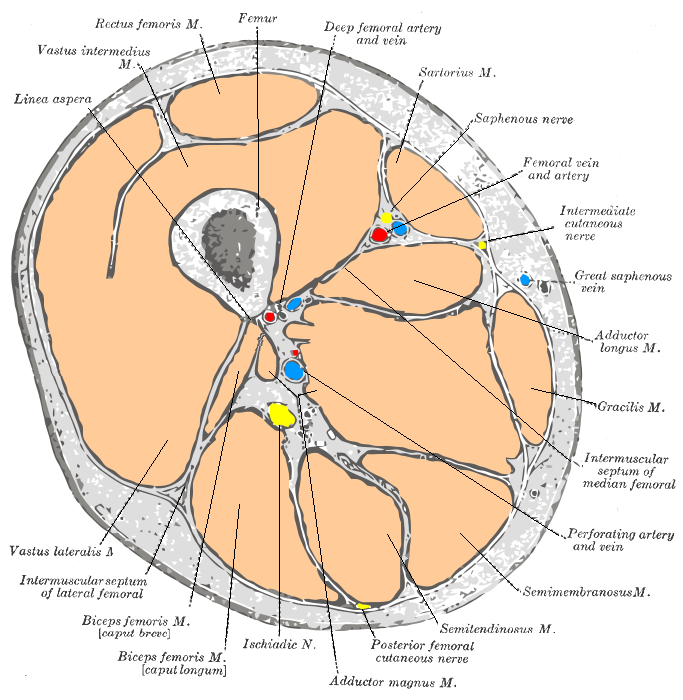
Image:Gray432 color.png|Cross-section through the middle of the thigh. | Image:Gray432 color.png|Cross-section through the middle of the [[thigh]]. | ||
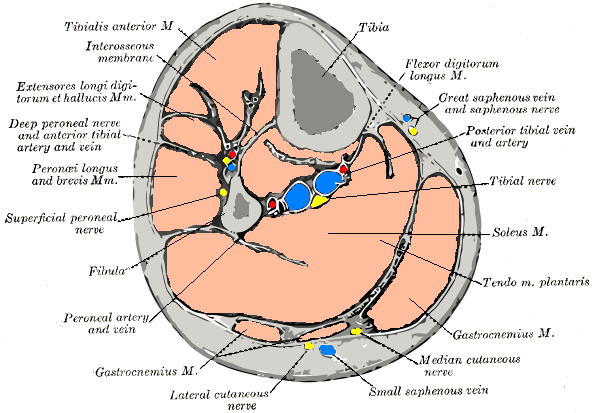
Image:Gray440_color.png|Cross-section through middle of leg. | Image:Gray440_color.png|Cross-section through the middle of the [[leg]]. | ||
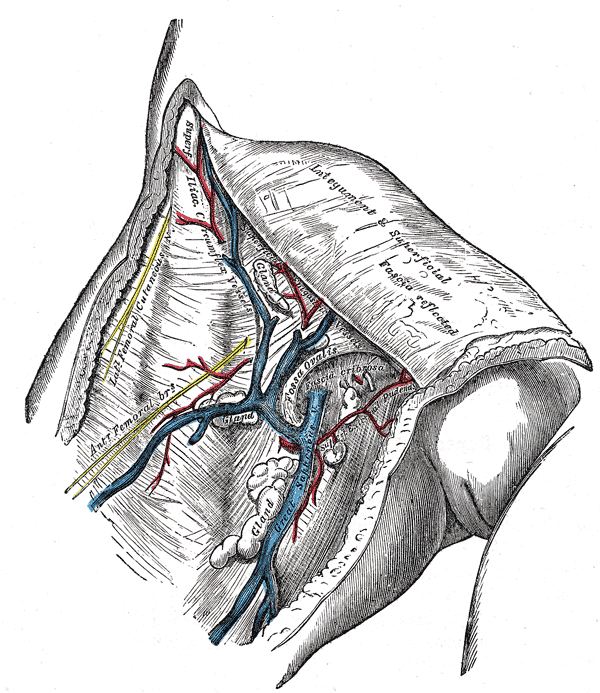
Image:Great_saphenous_vein.png|The great saphenous vein and landmarks along its course | Image:Great_saphenous_vein.png|The [[great saphenous vein]] and landmarks along its course | ||
Image:Gray580.png|The great saphenous vein and its tributaries at the [[Saphenous opening|fossa ovalis]] in the [[groin]]. | Image:Gray580.png|The [[great saphenous vein]] and its tributaries at the [[Saphenous opening|fossa ovalis]] in the [[groin]]. | ||
Image:Gray582.png|Small saphenous vein and its tributaries. | Image:Gray582.png|Small [[saphenous vein]] and its tributaries. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
====Saphenous vein harvesting==== | |||
The saphenous vein can be harvested by either direct visualization or via an endoscopic approach. | *The [[saphenous vein]] can be harvested by either direct visualization or via an [[endoscopy|endoscopic approach]]. [[Veins]] that are used either have their valves removed or are turned around so that the [[valves]] in them do not occlude [[blood flow]] in the [[graft]]. The technique of [[saphenous vein]] harvesting may influence later [[SVG]] patency. The process of harvesting the [[vein]] and [[pressure]] testing the [[vein]] for a leak may damage the [[endothelium]].<ref>Lawrie GM, Weilbacher DE, Henry PD. Endothelium-dependent relaxation in human saphenous vein grafts. Effects of preparation and clinicopathologic correlations. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1990;100:612—20.</ref><ref>Souza DS, Johansson B, Bojo¨ L, Karlsson R, Geijer H, Filbey D, Bodin L, Arbeus M, Dashwood MR. Harvesting the saphenous vein with surrounding tissue for CABG provides long-term graft patency comparable to the left internal thoracic artery: results of a randomized longitudinal trial. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2006;132:373—8.</ref> | ||
*The [[endoscopy|endoscopic approach]] has been associated with lower rates of [[wound]] [[infection]], greater [[patient]] satisfaction, and earlier mobilization.<ref name="pmid11828277">{{cite journal |author=Kiaii B, Moon BC, Massel D, Langlois Y, Austin TW, Willoughby A, Guiraudon C, Howard CR, Guo LR |title=A prospective randomized trial of endoscopic versus conventional harvesting of the saphenous vein in coronary artery bypass surgery |journal=[[J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg.]] |volume=123 |issue=2 |pages=204–12 |year=2002 |month=February |pmid=11828277 |doi= |url=http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0022522302096046 |issn= |accessdate=2010-07-23}}</ref><ref name="pmid19605828">{{cite journal |author=Lopes RD, Hafley GE, Allen KB, Ferguson TB, Peterson ED, Harrington RA, Mehta RH, Gibson CM, Mack MJ, Kouchoukos NT, Califf RM, Alexander JH |title=Endoscopic versus open vein-graft harvesting in coronary-artery bypass surgery |journal=[[The New England Journal of Medicine]] |volume=361 |issue=3 |pages=235–44 |year=2009 |month=July |pmid=19605828 |doi=10.1056/NEJMoa0900708 |url=http://content.nejm.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=short&pmid=19605828&promo=ONFLNS19 |issn= |accessdate=2010-07-12}}</ref><ref name="pmid15746730">{{cite journal |author=Yun KL, Wu Y, Aharonian V, Mansukhani P, Pfeffer TA, Sintek CF, Kochamba GS, Grunkemeier G, Khonsari S |title=Randomized trial of endoscopic versus open vein harvest for coronary artery bypass grafting: six-month patency rates |journal=[[J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg.]] |volume=129 |issue=3 |pages=496–503 |year=2005 |month=March |pmid=15746730 |doi=10.1016/j.jtcvs.2004.08.054 |url=http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0022522304015855 |issn= |accessdate=2010-07-23}}</ref><ref name="pmid15115999">{{cite journal |author=Perrault LP, Jeanmart H, Bilodeau L, Lespérance J, Tanguay JF, Bouchard D, Pagé P, Carrier M |title=Early quantitative coronary angiography of saphenous vein grafts for coronary artery bypass grafting harvested by means of open versus endoscopic saphenectomy: a prospective randomized trial |journal=[[J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg.]] |volume=127 |issue=5 |pages=1402–7 |year=2004 |month=May |pmid=15115999 |doi=10.1016/j.jtcvs.2003.10.040 |url=http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0022522303018798 |issn= |accessdate=2010-07-23}}</ref> One small randomized study of 144 patients showed no difference in histologic findings between the traditional and endoscopic techniques.<ref name="pmid11828277">{{cite journal |author=Kiaii B, Moon BC, Massel D, Langlois Y, Austin TW, Willoughby A, Guiraudon C, Howard CR, Guo LR |title=A prospective randomized trial of endoscopic versus conventional harvesting of the saphenous vein in coronary artery bypass surgery |journal=[[J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg.]] |volume=123 |issue=2 |pages=204–12 |year=2002 |month=February |pmid=11828277|doi=|url=http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0022522302096046 |issn= |accessdate=2010-07-23}}</ref>In another small study of 40 patients randomized to the two techniques, no difference was seen in angiographic patency at 3 months.<ref name="pmid15115999">{{cite journal |author=Perrault LP, Jeanmart H, Bilodeau L, Lespérance J, Tanguay JF, Bouchard D, Pagé P, Carrier M |title=Early quantitative coronary angiography of saphenous vein grafts for coronary artery bypass grafting harvested by means of open versus endoscopic saphenectomy: a prospective randomized trial |journal=[[J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg.]] |volume=127 |issue=5 |pages=1402–7 |year=2004 |month=May |pmid=15115999 |doi=10.1016/j.jtcvs.2003.10.040 |url=http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0022522303018798 |issn= |accessdate=2010-07-23}}</ref>Another small randomized study of 144 patients who returned for angiography demonstrated an occlusion rate of 21.7% for the endoscopic approach vs 17.6% for the open approach.<ref name="pmid15746730">{{cite journal |author=Yun KL, Wu Y, Aharonian V, Mansukhani P, Pfeffer TA, Sintek CF, Kochamba GS, Grunkemeier G, Khonsari S |title=Randomized trial of endoscopic versus open vein harvest for coronary artery bypass grafting: six-month patency rates |journal=[[J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg.]] |volume=129 |issue=3 |pages=496–503 |year=2005 |month=March |pmid=15746730 |doi=10.1016/j.jtcvs.2004.08.054 |url=http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0022522304015855 |issn= |accessdate=2010-07-23}}</ref> | |||
*However, non-[[randomized]] data from a much larger multicenter study does suggest that [[endoscopyendoscopic harvesting]] may be associated with a higher rate of failure and adverse events such as death and [[MI]].<ref name="pmid19605828">{{cite journal |author=Lopes RD, Hafley GE, Allen KB, Ferguson TB, Peterson ED, Harrington RA, Mehta RH, Gibson CM, Mack MJ, Kouchoukos NT, Califf RM, Alexander JH |title=Endoscopic versus open vein-graft harvesting in coronary-artery bypass surgery |journal=[[The New England Journal of Medicine]] |volume=361 |issue=3 |pages=235–44 |year=2009 |month=July |pmid=19605828 |doi=10.1056/NEJMoa0900708 |url=http://content.nejm.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=short&pmid=19605828&promo=ONFLNS19 |issn= |accessdate=2010-07-12}}</ref> | |||
*[[Complications]] associated with [[Saphenous vein graft|saphenous vein harvesting]] include the following: | |||
** [[Saphenous nerve]] [[injury]] | |||
** [[Infection]] at [[incision]] sites or [[sepsis]]. | |||
** [[Deep vein thrombosis]] ([[DVT]]) | |||
** [[Keloid|Keloid scarring]] | |||
** [[Chronic pain]] at [[incision]] sites | |||
The | ==The Internal Thoracic Artery== | ||
*Numerous studies support the use of the [[Internal thoracic artery|left internal thoracic artery]] ([[Internal thoracic artery|LITA]]) (also known as the [[Internal thoracic artery|left internal mammary artery]] ([[Internal thoracic artery|LIMA]])) to [[graft]] the [[LAD]] in order to improve survival unless [[contraindications|contraindicated]].<ref name="pmid34895950">{{cite journal| author=Writing Committee Members. Lawton JS, Tamis-Holland JE, Bangalore S, Bates ER, Beckie TM | display-authors=etal| title=2021 ACC/AHA/SCAI Guideline for Coronary Artery Revascularization: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. | journal=J Am Coll Cardiol | year= 2022 | volume= 79 | issue= 2 | pages= e21-e129 | pmid=34895950 | doi=10.1016/j.jacc.2021.09.006 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=34895950 }} </ref><ref name="pmid8531997">{{cite journal| author=Cameron A, Davis KB, Green G, Schaff HV| title=Coronary bypass surgery with internal-thoracic-artery grafts--effects on survival over a 15-year period. | journal=N Engl J Med | year= 1996 | volume= 334 | issue= 4 | pages= 216-9 | pmid=8531997 | doi=10.1056/NEJM199601253340402 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=8531997 }} </ref><ref name="pmid3259128">{{cite journal| author=Zeff RH, Kongtahworn C, Iannone LA, Gordon DF, Brown TM, Phillips SJ | display-authors=etal| title=Internal mammary artery versus saphenous vein graft to the left anterior descending coronary artery: prospective randomized study with 10-year follow-up. | journal=Ann Thorac Surg | year= 1988 | volume= 45 | issue= 5 | pages= 533-6 | pmid=3259128 | doi=10.1016/s0003-4975(10)64526-2 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=3259128 }} </ref><ref name="pmid8127094">{{cite journal| author=Boylan MJ, Lytle BW, Loop FD, Taylor PC, Borsh JA, Goormastic M | display-authors=etal| title=Surgical treatment of isolated left anterior descending coronary stenosis. Comparison of left internal mammary artery and venous autograft at 18 to 20 years of follow-up. | journal=J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg | year= 1994 | volume= 107 | issue= 3 | pages= 657-62 | pmid=8127094 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=8127094 }} </ref> | |||
