Gadoxetate
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Rabin Bista, M.B.B.S. [2]
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Black Box Warning
|
WARNING:
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS (NSF):
The risk for NSF appears highest among patients with: Chronic, severe kidney disease (GFR < 30 mL/min/1.73m2), or Acute kidney injury. Screen patients for acute kidney injury and other conditions that may reduce renal function. For patients at risk for chronically reduced renal function (for example, age > 60 years, hypertension or diabetes), estimate the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) through laboratory testing. For patients at highest risk for NSF, do not exceed the recommended EOVIST dose and allow a sufficient period of time for elimination of the drug from the body prior to any re-administration |
Overview
Gadoxetate is a Diagnostic Agent that is FDA approved for the diagnosis of known or suspected focal liver disease through MRI. There is a Black Box Warning for this drug as shown here. Common adverse reactions include nausea, headache, feeling hot, dizziness, and back pain.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Indications
- EOVIST is indicated for intravenous use in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the liver to detect and characterize lesions in patients with known or suspected focal liver disease.
Dosage
- The recommended dose of EOVIST is 0.1 mL/kg body weight (0.025 mmol/kg body weight).
Drug Handling and Administration
- Use sterile technique when preparing and administering EOVIST
- Visually inspect EOVIST, supplied in a single-use vial, for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. Do not use the solution if it is discolored or if particulate matter is present
- Use EOVIST immediately after obtaining appropriate dose from vial. The rubber stopper should never be pierced more than once. Discard any unused portion of an EOVIST vial
- Administer EOVIST undiluted as an intravenous bolus injection at a flow rate of approximately 2 mL/second
- Do not mix EOVIST with other medications and do not administer EOVIST in the same intravenous line simultaneously with other medications
- Flush the intravenous cannula with a normal saline solution after EOVIST injection
- Imaging can commence immediately following EOVIST administration
Imaging
- Liver lesions are detected and characterized with pre-contrast MRI and EOVIST MRI obtained during dynamic and hepatocyte imaging phases. Perform a pre-contrast MRI, inject EOVIST and begin dynamic imaging approximately 15–25 seconds after completion of the injection. Dynamic imaging consists of the arterial, the porto-venous (approximately 60 seconds post-injection), and the blood equilibrium (approximately 120 seconds) phases.
- Begin the hepatocyte imaging phase approximately 20 minutes post-injection. Hepatocyte phase imaging may be performed up to 120 minutes post-injection.
Elevated intrinsic levels of bilirubin (>3 mg/dL) or ferritin can reduce the hepatic contrast effect of EOVIST. Perform MR imaging no later than 60 minutes following EOVIST administration to patients with these laboratory abnormalities, including patients who have elevated ferritin levels due to hemodialysis.
- Lesions with no or minimal hepatocyte function (cysts, metastases, and the majority of hepatocellular carcinomas) generally will not accumulate EOVIST. Well-differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma may contain functioning hepatocytes and can show some enhancement in the hepatocyte imaging phase. Additional clinical information is therefore needed to support a diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Gadoxetate in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Gadoxetate in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
- Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients has not been established.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Gadoxetate in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Gadoxetate in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- EOVIST is contraindicated in patients with history of severe hypersensitivity reactions to EOVIST.
Warnings
|
WARNING:
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS (NSF):
The risk for NSF appears highest among patients with: Chronic, severe kidney disease (GFR < 30 mL/min/1.73m2), or Acute kidney injury. Screen patients for acute kidney injury and other conditions that may reduce renal function. For patients at risk for chronically reduced renal function (for example, age > 60 years, hypertension or diabetes), estimate the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) through laboratory testing. For patients at highest risk for NSF, do not exceed the recommended EOVIST dose and allow a sufficient period of time for elimination of the drug from the body prior to any re-administration |
Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis (NSF)
- Gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) increase the risk for nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF) among patients with impaired elimination of the drugs. Avoid use of GBCAs among these patients unless the diagnostic information is essential and not available with non-contrast enhanced MRI or other modalities. The GBCA-associated NSF risk appears highest for patients with chronic, severe kidney disease (GFR < 30 mL/min/1.73m2) as well as patients with acute kidney injury. The risk appears lower for patients with chronic, moderate kidney disease (GFR 30 to 59 mL/min/1.73m2) and little, if any, for patients with chronic, mild kidney disease (GFR 60 to 89 mL/min/1.73m2). NSF may result in fatal or debilitating fibrosis affecting the skin, muscle and internal organs. Report any diagnosis of NSF following EOVIST administration to Bayer HealthCare (1-888-842-2937) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch).
