Adenosine: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
m (Protected "Adenosine": Bot: Protecting all pages from category Drug ([Edit=Allow only administrators] (indefinite) [Move=Allow only administrators] (indefinite))) |
||
| (22 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
|hasBlackBoxWarning= | |hasBlackBoxWarning= | ||
|adverseReactions= | |adverseReactions= | ||
[[chest discomfort]], [[flushing]], [[abdominal discomfort]], [[pain]] of head and neck region, [[dizziness]], [[headache]], and [[dyspnea]] | |||
<!--Black Box Warning--> | <!--Black Box Warning--> | ||
| Line 46: | Line 44: | ||
|fdaLIADAdult= | |fdaLIADAdult= | ||
===== | =====Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia===== | ||
* | * Adenocard (adenosine injection) should be given as a rapid bolus by the peripheral [[intravenous]] route. To be certain the solution reaches the systemic circulation, it should be administered either directly into a vein or, if given into an IV line, it should be given as close to the patient as possible and followed by a rapid saline flush. | ||
======Adult Patients====== | |||
* The dose recommendation is based on clinical studies with peripheral venous bolus dosing. Central venous (CVP or other) administration of Adenocard has not been systematically studied. | |||
* Dosing Information | * Dosing Information | ||
:* Initial dose: '''6 mg''' given as a rapid intravenous bolus (administered over a 1-2 second period). | |||
:* Repeat administration: If the first dose does not result in elimination of the supraventricular tachycardia within 1-2 minutes, '''12 mg''' should be given as a rapid intravenous bolus. This '''12 mg''' dose may be repeated a second time if required. | |||
=====Pediatric Patients with a Body Weight < 50 kg===== | |||
===== | |||
* Dosing Information | * Dosing Information | ||
:* Give '''0.05 to 0.1 mg/kg''' as a rapid IV bolus given either centrally or peripherally. A saline flush should follow. | |||
:* Repeat administration: If conversion of [[PSVT]] does not occur within 1-2 minutes, additional bolus injections of adenosine can be administered at incrementally higher doses, increasing the amount given by '''0.05 to 0.1 mg/kg'''. Follow each bolus with a saline flush. This process should continue until sinus rhythm is established or a maximum single dose of '''0.3 mg/kg''' is used. | |||
======Pediatric Patients with a Body Weight ≥ 50 kg====== | |||
===== | |||
* Administer the adult dose. | |||
<!--Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)--> | <!--Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)--> | ||
| Line 76: | Line 72: | ||
|offLabelAdultGuideSupport= | |offLabelAdultGuideSupport= | ||
===== | =====Supraventricular Tachycardia===== | ||
* Developed by: | * Developed by: [[ACC AHA guidelines classification scheme|ACCF/AHA]] | ||
* Class of Recommendation: | * Class of Recommendation: Class I | ||
* Strength of Evidence: | * Strength of Evidence: Category B | ||
* Dosing Information | * Dosing Information | ||
:* | :* '''6 mg''', followed by '''12 mg''' as needed<ref>{{Cite journal | issn = 0003-4819 | volume = 113 | issue = 2 | pages = 104–110 | last = DiMarco | first = J. P. | coauthors = W. Miles, M. Akhtar, S. Milstein, A. D. Sharma, E. Platia, B. McGovern, M. M. Scheinman, W. C. Govier | title = Adenosine for paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia: dose ranging and comparison with verapamil. Assessment in placebo-controlled, multicenter trials. The Adenosine for PSVT Study Group | journal = Annals of Internal Medicine | date = 1990-07-15 | pmid = 2193560 }}</ref> | ||
===== | |||
<!--Non–Guideline-Supported Use (Adult)--> | <!--Non–Guideline-Supported Use (Adult)--> | ||
| Line 96: | Line 88: | ||
|offLabelAdultNoGuideSupport= | |offLabelAdultNoGuideSupport= | ||
===== | =====Preventing Graft Occlusion Following Aortocoronary Bypass Surgery===== | ||
* Dosing Information | * Dosing Information | ||
:* | :* Intraoperative administration of blood cardioplegia containing containing 0.5–2 mM adenosine. Patients receiving adenosine cardioplegia were also given an infusion of adenosine (200 microg/kg/min) 10 minutes before and 15 minutes after removal of the aortic crossclamp.<ref>{{Cite journal | issn = 0003-4975 | volume = 63 | issue = 6 Suppl | pages = –30-34 | last = Robinson | first = M. C. | coauthors = K. A. Thielmeier, B. B. Hill | title = Transient ventricular asystole using adenosine during minimally invasive and open sternotomy coronary artery bypass grafting | journal = The Annals of Thoracic Surgery | date = 1997-06 | pmid = 9203593 }}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal | issn = 0002-9149 | volume = 79 | issue = 12A | pages = 38–43 | last = Mentzer | first = R. M. | coauthors = P. S. Rahko, V. Molina-Viamonte, C. C. Canver, P. S. Chopra, R. B. Love, T. D. Cook, J. O. Hegge, R. D. Lasley | title = Safety, tolerance, and efficacy of adenosine as an additive to blood cardioplegia in humans during coronary artery bypass surgery | journal = The American Journal of Cardiology | date = 1997-06-19 | pmid = 9223362 }}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal | issn = 0003-4932 | volume = 229 | issue = 5 | pages = 643–649; discussion 649-650 | last = Mentzer | first = R. M. | coauthors = V. Birjiniuk, S. Khuri, J. E. Lowe, P. S. Rahko, R. D. Weisel, H. A. Wellons, M. L. Barker, R. D. Lasley | title = Adenosine myocardial protection: preliminary results of a phase II clinical trial | journal = Annals of Surgery | date = 1999-05 | pmid = 10235522 | pmc = PMC1420808 }}</ref> | ||
=====Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty===== | |||
* Dosing Information | |||
