|
|
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| | __NOTOC__ |
| | '''For patient information click [[{{PAGENAME}} (patient information)|here]]''' |
| | |
| {{Infobox_Disease | | | {{Infobox_Disease | |
| Name = Beriberi | | | Name = Beriberi | |
| Line 9: |
Line 12: |
| OMIM = | | | OMIM = | |
| MedlinePlus = | | | MedlinePlus = | |
| eMedicineSubj = ped | | | eMedicineSubj = | |
| eMedicineTopic = 229 | | | eMedicineTopic = | |
| eMedicine_mult = {{eMedicine2|med|221}} | | | eMedicine_mult = | |
| MeshID = D001602 | | | MeshID = D001602 | |
| }} | | }} |
| {{SI}}
| | |
| '''Editor-In-Chief:''' [[User:TimothyKoch|Timothy R. Koch, M.D., Professor of Medicine, Gastroenterology, Georgetown University School of Medicine]]. You can email Dr. Koch [mailto:Timothy.R.Koch@MedStar.net here]; Bikram Bal, M.D., Section of Gastroenterology, Washington Hospital Center. | | '''Editor-In-Chief:''' [[User:TimothyKoch|Timothy R. Koch, M.D., Professor of Medicine, Gastroenterology, Georgetown University School of Medicine]]. You can email Dr. Koch [mailto:Timothy.R.Koch@MedStar.net here]; Bikram Bal, M.D., Section of Gastroenterology, Washington Hospital Center. |
|
| |
|
| '''Associate Editor-in-Chief:''' [[C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D.]] | | '''Associate Editor-in-Chief:''' [[C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D.]] |
| | {{Beriberi}} |
|
| |
|
| | {{SK}} Thiamine (Vitamin B1) deficiency; wet beriberi; dry beriberi; Wericke disease; Korsakoff disease; Korsakov disease |
|
| |
|
| | ==[[Beriberi overview|Overview]]== |
|
| |
|
| ==Overview== | | ==[[Beriberi historical perspective|Historical Perspective]]== |
| Beriberi is a dietary-deficiency disease caused by a lack of thiamine in the diet. Thiamine, initially named "the anti-beriberi factor" in 1926 was the first B vitamin to be identified and is therefore referred to as vitamin B1. Thiamine is soluble in water and partly soluble in alcohol. It consists of a pyrimidine and a thiazole moiety, both of which are essential for its activity.
| |
| | |
| Thiamine functions in the decarboxylation of α-ketoacids, such as pyruvate α-ketoglutarate, and branched-chain amino acids and thus is a source of energy generation. In addition, thiamine pyrophosphate acts as a coenzyme for a transketolase reaction that mediates the conversion of hexose and pentose phosphates.
| |
| | |
| ==Etymology==
| |
| The origin of the word is from a Sinhalese phrase meaning "I cannot, I cannot", the word being doubled for emphasis.
| |
| | |
| ==History==
| |
| It is a disease that has killed probably close to a million people worldwide. References to this disease can be found in Chinese medical texts dating as far back as 2697 BC. In the 19th century it was the “national disease” of Japan. It first attracted the attention of Western scientists in the 1880s, when Dutch military personnel experienced an epidemic of the disease while operating in Sumatra. Its association with the consumption of highly polished rice was noted in the first decade of the twentieth century. It took some 50 years and lifetimes of dedication by dozens of scientists from many different fields and of various nationalities before the mysteries of beriberi were unraveled. [[Christiaan Eijkman]] a Dutch [[physician]] and [[pathologist]] first demonstrated that [[beriberi]] is caused by poor diet led to the discovery of [[vitamin]]s. Together with Sir [[Frederick Hopkins]], he was awarded the 1929 [[Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine]] for the discovery. But the ability to produce a synthetic vitamin on a commercial scale has been by no means the end of the story.
| |
| | |
| ==Differential Diagnosis of Underlying Causes==
| |
| Thiamine deficiency can be a result of:
| |
| | |
| '''1. Inadequate intake:'''
| |
| :[[Alcoholism]]
| |
| :[[Anorexia]]
| |
| :Intentional dieting
| |
| :[[Starvation]]
| |
| :[[Bulimia]]
| |
| :Protein energy [[malnutrition]] in developing countries
| |
| :[[Total parenteral nutrition]]
| |
| :Infants breast fed by [[thiamine]] deficient mothers
| |
| | |
| '''2. Increased losses:'''
| |
| :Protracted [[vomiting]] in [[chemotherapy]] patients
| |
| :[[Hyperemesis gravidarum]] in [[pregnant]] women
| |
| | |
| '''3. Inadequate absorption'''
| |
| :Post gastric bypass surgery patients
| |
| :Genetic loss of ability to absorb [[thiamine]]
| |
| | |
| | |
|
| |
|
| | ==[[Beriberi classification|Classification]]== |
|
| |
|
| ===Signs and Symptoms=== | | ==[[Beriberi pathophysiology|Pathophysiology]]== |
|
| |
|
| '''Cardiovascular or wet beriberi:''' is manifested by heart hypertrophy and dilatation (particularly of the right ventricle), [[tachycardia]], respiratory distress, [[edema]] of the legs and [[heart failure]] with high [[cardiac output]]. Severe [[lactic acidosis]] is characteristic (1).
