Acinic cell carcinoma physical examination
|
Acinic cell carcinoma Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case studies |
|
Acinic cell carcinoma physical examination On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Acinic cell carcinoma physical examination |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Acinic cell carcinoma physical examination |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Ramyar Ghandriz MD[2]
Overview
Common physical examination findings of salivary gland cancer include painless, firm swelling in one of the salivary gland, cervical lymphadenopathy, difficulty swallowing, trouble opening the mouth widely, difficulty moving one side of the face and muscle weakness on one side of the face suggestive of cranial nerve VII deficit, loss of corneal reflex, localized or regional pain, numbness, paresthesia, causalgia, or a loss of motor function suggestive of cranial nerve V deficit.[1]
Physical Examination
Physical examination should document size of the mass, mobility of the mass, fixation of the mass to the overlying skin or to the deep structures, pain with palpation, any limitation in jaw opening, buccal involvement or pharyngeal asymmetry, skin or scalp lesions indicative of primary malignancy.
HEENT
Fluid draining from the ear
Neck
- Painless, firm swelling or a lump in one of the salivary glands
- Cervical lymphadenopathy
- Difficulty swallowing
- Trouble opening the mouth widely[1]
Neuromuscular
- Difficulty moving one side of the face and muscle weakness on one side of the face suggestive of cranial nerve VII deficit
- Loss of corneal reflex, localized or regional pain, numbness, paresthesia, causalgia, or a loss of motor function suggestive of loss of cranial nerve V deficit
- Facial nerve weakness
Neck
-
SALIVARY GLANDS: MIXED TUMOR OF PAROTID. The pre-auricular mass had enlarged to this size over a period of 5 years.(Courtesy of Dr. Charles E. Tomich, Indianapolis, IN.)
-
SALIVARY GLANDS: RECURRENT MIXED TUMOR. The characteristic multinodular growth of recurrent mixed tumor is obvious inthis parotid mass. (Courtesy of Dr. Lewis R. Eversole, Los Angeles, CA.)
-
SALIVARY GLANDS: MIXED TUMOR OF PALATE. Most mixed tumors involve only one side of the palate because there are few minor glands in the midline. In this case the tumor appears symmetrical on either side of the midline. Large intraoral tumors are susceptible to trauma-related ulceration, as illustrated here. (Courtesy of F. J.Kratochvil, Bethesda, MD.)
-
SALIVARY GLANDS: CANALICULAR ADENOMA. The upper lip is the site for over 70% of canalicular adenomas.
-
SALIVARY GLANDS: MUCOEPIDERMOID CARCINOMA OF PALATE. These tumors frequently are slightly raised, fluctuant, bluish discolorations of the palatal mucosa that are clinically thought to represent mucous escapereactions.
-
SALIVARY GLANDS: ACINIC CELL ADENOCARCINOMA: CLINICAL PRESENTATION: A 2.0-cm raised subcutaneous nodule just anterior to the lower portion of the ear is a common clinical presentation for acinic cell adenocarcinoma. The tumor is in the superficial lobe of the left parotid gland of this 24-year-old man.
-
SALIVARY GLANDS: ACINIC CELL ADENOCARCINOMA: CLINICAL PRESENTATION. The upper lip, or any other intra oral site, is an uncommon location for acinic cell adenocarcinoma.
-
SALIVARY GLANDS: ADENOID CYSTIC CARCINOMA. This sublingual gland tumor slowly enlarged to produce a large, lobulated mass in the anterior floor of the mouth. The oral mucosa is intact.
-
SALIVARY GLANDS: POLYMORPHOUS LOW-GRADE ADENOCARCINOMA. This tumor presented as a well-circumscribed, slow growing mass at the junction of the hard and soft palates. Pronounced telangiectasia of the overlying mucosa is evident. (Courtesy of Dr. Richard Canaan, Ocean Springs,MS.)
-
SALIVARY GLANDS: NECROTIZING SIALOMETAPLASIA. Swelling, as shown in this photograph of a palatal lesion, is a frequent initial clinical presentation. Many of the swellings subsequently ulcerate. (Courtesy of Dr. Ralph Correll, LosAngeles, CA.)