:* '''20 mg''' in 50 milliliters (mL) saline infused at a rate of 2 mg/minute<ref>{{Cite journal | issn = 0009-7322 | volume = 95 | issue = 11 | pages = 2500–2507 | last = Leesar | first = M. A. | coauthors = M. Stoddard, M. Ahmed, J. Broadbent, R. Bolli | title = Preconditioning of human myocardium with adenosine during coronary angioplasty | journal = Circulation | date = 1997-06-03 | pmid = 9184580 }}</ref> | |||
<!--Pediatric Indications and Dosage--> | <!--Pediatric Indications and Dosage--> | ||
| Line 111: | Line 105: | ||
|fdaLIADPed= | |fdaLIADPed= | ||
There is limited information regarding <i>FDA-Labeled Use</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in pediatric patients. | There is limited information regarding <i>FDA-Labeled Use</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in pediatric patients. | ||
| Line 128: | Line 114: | ||
|offLabelPedGuideSupport= | |offLabelPedGuideSupport= | ||
===== | =====Supraventricular Tachycardia===== | ||
* Developed by: | * Developed by: [[ACC AHA guidelines classification scheme|ACCF/AHA]] | ||
* Class of Recommendation: | * Class of Recommendation: Class IIa | ||
* Strength of Evidence: | * Strength of Evidence: Category B | ||
* Dosing Information | * Dosing Information | ||
:* | :* '''0.05–0.3 mg/kg'''<ref>{{Cite journal | issn = 0196-0644 | volume = 33 | issue = 2 | pages = 185–191 | last = Losek | first = J. D. | coauthors = E. Endom, A. Dietrich, G. Stewart, W. Zempsky, K. Smith | title = Adenosine and pediatric supraventricular tachycardia in the emergency department: multicenter study and review | journal = Annals of Emergency Medicine | date = 1999-02 | pmid = 9922414 }}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal | issn = 0374-5600 | volume = 39 | issue = 5 | pages = 570–577 | last = Lenk | first = M. | coauthors = A. Celiker, D. Alehan, G. Koçak, S. Ozme | title = Role of adenosine in the diagnosis and treatment of tachyarrhythmias in pediatric patients | journal = Acta Paediatrica Japonica; Overseas Edition | date = 1997-10 | pmid = 9363655 }}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal | doi = 10.1055/s-2007-994353 | issn = 0735-1631 | volume = 13 | issue = 6 | pages = 343–346 | last = Paret | first = G. | coauthors = D. Steinmetz, J. Kuint, J. Hegesh, M. Frand, Z. Barzilay | title = Adenosine for the treatment of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia in full-term and preterm newborn infants | journal = American Journal of Perinatology | date = 1996-08 | pmid = 8865979 }}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal | issn = 0007-0769 | volume = 62 | issue = 3 | pages = 204–211 | last = Till | first = J. | coauthors = E. A. Shinebourne, M. L. Rigby, B. Clarke, D. E. Ward, E. Rowland | title = Efficacy and safety of adenosine in the treatment of supraventricular tachycardia in infants and children | journal = British Heart Journal | date = 1989-09 | pmid = 2789912 | pmc = PMC1216763 }}</ref> | ||
===== | |||
<!--Non–Guideline-Supported Use (Pediatric)--> | <!--Non–Guideline-Supported Use (Pediatric)--> | ||
|offLabelPedNoGuideSupport= | |offLabelPedNoGuideSupport= | ||
There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in pediatric patients. | There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in pediatric patients. | ||
| Line 162: | Line 136: | ||
|contraindications= | |contraindications= | ||
* | * Second- or third-degree [[A-V]] block (except in patients with a functioning artificial [[pacemaker]]) | ||
* [[Sinus node]] disease, such as [[sick sinus syndrome]] or symptomatic [[bradycardia]] (except in patients with a functioning artificial pacemaker) | |||
* [[Hypersensitivity]] to adenosine | |||
<!--Warnings--> | <!--Warnings--> | ||
| Line 168: | Line 144: | ||
|warnings= | |warnings= | ||
* | * Heart Block | ||
:* Adenocard (adenosine injection) exerts its effect by decreasing conduction through the [[A-V node]] and may produce a short lasting first-, second- or third-degree [[heart block]]. Appropriate therapy should be instituted as needed. Patients who develop high-level block on one dose of Adenocard should not be given additional doses. Because of the very short half-life of adenosine, these effects are generally self-limiting. Appropriate resuscitative measures should be available. | |||
* | :* Transient or prolonged episodes of [[asystole]] have been reported with fatal outcomes in some cases. Rarely, [[ventricular fibrillation]] has been reported following Adenocard administration, including both resuscitated and fatal events. In most instances, these cases were associated with the concomitant use of [[digoxin]] and, less frequently with [[digoxin]] and [[verapamil]]. Although no causal relationship or drug-drug interaction has been established, Adenocard should be used with caution in patients receiving [[digoxin]] or [[digoxin]] and [[verapamil]] in combination. | ||
* Arrhythmias at Time of Conversion | |||
:* At the time of conversion to [[normal sinus rhythm]], a variety of new rhythms may appear on the [[electrocardiogram]]. They generally last only a few seconds without intervention, and may take the form of [[premature ventricular contraction]]s, atrial premature contractions, [[atrial fibrillation]], [[sinus bradycardia]], [[sinus tachycardia]], skipped beats, and varying degrees of [[A-V nodal block]]. Such findings were seen in 55% of patients. | |||
* Bronchoconstriction | |||
:* Adenocard (adenosine injection) is a respiratory stimulant (probably through activation of [[carotid body]] chemoreceptors) and [[intravenous]] administration in man has been shown to increase minute ventilation (Ve) and reduce arterial PCO2 causing [[respiratory alkalosis]]. | |||