*In a study evaluating almost 6,000 [[patients]], [[LIMA]] [[grafting]] was able to reduce the rate of [[heart|cardiac]]-related [[hospital|rehospitalization]] and [[revascularization]]. In addition, this study showed a lower rate of death and recurrent [[infarction]] in those who undergone [[LIMA]] [[grafting]].<ref name="pmid3484393">{{cite journal| author=Loop FD, Lytle BW, Cosgrove DM, Stewart RW, Goormastic M, Williams GW | display-authors=etal| title=Influence of the internal-mammary-artery graft on 10-year survival and other cardiac events. | journal=N Engl J Med | year= 1986 | volume= 314 | issue= 1 | pages= 1-6 | pmid=3484393 | doi=10.1056/NEJM198601023140101 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=3484393 }} </ref> | |||
*Evidence shows that the right [[IMA]] can be used to [[graft]] the [[LAD]] if the [[LIMA]] is impractical and unusable. Furthermore, the right [[IMA]] can be used in conjunction with the [[LIMA]] which is called bilateral [[internal mammary artery]] (BIMA) [[grafting]].<ref name="pmid34895950">{{cite journal| author=Writing Committee Members. Lawton JS, Tamis-Holland JE, Bangalore S, Bates ER, Beckie TM | display-authors=etal| title=2021 ACC/AHA/SCAI Guideline for Coronary Artery Revascularization: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. | journal=J Am Coll Cardiol | year= 2022 | volume= 79 | issue= 2 | pages= e21-e129 | pmid=34895950 | doi=10.1016/j.jacc.2021.09.006 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=34895950 }} </ref> | |||
**Based on observational studies, BIMA [[grafting]] has a survival advantage when compared with [[CABG]] with a single [[IMA]].<ref name="pmid34895950">{{cite journal| author=Writing Committee Members. Lawton JS, Tamis-Holland JE, Bangalore S, Bates ER, Beckie TM | display-authors=etal| title=2021 ACC/AHA/SCAI Guideline for Coronary Artery Revascularization: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. | journal=J Am Coll Cardiol | year= 2022 | volume= 79 | issue= 2 | pages= e21-e129 | pmid=34895950 | doi=10.1016/j.jacc.2021.09.006 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=34895950 }} </ref><ref name="pmid30636525">{{cite journal| author=Gaudino M, Lorusso R, Rahouma M, Abouarab A, Tam DY, Spadaccio C | display-authors=etal| title=Radial Artery Versus Right Internal Thoracic Artery Versus Saphenous Vein as the Second Conduit for Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery: A Network Meta-Analysis of Clinical Outcomes. | journal=J Am Heart Assoc | year= 2019 | volume= 8 | issue= 2 | pages= e010839 | pmid=30636525 | doi=10.1161/JAHA.118.010839 | pmc=6497341 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=30636525 }} </ref><ref name="pmid24916209">{{cite journal| author=Yi G, Shine B, Rehman SM, Altman DG, Taggart DP| title=Effect of bilateral internal mammary artery grafts on long-term survival: a meta-analysis approach. | journal=Circulation | year= 2014 | volume= 130 | issue= 7 | pages= 539-45 | pmid=24916209 | doi=10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.004255 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=24916209 }} </ref><ref name="pmid24521973">{{cite journal| author=Takagi H, Goto SN, Watanabe T, Mizuno Y, Kawai N, Umemoto T| title=A meta-analysis of adjusted hazard ratios from 20 observational studies of bilateral versus single internal thoracic artery coronary artery bypass grafting. | journal=J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg | year= 2014 | volume= 148 | issue= 4 | pages= 1282-90 | pmid=24521973 | doi=10.1016/j.jtcvs.2014.01.010 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=24521973 }} </ref><ref name="pmid29306899">{{cite journal| author=Gaudino M, Di Franco A, Rahouma M, Tam DY, Iannaccone M, Deb S | display-authors=etal| title=Unmeasured Confounders in Observational Studies Comparing Bilateral Versus Single Internal Thoracic Artery for Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting: A Meta-Analysis. | journal=J Am Heart Assoc | year= 2018 | volume= 7 | issue= 1 | pages= | pmid=29306899 | doi=10.1161/JAHA.117.008010 | pmc=5778975 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=29306899 }} </ref> | |||
**Reports from a [[meta-analysis]] of 38 studies, including 174,205 [[patients]] demonstrated a decreased [[mortality rate]] at 7.25 years follow up among [[patients]] who had BIMA [[grafting]].<ref name="pmid29306899">{{cite journal| author=Gaudino M, Di Franco A, Rahouma M, Tam DY, Iannaccone M, Deb S | display-authors=etal| title=Unmeasured Confounders in Observational Studies Comparing Bilateral Versus Single Internal Thoracic Artery for Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting: A Meta-Analysis. | journal=J Am Heart Assoc | year= 2018 | volume= 7 | issue= 1 | pages= | pmid=29306899 | doi=10.1161/JAHA.117.008010 | pmc=5778975 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=29306899 }} </ref> | |||
**On the other hand, a single large [[randomized controlled trial]] reported no difference in 10-year all-cause [[mortality rate|mortality]] when BIMA was compared with single [[IMA]]. Furthermore, this study highlighted the importance of [[surgery|surgical expertise]] in BIMA [[grafting]].<ref name="pmid30699314">{{cite journal| author=Taggart DP, Benedetto U, Gerry S, Altman DG, Gray AM, Lees B | display-authors=etal| title=Bilateral versus Single Internal-Thoracic-Artery Grafts at 10 Years. | journal=N Engl J Med | year= 2019 | volume= 380 | issue= 5 | pages= 437-446 | pmid=30699314 | doi=10.1056/NEJMoa1808783 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=30699314 }} </ref> | |||
**It is critical to consider the higher risk of [[sternum|sternal]] [[infection]] with BIMA [[grafting]].<ref name="pmid29453002">{{cite journal| author=Schwann TA, Habib RH, Wallace A, Shahian DM, O'Brien S, Jacobs JP | display-authors=etal| title=Operative Outcomes of Multiple-Arterial Versus Single-Arterial Coronary Bypass Grafting. | journal=Ann Thorac Surg | year= 2018 | volume= 105 | issue= 4 | pages= 1109-1119 | pmid=29453002 | doi=10.1016/j.athoracsur.2017.10.058 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=29453002 }} </ref> | |||
*In multiple [[artery|arterial]] [[revascularization]] during [[Coronary artery bypass surgery]], the [[Internal thoracic artery|right internal thoracic artery]] ([[Internal thoracic artery|RITA]]) has been proofed to be a better choice as a conduit than the [[radial artery]]. This has been published at the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) 2011 Congress, after a [[clinical trial|trial]] on more than 1000 [[patients]] who had the operation in 10 years [[clinical trial|trial]]. | |||
*The [[Internal thoracic artery|left internal thoracic artery]] ([[Internal thoracic artery|LITA]]) (also known as the [[Internal thoracic artery|left internal mammary artery]] ([[Internal thoracic artery|LIMA]])) is the best [[vessel]] to use for [[coronary artery bypass surgery]] when only one [[artery]] is required. | |||
