Sickle-cell disease differential diagnosis: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Shyam Patel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Ahmed Younes (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
[[Image:Home_logo1.png|right|250px|link=https://www.wikidoc.org/index.php/Sickle-cell_disease]] | |||
{{CMG}} {{AE}} | {{CMG}} {{AE}} {{shyam}} | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
In some cases, it can be difficult to differentiate sickle cell disease from other diagnoses, given that there may be significant overlap of symptoms. | In some cases, it can be difficult to differentiate sickle cell disease from other diagnoses, given that there may be significant overlap of symptoms.<ref name="pmid25742458">{{cite journal| author=Sankaran VG, Weiss MJ| title=Anemia: progress in molecular mechanisms and therapies. | journal=Nat Med | year= 2015 | volume= 21 | issue= 3 | pages= 221-30 | pmid=25742458 | doi=10.1038/nm.3814 | pmc=4452951 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=25742458 }} </ref> | ||
==Differential Diagnosis== | ==Differential Diagnosis== | ||
*The differential diagnosis of sickle cell disease includes other conditions that may present with fatigue, infection, bone pain, such as: | *The differential diagnosis of sickle cell disease includes other conditions that may present with fatigue, infection, bone pain, such as: | ||
:* | :*[[Thalassemia]] | ||
:* | :*Acute leukemia | ||
:* | :*[[Autoimmune hemolytic anemia]]<ref name="pmid25742458">{{cite journal| author=Sankaran VG, Weiss MJ| title=Anemia: progress in molecular mechanisms and therapies. | journal=Nat Med | year= 2015 | volume= 21 | issue= 3 | pages= 221-30 | pmid=25742458 | doi=10.1038/nm.3814 | pmc=4452951 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=25742458 }} </ref> | ||
:*HbSC disease | :*HbSC disease | ||
:*HbS-beta-thalassemia | :*HbS-beta-thalassemia | ||
:* | :*Septic arthritis<ref name="pmid19885711">{{cite journal| author=Hernigou P, Daltro G, Flouzat-Lachaniette CH, Roussignol X, Poignard A| title=Septic arthritis in adults with sickle cell disease often is associated with osteomyelitis or osteonecrosis. | journal=Clin Orthop Relat Res | year= 2010 | volume= 468 | issue= 6 | pages= 1676-81 | pmid=19885711 | doi=10.1007/s11999-009-1149-3 | pmc=2865595 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=19885711 }} </ref> | ||