:* Adenosine administered by inhalation has been reported to cause [[bronchoconstriction]] in [[asthma]]tic patients, presumably due to [[mast cell]] degranulation and [[histamine]] release. These effects have not been observed in normal subjects. Adenocard has been administered to a limited number of patients with asthma and mild to moderate exacerbation of their symptoms has been reported. Respiratory compromise has occurred during adenosine infusion in patients with obstructive pulmonary disease. Adenocard should be used with caution in patients with obstructive lung disease not associated with [[bronchoconstriction]] (e.g., [[emphysema]], [[bronchitis]], etc.) and should be avoided in patients with bronchoconstriction or [[bronchospasm]] (e.g., [[asthma]]). Adenocard should be discontinued in any patient who develops severe respiratory difficulties. | |||
<!--Adverse Reactions--> | |||
<!--Clinical Trials Experience--> | |||
|clinicalTrials= | |||
=====Cardiovascular===== | =====Cardiovascular===== | ||
Facial [[flushing]] (18%), [[headache]] (2%), [[sweating]], [[palpitations]], [[chest pain]], [[hypotension]] (less than 1%). | |||
=====Digestive===== | =====Digestive===== | ||
[[Nausea]] (3%), metallic taste, tightness in throat, pressure in groin (less than 1%). | |||
=====Neurologic===== | =====Neurologic===== | ||
[[Lightheadedness]] (2%), [[dizziness]], [[tingling]] in arms, [[numbness]] (1%), apprehension, [[blurred vision]], burning sensation, heaviness in arms, neck and back pain (less than 1%). | |||
=====Respiratory===== | =====Respiratory===== | ||
[[Shortness of breath]]/[[dyspnea]] (12%), chest pressure (7%), [[hyperventilation]], head pressure (less than 1%). | |||
<!--Postmarketing Experience--> | <!--Postmarketing Experience--> | ||
|postmarketing= | |postmarketing= | ||
=====Cardiovascular===== | =====Cardiovascular===== | ||
Prolonged [[asystole]], [[ventricular tachycardia]], [[ventricular fibrillation]], transient increase in [[blood pressure]], [[bradycardia]], [[atrial fibrillation]], and [[Torsade de Pointes]] | |||
=====Neurologic===== | =====Neurologic===== | ||
[[Seizure]] activity, including tonic clonic (grand mal) seizures, and loss of consciousness. | |||
=====Respiratory===== | =====Respiratory===== | ||
[[Bronchospasm]] | |||
<!--Drug Interactions--> | <!--Drug Interactions--> | ||
| Line 310: | Line 202: | ||
|drugInteractions= | |drugInteractions= | ||
* | * Intravenous Adenocard (adenosine injection) has been effectively administered in the presence of other cardioactive drugs, such as [[quinidine]], [[beta blocker|beta-adrenergic blocking agents]], [[calcium channel blocking agents]], and [[ACEI|angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors]], without any change in the adverse reaction profile. [[Digoxin]] and [[verapamil]] use may be rarely associated with [[ventricular fibrillation]] when combined with Adenocard (see Warnings). Because of the potential for additive or synergistic depressant effects on the SA and AV nodes, however, Adenocard should be used with caution in the presence of these agents. The use of Adenocard in patients receiving digitalis may be rarely associated with [[ventricular fibrillation]]. | ||
* The effects of adenosine are antagonized by [[methylxanthine]]s such as [[caffeine]] and [[theophylline]]. In the presence of these [[methylxanthine]]s, larger doses of [[adenosine]] may be required or adenosine may not be effective. Adenosine effects are potentiated by [[dipyridamole]]. Thus, smaller doses of adenosine may be effective in the presence of [[dipyridamole]]. [[Carbamazepine]] has been reported to increase the degree of [[heart block]] produced by other agents. As the primary effect of adenosine is to decrease conduction through the A-V node, higher degrees of [[heart block]] may be produced in the presence of [[carbamazepine]]. | |||
<!--Use in Specific Populations--> | <!--Use in Specific Populations--> | ||
|useInPregnancyFDA= | |useInPregnancyFDA= | ||
* '''Pregnancy Category''' | * '''Pregnancy Category C''' | ||
:* Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with adenosine; nor have studies been performed in pregnant women. As adenosine is a naturally occurring material, widely dispersed throughout the body, no fetal effects would be anticipated. However, since it is not known whether Adenocard can cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women, Adenocard should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed. | |||
|useInPregnancyAUS= | |useInPregnancyAUS= | ||
| Line 330: | Line 224: | ||
|useInPed= | |useInPed= | ||
* No controlled studies have been conducted in pediatric patients to establish the safety and efficacy of Adenocard for the conversion of [[paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia]] (PSVT). However, [[intravenous]] adenosine has been used for the treatment of [[PSVT]] in neonates, infants, children and adolescents. | |||
|useInGeri= | |useInGeri= | ||
* Clinical studies of Adenocard did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between elderly and younger patients. In general, Adenocard in geriatric patients should be used with caution since this population may have a diminished cardiac function, nodal dysfunction, concomitant diseases or drug therapy that may alter hemodynamic function and produce severe [[bradycardia]] or [[AV block]]. | |||
|useInGender= | |useInGender= | ||
| Line 356: | Line 250: | ||
|administration= | |administration= | ||
* Intravenous | * Intravenous | ||
| Line 364: | Line 256: | ||
There is limited information regarding <i>Monitoring</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | There is limited information regarding <i>Monitoring</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | ||
<!--IV Compatibility--> | <!--IV Compatibility--> | ||
| Line 383: | Line 271: | ||
====Signs and Symptoms==== | ====Signs and Symptoms==== | ||
* | * The half-life of Adenocard (adenosine injection) is less than 10 seconds. Thus, adverse effects are generally rapidly self-limiting. | ||
====Management==== | ====Management==== | ||
* | * Treatment of any prolonged adverse effects should be individualized and be directed toward the specific effect. [[Methylxanthine]]s, such as [[caffeine]] and [[theophylline]], are competitive antagonists of adenosine. | ||