- Screen patients for acute kidney injury and other conditions that may reduce renal function. Features of acute kidney injury consist of rapid (over hours to days) and usually reversible decrease in kidney function, commonly in the setting of surgery, severe infection, injury or drug-induced kidney toxicity. Serum creatinine levels and estimated GFR may not reliably assess renal function in the setting of acute kidney injury. For patients at risk for chronically reduced renal function (for example, age > 60 years, diabetes mellitus or chronic hypertension), estimate the GFR through laboratory testing.
- Among the factors that may increase the risk for NSF are repeated or higher than recommended doses of a GBCA and degree of renal impairment at the time of exposure. Record the specific GBCA and the dose administrated to a patient. For patients at highest risk for NSF, do not exceed the recommended EOVIST dose and allow a sufficient period of time for elimination of the drug prior to any re-administration. For patients receiving hemodialysis, physicians may consider the prompt initiation of hemodialysis following the administration of a GBCA in order to enhance the contrast agent’s elimination. The usefulness of hemodialysis in the prevention of NSF is unknown.
Hypersensitivity Reactions
- Anaphylactic and other hypersensitivity reactions with cardiovascular, respiratory and cutaneous manifestations, ranging from mild to severe, including shock have uncommonly occurred following EOVIST administration.
- Before EOVIST administration, assess all patients for any history of a reaction to contrast media, bronchial asthma and allergic disorders. These patients may have an increased risk for a hypersensitivity reaction to EOVIST.
- Administer EOVIST only in situations where trained personnel and therapies are promptly available for the treatment of hypersensitivity reactions, including personnel trained in resuscitation.
- Most hypersensitivity reactions to EOVIST have occurred within half an hour after administration. Delayed reactions can occur up to several days after EOVIST administration. Observe patients for signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity reactions during and following EOVIST administration.
Acute Kidney Injury
- In patients with chronic renal impairment, acute kidney injury sometimes requiring dialysis has been observed with the use of some GBCAs. The risk of acute kidney injury might be lower with EOVIST due to its dual excretory pathways. Do not exceed the recommended dose; the risk of acute kidney injury may increase with higher than recommended doses.
Extravasation and Injection Site Reactions
- Ensure catheter and venous patency before the injection of EOVIST. Extravasation into tissues during EOVIST administration may result in local tissue reactions. Strictly avoid intramuscular administration of EOVIST because it may cause myocyte necrosis and inflammation.
Interference with Laboratory Tests
- Serum iron determination using complexometric methods (for example, ferrocene complexation method) may result in falsely high or low values for up to 24 hours after the examination with EOVIST because of the caloxetate trisodium excipients.
Interference with Visualization of Liver Lesions
- Severe renal or hepatic failure may impair EOVIST imaging performance. In patients with end-stage renal failure, hepatic contrast was markedly reduced and was attributed to elevated serum ferritin levels. In patients with abnormally high (>3 mg/dL) serum bilirubin, reduced hepatic contrast was observed. If EOVIST is used in these patients, complete MRI no later than 60 minutes after EOVIST administration and use a paired non-contrast and contrast MRI set for diagnosis.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
- The following serious adverse reactionsare discussed elsewhere in the labeling:
Clinical Trials Experience
- Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
- The adverse reactions described in this section reflect EOVIST exposure in 1,989 subjects with the majority (1,581 subjects) receiving the recommended dose. Overall, 59% of the subjects were men and the ethnic distribution was 64% Caucasian, 22% Asian, 3% Hispanic, 2% Black, and 0.5% of subjects consisted of other ethnic groups. The average age was 57 years (age range from 19 to 84 years).
- Overall, 4% of subjects reported one or more adverse reactions following EOVIST administration. The most frequent (≥ 0.5%) adverse reactions associated with the use of EOVIST were nausea, headache, feeling hot, dizziness, and back pain. Adverse reactions were predominantly of mild to moderate severity.
Table 1 lists adverse reactions that occurred in ≥ 0.1% of subjects treated with EOVIST.