**It was known that the long-term outcomes of the [[artery|arterial]] [[graft]]s are much better than [[saphenous vein grafts]] (SVGs) and has less [[morbidity]] and [[mortality rates]].<ref name="pmid23428216">{{cite journal| author=Beach JM, Mihaljevic T, Svensson LG, Rajeswaran J, Marwick T, Griffin B | display-authors=etal| title=Coronary artery disease and outcomes of aortic valve replacement for severe aortic stenosis. | journal=J Am Coll Cardiol | year= 2013 | volume= 61 | issue= 8 | pages= 837-48 | pmid=23428216 | doi=10.1016/j.jacc.2012.10.049 | pmc=4262244 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=23428216 }} </ref><ref name="pmid3484393">{{cite journal| author=Loop FD, Lytle BW, Cosgrove DM, Stewart RW, Goormastic M, Williams GW | display-authors=etal| title=Influence of the internal-mammary-artery graft on 10-year survival and other cardiac events. | journal=N Engl J Med | year= 1986 | volume= 314 | issue= 1 | pages= 1-6 | pmid=3484393 | doi=10.1056/NEJM198601023140101 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=3484393 }} </ref><ref name="pmid3259128">{{cite journal| author=Zeff RH, Kongtahworn C, Iannone LA, Gordon DF, Brown TM, Phillips SJ | display-authors=etal| title=Internal mammary artery versus saphenous vein graft to the left anterior descending coronary artery: prospective randomized study with 10-year follow-up. | journal=Ann Thorac Surg | year= 1988 | volume= 45 | issue= 5 | pages= 533-6 | pmid=3259128 | doi=10.1016/s0003-4975(10)64526-2 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=3259128 }} </ref><ref name="pmid8127094">{{cite journal| author=Boylan MJ, Lytle BW, Loop FD, Taylor PC, Borsh JA, Goormastic M | display-authors=etal| title=Surgical treatment of isolated left anterior descending coronary stenosis. Comparison of left internal mammary artery and venous autograft at 18 to 20 years of follow-up. | journal=J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg | year= 1994 | volume= 107 | issue= 3 | pages= 657-62 | pmid=8127094 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=8127094 }} </ref> | |||
**The [[right internal thoracic artery]] (RITA) is the best second conduit for the [[bypass]] and has better long-term outcomes than the [[radial artery]]. The use of the [[Internal thoracic artery|RITA]] results in the following in comparison with [[SVG]]: | |||
***Less major adverse [[heart|cardiac]] and cerebrovascular events. | |||
***Less [[surgery|perioperative]] [[myocardial infarction]] rates. | |||
***Less [[surgery|perioperative]] [[stroke]] rates. | |||
***Less [[heart|cardiac]]-related deaths. | |||
*There have been good clinical results with the single left [[internal thoracic artery]] [[grafting]] compared with [[saphenous vein]] [[grafting]]. This prompted surgeons to use both ITAs. Bilateral ITA [[grafting]] could improve long-term survival. Late [[Complication (medicine)|complications]] like [[myocardial infarction]] and need to [[surgery|reoperate]] may be avoided. However, mathematical modeling is required to assist in developing a strategy for use of such [[grafts]].<ref name="pmid9852872">{{cite journal| author=Buxton BF, Komeda M, Fuller JA, Gordon I| title=Bilateral internal thoracic artery grafting may improve the outcome of coronary artery surgery. Risk-adjusted survival. | journal=Circulation | year= 1998 | volume= 98 | issue= 19 Suppl | pages= II1-6 | pmid=9852872 | doi= | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=9852872 }} </ref> | |||
*In a [[cohort study]] of 8123 [[patients]] who received single [[internal thoracic artery]] [[grafts]] and 2001 who received bilateral [[internal thoracic artery]] [[grafts]] for [[multivessel coronary artery disease]] for a duration of 20 years, it was found that the latter produces improved survival compared with single [[internal thoracic artery]] [[grafting]] during the second [[surgery|postoperative]] decade, and the magnitude of that benefit increases through 20 [[surgery|postoperative]] years.<ref name="pmid15561021">{{cite journal| author=Lytle BW, Blackstone EH, Sabik JF, Houghtaling P, Loop FD, Cosgrove DM| title=The effect of bilateral internal thoracic artery grafting on survival during 20 postoperative years. | journal=Ann Thorac Surg | year= 2004 | volume= 78 | issue= 6 | pages= 2005-12; discussion 2012-4 | pmid=15561021 | doi=10.1016/j.athoracsur.2004.05.070 | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=15561021 }} </ref> | |||
*It's easy to harvest the [[radial artery]], but it has a higher risk for [[vasospasm]] and [[atherosclerosis]] than the [[right internal thoracic artery]] ([[RITA]]). Some institution solves this problem ([[vasospasm]]) by preparing the [[radial artery|radial arteries]] with [[phenoxybenzamine]]. | |||
*Although the fact that using both [[internal thoracic arteries]] for [[coronary artery bypass surgery]] takes a longer time, it has better long-term results and [[surgery|perioperative]] outcomes. This has to be proofed and confirmed by more [[randomized]] and controlled trials. | |||
==Radial Artery== | |||
*Numerous [[clinical trials]] have demonstrated better patency rates (in mid- and long-term) when the [[radial artery]] is used in comparison with the [[saphenous vein]].<ref name="pmid32662861">{{cite journal| author=Gaudino M, Benedetto U, Fremes S, Ballman K, Biondi-Zoccai G, Sedrakyan A | display-authors=etal| title=Association of Radial Artery Graft vs Saphenous Vein Graft With Long-term Cardiovascular Outcomes Among Patients Undergoing Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. | journal=JAMA | year= 2020 | volume= 324 | issue= 2 | pages= 179-187 | pmid=32662861 | doi=10.1001/jama.2020.8228 | pmc=7361649 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=32662861 }} </ref><ref name="pmid22871565">{{cite journal| author=Cao C, Manganas C, Horton M, Bannon P, Munkholm-Larsen S, Ang SC | display-authors=etal| title=Angiographic outcomes of radial artery versus saphenous vein in coronary artery bypass graft surgery: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. | journal=J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg | year= 2013 | volume= 146 | issue= 2 | pages= 255-61 | pmid=22871565 | doi=10.1016/j.jtcvs.2012.07.014 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=22871565 }} </ref><ref name="pmid24686003">{{cite journal| author=Benedetto U, Raja SG, Albanese A, Amrani M, Biondi-Zoccai G, Frati G| title=Searching for the second best graft for coronary artery bypass surgery: a network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials†. | journal=Eur J Cardiothorac Surg | year= 2015 | volume= 47 | issue= 1 | pages= 59-65; discussion 65 | pmid=24686003 | doi=10.1093/ejcts/ezu111 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=24686003 }} </ref> | |||
*Furthermore, several [[observational studies]] reported a better survival rate when the [[radial artery]] is used instead of the [[saphenous vein]] for [[CABG]].<ref name="pmid30636525">{{cite journal| author=Gaudino M, Lorusso R, Rahouma M, Abouarab A, Tam DY, Spadaccio C | display-authors=etal| title=Radial Artery Versus Right Internal Thoracic Artery Versus Saphenous Vein as the Second Conduit for Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery: A Network Meta-Analysis of Clinical Outcomes. | journal=J Am Heart Assoc | year= 2019 | volume= 8 | issue= 2 | pages= e010839 | pmid=30636525 | doi=10.1161/JAHA.118.010839 | pmc=6497341 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=30636525 }} </ref><ref name="pmid29708851">{{cite journal| author=Gaudino M, Benedetto U, Fremes S, Biondi-Zoccai G, Sedrakyan A, Puskas JD | display-authors=etal| title=Radial-Artery or Saphenous-Vein Grafts in Coronary-Artery Bypass Surgery. | journal=N Engl J Med | year= 2018 | volume= 378 | issue= 22 | pages= 2069-2077 | pmid=29708851 | doi=10.1056/NEJMoa1716026 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=29708851 }} </ref><ref name="pmid32662861">{{cite journal| author=Gaudino M, Benedetto U, Fremes S, Ballman K, Biondi-Zoccai G, Sedrakyan A | display-authors=etal| title=Association of Radial Artery Graft vs Saphenous Vein Graft With Long-term Cardiovascular Outcomes Among Patients Undergoing Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. | journal=JAMA | year= 2020 | volume= 324 | issue= 2 | pages= 179-187 | pmid=32662861 | doi=10.1001/jama.2020.8228 | pmc=7361649 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=32662861 }} </ref> | |||
*Based on the 2021 ACA Revascularization guideline, the following [[patients]] benefit the most from the [[radial artery]] use:<ref name="pmid34895950">{{cite journal| author=Writing Committee Members. Lawton JS, Tamis-Holland JE, Bangalore S, Bates ER, Beckie TM | display-authors=etal| title=2021 ACC/AHA/SCAI Guideline for Coronary Artery Revascularization: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. | journal=J Am Coll Cardiol | year= 2022 | volume= 79 | issue= 2 | pages= e21-e129 | pmid=34895950 | doi=10.1016/j.jacc.2021.09.006 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=34895950 }} </ref> | |||
**[[Patients]] younger than 75 years old | |||
**[[Females]] | |||
**[[Patients]] with preserved [[renal function]] | |||
*There is some limited data regarding the vulnerability to the effect of [[Chronic (medical)|chronic]] native competitive flow in composite [[radial artery]] [[grafts]].<ref name="pmid14726046">{{cite journal| author=Abu-Omar Y, Mussa S, Anastasiadis K, Steel S, Hands L, Taggart DP| title=Duplex ultrasonography predicts safety of radial artery harvest in the presence of an abnormal Allen test. | journal=Ann Thorac Surg | year= 2004 | volume= 77 | issue= 1 | pages= 116-9 | pmid=14726046 | doi=10.1016/s0003-4975(03)01515-7 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=14726046 }} </ref> | |||
* [[ | ==Conduit Nomenclature== | ||
* [[ | *The terms ''single bypass'', ''double bypass'', ''triple bypass'', ''quadruple bypass'' and ''quintuple bypass'' refer to the number of [[coronary arteries]] [[Coronary artery bypass surgery|bypassed]] in the procedure. In other words, a double [[bypass]] means two [[coronary arteries]] are [[bypass|bypassed]] (such as [[left anterior descending|left anterior descending (LAD)]] [[coronary artery]] and [[right coronary artery|right coronary artery (RCA)]]); a triple [[bypass]] means three [[vessels]] are [[bypass|bypassed]] (such as [[LAD]], [[RCA]], and [[left circumflex artery|left circumflex artery (LCX)]]); a quadruple [[bypass]] means four vessels are bypassed (such as [[LAD]], [[RCA]], [[LCX]], first [[Left coronary artery|diagonal artery]] of the [[LAD]]). Less commonly more than four [[coronary arteries]] may be bypassed. | ||