===Chronic Overdose=== | ===Chronic Overdose=== | ||
| Line 399: | Line 287: | ||
|drugBox= | |drugBox= | ||
{{drugbox2 | |||
| Verifiedfields = changed | |||
| Watchedfields = changed | |||
| Verifiedfields=changed | |||
| verifiedrevid=477242323 | |||
| IUPAC_name=(2''R'',3''R'',4''S'',5''R'')-2-(6-amino-9''H''-purin-9-yl)-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolane-3,4-diol | |||
| image=Adenosine.png | |||
| image2=Adenosine_spacefilling.png | |||
<!--Clinical data--> | |||
| tradename=Adenocard | |||
| Drugs.com={{drugs.com|monograph|adenosine}} | |||
| pregnancy_AU=<!-- A / B1 / B2 / B3 / C / D / X --> | |||
| pregnancy_US=<!-- A / B / C / D / X --> | |||
| pregnancy_category=C | |||
| legal_UK=POM | |||
| legal_US=Rx-only | |||
| routes_of_administration=Intravenous, injection | |||
<!--Pharmacokinetic data--> | |||
| bioavailability=Rapidly cleared from circulation via cellular uptake | |||
| protein_bound=No | |||
| metabolism=Rapidly converted to inosine and adenosine monophosphate | |||
| elimination_half-life=cleared plasma <30 seconds – half-life <10 seconds | |||
| excretion=can leave cell intact or can be degraded to hypoxanthine, xanthine, and ultimately uric acid | |||
<!--Identifiers--> | |||
| CASNo_Ref={{cascite|correct|CAS}} | |||
| CAS_number_Ref = {{cascite|correct|??}} | |||
| CAS_number=58-61-7 | |||
| ATC_prefix=C01 | |||
| ATC_suffix=EB10 | |||
| PubChem=60961 | |||
| IUPHAR_ligand_Ref={{iupharcite|correct|IUPHAR}} | |||
| IUPHAR_ligand=2844 | |||
| DrugBank_Ref = {{drugbankcite|correct|drugbank}} | |||
| DrugBank=DB00640 | |||
| ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| ChemSpiderID=54923 | |||
| UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} | |||
| UNII=K72T3FS567 | |||
| KEGG_Ref = {{keggcite|correct|kegg}} | |||
| KEGG=C00212 | |||
| ChEBI_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} | |||
| ChEBI=16335 | |||
| ChEMBL_Ref = {{ebicite|changed|EBI}} | |||
| ChEMBL=477 | |||
<!--Chemical data--> | |||
| C=10|H=13|N=5|O=4 | |||
| molecular_weight=267.241 g/mol | |||
| smiles=n2c1c(ncnc1n(c2)[C@@H]3O[C@@H]([C@@H](O)[C@H]3O)CO)N | |||
| InChI=1/C10H13N5O4/c11-8-5-9(13-2-12-8)15(3-14-5)10-7(18)6(17)4(1-16)19-10/h2-4,6-7,10,16-18H,1H2,(H2,11,12,13)/t4-,6-,7-,10-/m1/s1 | |||
| StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| StdInChI=1S/C10H13N5O4/c11-8-5-9(13-2-12-8)15(3-14-5)10-7(18)6(17)4(1-16)19-10/h2-4,6-7,10,16-18H,1H2,(H2,11,12,13)/t4-,6-,7-,10-/m1/s1 | |||
| StdInChIKey_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| StdInChIKey=OIRDTQYFTABQOQ-KQYNXXCUSA-N | |||
}} | |||
<!--Mechanism of Action--> | <!--Mechanism of Action--> | ||
| Line 405: | Line 350: | ||
|mechAction= | |mechAction= | ||
* | * Adenocard (adenosine injection) slows conduction time through the [[AV node]], can interrupt the reentry pathways through the [[AV node]], and can restore normal sinus rhythm in patients with [[PSVT|paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT)]], including [[PSVT]] associated with [[Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome]]. | ||
* Adenocard is antagonized competitively by methylxanthines such as [[caffeine]] and [[theophylline]], and potentiated by blockers of nucleoside transport such as [[dipyridamole]]. Adenocard is not blocked by [[atropine]]. | |||
<!--Structure--> | <!--Structure--> | ||
| Line 411: | Line 358: | ||
|structure= | |structure= | ||
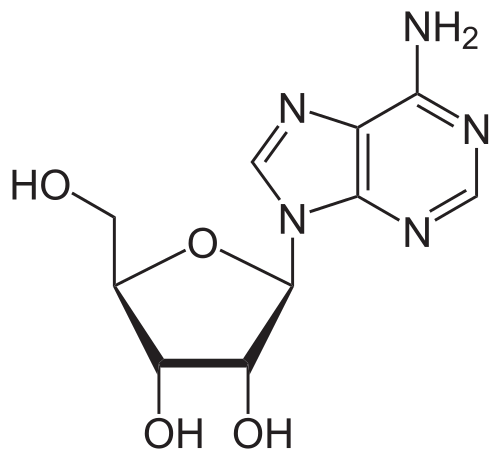
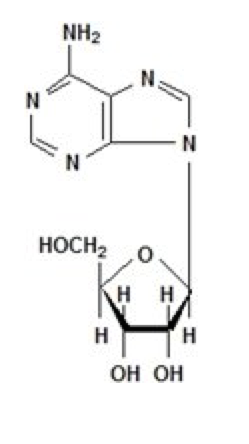
* | * Adenosine is an endogenous [[nucleoside]] occurring in all cells of the body. It is chemically 6-amino-9-β-D-ribofuranosyl-9-H-purine and has the following structural formula: | ||
: [[File:{{PAGENAME}}01.png|thumb|none|600px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | : [[File:{{PAGENAME}}01.png|thumb|none|600px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | ||
* [[Adenosine]] is a white crystalline powder. It is soluble in water and practically insoluble in alcohol. Solubility increases by warming and lowering the pH. Adenosine is not chemically related to other [[antiarrhythmic drug]]s. Adenocard® (adenosine injection) is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution for rapid bolus [[intravenous]] injection. Each mL contains 3 mg adenosine and 9 mg sodium chloride in Water for Injection. The pH of the solution is between 4.5 and 7.5. | |||
* The Ansyr® plastic syringe is molded from a specially formulated polypropylene. Water permeates from inside the container at an extremely slow rate which will have an insignificant effect on solution concentration over the expected shelf life. | |||
* Solutions in contact with the plastic container may leach out certain chemical components from the plastic in very small amounts; however, biological testing was supportive of the safety of the syringe material. | |||
<!--Pharmacodynamics--> | <!--Pharmacodynamics--> | ||
| Line 419: | Line 372: | ||
|PD= | |PD= | ||
* The intravenous bolus dose of 6 or 12 mg Adenocard (adenosine injection) usually has no systemic hemodynamic effects. When larger doses are given by infusion, adenosine decreases [[blood pressure]] by decreasing peripheral resistance. | |||
<!--Pharmacokinetics--> | <!--Pharmacokinetics--> | ||
| Line 425: | Line 378: | ||
|PK= | |PK= | ||