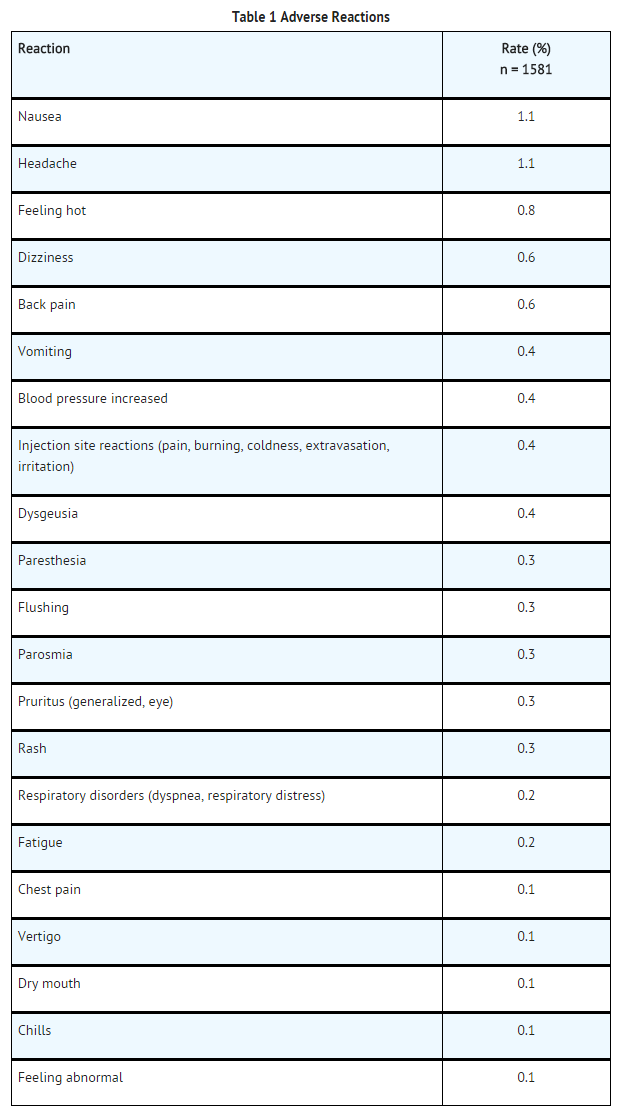
- Adverse reactions that occurred with a frequency of < 0.1% in subjects who received EOVIST include: tremor, akathisia, bundle branch block, palpitation, oral discomfort, salivary hypersecretion, maculopapular rash, hyperhidrosis, discomfort, and malaise.
- Elevation of serum iron values and serum bilirubin laboratory values were reported in less than 1% of patients after administration of EOVIST. The values did not exceed more than 3 times the baseline values and returned to baseline within 1 to 4 days.
Postmarketing Experience
- The following additional adverse reactions have been reported during the postmarketing use of EOVIST. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Hypersensitivity reactions (anaphylacticshock, hypotension, pharyngolaryngeal edema, urticaria, face edema, rhinitis, conjunctivitis, abdominal pain, hypoesthesia, sneezing, cough and pallor),Tachycardia, Restlessness
Drug Interactions
There is limited information regarding Gadoxetate Drug Interactions in the drug label.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- There are no studies of EOVIST in pregnant women to inform the drug-associated risk. Gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) are reported to cross the placenta and limited published data do not report adverse effects in neonates who were exposed to GBCAs in-utero. The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. However, the background risk in the U.S. general population of major birth defects is 2 to 4% and of miscarriage is 15 to 20% of clinically recognized pregnancies. No teratogenicity was observed with repeated daily intravenous administration of gadoxetate disodium to rats during organogenesis at doses up to 32 times the recommended single human dose; however, an increase in preimplantation loss was noted at doses 3.2 times the single human dose. Post implantation loss was observed with repeated daily intravenous administration of gadoxetate disodium to rabbits on gestation days 6 through 18 at doses 26 times the recommended single human dose [see Data]. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
Data
Animal Data
- Animal reproductive and developmental toxicity studies were done in rats and rabbits. Gadoxetate disodium was not teratogenic when given intravenously during organogenesis to pregnant rats at doses up to 32 times the recommended single human dose (mmol/m2 basis). However, an increase in preimplantation loss was noted at 3.2 times the human dose (mmol/m2 basis). Compared to untreated controls, rates of postimplantation loss and absorption increased and litter size decreased when pregnant rabbits received gadoxetate disodium at doses 26 times the recommended human single dose (mmol/m2 basis). This occurred without evidence of maternal toxicity. Because pregnant animals received repeated daily doses of gadoxetate disodium, their overall exposure was significantly higher than that achieved with the standard single dose administered to humans.