* [[ | *A greater number of bypasses does not imply a [[patient]] is "sicker," nor does a lesser number imply a [[patient]] is "healthier".<ref>{{cite journal |author=Ohki S, Kaneko T, Satoh Y, ''et al'' |title=[Coronary artery bypass grafting in octogenarian] |language=Japanese |journal=Kyobu geka. The Japanese journal of thoracic surgery |volume=55 |issue=10 |pages=829–33; discussion 833–6 |year=2002 |pmid=12233100 |doi=}}</ref> | ||
* [[ | *A [[patient]] with a large amount of [[coronary artery disease|coronary artery disease]] ([[coronary artery disease|CAD]]) may receive fewer [[bypass]] [[grafts]] owing to the lack of suitable "target" [[vessels]]. | ||
*A [[patient]] with a single [[stenosis]] of the [[Left coronary artery|left main]] [[coronary artery]] often requires only two [[bypasses]] (to the [[LAD]] and the [[LCX]]). However, depending upon the [[anatomy]], grafts may also need to be placed to a large [[diagonal artery]], or to additional large [[obtuse marginal]] branches. | |||
== | ==Assessment of Target Vessels for Bypass Grafting== | ||
A [[coronary artery]] may be unsuitable for [[bypass]] [[grafting]] for the following reasons: | |||
*'''Size:''' If the native target [[artery]] it is small (< 1 mm or < 1.5 mm depending on surgeon preference) | |||
*'''Location:''' Some [[Anatomical terms of location|distal locations]] of the native target [[artery]] may not be accessible, or a conduit may not reach far down the native [[artery]]. | |||
*'''Native artery calcification:''' Heavily [[calcification|calcified]] native [[arteries]] are sometimes technically not amenable to [[anastomosis]] of a conduit. | |||
*'''Diffuse disease:''' The native [[artery]] may not have a section of the [[vessel]] that has a minimal [[disease]] where a conduit can be [[grafting|grafted]] to. | |||
*'''The native [[artery]] lies in the [[heart]] [[muscle]] or is intramyocardial:''' In this scenario, the native [[coronary artery]] is located within the [[heart]] [[muscle]] rather than on the surface of the [[heart]] and a [[graft]] cannot be attached to it. | |||
Although the cardiothoracic surgeon reviews the [[coronary angiogram]] prior to [[surgery]] and identifies the [[lesions]] (or "blockages") in the [[coronary arteries]] and will estimate the number of [[bypass]] [[grafts]] prior to [[surgery]], the final decision is made in the [[surgery|operating room]] based upon the direct examination of the [[heart]] and the suitability of the native target [[vessel]] for [[bypass|bypassing]]. | |||
==2021 ACA Revascularization Guideline== | |||
{|class="wikitable" | |||
|- | |||
| colspan="1" style="text-align:center; background:LightGreen"|Class 1 Recommendation, Level of Evidence: B-R<ref name="pmid34895950">{{cite journal| author=Writing Committee Members. Lawton JS, Tamis-Holland JE, Bangalore S, Bates ER, Beckie TM | display-authors=etal| title=2021 ACC/AHA/SCAI Guideline for Coronary Artery Revascularization: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. | journal=J Am Coll Cardiol | year= 2022 | volume= 79 | issue= 2 | pages= e21-e129 | pmid=34895950 | doi=10.1016/j.jacc.2021.09.006 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=34895950 }} </ref><ref name="pmid29708851">{{cite journal| author=Gaudino M, Benedetto U, Fremes S, Biondi-Zoccai G, Sedrakyan A, Puskas JD | display-authors=etal| title=Radial-Artery or Saphenous-Vein Grafts in Coronary-Artery Bypass Surgery. | journal=N Engl J Med | year= 2018 | volume= 378 | issue= 22 | pages= 2069-2077 | pmid=29708851 | doi=10.1056/NEJMoa1716026 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=29708851 }} </ref><ref name="pmid22871565">{{cite journal| author=Cao C, Manganas C, Horton M, Bannon P, Munkholm-Larsen S, Ang SC | display-authors=etal| title=Angiographic outcomes of radial artery versus saphenous vein in coronary artery bypass graft surgery: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. | journal=J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg | year= 2013 | volume= 146 | issue= 2 | pages= 255-61 | pmid=22871565 | doi=10.1016/j.jtcvs.2012.07.014 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=22871565 }} </ref><ref name="pmid30636525">{{cite journal| author=Gaudino M, Lorusso R, Rahouma M, Abouarab A, Tam DY, Spadaccio C | display-authors=etal| title=Radial Artery Versus Right Internal Thoracic Artery Versus Saphenous Vein as the Second Conduit for Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery: A Network Meta-Analysis of Clinical Outcomes. | journal=J Am Heart Assoc | year= 2019 | volume= 8 | issue= 2 | pages= e010839 | pmid=30636525 | doi=10.1161/JAHA.118.010839 | pmc=6497341 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=30636525 }} </ref> | |||
|- | |||
| bgcolor="LightGreen"| To improve long-term [[heart|cardiac]] outcomes, using a [[radial artery]] is recommended in preference to a [[saphenous vein]] conduit to graft the second most important, significantly stenosed non–[[LAD]] vessel. | |||
|} | |||
{|class="wikitable" | |||
|- | |||
| colspan="1" style="text-align:center; background:yellow"|Class 1 Recommendation, Level of Evidence: B-NR <ref name="pmid34895950">{{cite journal| author=Writing Committee Members. Lawton JS, Tamis-Holland JE, Bangalore S, Bates ER, Beckie TM | display-authors=etal| title=2021 ACC/AHA/SCAI Guideline for Coronary Artery Revascularization: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. | journal=J Am Coll Cardiol | year= 2022 | volume= 79 | issue= 2 | pages= e21-e129 | pmid=34895950 | doi=10.1016/j.jacc.2021.09.006 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=34895950 }} </ref><ref name="pmid3259128">{{cite journal| author=Zeff RH, Kongtahworn C, Iannone LA, Gordon DF, Brown TM, Phillips SJ | display-authors=etal| title=Internal mammary artery versus saphenous vein graft to the left anterior descending coronary artery: prospective randomized study with 10-year follow-up. | journal=Ann Thorac Surg | year= 1988 | volume= 45 | issue= 5 | pages= 533-6 | pmid=3259128 | doi=10.1016/s0003-4975(10)64526-2 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=3259128 }} </ref><ref name="pmid3484393">{{cite journal| author=Loop FD, Lytle BW, Cosgrove DM, Stewart RW, Goormastic M, Williams GW | display-authors=etal| title=Influence of the internal-mammary-artery graft on 10-year survival and other cardiac events. | journal=N Engl J Med | year= 1986 | volume= 314 | issue= 1 | pages= 1-6 | pmid=3484393 | doi=10.1056/NEJM198601023140101 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=3484393 }} </ref><ref name="pmid8127094">{{cite journal| author=Boylan MJ, Lytle BW, Loop FD, Taylor PC, Borsh JA, Goormastic M | display-authors=etal| title=Surgical treatment of isolated left anterior descending coronary stenosis. Comparison of left internal mammary artery and venous autograft at 18 to 20 years of follow-up. | journal=J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg | year= 1994 | volume= 107 | issue= 3 | pages= 657-62 | pmid=8127094 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=8127094 }} </ref><ref name="pmid8531997">{{cite journal| author=Cameron A, Davis KB, Green G, Schaff HV| title=Coronary bypass surgery with internal-thoracic-artery grafts--effects on survival over a 15-year period. | journal=N Engl J Med | year= 1996 | volume= 334 | issue= 4 | pages= 216-9 | pmid=8531997 | doi=10.1056/NEJM199601253340402 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=8531997 }} </ref><ref name="pmid27343909">{{cite journal| author=Magruder JT, Young A, Grimm JC, Conte JV, Shah AS, Mandal K | display-authors=etal| title=Bilateral internal thoracic artery grafting: Does graft configuration affect outcome? | journal=J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg | year= 2016 | volume= 152 | issue= 1 | pages= 120-7 | pmid=27343909 | doi=10.1016/j.jtcvs.2016.03.022 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=27343909 }} </ref> | |||
|- | |||
| bgcolor="yellow"| When [[bypass]] of the [[LAD]] is indicated to improve survival and reduce recurrent [[ischemia|ischemic events]], an [[internal thoracic artery]] ([[IMA]]), preferably the left, should be used to [[bypass]] the [[LAD]]. | |||
|} | |||
{|class="wikitable" | |||
|- | |||
| colspan="1" style="text-align:center; background:Lightblue"|Class 2a Recommendation, Level of Evidence: B-NR <ref name="pmid34895950">{{cite journal| author=Writing Committee Members. Lawton JS, Tamis-Holland JE, Bangalore S, Bates ER, Beckie TM | display-authors=etal| title=2021 ACC/AHA/SCAI Guideline for Coronary Artery Revascularization: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. | journal=J Am Coll Cardiol | year= 2022 | volume= 79 | issue= 2 | pages= e21-e129 | pmid=34895950 | doi=10.1016/j.jacc.2021.09.006 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=34895950 }} </ref> | |||
|- | |||
| bgcolor="lightblue"| Among [[patients]] undergoing [[CABG]], grafting the bilateral [[IMA]] (BIMA) by experienced operators is beneficial in improving long-term [[heart|cardiac]] outcomes (only if [[patients]] are selected appropriately). | |||