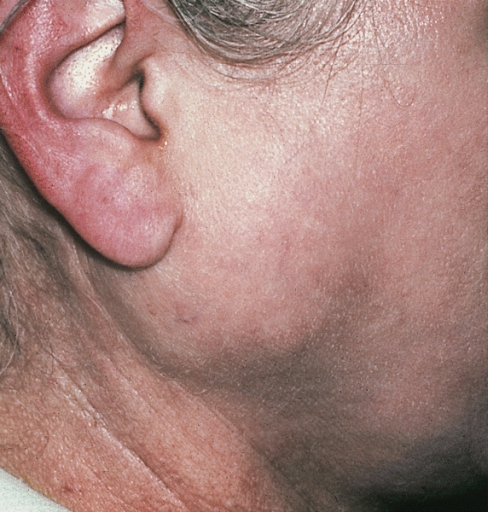
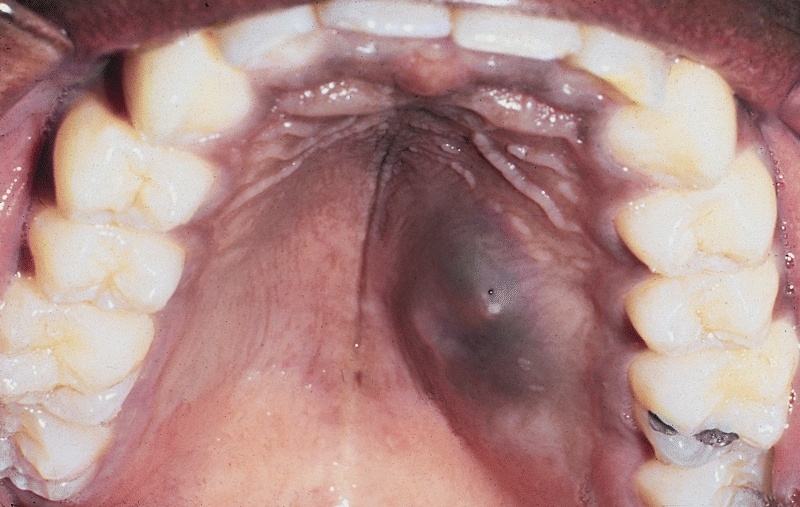
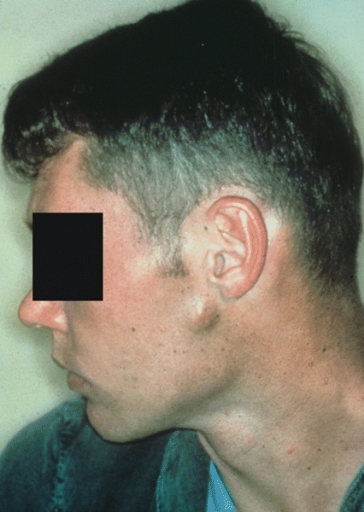
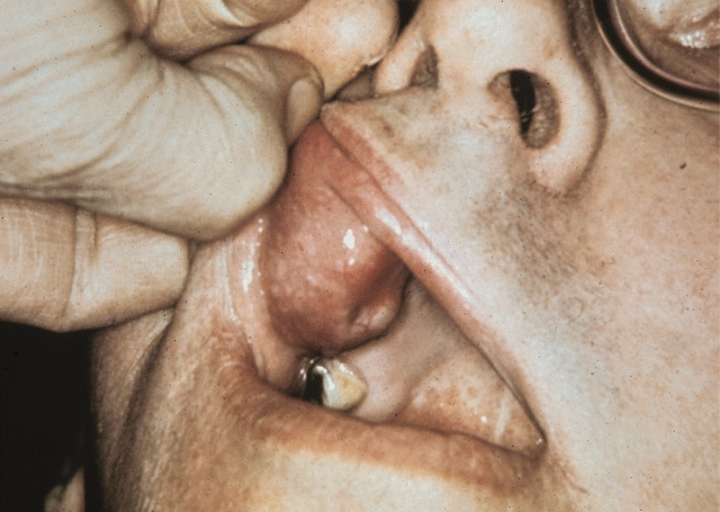
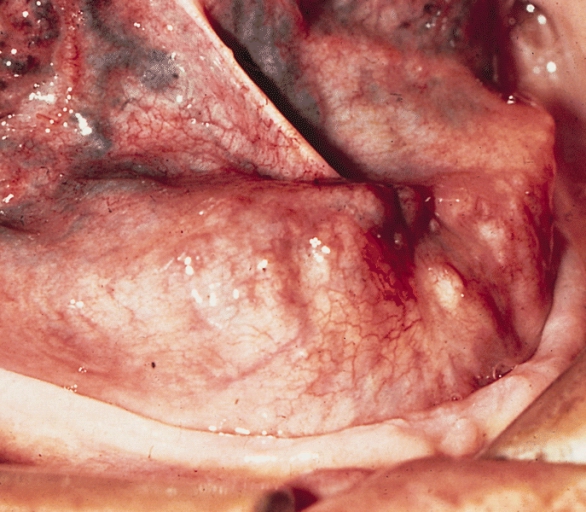
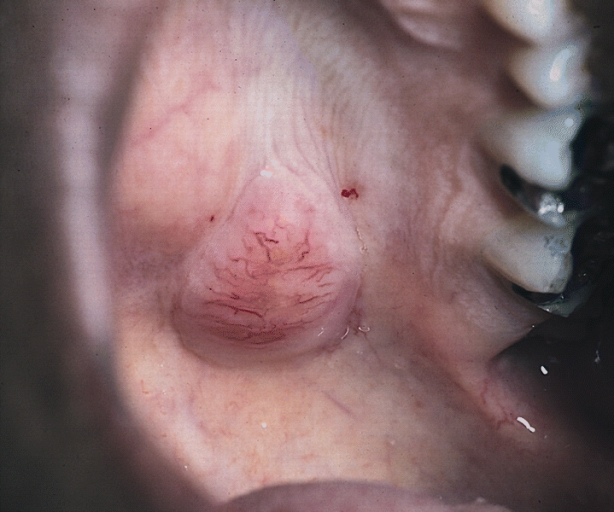
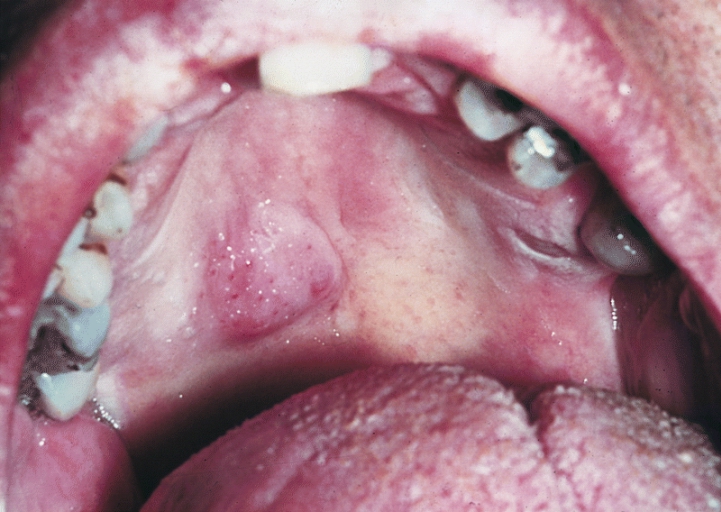
Parotid carcinoma
-
Parotid carcinoma. Adapted from Dermatology Atlas.[2]
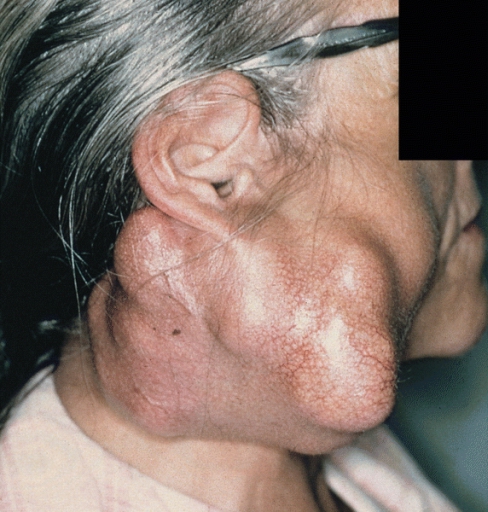
-
Parotid carcinoma. Adapted from Dermatology Atlas.[2]
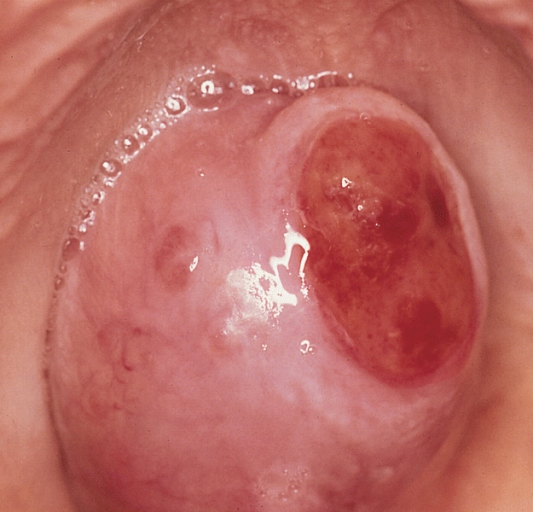
-
Parotid carcinoma. Adapted from Dermatology Atlas.[2]
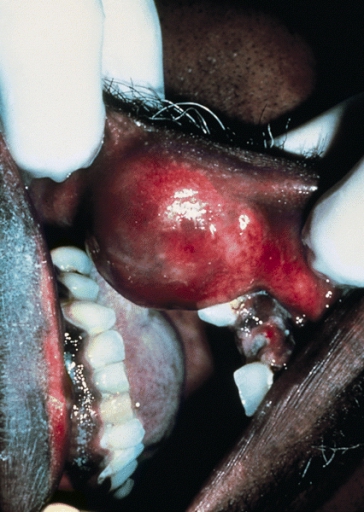
-
Parotid carcinoma. Adapted from Dermatology Atlas.[2]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Salivary gland cancer. Canadian cancer society(2015)http://www.cancer.ca/en/cancer-information/cancer-type/salivary-gland/signs-and-symptoms/?region=sk Accessed on November 8, 2015
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 "Dermatology Atlas".
![Parotid carcinoma. Adapted from Dermatology Atlas.[2]](/images/d/d1/Parotid_carcinoma01.jpg)
![Parotid carcinoma. Adapted from Dermatology Atlas.[2]](/images/a/a8/Parotid_carcinoma02.jpg)
![Parotid carcinoma. Adapted from Dermatology Atlas.[2]](/images/e/ea/Parotid_carcinoma03.jpg)
![Parotid carcinoma. Adapted from Dermatology Atlas.[2]](/images/f/fa/Parotid_carcinoma04.jpg)