Gemfibrozil: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
6. [[Cataract]]s – Subcapsular bilateral [[cataract]]s occurred in 10%, and unilateral in 6.3%, of male rats treated with gemfibrozil at 10 times the human dose. | 6. [[Cataract]]s – Subcapsular bilateral [[cataract]]s occurred in 10%, and unilateral in 6.3%, of male rats treated with gemfibrozil at 10 times the human dose. | ||
|clinicalTrials= | |clinicalTrials=====Gastrointestinal==== | ||
* [[Cholestatic jaundice]] | |||
* | |||
====Central Nervous System==== | |||
* [[Dizziness]] | |||
* [[Somnolence]] | |||
* [[Paresthesia]] | |||
* [[Peripheral neuritis]] | |||
* Decreased [[libido]] | |||
* [[Depression]] | |||
* [[Headache]] | |||
* [[Blurred vision]] | |||
====Genitourinary==== | |||
* [[Impotence]] | |||
====Musculoskeletal==== | |||
* [[Myopathy]] | |||
* [[Myasthenia]] | |||
* [[Myalgia]] | |||
* [[Painful extremities]] | |||
* [[Arthralgia ]] | |||
* [[Synovitis ]] | |||
* [[Rhabdomyolysis]] | |||
====Clinical Laboratory==== | |||
* Increased [[creatine phosphokinase]] ([[CPK]]) | |||
* Increased [[bilirubin]] | |||
* Increased liver [[transaminases]] (AST , ALT) | |||
* Increased [[alkaline phosphatase]] | |||
====Hematopoietic==== | |||
* [[Anemia]] | |||
* [[Leukopenia]] | |||
* Bone marrow hypoplasia | |||
* [[Eosinophilia]] | |||
====Immunologic==== | |||
* [[Angioedema]] | |||
* [[Laryngeal edema]] | |||
* Exfoliative dermatitis | |||
====Dermatologic==== | |||
* [[Rash]] | |||
* [[Dermatitis]] | |||
* [[Pruritus]] | |||
|drugInteractions=====HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors==== | |drugInteractions=====HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors==== | ||
Revision as of 21:05, 27 June 2014
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Alejandro Lemor, M.D. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Gemfibrozil is a lipid regulating agent that is FDA approved for the {{{indicationType}}} of types IV and V hyperlipidemia at risk of pancreatitis and who do not respond adequately to a determined dietary effort to control them, and reducing the risk of developing coronary heart disease only in Type IIb patients without history of or symptoms of existing coronary heart disease who have had an inadequate response to weight loss, dietary therapy, exercise, and other pharmacologic agents (such as bile acid sequestrants and nicotinic acid) and who have the following triad of lipid abnormalities: low HDL-cholesterol levels in addition to elevated LDL-cholesterol and elevated triglycerides. Common adverse reactions include dyspepsia, abdominal pain, acute appendicitis, atrial fibrillation, diarrhea, fatigue, eczema, rash, vertigo, constipation, headache.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
- Dosing Information
- 600 mg PO every 12 hours (30 minutes before the morning and evening meals)
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information about Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Gemfibrozil in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information about Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Gemfibrozil in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
There is limited information regarding Gemfibrozil FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric) in the drug label.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information about Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Gemfibrozil in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information about Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Gemfibrozil in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- Hepatic or severe renal dysfunction, including primary biliary cirrhosis.
- Preexisting gallbladder disease.
- Hypersensitivity to gemfibrozil.
- Combination therapy of gemfibrozil with repaglinide
- Combination therapy of gemfibrozil with simvastatin
Warnings
1. Because of chemical, pharmacological, and clinical similarities between gemfibrozil and clofibrate, the adverse findings with clofibrate in two large clinical studies may also apply to gemfibrozil. In the first of those studies, the Coronary Drug Project, 1000 subjects with previous myocardial infarction were treated for five years with clofibrate. There was no difference in mortality between the clofibrate-treated subjects and 3000 placebo-treated subjects, but twice as many clofibrate-treated subjects developed cholelithiasis and cholecystitis requiring surgery. In the other study, conducted by the World Health Organization (WHO), 5000 subjects without known coronary heart disease were treated with clofibrate for five years and followed one year beyond. There was a statistically significant (44%) higher age-adjusted total mortality in the clofibrate-treated group than in a comparable placebo-treated control group during the trial period. The excess mortality was due to a 33% increase in non-cardiovascular causes, including malignancy, post-cholecystectomy complications, and pancreatitis. The higher risk of clofibrate-treated subjects for gallbladder disease was confirmed.