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Gadoxetate in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Gadoxetate during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
- Risk Summary
- There is no information regarding the presence of gadoxetate disodium in human milk, the effects of the drug in a breastfed infant, or the effects of the drug on milk production. However, published lactation data on other GBCAs report that 0.01 to 0.04% of the maternal gadolinium dose is present in breast milk and there is limited GBCA gastrointestinal absorption in the breastfed infant. In rat lactation studies with [153Gd] gadoxetate disodium, less than 0.5% of the total administered radioactivity was transferred to the nursing pup.
Clinical Considerations
- A lactating woman may consider interrupting breastfeeding and pumping and discarding breast milk for up to 10 hours after EOVIST administration in order to minimize exposure to a breastfed infant.
Data
Animal Data
- In lactating rats given 0.1 mmol/kg [153Gd] gadoxetate disodium, less than 0.5% of the total administered radioactivity was transferred to the neonates via maternal milk, mostly within 2 hours.
Pediatric Use
- Adequate and well-controlled studies of EOVIST in pediatric patients have not been conducted. An observational study with EOVIST was performed in 52 patients (aged > 2 months and < 18 years) referred for evaluation of suspected or known focal liver lesions. EOVIST improved border delineation and increased contrast of the primary lesion in the majority of patients when compared to non-contrast images. No safety issues were identified.
- No dose adjustment according to age is necessary in pediatric patients. The safety and effectiveness of EOVIST have not been established in premature infants.
NSF Risk
- No case of NSF associated with EOVIST or any other GBCA has been identified in pediatric patients ages 6 years and younger.
Juvenile Animal Data
- Single and repeat-dose toxicity studies in neonatal and juvenile rats did not reveal findings suggestive of a specific risk for use in pediatric patients including term neonates and infants.
Geriatic Use
- In clinical studies of EOVIST, 674 (34%) patients were 65 years of age and over, while 20 (1%) were 80 years of age and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, use of EOVIST in an elderly patient should be cautious, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal or cardiac function and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
- In a clinical pharmacology study, slight to moderate differences in pharmacokinetic parameters of gadoxetate disodium (increased AUC and terminal half-life, decreased total clearance) were found in a group of geriatric volunteers in comparison to non-geriatric volunteers. No clinically relevant differences in liver contrast enhancement were found.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Gadoxetate with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Gadoxetate with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
- In a clinical pharmacology study in a group of patients with moderate renal impairment, a moderate increase in AUC and terminal half-life was observed in comparison to healthy volunteers with normal renal function. Hepatic contrast did not differ among the groups.
- End-stage renal failure may impair EOVIST imaging performance. In a study of patients with end-stage renal failure, the terminal half-life was prolonged about 12-fold and the AUC was increased about 6-fold. Hepatic contrast was markedly reduced in these patients, which was attributed to significantly elevated serum ferritin levels. Approximately 30% of the injected dose was removed by dialysis in a single 3-hour dialysis session, which started one hour after an EOVIST dose. EOVIST was almost completely eliminated via dialysis and biliary excretion within the observation period of 6 days, predominantly within the first 3 days.
Hepatic Impairment
- In a clinical pharmacology study in groups of patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment, a slight to moderate increase in plasma AUC, half-life and urinary excretion, as well as decrease in hepatobiliary excretion was observed in comparison to healthy subjects with normal liver function. Hepatic contrast signal did not differ among the groups.
- Severe hepatic impairment may impair EOVIST imaging performance [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].In patients with severe hepatic impairment, especially in patients with abnormally high (> 3 mg/dL) serum bilirubin levels, the AUC was increased up to 60% and the elimination half-life was increased up to 49%. The hepatobiliary excretion substantially decreased to about 5% of the administered dose and reduced hepatic contrast signal was observed.
A dose adjustment is not necessary for patients with hepatic impairment.
- In clinical studies, 489 patients had a diagnosis of liver cirrhosis (Child-Pugh category A, n = 270; category B, n = 98; category C, n = 24; unknown category, n = 97). No difference in diagnostic performance and safety was observed among these patients.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Gadoxetate in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Gadoxetate in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Gadoxetate in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Gadoxetate in the drug label.