* Intravenously administered adenosine is rapidly cleared from the circulation via cellular uptake, primarily by [[erythrocyte]]s and vascular [[endothelial cell]]s. This process involves a specific transmembrane nucleoside carrier system that is reversible, nonconcentrative, and bidirectionally symmetrical. Intracellular adenosine is rapidly metabolized either via [[phosphorylation]] to adenosine monophosphate by adenosine kinase, or via deamination to [[inosine]] by [[adenosine deaminase]] in the cytosol. Since [[adenosine kinase]] has a lower Km and Vmax than [[adenosine deaminase]], deamination plays a significant role only when cytosolic adenosine saturates the [[phosphorylation]] pathway. Inosine formed by deamination of adenosine can leave the cell intact or can be degraded to [[hypoxanthine]], [[xanthine]], and ultimately [[uric acid]]. [[Adenosine monophosphate]] formed by phosphorylation of adenosine is incorporated into the high-energy phosphate pool. While extracellular adenosine is primarily cleared by cellular uptake with a half-life of less than 10 seconds in whole blood, excessive amounts may be deaminated by an ecto-form of adenosine deaminase. As Adenocard requires no hepatic or renal function for its activation or inactivation, hepatic and renal failure would not be expected to alter its effectiveness or tolerability. | |||
<!--Nonclinical Toxicology--> | <!--Nonclinical Toxicology--> | ||
| Line 431: | Line 384: | ||
|nonClinToxic= | |nonClinToxic= | ||
* Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility | |||
:* Studies in animals have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of Adenocard (adenosine injection). Adenosine was negative for genotoxic potential in the [[Salmonella]] (Ames Test) and Mammalian Microsome Assay. | |||
:* [[Adenosine]], however, like other [[nucleoside]]s at millimolar concentrations present for several doubling times of cells in culture, is known to produce a variety of chromosomal alterations. Fertility studies in animals have not been conducted with adenosine. | |||
<!--Clinical Studies--> | <!--Clinical Studies--> | ||
| Line 437: | Line 394: | ||
|clinicalStudies= | |clinicalStudies= | ||
* In controlled studies in the United States, bolus doses of 3, 6, 9, and 12 mg were studied. A cumulative 60% of patients with paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia had converted to [[normal sinus rhythm]] within one minute after an intravenous bolus dose of 6 mg Adenocard (some converted on 3 mg and failures were given 6 mg), and a cumulative 92% converted after a bolus dose of 12 mg. Seven to sixteen percent of patients converted after 1-4 placebo bolus injections. Similar responses were seen in a variety of patient subsets, including those using or not using digoxin, those with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, males, females, blacks, Caucasians, and Hispanics. | |||
* | * Adenosine is not effective in converting rhythms other than [[PSVT]], such as [[atrial flutter]], [[atrial fibrillation]], or [[ventricular tachycardia]], to [[normal sinus rhythm]]. | ||
<!--How Supplied--> | <!--How Supplied--> | ||
| Line 447: | Line 402: | ||
|howSupplied= | |howSupplied= | ||
* | * Adenocard® (adenosine injection) is supplied as a sterile non-pyrogenic solution in normal saline. | ||
:: NDC 0469-8234-12 Product Code 823412 | |||
:: 6 mg/2 mL (3 mg/mL) in 2 mL (fill volume) Ansyr® plastic disposable syringe, in a package of ten. | |||
:: NDC 0469-8234-14 Product Code 823414 | |||
:: 12 mg/4 mL (3 mg/mL) in 4 mL (fill volume) Ansyr® plastic disposable syringe, in a package of ten. | |||
* Store at controlled room temperature 15º-30ºC (59º-86ºF). | |||
* DO NOT REFRIGERATE as crystallization may occur. If crystallization has occurred, dissolve crystals by warming to room temperature. The solution must be clear at the time of use. | |||
* Contains no preservatives. Discard unused portion. | |||
* May require needle or blunt. To prevent needle-stick injuries, needles should not be recapped, purposely bent or broken by hand. | |||
<!--Patient Counseling Information--> | <!--Patient Counseling Information--> | ||
| Line 465: | Line 436: | ||
|brandNames= | |brandNames= | ||
* | * Adenocard®<ref>{{Cite web | title = ADENOCARD (adenosine) solution | url = http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=3d8fc3cd-6ff4-4ee3-98cb-1875775bbbe6 }}</ref> | ||
<!--Look-Alike Drug Names--> | <!--Look-Alike Drug Names--> | ||
| Line 471: | Line 442: | ||
|lookAlike= | |lookAlike= | ||
* | * N/A<ref name="www.ismp.org">{{Cite web | last = | first = | title = http://www.ismp.org | url = http://www.ismp.org | publisher = | date = }}</ref> | ||
<!--Drug Shortage Status--> | <!--Drug Shortage Status--> | ||
| Line 498: | Line 469: | ||
{{LabelImage | {{LabelImage | ||
|fileName={{PAGENAME}} | |fileName={{PAGENAME}}02.png|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine. | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{LabelImage | {{LabelImage | ||
|fileName={{PAGENAME}} | |fileName={{PAGENAME}}03.png|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine. | ||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 509: | Line 480: | ||
[[Category:Cardiovascular Drugs]] | [[Category:Cardiovascular Drugs]] | ||
[[Category:Drug]] | [[Category:Drug]] | ||
[[Category:Antiarrhythmic agents]] | |||
[[Category:Vasodilators]] | |||
Latest revision as of 17:15, 18 August 2015
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Gerald Chi
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Adenosine is an adenosine receptor agonist and antiarrhythmic that is FDA approved for the {{{indicationType}}} of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT), including that associated with accessory bypass tracts (Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome).. Common adverse reactions include chest discomfort, flushing, abdominal discomfort, pain of head and neck region, dizziness, headache, and dyspnea.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia
- Adenocard (adenosine injection) should be given as a rapid bolus by the peripheral intravenous route. To be certain the solution reaches the systemic circulation, it should be administered either directly into a vein or, if given into an IV line, it should be given as close to the patient as possible and followed by a rapid saline flush.