|} | |||
==2011 ACCF/AHA Guideline for Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery (DO NOT EDIT)<ref name="pmid22064599">{{cite journal| author=Hillis LD, Smith PK, Anderson JL, Bittl JA, Bridges CR, Byrne JG et al.| title=2011 ACCF/AHA Guideline for Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery: A Report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. | journal=Circulation | year= 2011 | volume= | issue= | pages= | pmid=22064599 | doi=10.1161/CIR.0b013e31823c074e | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=22064599 }} </ref>== | |||
{|class="wikitable" | {|class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 90: | Line 165: | ||
|bgcolor="LemonChiffon"|<nowiki>"</nowiki>'''3.''' Use of a [[radial artery]] graft may be reasonable when grafting left-sided coronary arteries with severe stenoses (>70%) and right-sided arteries with critical stenoses (≥90%) that perfuse LV myocardium.<ref name="pmid9832690">{{cite journal| author=Acar C, Ramsheyi A, Pagny JY, Jebara V, Barrier P, Fabiani JN et al.| title=The radial artery for coronary artery bypass grafting: clinical and angiographic results at five years. | journal=J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg | year= 1998 | volume= 116 | issue= 6 | pages= 981-9 | pmid=9832690 | doi= | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=9832690 }} </ref><ref name="pmid11782755">{{cite journal| author=Maniar HS, Sundt TM, Barner HB, Prasad SM, Peterson L, Absi T et al.| title=Effect of target stenosis and location on radial artery graft patency. | journal=J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg | year= 2002 | volume= 123 | issue= 1 | pages= 45-52 | pmid=11782755 | doi= | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=11782755 }} </ref><ref name="pmid11722042">{{cite journal| author=Moran SV, Baeza R, Guarda E, Zalaquett R, Irarrazaval MJ, Marchant E et al.| title=Predictors of radial artery patency for coronary bypass operations. | journal=Ann Thorac Surg | year= 2001 | volume= 72 | issue= 5 | pages= 1552-6 | pmid=11722042 | doi= | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=11722042 }} </ref><ref name="pmid9832694">{{cite journal| author=Possati G, Gaudino M, Alessandrini F, Luciani N, Glieca F, Trani C et al.| title=Midterm clinical and angiographic results of radial artery grafts used for myocardial revascularization. | journal=J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg | year= 1998 | volume= 116 | issue= 6 | pages= 1015-21 | pmid=9832694 | doi= | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=9832694 }} </ref><ref name="pmid10758391">{{cite journal| author=Royse AG, Royse CF, Tatoulis J, Grigg LE, Shah P, Hunt D et al.| title=Postoperative radial artery angiography for coronary artery bypass surgery. | journal=Eur J Cardiothorac Surg | year= 2000 | volume= 17 | issue= 3 | pages= 294-304 | pmid=10758391 | doi= | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=10758391 }} </ref><ref name="pmid15564545">{{cite journal| author=Desai ND, Cohen EA, Naylor CD, Fremes SE, Radial Artery Patency Study Investigators| title=A randomized comparison of radial-artery and saphenous-vein coronary bypass grafts. | journal=N Engl J Med | year= 2004 | volume= 351 | issue= 22 | pages= 2302-9 | pmid=15564545 | doi=10.1056/NEJMoa040982 | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=15564545 }} </ref> ''([[ACC AHA guidelines classification scheme#Level of Evidence|Level of Evidence: B]])''<nowiki>"</nowiki> | |bgcolor="LemonChiffon"|<nowiki>"</nowiki>'''3.''' Use of a [[radial artery]] graft may be reasonable when grafting left-sided coronary arteries with severe stenoses (>70%) and right-sided arteries with critical stenoses (≥90%) that perfuse LV myocardium.<ref name="pmid9832690">{{cite journal| author=Acar C, Ramsheyi A, Pagny JY, Jebara V, Barrier P, Fabiani JN et al.| title=The radial artery for coronary artery bypass grafting: clinical and angiographic results at five years. | journal=J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg | year= 1998 | volume= 116 | issue= 6 | pages= 981-9 | pmid=9832690 | doi= | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=9832690 }} </ref><ref name="pmid11782755">{{cite journal| author=Maniar HS, Sundt TM, Barner HB, Prasad SM, Peterson L, Absi T et al.| title=Effect of target stenosis and location on radial artery graft patency. | journal=J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg | year= 2002 | volume= 123 | issue= 1 | pages= 45-52 | pmid=11782755 | doi= | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=11782755 }} </ref><ref name="pmid11722042">{{cite journal| author=Moran SV, Baeza R, Guarda E, Zalaquett R, Irarrazaval MJ, Marchant E et al.| title=Predictors of radial artery patency for coronary bypass operations. | journal=Ann Thorac Surg | year= 2001 | volume= 72 | issue= 5 | pages= 1552-6 | pmid=11722042 | doi= | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=11722042 }} </ref><ref name="pmid9832694">{{cite journal| author=Possati G, Gaudino M, Alessandrini F, Luciani N, Glieca F, Trani C et al.| title=Midterm clinical and angiographic results of radial artery grafts used for myocardial revascularization. | journal=J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg | year= 1998 | volume= 116 | issue= 6 | pages= 1015-21 | pmid=9832694 | doi= | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=9832694 }} </ref><ref name="pmid10758391">{{cite journal| author=Royse AG, Royse CF, Tatoulis J, Grigg LE, Shah P, Hunt D et al.| title=Postoperative radial artery angiography for coronary artery bypass surgery. | journal=Eur J Cardiothorac Surg | year= 2000 | volume= 17 | issue= 3 | pages= 294-304 | pmid=10758391 | doi= | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=10758391 }} </ref><ref name="pmid15564545">{{cite journal| author=Desai ND, Cohen EA, Naylor CD, Fremes SE, Radial Artery Patency Study Investigators| title=A randomized comparison of radial-artery and saphenous-vein coronary bypass grafts. | journal=N Engl J Med | year= 2004 | volume= 351 | issue= 22 | pages= 2302-9 | pmid=15564545 | doi=10.1056/NEJMoa040982 | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=15564545 }} </ref> ''([[ACC AHA guidelines classification scheme#Level of Evidence|Level of Evidence: B]])''<nowiki>"</nowiki> | ||
|} | |} | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 06:27, 29 August 2022
|
Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery Microchapters | |
|
Pathophysiology | |
|---|---|
|
Diagnosis | |
|
Treatment | |
|
Perioperative Monitoring | |
|
Surgical Procedure | |
|
Special Scenarios | |
|
Coronary artery bypass surgery conduits used for bypass On the Web | |
|
FDA on Coronary artery bypass surgery conduits used for bypass | |
|
CDC on Coronary artery bypass surgery conduits used for bypass | |
|
Coronary artery bypass surgery conduits used for bypass in the news | |
|
Blogs on Coronary artery bypass surgery conduits used for bypass|- |
|
|
Directions to Hospitals Performing Coronary artery bypass surgery conduits used for bypass | |
|
Risk calculators for Coronary artery bypass surgery conduits used for bypass | |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editors-in-Chief: Cafer Zorkun, M.D., Ph.D. [2], Mohammed A. Sbeih, M.D. Anahita Deylamsalehi, M.D.[3]
Overview
The choice of conduits (arteries and/or veins from elsewhere in the body) to bypass the blockages is highly surgeon and institution dependent. To choose the proper conduits for CABG both clinical and technical factors such as life expectancy, presence of diabetes, chronic renal failure, and degree of the target stenosis must be considered. Saphenous vein, internal thoracic artery, and radial artery are the most used vessels to harvest for grafting. The saphenous vein can be harvested by either direct visualization or via an endoscopic approach. Among these two methods the endoscopic approach has been associated with lower rates of wound infection, greater patient satisfaction, and earlier mobilization. However, non-randomized data from a much larger multicenter study does suggest that endoscopyendoscopic harvesting may be associated with a higher rate of failure and adverse events such as death and MI. Veins that are used either have their valves removed or are turned around so that the valves in them do not occlude blood flow in the graft. On the other hand, numerous studies support the use of the left internal thoracic artery (LITA) (also known as the left internal mammary artery (LIMA)) to graft the LAD in order to improve survival unless contraindicated. Evidence shows that the right IMA can be used to graft the LAD if the LIMA is impractical and unusable. Furthermore, the right IMA can be used in conjunction with the LIMA which is called bilateral internal mammary artery (BIMA) grafting. The latter method showed a better outcome based on multiple studies. In multiple arterial revascularization during Coronary artery bypass surgery, the right internal thoracic artery (RITA) has been proofed to be a better choice as a conduit than the radial artery. On the other hand, numerous clinical trials have demonstrated better patency rates (in mid- and long-term) when the radial artery is used in comparison with the saphenous vein.