Overdosage
The maximum dose studied in MR imaging was 0.4 mL/kg (0.1 mmol/kg) body weight and was tolerated in a manner similar to lower doses. In case of inadvertent overdosage in patients with severely impaired renal and/or hepatic function, EOVIST can be partially removed by hemodialysis
Pharmacology
| |
Gadoxetate
| |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| 2-[[2-[bis(2-oxido-2-oxoethyl)amino]-3-(4-ethoxyphenyl)propyl]-[2-[bis(2-oxido-2-oxoethyl)amino]ethyl]amino]acetate; gadolinium(+3) cation | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | |
| ATC code | V08 |
| PubChem | |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | Template:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox |
| Mol. mass | 681.75 g/mol |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ? |
| Metabolism | ? |
| Half life | ? |
| Excretion | ? |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. |
? |
| Legal status | |
| Routes | ? |
Mechanism of Action
- Gadoxetate disodium is a paramagnetic compound and develops a magnetic moment when placed in a magnetic field. The relatively large magnetic moment produced by gadoxetate disodium results in a local magnetic field, yielding enhanced relaxation rates (shortening of relaxation times) of water protons in the vicinity of the paramagnetic agent, which leads to an increase in signal intensity (brightening) of blood and tissue.
- In MRI, visualization of normal and pathological tissue depends in part on variations in the radiofrequency signal intensity that occur with 1) differences in proton density; 2) differences of the spin-lattice or longitudinal relaxation times (T1); and 3) differences in the spin-spin or transverse relaxation time (T2). When placed in a magnetic field, gadoxetate disodium decreases the T1 and T2 relaxation time in target tissue. At the recommended dose, the effect is observed with greatest sensitivity in T1-weighted MR sequences.
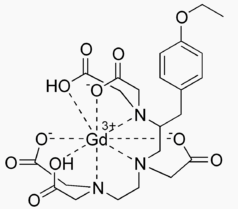
Structure
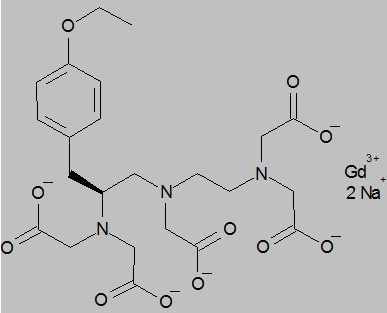
- EOVIST (gadoxetate disodium) is a paramagnetic contrast agent administered for MRI. EOVIST is provided as a sterile, clear, colorless to pale yellow aqueous solution for intravenous injection.
- EOVIST contains the active pharmaceutical ingredient, gadoxetate disodium (Gd‑EOB‑DTPA). The chemical name for gadoxetate disodium is (4S)-4-(4-Ethoxybenzyl)-3,6,9-tris(carboxylatomethyl)-3,6,9-triazaundecanedioic acid, gadolinium complex, disodium salt. Gadoxetate disodium has a molecular weight of 725.72 and an empirical formula of GdC23H28N3O11Na2. The structural formula of gadoxetate disodium in aqueous solution is:
Pharmacodynamics
- EOB-DTPA forms a stable complex with the paramagnetic gadolinium ion with a thermodynamic stability of log KGdL=‑23.46. Gadoxetate disodium is a highly water-soluble, hydrophilic compound with a lipophilic moiety, the ethoxybenzyl group (EOB). Gadoxetate disodium shows a weak (<10%), transient protein binding and the relaxivity in plasma is about 8.7 L/mmol/sec at pH 7, 39°C and 0.47 T.
- Gadoxetate disodium is selectively taken up by hepatocytes resulting in increased signal intensity in liver tissue.
- EOVIST exhibits a biphasic mode of action: first, distribution in the extracellular space after bolus injection and subsequently, selective uptake by hepatocytes (and biliary excretion) due to the lipophilic (EOB) moiety.
Pharmacokinetics
Distribution
- After intravenous administration, the plasma concentration time profile of gadoxetate disodium is characterized by a bi-exponential decline. The total distribution volume of gadoxetate disodium at steady state is about 0.21 L/kg (extracellular space); plasma protein binding is less than 10%. Gadoxetate disodium does not penetrate the intact blood-brain barrier and it does diffuse through the placental barrier.