Because of the more limited size of the Helsinki Heart Study, the observed difference in mortality from any cause between the LOPID and placebo groups is not statistically significantly different from the 29% excess mortality reported in the clofibrate group in the separate WHO study at the nine year follow-up. Noncoronary heart disease related mortality showed an excess in the group originally randomized to LOPID primarily due to cancer deaths observed during the open-label extension.
During the five year primary prevention component of the Helsinki Heart Study, mortality from any cause was 44 (2.2%) in the LOPID group and 43 (2.1%) in the placebo group; including the 3.5 year follow-up period since the trial was completed, cumulative mortality from any cause was 101 (4.9%) in the LOPID group and 83 (4.1%) in the group originally randomized to placebo (hazard ratio 1:20 in favor of placebo). Because of the more limited size of the Helsinki Heart Study, the observed difference in mortality from any cause between the LOPID and placebo groups at Year-5 or at Year-8.5 is not statistically significantly different from the 29% excess mortality reported in the clofibrate group in the separate WHO study at the nine year follow-up. Noncoronary heart disease related mortality showed an excess in the group originally randomized to LOPID at the 8.5 year follow-up (65 LOPID versus 45 placebo noncoronary deaths).
The incidence of cancer (excluding basal cell carcinoma) discovered during the trial and in the 3.5 years after the trial was completed was 51 (2.5%) in both originally randomized groups. In addition, there were 16 basal cell carcinomas in the group originally randomized to LOPID and 9 in the group originally randomized to placebo (p=0.22). There were 30 (1.5%) deaths attributed to cancer in the group originally randomized to LOPID and 18 (0.9%) in the group originally randomized to placebo (p=0.11). Adverse outcomes, including coronary events, were higher in gemfibrozil patients in a corresponding study in men with a history of known or suspected coronary heart disease in the secondary prevention component of the Helsinki Heart Study.
A comparative carcinogenicity study was also done in rats comparing three drugs in this class: fenofibrate (10 and 60 mg/kg; 0.3 and 1.6 times the human dose, respectively), clofibrate (400 mg/kg; 1.6 times the human dose), and gemfibrozil (250 mg/kg; 1.7 times the human dose). Pancreatic acinar adenomas were increased in males and females on fenofibrate; hepatocellular carcinoma and pancreatic acinar adenomas were increased in males and hepatic neoplastic nodules in females treated with clofibrate; hepatic neoplastic nodules were increased in males and females treated with clofibrate; hepatic neoplastic nodules were increased in males and females treated with gemfibrozil while testicular interstitial cell (Leydig cell) tumors were increased in males on all three drugs.
2. A gallstone prevalence substudy of 450 Helsinki Heart Study participants showed a trend toward a greater prevalence of gallstones during the study within the LOPID treatment group (7.5% versus 4.9% for the placebo group, a 55% excess for the gemfibrozil group). A trend toward a greater incidence of gallbladder surgery was observed for the LOPID group (17 versus 11 subjects, a 54% excess). This result did not differ statistically from the increased incidence of cholecystectomy observed in the WHO study in the group treated with clofibrate. Both clofibrate and gemfibrozil may increase cholesterol excretion into the bile, leading to cholelithiasis. If cholelithiasis is suspected, gallbladder studies are indicated. LOPID therapy should be discontinued if gallstones are found. Cases of cholelithiasis have been reported with gemfibrozil therapy.
3. Since a reduction of mortality from coronary heart disease has not been demonstrated and because liver and interstitial cell testicular tumors were increased in rats, LOPID should be administered only to those patients described in the INDICATIONS AND USAGE section. If a significant serum lipid response is not obtained, LOPID should be discontinued.
4. Concomitant Anticoagulants – Caution should be exercised when anticoagulants are given in conjunction with LOPID. The dosage of the anticoagulant should be reduced to maintain the prothrombin time at the desired level to prevent bleeding complications. Frequent prothrombin determinations are advisable until it has been definitely determined that the prothrombin level has stabilized.
5. The concomitant administration of LOPID with simvastatin is contraindicated. Concomitant therapy with LOPID and an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor is associated with an increased risk of skeletal muscle toxicity manifested as rhabdomyolysis, markedly elevated creatine kinase (CPK) levels, and myoglobinuria, leading in a high proportion of cases to acute renal failure and death. IN PATIENTS WHO HAVE HAD AN UNSATISFACTORY LIPID RESPONSE TO EITHER DRUG ALONE, THE BENEFIT OF COMBINED THERAPY WITH LOPID AND an HMG-CoA REDUCTASE INHIBITOR DOES NOT OUTWEIGH THE RISKS OF SEVERE MYOPATHY, rhabdomyolysis, AND ACUTE RENAL FAILURE. The use of fibrates alone, including LOPID, may occasionally be associated with myositis. Patients receiving LOPID and complaining of muscle pain, tenderness, or weakness should have prompt medical evaluation for myositis, including serum creatine–kinase level determination. If myositis is suspected or diagnosed, LOPID therapy should be withdrawn.