Conduits used for bypass
- The choice of conduits (arteries and/or veins from elsewhere in the body) to bypass the blockages is highly surgeon and institution dependent.
- To choose the proper conduits for CABG both clinical and technical factors such as life expectancy, presence of diabetes, chronic renal failure, and degree of the target stenosis must be considered.[1]
- The following table published by 2021 ACA Revascularization Guideline presents the best practices for the Use of bypass conduits in CABG:[1]
| Assessing palmar arch completeness and ulnar compensation before harvesting the radial artery. If radial artery harvesting is considered it is recommended to use the arm with the best ulnar compensation. |
| It is recommended to use radial artery grafts to target vessels with subocclusive stenosis. |
| It is recommended to avoid radial artery use after transradial catheterization. |
| It is recommended to avoid radial artery use in chronic kidney disease patients and in those with a high likelihood of rapid progression to hemodialysis. |
| It is recommended to avoid oral calcium channel blockers for the first postoperative year after radial artery grafting. |
| It is recommended to avoid bilateral percutaneous or surgical radial artery procedures in patients with coronary artery disease with a goal to preserve the artery for future use. |
| It is recommended to use the internal mammary artery (using the skeletonization technique) to reduce the risk of sternal wound complications. |
| It is recommended to use an endoscopic saphenous vein harvest technique in patients at risk of wound complications. |
| For patients at low risk of wound complications, it is recommended to use a no-touch saphenous vein harvest technique. |
| It is recommended to use the skeletonized right gastroepiploic artery to graft right coronary artery target vessels with subocclusive stenosis if the operator is experienced with the use of the artery. |
- Typically, the left internal thoracic artery (LITA) (also referred to as the left internal mammary artery or LIMA) is grafted to the Left Anterior Descending artery and a combination of other arteries and veins is used for other coronary arteries.
- The right internal thoracic artery (RITA), the great saphenous vein from the leg and the radial artery from the forearm are frequently used.
- The right gastroepiploic artery from the stomach is infrequently used given the difficult mobilization from the abdomen.
Saphenous vein
Saphenous vein anatomy
- The great saphenous vein (GSV) is frequently used as a conduit for CABG. It originates from where the dorsal vein of the first digit (the large toe) merges with the dorsal venous arch of the foot.
- After passing anterior to the medial malleolus (where it often can be visualized and palpated), it runs up the medial side of the leg. At knee, it runs over the posterior border of the medial epicondyle of the femur bone.
- The great saphenous vein then courses laterally to lie on the anterior surface of the thigh before entering an opening in the fascia lata called the saphenous opening. It joins with the femoral vein in the region of the femoral triangle at the saphenofemoral junction.
- The small saphenous vein (also lesser saphenous vein) originates where the dorsal vein from the fifth digit (smallest toe) merges with the [[dorsal venous arch of the foot, which attaches to the great saphenous vein. It is considered a superficial vein and is subcutaneous (just under the skin). From its origin, it courses around the lateral aspect of the foot (inferior and posterior to the lateral malleolus) and runs along the posterior aspect of the leg (with the sural nerve), passes between the heads of the gastrocnemius muscle, and drains into the popliteal vein, approximately at or above the level of the knee joint.
-
Cross-section through the middle of the thigh.
-
Cross-section through the middle of the leg.
-
The great saphenous vein and landmarks along its course
-
The great saphenous vein and its tributaries at the fossa ovalis in the groin.
-
Small saphenous vein and its tributaries.
Saphenous vein harvesting
- The saphenous vein can be harvested by either direct visualization or via an endoscopic approach. Veins that are used either have their valves removed or are turned around so that the valves in them do not occlude blood flow in the graft. The technique of saphenous vein harvesting may influence later SVG patency. The process of harvesting the vein and pressure testing the vein for a leak may damage the endothelium.[2][3]
- The endoscopic approach has been associated with lower rates of wound infection, greater patient satisfaction, and earlier mobilization.[4][5][6][7] One small randomized study of 144 patients showed no difference in histologic findings between the traditional and endoscopic techniques.[4]In another small study of 40 patients randomized to the two techniques, no difference was seen in angiographic patency at 3 months.[7]Another small randomized study of 144 patients who returned for angiography demonstrated an occlusion rate of 21.7% for the endoscopic approach vs 17.6% for the open approach.[6]
- However, non-randomized data from a much larger multicenter study does suggest that endoscopyendoscopic harvesting may be associated with a higher rate of failure and adverse events such as death and MI.[5]
- Complications associated with saphenous vein harvesting include the following:
- Saphenous nerve injury
- Infection at incision sites or sepsis.
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
- Keloid scarring
- Chronic pain at incision sites
The Internal Thoracic Artery
- Numerous studies support the use of the left internal thoracic artery (LITA) (also known as the left internal mammary artery (LIMA)) to graft the LAD in order to improve survival unless contraindicated.[1][8][9][10]
- In a study evaluating almost 6,000 patients, LIMA grafting was able to reduce the rate of cardiac-related rehospitalization and revascularization. In addition, this study showed a lower rate of death and recurrent infarction in those who undergone LIMA grafting.[11]
- Evidence shows that the right IMA can be used to graft the LAD if the LIMA is impractical and unusable. Furthermore, the right IMA can be used in conjunction with the LIMA which is called bilateral internal mammary artery (BIMA) grafting.[1]
- Based on observational studies, BIMA grafting has a survival advantage when compared with CABG with a single IMA.[1][12][13][14][15]
- Reports from a meta-analysis of 38 studies, including 174,205 patients demonstrated a decreased mortality rate at 7.25 years follow up among patients who had BIMA grafting.[15]
- On the other hand, a single large randomized controlled trial reported no difference in 10-year all-cause mortality when BIMA was compared with single IMA. Furthermore, this study highlighted the importance of surgical expertise in BIMA grafting.[16]
- It is critical to consider the higher risk of sternal infection with BIMA grafting.[17]
- In multiple arterial revascularization during Coronary artery bypass surgery, the right internal thoracic artery (RITA) has been proofed to be a better choice as a conduit than the radial artery. This has been published at the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) 2011 Congress, after a trial on more than 1000 patients who had the operation in 10 years trial.
- The left internal thoracic artery (LITA) (also known as the left internal mammary artery (LIMA)) is the best vessel to use for coronary artery bypass surgery when only one artery is required.
- It was known that the long-term outcomes of the arterial grafts are much better than saphenous vein grafts (SVGs) and has less morbidity and mortality rates.[18][11][9][10]
- The right internal thoracic artery (RITA) is the best second conduit for the bypass and has better long-term outcomes than the radial artery. The use of the RITA results in the following in comparison with SVG:
- Less major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events.
- Less perioperative myocardial infarction rates.
- Less perioperative stroke rates.
- Less cardiac-related deaths.