:* | :*[[Polycythemia vera]] | ||
:* | :*[[Systemic lupus erythematosus]] | ||
:*other | :*Other hemoglobinopathies | ||
Sickle cell disease must be differentiated from other causes of diabetes insipidus. | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
!Type of DI | |||
!Subclass | |||
!Disease | |||
!Defining signs and symptoms | |||
!Lab/Imaging findings | |||
|- | |||
| rowspan="5" |Central | |||
| rowspan="3" |Acquired | |||
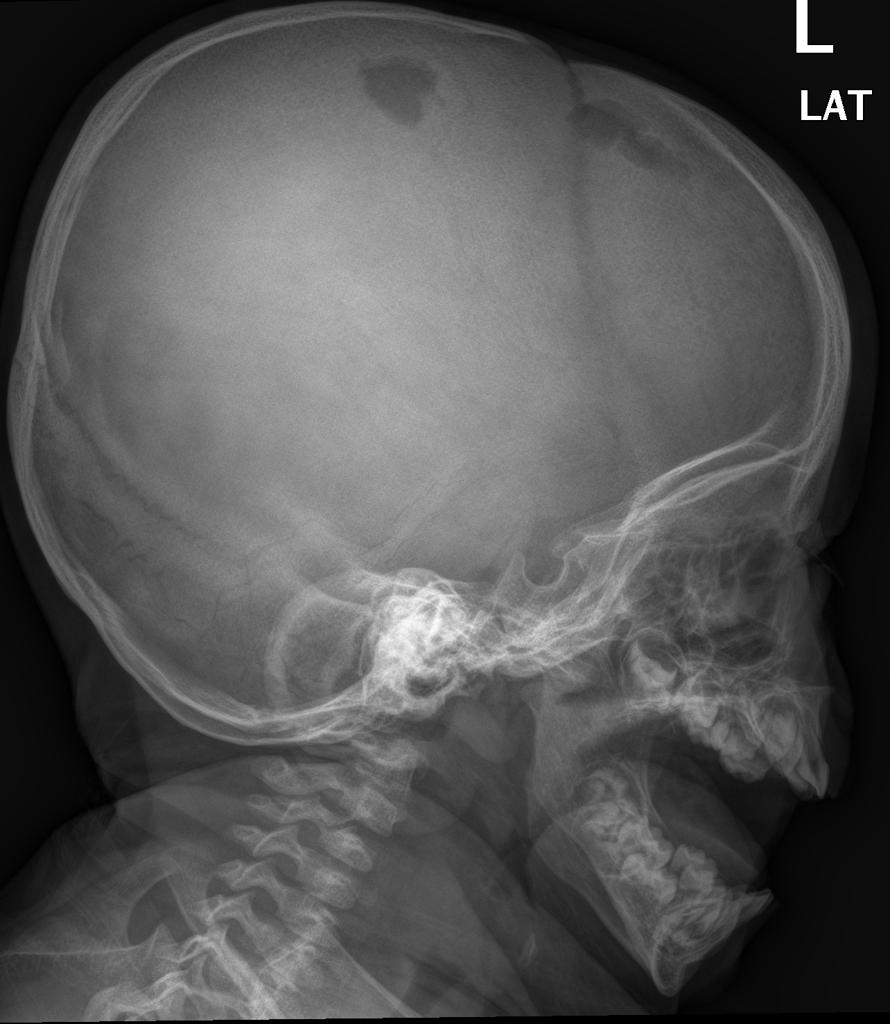
|[[Histiocytosis]] | |||
| | |||
* Bone lysis and [[Bone fracture|fracture]] | |||
* Purulent [[otitis media]] | |||
* [[Diabetes insipidus]] and delayed puberty | |||
* [[Maxillary]], [[mandibular]], and [[gingival]] disease | |||
* [[Rash]] and [[Erythematous|maculoerythematous]] skin lesions | |||
* Scaly, [[erythematous]] scalp patches | |||
* [[Lung]] involvement | |||
* [[GI bleeding]] | |||
* [[Lymphadenopathy|Lymph node enlargement]]<ref name="pmid1340034">{{cite journal| author=Ghosh KN, Bhattacharya A| title=Gonotrophic nature of Phlebotomus argentipes (Diptera: Psychodidae) in the laboratory. | journal=Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo | year= 1992 | volume= 34 | issue= 2 | pages= 181-2 | pmid=1340034 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=1340034 }} </ref> | |||
| | |||
* CD1a and CD45 + | |||
* Interleukin-17 (ILITA) | |||
[[Image:Langerhans Skull X ray.jpg|center|300px|thumb|Skull x-ray of a patient with Langerhan's histiocytosis showing lytic lesions - Case courtesy of Dr Hani Salam, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 9459]] | |||
|- | |||
|[[Craniopharyngioma]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Headache]] | |||
* [[Endocrine disorders|Endocrine dysfunction]] | |||
** [[Diabetes insipidus]] | |||
** [[Hypothyroidism]] | |||
** [[Adrenal failure]] | |||
** [[Diabetes insipidus]] (e.g., excessive fluid intake and urination) | |||
** Growth failure and [[delayed puberty]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Suprasellar]] calcified cyst on [[MRI]] | |||
[[Image:Craniopharyngioma-papillary-1.jpg|center|300px|thumb|Brain MRI showing suprasellar mass consistent with the diagnosis of craniopharyngioma - Case courtesy of A.Prof Frank Gaillard, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 16812]] | |||
|- | |||
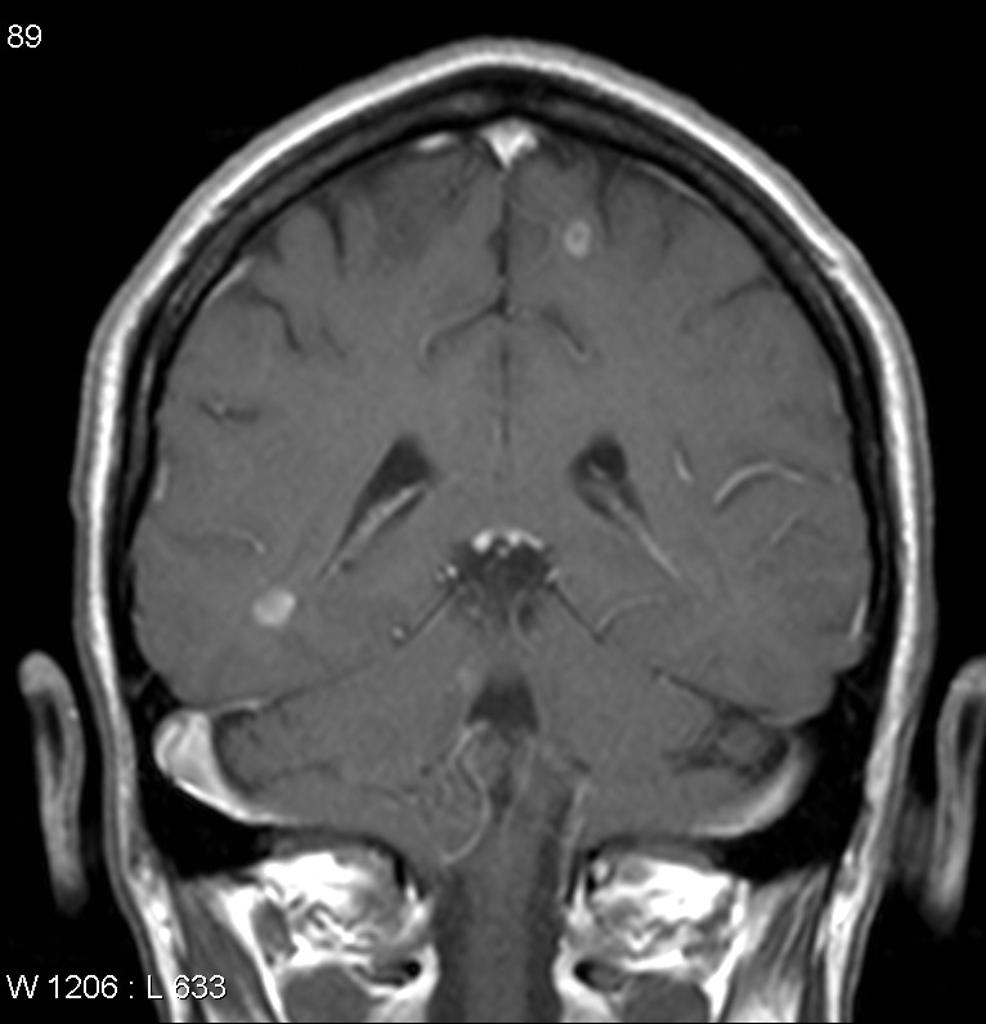
|[[Sarcoidosis]] | |||
| | |||
* Systemic complaints | |||