Elimination
- Gadoxetate disodium is equally eliminated via the renal and hepatobiliary routes. The mean terminal elimination half-life of gadoxetate disodium (0.01 to 0.1 mmol/kg) has been observed in healthy volunteers of 22–39 years of age to be 0.91 to 0.95 hour. Clearance appeared to decrease slightly with increasing age. The pharmacokinetics are dose-linear up to a dose of 0.4 mL/kg (0.1 mmol/kg), which is 4 times the recommended dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4, 8.5, 8.6, and8.7)].
- A total serum clearance (Cltot) was 250 mL/min, whereas the renal clearance (Clr) corresponds to about 120 mL/min, a value similar to the glomerular filtration rate in healthy subjects.
Metabolism
- Gadoxetate disodium is not metabolized.
Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
- No carcinogenicity studies of EOVIST have been conducted.
- Gadoxetate disodium was not mutagenic in in vitro reverse mutation tests in bacteria, or in chromosome aberration tests in human peripheral blood lymphocytes, and was negative in an in vivo micronucleus test in mice after intravenous injection of doses up to 4 mmol/kg.
- Gadoxetate disodium had no effect on fertility and general reproductive performance of male and female rats when given in doses 6.5 times the human dose (based on body surface area).
Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
- A dose-related increase in QTc which was resolved by 30 minutes post dosing was observed in dogs when given a single dose of EOVIST. The increase was noted when given in doses equal to or greater than 0.1 mmol/kg (2.2 times the human dose). Maximum increase in QTcF was equal to or less than 20 ms at doses up to 0.5 mmol/kg (11 times the human dose).
- A gait disturbance was observed in 1 of 3 mice when givenEOVIST at a dose of approximately 1.1 mmol/kg (3.6 times the human dose); the disturbance occurred at 30 minutes post dosing and resolved at 4 hours post dosing.
- Local intolerance reactions, including moderate interstitial hemorrhage, edema, and focal muscle fiber necrosis, were observed after intramuscular administration of EOVIST
Clinical Studies
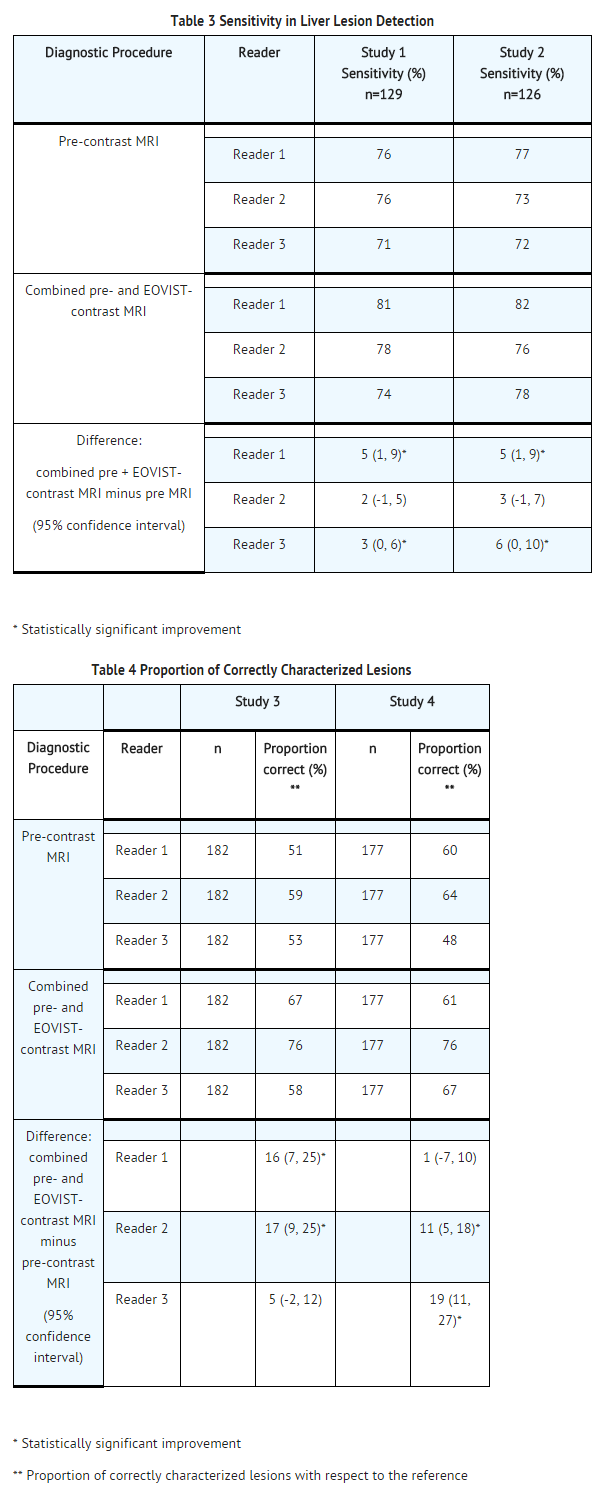
- Patients with suspected or known focal liver lesions were enrolled in two of four non-randomized, intrapatient-controlled studies that evaluated predominantly the detection (studies 1 and 2) or morphological characterization (studies 3 and 4) of liver lesions. Studies 1 and 2 ("detection" studies) enrolled patients who were scheduled for liver surgery. MRI results were compared to a reference standard that consisted of surgical histopathology and the results from intra-operative ultrasound of the liver. The studies assessed the sensitivity of pre-contrast MRI and EOVIST-contrasted MRI for the detection of liver lesions, when each set of images was compared to the reference.