Adult Patients
- The dose recommendation is based on clinical studies with peripheral venous bolus dosing. Central venous (CVP or other) administration of Adenocard has not been systematically studied.
- Dosing Information
- Initial dose: 6 mg given as a rapid intravenous bolus (administered over a 1-2 second period).
- Repeat administration: If the first dose does not result in elimination of the supraventricular tachycardia within 1-2 minutes, 12 mg should be given as a rapid intravenous bolus. This 12 mg dose may be repeated a second time if required.
Pediatric Patients with a Body Weight < 50 kg
- Dosing Information
- Give 0.05 to 0.1 mg/kg as a rapid IV bolus given either centrally or peripherally. A saline flush should follow.
- Repeat administration: If conversion of PSVT does not occur within 1-2 minutes, additional bolus injections of adenosine can be administered at incrementally higher doses, increasing the amount given by 0.05 to 0.1 mg/kg. Follow each bolus with a saline flush. This process should continue until sinus rhythm is established or a maximum single dose of 0.3 mg/kg is used.
Pediatric Patients with a Body Weight ≥ 50 kg
- Administer the adult dose.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
Supraventricular Tachycardia
- Developed by: ACCF/AHA
- Class of Recommendation: Class I
- Strength of Evidence: Category B
- Dosing Information
- 6 mg, followed by 12 mg as needed[1]
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Preventing Graft Occlusion Following Aortocoronary Bypass Surgery
- Dosing Information
Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty
- Dosing Information
- 20 mg in 50 milliliters (mL) saline infused at a rate of 2 mg/minute[5]
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
There is limited information regarding FDA-Labeled Use of Adenosine in pediatric patients.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
Supraventricular Tachycardia
- Developed by: ACCF/AHA
- Class of Recommendation: Class IIa
- Strength of Evidence: Category B
- Dosing Information
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Adenosine in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- Second- or third-degree A-V block (except in patients with a functioning artificial pacemaker)
- Sinus node disease, such as sick sinus syndrome or symptomatic bradycardia (except in patients with a functioning artificial pacemaker)
- Hypersensitivity to adenosine
Warnings
- Heart Block
- Adenocard (adenosine injection) exerts its effect by decreasing conduction through the A-V node and may produce a short lasting first-, second- or third-degree heart block. Appropriate therapy should be instituted as needed. Patients who develop high-level block on one dose of Adenocard should not be given additional doses. Because of the very short half-life of adenosine, these effects are generally self-limiting. Appropriate resuscitative measures should be available.
- Transient or prolonged episodes of asystole have been reported with fatal outcomes in some cases. Rarely, ventricular fibrillation has been reported following Adenocard administration, including both resuscitated and fatal events. In most instances, these cases were associated with the concomitant use of digoxin and, less frequently with digoxin and verapamil. Although no causal relationship or drug-drug interaction has been established, Adenocard should be used with caution in patients receiving digoxin or digoxin and verapamil in combination.
- Arrhythmias at Time of Conversion
- At the time of conversion to normal sinus rhythm, a variety of new rhythms may appear on the electrocardiogram. They generally last only a few seconds without intervention, and may take the form of premature ventricular contractions, atrial premature contractions, atrial fibrillation, sinus bradycardia, sinus tachycardia, skipped beats, and varying degrees of A-V nodal block. Such findings were seen in 55% of patients.
- Bronchoconstriction
- Adenocard (adenosine injection) is a respiratory stimulant (probably through activation of carotid body chemoreceptors) and intravenous administration in man has been shown to increase minute ventilation (Ve) and reduce arterial PCO2 causing respiratory alkalosis.
- Adenosine administered by inhalation has been reported to cause bronchoconstriction in asthmatic patients, presumably due to mast cell degranulation and histamine release. These effects have not been observed in normal subjects. Adenocard has been administered to a limited number of patients with asthma and mild to moderate exacerbation of their symptoms has been reported. Respiratory compromise has occurred during adenosine infusion in patients with obstructive pulmonary disease. Adenocard should be used with caution in patients with obstructive lung disease not associated with bronchoconstriction (e.g., emphysema, bronchitis, etc.) and should be avoided in patients with bronchoconstriction or bronchospasm (e.g., asthma). Adenocard should be discontinued in any patient who develops severe respiratory difficulties.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
Cardiovascular
Facial flushing (18%), headache (2%), sweating, palpitations, chest pain, hypotension (less than 1%).