- There have been good clinical results with the single left internal thoracic artery grafting compared with saphenous vein grafting. This prompted surgeons to use both ITAs. Bilateral ITA grafting could improve long-term survival. Late complications like myocardial infarction and need to reoperate may be avoided. However, mathematical modeling is required to assist in developing a strategy for use of such grafts.[19]
- In a cohort study of 8123 patients who received single internal thoracic artery grafts and 2001 who received bilateral internal thoracic artery grafts for multivessel coronary artery disease for a duration of 20 years, it was found that the latter produces improved survival compared with single internal thoracic artery grafting during the second postoperative decade, and the magnitude of that benefit increases through 20 postoperative years.[20]
- It's easy to harvest the radial artery, but it has a higher risk for vasospasm and atherosclerosis than the right internal thoracic artery (RITA). Some institution solves this problem (vasospasm) by preparing the radial arteries with phenoxybenzamine.
- Although the fact that using both internal thoracic arteries for coronary artery bypass surgery takes a longer time, it has better long-term results and perioperative outcomes. This has to be proofed and confirmed by more randomized and controlled trials.
Radial Artery
- Numerous clinical trials have demonstrated better patency rates (in mid- and long-term) when the radial artery is used in comparison with the saphenous vein.[21][22][23]
- Furthermore, several observational studies reported a better survival rate when the radial artery is used instead of the saphenous vein for CABG.[12][24][21]
- Based on the 2021 ACA Revascularization guideline, the following patients benefit the most from the radial artery use:[1]
- Patients younger than 75 years old
- Females
- Patients with preserved renal function
- There is some limited data regarding the vulnerability to the effect of chronic native competitive flow in composite radial artery grafts.[25]
Conduit Nomenclature
- The terms single bypass, double bypass, triple bypass, quadruple bypass and quintuple bypass refer to the number of coronary arteries bypassed in the procedure. In other words, a double bypass means two coronary arteries are bypassed (such as left anterior descending (LAD) coronary artery and right coronary artery (RCA)); a triple bypass means three vessels are bypassed (such as LAD, RCA, and left circumflex artery (LCX)); a quadruple bypass means four vessels are bypassed (such as LAD, RCA, LCX, first diagonal artery of the LAD). Less commonly more than four coronary arteries may be bypassed.
- A greater number of bypasses does not imply a patient is "sicker," nor does a lesser number imply a patient is "healthier".[26]
- A patient with a large amount of coronary artery disease (CAD) may receive fewer bypass grafts owing to the lack of suitable "target" vessels.
- A patient with a single stenosis of the left main coronary artery often requires only two bypasses (to the LAD and the LCX). However, depending upon the anatomy, grafts may also need to be placed to a large diagonal artery, or to additional large obtuse marginal branches.
Assessment of Target Vessels for Bypass Grafting
A coronary artery may be unsuitable for bypass grafting for the following reasons:
- Size: If the native target artery it is small (< 1 mm or < 1.5 mm depending on surgeon preference)
- Location: Some distal locations of the native target artery may not be accessible, or a conduit may not reach far down the native artery.
- Native artery calcification: Heavily calcified native arteries are sometimes technically not amenable to anastomosis of a conduit.
- Diffuse disease: The native artery may not have a section of the vessel that has a minimal disease where a conduit can be grafted to.
- The native artery lies in the heart muscle or is intramyocardial: In this scenario, the native coronary artery is located within the heart muscle rather than on the surface of the heart and a graft cannot be attached to it.
Although the cardiothoracic surgeon reviews the coronary angiogram prior to surgery and identifies the lesions (or "blockages") in the coronary arteries and will estimate the number of bypass grafts prior to surgery, the final decision is made in the operating room based upon the direct examination of the heart and the suitability of the native target vessel for bypassing.
2021 ACA Revascularization Guideline
| Class 1 Recommendation, Level of Evidence: B-R[1][24][22][12] |
| To improve long-term cardiac outcomes, using a radial artery is recommended in preference to a saphenous vein conduit to graft the second most important, significantly stenosed non–LAD vessel. |
| Class 1 Recommendation, Level of Evidence: B-NR [1][9][11][10][8][27] |
| When bypass of the LAD is indicated to improve survival and reduce recurrent ischemic events, an internal thoracic artery (IMA), preferably the left, should be used to bypass the LAD. |
| Class 2a Recommendation, Level of Evidence: B-NR [1] |
| Among patients undergoing CABG, grafting the bilateral IMA (BIMA) by experienced operators is beneficial in improving long-term cardiac outcomes (only if patients are selected appropriately). |
2011 ACCF/AHA Guideline for Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery (DO NOT EDIT)[28]
| Class I |
| "1. If possible, the left internal mammary artery (LIMA) should be used to bypass the left anterior descending (LAD) artery when bypass of the LAD artery is indicated.[10][8][11][29] (Level of Evidence: B)" |
| Class III: HARM |
| "1. An arterial graft should not be used to bypass the right coronary artery with less than a critical stenosis (<90%).[29] (Level of Evidence: C)" |
| Class IIa |
| "1. The right internal mammary artery is probably indicated to bypass the LAD artery when the LIMA is unavailable or unsuitable as a bypass conduit. (Level of Evidence: C)" |
| "2. When anatomically and clinically suitable, use of a second internal mammary artery to graft the left circumflex or right coronary artery (when critically stenosed and perfusing LV myocardium) is reasonable to improve the likelihood of survival and to decrease reintervention.[30][20][31][32][33] (Level of Evidence: B)" |
| Class IIb |
| "1. Complete arterial revascularization may be reasonable in patients less than or equal to 60 years of age with few or no comorbidities. (Level of Evidence: C)" |
| "2. Arterial grafting of the right coronary artery may be reasonable when a critical (≥90%) stenosis is present.[29][32][34] (Level of Evidence: B)" |
| "3. Use of a radial artery graft may be reasonable when grafting left-sided coronary arteries with severe stenoses (>70%) and right-sided arteries with critical stenoses (≥90%) that perfuse LV myocardium.[35][36][37][38][39][40] (Level of Evidence: B)" |
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 Writing Committee Members. Lawton JS, Tamis-Holland JE, Bangalore S, Bates ER, Beckie TM; et al. (2022). "2021 ACC/AHA/SCAI Guideline for Coronary Artery Revascularization: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines". J Am Coll Cardiol. 79 (2): e21–e129. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2021.09.006. PMID 34895950 Check
|pmid=value (help). - ↑ Lawrie GM, Weilbacher DE, Henry PD. Endothelium-dependent relaxation in human saphenous vein grafts. Effects of preparation and clinicopathologic correlations. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1990;100:612—20.
- ↑ Souza DS, Johansson B, Bojo¨ L, Karlsson R, Geijer H, Filbey D, Bodin L, Arbeus M, Dashwood MR. Harvesting the saphenous vein with surrounding tissue for CABG provides long-term graft patency comparable to the left internal thoracic artery: results of a randomized longitudinal trial. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2006;132:373—8.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Kiaii B, Moon BC, Massel D, Langlois Y, Austin TW, Willoughby A, Guiraudon C, Howard CR, Guo LR (2002). "A prospective randomized trial of endoscopic versus conventional harvesting of the saphenous vein in coronary artery bypass surgery". J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 123 (2): 204–12. PMID 11828277. Retrieved 2010-07-23. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ 5.0 5.1 Lopes RD, Hafley GE, Allen KB, Ferguson TB, Peterson ED, Harrington RA, Mehta RH, Gibson CM, Mack MJ, Kouchoukos NT, Califf RM, Alexander JH (2009). "Endoscopic versus open vein-graft harvesting in coronary-artery bypass surgery". The New England Journal of Medicine. 361 (3): 235–44. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0900708. PMID 19605828. Retrieved 2010-07-12. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ 6.0 6.1 Yun KL, Wu Y, Aharonian V, Mansukhani P, Pfeffer TA, Sintek CF, Kochamba GS, Grunkemeier G, Khonsari S (2005). "Randomized trial of endoscopic versus open vein harvest for coronary artery bypass grafting: six-month patency rates". J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 129 (3): 496–503. doi:10.1016/j.jtcvs.2004.08.054. PMID 15746730. Retrieved 2010-07-23. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ 7.0 7.1 Perrault LP, Jeanmart H, Bilodeau L, Lespérance J, Tanguay JF, Bouchard D, Pagé P, Carrier M (2004). "Early quantitative coronary angiography of saphenous vein grafts for coronary artery bypass grafting harvested by means of open versus endoscopic saphenectomy: a prospective randomized trial". J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 127 (5): 1402–7. doi:10.1016/j.jtcvs.2003.10.040. PMID 15115999. Retrieved 2010-07-23. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Cameron A, Davis KB, Green G, Schaff HV (1996). "Coronary bypass surgery with internal-thoracic-artery grafts--effects on survival over a 15-year period". N Engl J Med. 334 (4): 216–9. doi:10.1056/NEJM199601253340402. PMID 8531997.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 Zeff RH, Kongtahworn C, Iannone LA, Gordon DF, Brown TM, Phillips SJ; et al. (1988). "Internal mammary artery versus saphenous vein graft to the left anterior descending coronary artery: prospective randomized study with 10-year follow-up". Ann Thorac Surg. 45 (5): 533–6. doi:10.1016/s0003-4975(10)64526-2. PMID 3259128.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 Boylan MJ, Lytle BW, Loop FD, Taylor PC, Borsh JA, Goormastic M; et al. (1994). "Surgical treatment of isolated left anterior descending coronary stenosis. Comparison of left internal mammary artery and venous autograft at 18 to 20 years of follow-up". J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 107 (3): 657–62. PMID 8127094.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 Loop FD, Lytle BW, Cosgrove DM, Stewart RW, Goormastic M, Williams GW; et al. (1986). "Influence of the internal-mammary-artery graft on 10-year survival and other cardiac events". N Engl J Med. 314 (1): 1–6. doi:10.1056/NEJM198601023140101. PMID 3484393.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 Gaudino M, Lorusso R, Rahouma M, Abouarab A, Tam DY, Spadaccio C; et al. (2019). "Radial Artery Versus Right Internal Thoracic Artery Versus Saphenous Vein as the Second Conduit for Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery: A Network Meta-Analysis of Clinical Outcomes". J Am Heart Assoc. 8 (2): e010839. doi:10.1161/JAHA.118.010839. PMC 6497341. PMID 30636525.