- Studies 3 and 4 ("characterization" studies) enrolled patients with known or suspected focal liver lesions, including patients who were not scheduled for liver surgery. MRI results were compared to a reference standard that consisted of surgical histopathology and other prospectively defined criteria. The studies assessed the correctness of liver lesion characterization by pre-contrast MRI and EOVIST-contrasted MRI, when each set of images was compared to the reference. Lesions were characterized as one of the following choices: hepatocellular carcinoma, cholangiocarcinoma, metastasis, focal lymphoma, adenoma, focal nodular hyperplasia, hemangioma, abscess, focal liver fibrosis, regenerative nodule, focal fat, hydatid cyst, liver cyst, "not assessable", normal, no lesion or "other."
- In all four studies, patients underwent a baseline, pre-contrast MRI followed by the administration of EOVIST at a dose of 0.025 mmol/kg, with MRI performed immediately (the "dynamic" phase) and at 10 to 20 minutes following EOVIST administration (the "hepatocyte" phase). Patients also underwent computerized tomography with contrast examinations of the liver. Pre-contrast MRI and EOVIST-contrasted MR images were evaluated in a systematic, randomized, paired and unpaired fashion by three radiologists who were blinded to clinical information. CT images were also evaluated by the radiologists in a separate reading session.
- Diagnostic efficacy was determined in 621 patients. The average age was 57 years (range 19 to 84 years) and 54% were male. The ethnic representations were 90% Caucasian, 4% Black, 3% Hispanic, 2% Asian, and 1% of other ethnic groups.
- The combination of non-contrasted and EOVIST-contrasted MR images had improved sensitivity for the detection and characterization of liver lesions, compared to pre-contrasted MR images (Tables 3 and 4). The improved sensitivity in detection of lesions was predominantly related to the detection of additional lesions among patients with multiple lesions on the pre-contrast MR images. The false positive rates for detection of lesions were similar for non-contrasted MR images and EOVIST-contrasted MR images (32% versus 34%, respectively). Liver lesion detection and characterization results were similar between CT and the combination of pre-contrasted and EOVIST-contrasted MR images.
How Supplied
- EOVIST is supplied in single-dose, rubber stoppered vials containing 181.43 mg/mL of gadoxetate disodium (equivalent to 0.25 mmol/mL gadoxetate disodium), in the following sizes:
- 10 mL single-dose vials filled with 10 mL, boxes of 5 (NDC 50419-320-05)
- 15 mL single-dose vials filled with 15 mL, boxes of 5 (NDC 50419-320-15)
Storage
- Store at temperatures between 20 to 25° C (68 to77° F); excursions permitted to 15 to 30° C [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
- EOVIST is a ready-to-use solution for single use only. Visually inspect EOVIST for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. Do not use the solution if it is discolored or if particulate matter is present. The rubber stopper should not be pierced more than once. Use EOVIST immediately after opening. Unused portions should be discarded.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Gadoxetate |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
CARTON 5 X 10 ML
Ingredients and Appearance
{{#ask: Label Page::Gadoxetate |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Gadoxetate interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- EOVIST®[1]
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding look alike drug names.
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.