Digestive
Nausea (3%), metallic taste, tightness in throat, pressure in groin (less than 1%).
Neurologic
Lightheadedness (2%), dizziness, tingling in arms, numbness (1%), apprehension, blurred vision, burning sensation, heaviness in arms, neck and back pain (less than 1%).
Respiratory
Shortness of breath/dyspnea (12%), chest pressure (7%), hyperventilation, head pressure (less than 1%).
Postmarketing Experience
Cardiovascular
Prolonged asystole, ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, transient increase in blood pressure, bradycardia, atrial fibrillation, and Torsade de Pointes
Neurologic
Seizure activity, including tonic clonic (grand mal) seizures, and loss of consciousness.
Respiratory
Drug Interactions
- Intravenous Adenocard (adenosine injection) has been effectively administered in the presence of other cardioactive drugs, such as quinidine, beta-adrenergic blocking agents, calcium channel blocking agents, and angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors, without any change in the adverse reaction profile. Digoxin and verapamil use may be rarely associated with ventricular fibrillation when combined with Adenocard (see Warnings). Because of the potential for additive or synergistic depressant effects on the SA and AV nodes, however, Adenocard should be used with caution in the presence of these agents. The use of Adenocard in patients receiving digitalis may be rarely associated with ventricular fibrillation.
- The effects of adenosine are antagonized by methylxanthines such as caffeine and theophylline. In the presence of these methylxanthines, larger doses of adenosine may be required or adenosine may not be effective. Adenosine effects are potentiated by dipyridamole. Thus, smaller doses of adenosine may be effective in the presence of dipyridamole. Carbamazepine has been reported to increase the degree of heart block produced by other agents. As the primary effect of adenosine is to decrease conduction through the A-V node, higher degrees of heart block may be produced in the presence of carbamazepine.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Category C
- Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with adenosine; nor have studies been performed in pregnant women. As adenosine is a naturally occurring material, widely dispersed throughout the body, no fetal effects would be anticipated. However, since it is not known whether Adenocard can cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women, Adenocard should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Adenosine in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Adenosine during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Adenosine with respect to nursing mothers.
Pediatric Use
- No controlled studies have been conducted in pediatric patients to establish the safety and efficacy of Adenocard for the conversion of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT). However, intravenous adenosine has been used for the treatment of PSVT in neonates, infants, children and adolescents.
Geriatic Use
- Clinical studies of Adenocard did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between elderly and younger patients. In general, Adenocard in geriatric patients should be used with caution since this population may have a diminished cardiac function, nodal dysfunction, concomitant diseases or drug therapy that may alter hemodynamic function and produce severe bradycardia or AV block.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Adenosine with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Adenosine with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Adenosine in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Adenosine in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Adenosine in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Adenosine in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Intravenous
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Adenosine in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Adenosine in the drug label.
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
- The half-life of Adenocard (adenosine injection) is less than 10 seconds. Thus, adverse effects are generally rapidly self-limiting.
Management
- Treatment of any prolonged adverse effects should be individualized and be directed toward the specific effect. Methylxanthines, such as caffeine and theophylline, are competitive antagonists of adenosine.
Chronic Overdose
There is limited information regarding Chronic Overdose of Adenosine in the drug label.
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
- Adenocard (adenosine injection) slows conduction time through the AV node, can interrupt the reentry pathways through the AV node, and can restore normal sinus rhythm in patients with paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT), including PSVT associated with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome.
- Adenocard is antagonized competitively by methylxanthines such as caffeine and theophylline, and potentiated by blockers of nucleoside transport such as dipyridamole. Adenocard is not blocked by atropine.
Structure
- Adenosine is an endogenous nucleoside occurring in all cells of the body. It is chemically 6-amino-9-β-D-ribofuranosyl-9-H-purine and has the following structural formula:
- Adenosine is a white crystalline powder. It is soluble in water and practically insoluble in alcohol. Solubility increases by warming and lowering the pH. Adenosine is not chemically related to other antiarrhythmic drugs. Adenocard® (adenosine injection) is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution for rapid bolus intravenous injection. Each mL contains 3 mg adenosine and 9 mg sodium chloride in Water for Injection. The pH of the solution is between 4.5 and 7.5.
- The Ansyr® plastic syringe is molded from a specially formulated polypropylene. Water permeates from inside the container at an extremely slow rate which will have an insignificant effect on solution concentration over the expected shelf life.
- Solutions in contact with the plastic container may leach out certain chemical components from the plastic in very small amounts; however, biological testing was supportive of the safety of the syringe material.
Pharmacodynamics
- The intravenous bolus dose of 6 or 12 mg Adenocard (adenosine injection) usually has no systemic hemodynamic effects. When larger doses are given by infusion, adenosine decreases blood pressure by decreasing peripheral resistance.
Pharmacokinetics
- Intravenously administered adenosine is rapidly cleared from the circulation via cellular uptake, primarily by erythrocytes and vascular endothelial cells. This process involves a specific transmembrane nucleoside carrier system that is reversible, nonconcentrative, and bidirectionally symmetrical. Intracellular adenosine is rapidly metabolized either via phosphorylation to adenosine monophosphate by adenosine kinase, or via deamination to inosine by adenosine deaminase in the cytosol. Since adenosine kinase has a lower Km and Vmax than adenosine deaminase, deamination plays a significant role only when cytosolic adenosine saturates the phosphorylation pathway. Inosine formed by deamination of adenosine can leave the cell intact or can be degraded to hypoxanthine, xanthine, and ultimately uric acid. Adenosine monophosphate formed by phosphorylation of adenosine is incorporated into the high-energy phosphate pool. While extracellular adenosine is primarily cleared by cellular uptake with a half-life of less than 10 seconds in whole blood, excessive amounts may be deaminated by an ecto-form of adenosine deaminase. As Adenocard requires no hepatic or renal function for its activation or inactivation, hepatic and renal failure would not be expected to alter its effectiveness or tolerability.