6. Cataracts – Subcapsular bilateral cataracts occurred in 10%, and unilateral in 6.3%, of male rats treated with gemfibrozil at 10 times the human dose.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
Gastrointestinal
Central Nervous System
- Dizziness
- Somnolence
- Paresthesia
- Peripheral neuritis
- Decreased libido
- Depression
- Headache
- Blurred vision
Genitourinary
Musculoskeletal
Clinical Laboratory
- Increased creatine phosphokinase (CPK)
- Increased bilirubin
- Increased liver transaminases (AST , ALT)
- Increased alkaline phosphatase
Hematopoietic
- Anemia
- Leukopenia
- Bone marrow hypoplasia
- Eosinophilia
Immunologic
- Angioedema
- Laryngeal edema
- Exfoliative dermatitis
Dermatologic
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Gemfibrozil Postmarketing Experience in the drug label.
Drug Interactions
HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors
The concomitant administration of Gemfibrozil with simvastatin is contraindicated. The risk of myopathy and rhabdomyolysis is increased with combined gemfibrozil and HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor therapy. Myopathy or rhabdomyolysis with or without acute renal failure have been reported as early as three weeks after initiation of combined therapy or after several months. There is no assurance that periodic monitoring of creatine kinase will prevent the occurrence of severe myopathy and kidney damage.
Anticoagulants
Caution should be exercised when anti-coagulants are given in conjunction with gemfibrozil . The dosage of the anticoagulant should be reduced to maintain the prothrombin time at the desired level to prevent bleeding complications. Frequent prothrombin determinations are advisable until it has been definitely determined that the prothrombin level has stabilized.
Repaglinide
In healthy volunteers, co-administration with gemfibrozil (600 mg twice daily for 3 days) resulted in an 8.1-fold (range 5.5- to 15.0- fold) higher repaglinide AUC and a 28.6-fold (range 18.5- to 80.1-fold) higher repaglinide plasma concentration 7 hours after the dose. In the same study, gemfibrozil (600 mg twice daily for 3 days) + itraconazole (200 mg in the morning and 100 mg in the evening at Day 1, then 100 mg twice daily at Day 2–3) resulted in a 19.4- (range 12.9- to 24.7-fold) higher repaglinideAUC and a 70.4-fold (range 42.9- to 119.2-fold) higher repaglinideplasma concentration 7 hours after the dose. In addition, gemfibrozil alone or gemfibrozil + itraconazole prolonged the hypoglycemic effects of repaglinide. Co-administration of gemfibrozil and repaglinideincreases the risk of severe hypoglycemia and is contraindicated.
Bile Acid-Binding Resins
Gemfibrozil AUC was reduced by 30% when gemfibrozil was given (600 mg) simultaneously with resin-granule drugs such as colestipol (5 g). Administration of the drugs two hours or more apart is recommended because gemfibrozil exposure was not significantly affected when it was administered two hours apart from colestipol.
Colchicine
Myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis, has been reported with chronic administration of colchicine at therapeutic doses. Concomitant use of gemfibrozil may potentiate the development of myopathy. Patients with renal dysfunction and elderly patients are at increased risk. Caution should be exercised when prescribing gemfibrozil with colchicine, especially in elderly patients or patients with renal dysfunction.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category (FDA): C Gemfibrozil has been shown to produce adverse effects in rats and rabbits at doses between 0.5 and 3 times the human dose (based on surface area). There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Gemfibrozil should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Administration of gemfibrozil to female rats at 2 times the human dose (based on surface area) before and throughout gestation caused a dose-related decrease in conception rate, an increase in stillborns and a slight reduction in pup weight during lactation. There were also dose-related increased skeletal variations. Anophthalmia occurred, but rarely.
Administration of 0.6 and 2 times the human dose (based on surface area) of gemfibrozil to female rats from gestation day 15 through weaning caused dose-related decreases in birth weight and suppressions of pup growth during lactation.
Administration of 1 and 3 times the human dose (based on surface area) of gemfibrozil to female rabbits during organogenesis caused a dose-related decrease in litter size and, at the high dose, an increased incidence of parietal bone variations.
Pregnancy Category (AUS): B3
Drugs which have been taken by only a limited number of pregnant women and women of childbearing age, without an increase in the frequency of malformation or other direct or indirect harmful effects on the human fetus having been observed. Studies in animals have shown evidence of an increased occurrence of fetal damage, the significance of which is considered uncertain in humans.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Gemfibrozil during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for tumorigenicity shown for gemfibrozil in animal studies, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Pediatric Use
Safety and efficacy in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatic Use
Safety and efficacy in geriatric patients have not been established.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Gemfibrozil with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Gemfibrozil with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There have been reports of worsening renal insufficiency upon the addition of Gemfibrozil therapy in individuals with baseline plasma creatinine >2.0 mg/dL. In such patients, the use of alternative therapy should be considered against the risks and benefits of a lower dose of Gemfibrozil.