- ↑ Yi G, Shine B, Rehman SM, Altman DG, Taggart DP (2014). "Effect of bilateral internal mammary artery grafts on long-term survival: a meta-analysis approach". Circulation. 130 (7): 539–45. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.004255. PMID 24916209.
- ↑ Takagi H, Goto SN, Watanabe T, Mizuno Y, Kawai N, Umemoto T (2014). "A meta-analysis of adjusted hazard ratios from 20 observational studies of bilateral versus single internal thoracic artery coronary artery bypass grafting". J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 148 (4): 1282–90. doi:10.1016/j.jtcvs.2014.01.010. PMID 24521973.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 Gaudino M, Di Franco A, Rahouma M, Tam DY, Iannaccone M, Deb S; et al. (2018). "Unmeasured Confounders in Observational Studies Comparing Bilateral Versus Single Internal Thoracic Artery for Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting: A Meta-Analysis". J Am Heart Assoc. 7 (1). doi:10.1161/JAHA.117.008010. PMC 5778975. PMID 29306899.
- ↑ Taggart DP, Benedetto U, Gerry S, Altman DG, Gray AM, Lees B; et al. (2019). "Bilateral versus Single Internal-Thoracic-Artery Grafts at 10 Years". N Engl J Med. 380 (5): 437–446. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1808783. PMID 30699314.
- ↑ Schwann TA, Habib RH, Wallace A, Shahian DM, O'Brien S, Jacobs JP; et al. (2018). "Operative Outcomes of Multiple-Arterial Versus Single-Arterial Coronary Bypass Grafting". Ann Thorac Surg. 105 (4): 1109–1119. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2017.10.058. PMID 29453002.
- ↑ Beach JM, Mihaljevic T, Svensson LG, Rajeswaran J, Marwick T, Griffin B; et al. (2013). "Coronary artery disease and outcomes of aortic valve replacement for severe aortic stenosis". J Am Coll Cardiol. 61 (8): 837–48. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2012.10.049. PMC 4262244. PMID 23428216.
- ↑ Buxton BF, Komeda M, Fuller JA, Gordon I (1998). "Bilateral internal thoracic artery grafting may improve the outcome of coronary artery surgery. Risk-adjusted survival". Circulation. 98 (19 Suppl): II1–6. PMID 9852872.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 Lytle BW, Blackstone EH, Sabik JF, Houghtaling P, Loop FD, Cosgrove DM (2004). "The effect of bilateral internal thoracic artery grafting on survival during 20 postoperative years". Ann Thorac Surg. 78 (6): 2005–12, discussion 2012-4. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2004.05.070. PMID 15561021.
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 Gaudino M, Benedetto U, Fremes S, Ballman K, Biondi-Zoccai G, Sedrakyan A; et al. (2020). "Association of Radial Artery Graft vs Saphenous Vein Graft With Long-term Cardiovascular Outcomes Among Patients Undergoing Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis". JAMA. 324 (2): 179–187. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.8228. PMC 7361649 Check
|pmc=value (help). PMID 32662861 Check|pmid=value (help). - ↑ 22.0 22.1 Cao C, Manganas C, Horton M, Bannon P, Munkholm-Larsen S, Ang SC; et al. (2013). "Angiographic outcomes of radial artery versus saphenous vein in coronary artery bypass graft surgery: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials". J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 146 (2): 255–61. doi:10.1016/j.jtcvs.2012.07.014. PMID 22871565.
- ↑ Benedetto U, Raja SG, Albanese A, Amrani M, Biondi-Zoccai G, Frati G (2015). "Searching for the second best graft for coronary artery bypass surgery: a network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials†". Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 47 (1): 59–65, discussion 65. doi:10.1093/ejcts/ezu111. PMID 24686003.
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 Gaudino M, Benedetto U, Fremes S, Biondi-Zoccai G, Sedrakyan A, Puskas JD; et al. (2018). "Radial-Artery or Saphenous-Vein Grafts in Coronary-Artery Bypass Surgery". N Engl J Med. 378 (22): 2069–2077. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1716026. PMID 29708851.
- ↑ Abu-Omar Y, Mussa S, Anastasiadis K, Steel S, Hands L, Taggart DP (2004). "Duplex ultrasonography predicts safety of radial artery harvest in the presence of an abnormal Allen test". Ann Thorac Surg. 77 (1): 116–9. doi:10.1016/s0003-4975(03)01515-7. PMID 14726046.
- ↑ Ohki S, Kaneko T, Satoh Y; et al. (2002). "[Coronary artery bypass grafting in octogenarian]". Kyobu geka. The Japanese journal of thoracic surgery (in Japanese). 55 (10): 829–33, discussion 833–6. PMID 12233100.
- ↑ Magruder JT, Young A, Grimm JC, Conte JV, Shah AS, Mandal K; et al. (2016). "Bilateral internal thoracic artery grafting: Does graft configuration affect outcome?". J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 152 (1): 120–7. doi:10.1016/j.jtcvs.2016.03.022. PMID 27343909.
- ↑ Hillis LD, Smith PK, Anderson JL, Bittl JA, Bridges CR, Byrne JG; et al. (2011). "2011 ACCF/AHA Guideline for Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery: A Report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines". Circulation. doi:10.1161/CIR.0b013e31823c074e. PMID 22064599.
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 29.2 Sabik JF, Lytle BW, Blackstone EH, Houghtaling PL, Cosgrove DM (2005). "Comparison of saphenous vein and internal thoracic artery graft patency by coronary system". Ann Thorac Surg. 79 (2): 544–51, discussion 544-51. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2004.07.047. PMID 15680832.
- ↑ Lytle BW, Blackstone EH, Loop FD, Houghtaling PL, Arnold JH, Akhrass R; et al. (1999). "Two internal thoracic artery grafts are better than one". J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 117 (5): 855–72. PMID 10220677.
- ↑ Sabik JF, Blackstone EH, Gillinov AM, Banbury MK, Smedira NG, Lytle BW (2006). "Influence of patient characteristics and arterial grafts on freedom from coronary reoperation". J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 131 (1): 90–8. doi:10.1016/j.jtcvs.2005.05.024. PMID 16399299.
- ↑ 32.0 32.1 Sabik JF, Stockins A, Nowicki ER, Blackstone EH, Houghtaling PL, Lytle BW; et al. (2008). "Does location of the second internal thoracic artery graft influence outcome of coronary artery bypass grafting?". Circulation. 118 (14 Suppl): S210–5. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.760827. PMID 18824756.
- ↑ Stevens LM, Carrier M, Perrault LP, Hébert Y, Cartier R, Bouchard D; et al. (2004). "Single versus bilateral internal thoracic artery grafts with concomitant saphenous vein grafts for multivessel coronary artery bypass grafting: effects on mortality and event-free survival". J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 127 (5): 1408–15. doi:10.1016/j.jtcvs.2003.10.006. PMID 15116000.
- ↑ Sabik JF, Lytle BW, Blackstone EH, Khan M, Houghtaling PL, Cosgrove DM (2003). "Does competitive flow reduce internal thoracic artery graft patency?". Ann Thorac Surg. 76 (5): 1490–6, discussion 1497. PMID 14602274.
- ↑ Acar C, Ramsheyi A, Pagny JY, Jebara V, Barrier P, Fabiani JN; et al. (1998). "The radial artery for coronary artery bypass grafting: clinical and angiographic results at five years". J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 116 (6): 981–9. PMID 9832690.
- ↑ Maniar HS, Sundt TM, Barner HB, Prasad SM, Peterson L, Absi T; et al. (2002). "Effect of target stenosis and location on radial artery graft patency". J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 123 (1): 45–52. PMID 11782755.
- ↑ Moran SV, Baeza R, Guarda E, Zalaquett R, Irarrazaval MJ, Marchant E; et al. (2001). "Predictors of radial artery patency for coronary bypass operations". Ann Thorac Surg. 72 (5): 1552–6. PMID 11722042.
- ↑ Possati G, Gaudino M, Alessandrini F, Luciani N, Glieca F, Trani C; et al. (1998). "Midterm clinical and angiographic results of radial artery grafts used for myocardial revascularization". J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 116 (6): 1015–21. PMID 9832694.
- ↑ Royse AG, Royse CF, Tatoulis J, Grigg LE, Shah P, Hunt D; et al. (2000). "Postoperative radial artery angiography for coronary artery bypass surgery". Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 17 (3): 294–304. PMID 10758391.
- ↑ Desai ND, Cohen EA, Naylor CD, Fremes SE, Radial Artery Patency Study Investigators (2004). "A randomized comparison of radial-artery and saphenous-vein coronary bypass grafts". N Engl J Med. 351 (22): 2302–9. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa040982. PMID 15564545.