** [[Fever]] | |||
** [[Anorexia]] | |||
** [[Arthralgias]] | |||
* Pulmonary complaints | |||
** [[Dyspnea on exertion]] | |||
** [[Cough]] | |||
** Chest pain, | |||
** [[Hemoptysis]] (rare) | |||
* [[Diabetes mellitus]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Hypercalcemia]] | |||
* [[Hypercalciuria]] ([[Granulomas|noncaseating granulomas]]) | |||
* Elevated [[alkaline phosphatase]] | |||
* [[Serum amyloid A]] (SAA) | |||
* [[Angiotensin-converting enzyme|ACE]] levels may be elevated | |||
[[Image:Neurosarcoidosis.jpg|center|300px|thumb|Contrast-enhanced patches in a patient previously diagnosed with lung sarcoidosis - Case courtesy of A.Prof Frank Gaillard, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 10930]] | |||
|- | |||
| rowspan="2" |Congenital | |||
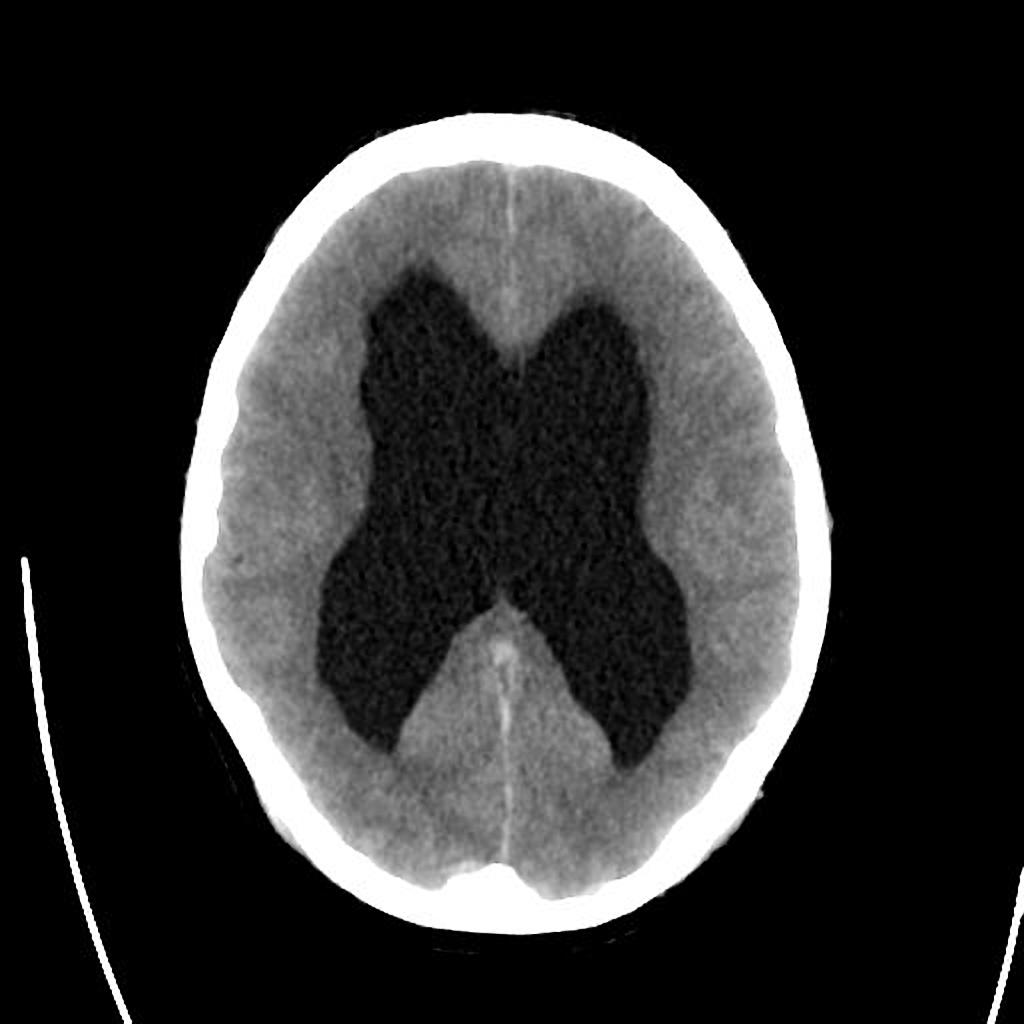
|[[Hydrocephalus]] | |||
| | |||
* Cognitive deterioration | |||
* [[Headaches]] | |||
* [[Neck pain]] | |||
* [[Blurred vision]] | |||
* [[Unsteady gait]] | |||
* [[Incontinence]] such as [[polyuria]] | |||
|Dilated [[ventricles]] on [[Computed tomography|CT]] and [[Magnetic resonance imaging|MRI]] | |||
[[Image:Obstructive-hydrocephalus.jpg|center|300px|thumb|Obstructive hydrocephalus showing dilated lateral ventricles - Case courtesy of Dr Paul Simkin, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 30453]] | |||
|- | |||
|[[Wolfram syndrome|Wolfram Syndrome]] (DIDMOAD) | |||
| | |||
* [[Diabetes insipidus|Diabetes Insipidus]] | |||
* [[Diabetes mellitus|Diabetes Mellitus]] | |||
* [[Optic atrophy|Optic Atrophy]] | |||
* [[Deafness]] | |||
| | |||
* Negative [[islet cell]] antibodies | |||
* [[Optic atrophy]] on [[electroretinogram]] | |||
* [[Deafness]] on [[audiogram]] | |||
* [[Atrophy]] of brain stem on [[Magnetic resonance imaging|MRI]] | |||
|- | |||
| rowspan="5" |[[Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus|Nephrogenic]] | |||
| rowspan="5" |[[Acquired disorder|Acquired]] | |||
|Drug-induced ([[demeclocycline]], [[lithium]]) | |||
| | |||
* [[Polyuria]] | |||
* [[Polydipsia]] | |||
* [[Nocturia]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Urine osmolality]] <100 mmol/ | |||
* [[Arginine vasopressin]] level >4.6 pmol/ | |||
* Little or no response to administration of exogenous [[arginine vasopressin]] | |||
|- | |||
|[[Hypercalcemia]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Polyuria]] | |||
* [[Polydipsia]] | |||