Nonclinical Toxicology
- Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
- Studies in animals have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of Adenocard (adenosine injection). Adenosine was negative for genotoxic potential in the Salmonella (Ames Test) and Mammalian Microsome Assay.
- Adenosine, however, like other nucleosides at millimolar concentrations present for several doubling times of cells in culture, is known to produce a variety of chromosomal alterations. Fertility studies in animals have not been conducted with adenosine.
Clinical Studies
- In controlled studies in the United States, bolus doses of 3, 6, 9, and 12 mg were studied. A cumulative 60% of patients with paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia had converted to normal sinus rhythm within one minute after an intravenous bolus dose of 6 mg Adenocard (some converted on 3 mg and failures were given 6 mg), and a cumulative 92% converted after a bolus dose of 12 mg. Seven to sixteen percent of patients converted after 1-4 placebo bolus injections. Similar responses were seen in a variety of patient subsets, including those using or not using digoxin, those with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, males, females, blacks, Caucasians, and Hispanics.
- Adenosine is not effective in converting rhythms other than PSVT, such as atrial flutter, atrial fibrillation, or ventricular tachycardia, to normal sinus rhythm.
How Supplied
- Adenocard® (adenosine injection) is supplied as a sterile non-pyrogenic solution in normal saline.
- NDC 0469-8234-12 Product Code 823412
- 6 mg/2 mL (3 mg/mL) in 2 mL (fill volume) Ansyr® plastic disposable syringe, in a package of ten.
- NDC 0469-8234-14 Product Code 823414
- 12 mg/4 mL (3 mg/mL) in 4 mL (fill volume) Ansyr® plastic disposable syringe, in a package of ten.
- Store at controlled room temperature 15º-30ºC (59º-86ºF).
- DO NOT REFRIGERATE as crystallization may occur. If crystallization has occurred, dissolve crystals by warming to room temperature. The solution must be clear at the time of use.
- Contains no preservatives. Discard unused portion.
- May require needle or blunt. To prevent needle-stick injuries, needles should not be recapped, purposely bent or broken by hand.
Storage
There is limited information regarding Adenosine Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Adenosine |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Adenosine |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Patient Counseling Information of Adenosine in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Adenosine interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- Adenocard®[10]
Look-Alike Drug Names
- N/A[11]
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ DiMarco, J. P. (1990-07-15). "Adenosine for paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia: dose ranging and comparison with verapamil. Assessment in placebo-controlled, multicenter trials. The Adenosine for PSVT Study Group". Annals of Internal Medicine. 113 (2): 104–110. ISSN 0003-4819. PMID 2193560. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help) - ↑ Robinson, M. C. (1997-06). "Transient ventricular asystole using adenosine during minimally invasive and open sternotomy coronary artery bypass grafting". The Annals of Thoracic Surgery. 63 (6 Suppl): –30-34. ISSN 0003-4975. PMID 9203593. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help); Check date values in:|date=(help) - ↑ Mentzer, R. M. (1997-06-19). "Safety, tolerance, and efficacy of adenosine as an additive to blood cardioplegia in humans during coronary artery bypass surgery". The American Journal of Cardiology. 79 (12A): 38–43. ISSN 0002-9149. PMID 9223362. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help) - ↑ Mentzer, R. M. (1999-05). "Adenosine myocardial protection: preliminary results of a phase II clinical trial". Annals of Surgery. 229 (5): 643–649, discussion 649-650. ISSN 0003-4932. PMC 1420808. PMID 10235522. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help); Check date values in:|date=(help) - ↑ Leesar, M. A. (1997-06-03). "Preconditioning of human myocardium with adenosine during coronary angioplasty". Circulation. 95 (11): 2500–2507. ISSN 0009-7322. PMID 9184580. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help) - ↑ Losek, J. D. (1999-02). "Adenosine and pediatric supraventricular tachycardia in the emergency department: multicenter study and review". Annals of Emergency Medicine. 33 (2): 185–191. ISSN 0196-0644. PMID 9922414. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help); Check date values in:|date=(help) - ↑ Lenk, M. (1997-10). "Role of adenosine in the diagnosis and treatment of tachyarrhythmias in pediatric patients". Acta Paediatrica Japonica; Overseas Edition. 39 (5): 570–577. ISSN 0374-5600. PMID 9363655. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help); Check date values in:|date=(help) - ↑ Paret, G. (1996-08). "Adenosine for the treatment of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia in full-term and preterm newborn infants". American Journal of Perinatology. 13 (6): 343–346. doi:10.1055/s-2007-994353. ISSN 0735-1631. PMID 8865979. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help); Check date values in:|date=(help) - ↑ Till, J. (1989-09). "Efficacy and safety of adenosine in the treatment of supraventricular tachycardia in infants and children". British Heart Journal. 62 (3): 204–211. ISSN 0007-0769. PMC 1216763. PMID 2789912. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help); Check date values in:|date=(help) - ↑ "ADENOCARD (adenosine) solution".
- ↑ "http://www.ismp.org". External link in
|title=(help)
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Adenosine |Pill Name=No image.jpg |Drug Name= |Pill Ingred=|+sep=; |Pill Imprint= |Pill Dosage= |Pill Color=|+sep=; |Pill Shape= |Pill Size (mm)= |Pill Scoring= |Pill Image= |Drug Author= |NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Adenosine |Label Name=Adenosine02.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Adenosine |Label Name=Adenosine03.png
}}