Hepatic Impairment
Abnormal liver function tests have been observed occasionally during Gemfibrozil administration, including elevations of AST,ALT, LDH, [bilirubin]], and alkaline phosphatase. These are usually reversible when Gemfibrozil is discontinued. Therefore, periodic liver function studies are recommended and Gemfibrozil therapy should be terminated if abnormalities persist.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Gemfibrozil in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Gemfibrozil in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
Oral
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Gemfibrozil Monitoring in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding the compatibility of Gemfibrozil and IV administrations.
Overdosage
There have been reported cases of overdosage with gemfibrozil. In one case, a 7-year-old child recovered after ingesting up to 9 grams of gemfibrozil. Symptoms reported with overdosage were ]]abdominal cramps]], abnormal liver function tests, diarrhea, increased CPK, joint and muscle pain, nausea and vomiting. Symptomatic supportive measures should be taken, should an overdose occur.
Pharmacology
| Template:Px | |
Gemfibrozil
| |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| 5-(2,5-dimethylphenoxy)-2,2-dimethyl-pentanoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | |
| ATC code | C10 |
| PubChem | |
| DrugBank | |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | Template:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox |
| Mol. mass | 250.333 g/mol |
| SMILES | & |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Close to 100% |
| Protein binding | 95% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic (CYP3A4) |
| Half life | 1.5 hours |
| Excretion | Renal 94% Feces 6% |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. |
Category C |
| Legal status |
By Prescription |
| Routes | Oral |
Mechanism of Action
Gemfibrozil is a lipid regulating agent which decreases serum triglycerides and very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) cholesterol, and increases high density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol. While modest decreases in total and low density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol may be observed with gemfibrozil therapy, treatment of patients with elevated triglycerides due to Type IV hyperlipoproteinemia often results in a rise in LDL-cholesterol. LDL-cholesterol levels in Type IIb patients with elevations of both serum LDL-cholesterol and triglycerides are, in general, minimally affected by gemfibrozil treatment; however, gemfibrozil usually raises HDL-cholesterol significantly in this group. Gemfibrozil increases levels of high density lipoprotein (HDL) subfractions HDL2 and HDL3, as well as apolipoproteins AI and AII. Epidemiological studies have shown that both low HDL-cholesterol and high LDL-cholesterol are independent risk factors for coronary heart disease.
Structure
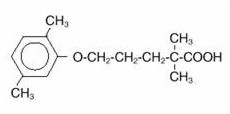
The empirical formula is C15H22O3 and the molecular weight is 250.35; the solubility in water and acid is 0.0019% and in dilute base it is greater than 1%. The melting point is 58°–61° C. Gemfibrozil is a white solid which is stable under ordinary conditions
Pharmacodynamics
(Description)
Pharmacokinetics
(Description)
Nonclinical Toxicology
(Description)
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Gemfibrozil Clinical Studies in the drug label.
How Supplied
Gemfibrozil Tablets USP are supplied as:
600 mg: White to off-white, elliptical, biconvex, film-coated tablets with 'N111' debossed and scored on one face and scored on the other face.
Bottles of 30 NDC 16714-101-01 Bottles of 60 NDC 16714-101-02 Bottles of 90 NDC 16714-101-03 Bottles of 100 NDC 16714-101-04 Bottles of 500 NDC 16714-101-05
Storage
Store at 20° - 25°C (68° - 77°F). Protect from light and humidity.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Gemfibrozil |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Gemfibrozil |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Gemfibrozil Patient Counseling Information in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-Gemfibrozil interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
There is limited information regarding Gemfibrozil Brand Names in the drug label.
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Gemfibrozil Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Gemfibrozil |Pill Name=No_image.jpg |Drug Name=Gemfibrozil |Pill Ingred=Cellulose microcrystalline, starch corn, hydroxypropyl cellulose low substituted, sodium starch glycolate type a potato, titanium dioxide, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromelloses, polysorbate 80, silicon dioxide, magnesium stearate|+sep=; |Pill Imprint=N111 |Pill Dosage=600 mg |Pill Color=White|+sep=; |Pill Shape=Oval |Pill Size (mm)=19.00 |Pill Scoring=2 |Pill Image= |Drug Author=Northstar RxLLC |NDC=16714-101-02
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Gemfibrozil |Label Name=Gemfibrozil label.jpg
}}