* [[Gastrointestinal]] disturbances | |||
* [[Bone fracture|Pathological fractures]] | |||
* [[Confusion]] | |||
* [[Palpitations]] and [[cardiac arrhythmias]] | |||
| | |||
* Ca levels greater than 11 meq/L | |||
|- | |||
|[[Hypokalemia]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Polyuria]] | |||
* [[Hyporeflexia]] | |||
* [[Palpitations]] and [[cardiac arrhythmias]] | |||
| | |||
* K levels less than 3meq/L on CBC | |||
|- | |||
|[[Multiple myeloma]] | |||
| | |||
* Pathologic [[bone fractures]] | |||
* [[Bleeding]] | |||
* [[Hypercalcemia]] leading to [[polyuria]] | |||
* [[Infection]] | |||
* [[Hyperviscosity]] | |||
* [[Anemia]] | |||
| | |||
* [[IgG]] or [[IgA]] spike on [[serum protein electrophoresis]] | |||
* [[Monoclonal antibody|Monoclonal M spike]] | |||
* Disordered [[plasma cell]] proliferation on [[bone marrow biopsy]] | |||
[[Image:Multiple-myeloma-skeletal-survey.jpg|center|300px|thumb|Skeletal survey in a patient with multiple myeloma showing multiple lytic lesions - Case courtesy of A.Prof Frank Gaillard, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 7682]] | |||
|- | |||
|[[Sickle-cell disease|Sickle cell disease]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Chronic pain]] | |||
* [[Anemia]] | |||
* [[Aplastic crisis]] | |||
* Splenic sequestration | |||
* [[Infection]] | |||
* [[Isosthenuria]] presenting with [[polyuria]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Hemoglobin]] level is 5-9 g/dL | |||
* [[Hematocrit]] is decreased to 17-29% | |||
* [[Peripheral blood smear|Peripheral blood smears]] demonstrate [[Target cell|target cells]], elongated cells, and characteristic sickle erythrocytes | |||
* MRI can demonstrate [[avascular necrosis]] of the [[femoral]] and [[humeral]] heads | |||
[[Image:Sickle cells.jpg|center|300px|thumb|Blood film showing the sickle cells - By Dr Graham Beards - Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=18421017]] | |||
|- | |||
| colspan="2" |Primary polydipsia | |||
|[[Psychogenic]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Polyuria]] | |||
* [[Polydipsia]] | |||
* [[Nocturia]] | |||
| | |||
* Dry mucus membrane | |||
* History of [[psychiatric disorders]] | |||
|- | |||
| colspan="3" |Gestational diabetes insipidus | |||
| | |||
* [[Polyuria]] | |||
* [[Polydipsia]] | |||
* [[Nocturia]] | |||
* [[Pregnancy]] | |||
| | |||
* Dry mucus membranes | |||
* [[Pregnancy]] | |||
|- | |||
| colspan="3" |[[Diabetes mellitus]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Polyuria]] | |||
* [[Polydipsia]] | |||
* [[Nocturia]] | |||
* [[Weight gain (patient information)|Weight gain]] | |||
| | |||
* Elevated blood sugar levels >126 | |||
* Elevated [[HbA1c]] > 6.5 | |||
|} | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 20:30, 27 February 2019

Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Shyam Patel [2]
Overview
In some cases, it can be difficult to differentiate sickle cell disease from other diagnoses, given that there may be significant overlap of symptoms.[1]
Differential Diagnosis
- The differential diagnosis of sickle cell disease includes other conditions that may present with fatigue, infection, bone pain, such as:
- Thalassemia
- Acute leukemia
- Autoimmune hemolytic anemia[1]
- HbSC disease
- HbS-beta-thalassemia
- Septic arthritis[2]
- Polycythemia vera
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Other hemoglobinopathies
Sickle cell disease must be differentiated from other causes of diabetes insipidus.
| Type of DI | Subclass | Disease | Defining signs and symptoms | Lab/Imaging findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Central | Acquired | Histiocytosis |
|
 |
| Craniopharyngioma |
|
 | ||
| Sarcoidosis |
|
 | ||
| Congenital | Hydrocephalus |
|
Dilated ventricles on CT and MRI
 | |
| Wolfram Syndrome (DIDMOAD) |
| |||
| Nephrogenic | Acquired | Drug-induced (demeclocycline, lithium) |
| |
| Hypercalcemia |
| |||
| Hypokalemia |
| |||
| Multiple myeloma |
|
 | ||
| Sickle cell disease |
|
 | ||
| Primary polydipsia | Psychogenic |
| ||
| Gestational diabetes insipidus |
| |||
| Diabetes mellitus |
| |||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Sankaran VG, Weiss MJ (2015). "Anemia: progress in molecular mechanisms and therapies". Nat Med. 21 (3): 221–30. doi:10.1038/nm.3814. PMC 4452951. PMID 25742458.
- ↑ Hernigou P, Daltro G, Flouzat-Lachaniette CH, Roussignol X, Poignard A (2010). "Septic arthritis in adults with sickle cell disease often is associated with osteomyelitis or osteonecrosis". Clin Orthop Relat Res. 468 (6): 1676–81. doi:10.1007/s11999-009-1149-3. PMC 2865595. PMID 19885711.
- ↑ Ghosh KN, Bhattacharya A (1992). "Gonotrophic nature of Phlebotomus argentipes (Diptera: Psychodidae) in the laboratory". Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 34 (2): 181–2. PMID 1340034.