| | ==[[Beriberi causes|Causes]]== |
|
| |
|
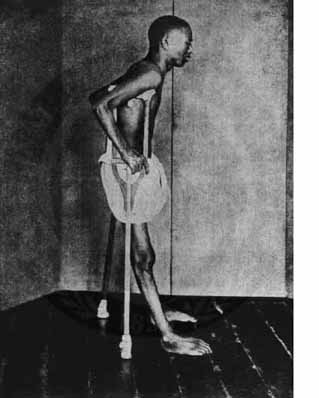
| '''Neurological or dry beriberi:''' is manifested by exaggeration of [[deep tendon reflexes]], [[polyneuritis]] (sometimes associated with paralysis) that typically affects lower extremities and in a subsequent stage, upper extremities, muscle weakness and pain, and [[convulsions]].
| | ==[[Beriberi differential diagnosis|Differentiating Beriberi from other Diseases]]== |
|
| |
|
| '''Gastrointestinal beriberi:''' Gastrointestinal symptoms are primarily due to the delayed emptying of the stomach and dilation of the [[colon]]. Loss of appetite, vague abdominal complaints, and [[constipation]] are common manifestations. As the disease progresses [[nausea]] and [[vomiting]] may occur.
| | ==[[Beriberi epidemiology and demographics|Epidemiology and Demographics]]== |
|
| |
|
| '''Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome:''' [[Wernicke's]] disease is a triad of [[nystagmus]], [[ophthalmoplegia]], and [[ataxia]], along with [[confusion]]. [[Korsakoff's]] [[psychosis]] is impaired short-term memory and confabulation with otherwise grossly normal cognition. This combination is almost exclusively described in chronic [[alcoholic]]s with thiamine deficiency. The two entities are not separate diseases, but a spectrum of signs and symptoms. Genetic abnormalities may underlie a predisposition to [[Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome]].
| | ==[[Beriberi risk factors|Risk Factors]]== |
|
| |
|
| '''Bariatric beriberi:''' Thiamine deficiency after Roux-en-Y [[gastric bypass]] surgery is common. After Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, thiamine deficiency has been reported in 18% of patients at one year post-surgical follow-up in a university hospital setting. Our group previously published that persistent thiamine deficiency is associated with small bowel bacterial overgrowth following gastric bypass surgery. Oral thiamine supplementation does not reverse thiamine deficiency in this patient population. Concurrent treatment of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth with antibiotics is needed to adequately treat the condition.
| | ==[[Beriberi natural history, complications and prognosis|Natural History, Complications and Prognosis]]== |
|
| |
|
| '''Psychotic beriberi:''' Psychotic beriberi manifesting with auditory and visual hallucinations, odd and aggressive behavior has been recently described in gastric bypass patients.
| | ==Diagnosis== |
|
| |
|
| | | [[Beriberi history and symptoms|History and Symptoms]] | [[Beriberi physical examination|Physical Examination]] | [[Beriberi laboratory findings|Laboratory Findings]] | [[Beriberi other diagnostic studies|Other Diagnostic Studies]] |
| ===Laboratory Studies===
| |
| The diagnosis of beriberi is assisted by a dietary history suggestive of a low thiamine intake and clinical manifestations. However, objective biochemical tests of thiamine status, particularly measurement of [[erythrocyte transketolase activity]] ([[ETKA]]) and the [[thiamine pyrophosphate effect]] ([[TPPE]]), provide a sensitive test for thiamine deficiency.
| |
|
| |
|
| ==Treatment== | | ==Treatment== |
| Treatment is with [[thiamine hydrochloride]], either in tablet form or injection. A rapid and dramatic recovery within hours can be made when this is administered to patients with beriberi. Thiamine occurs naturally in unrefined cereals and fresh foods, particularly fresh meat, legumes, green vegetables, fruit, and milk.
| |
|
| |
| == References ==
| |
| - Tanphaichitr, V., Shils, M. Modern Nutrition in Health and Medicine, 9th Ed, Lippincott, Philadelphia 2000. p.381.
| |
|
| |
| - Carpenter, K.J. Beriberi, White Rice, and Vitamin B: A disease, a cause, and a cure, Berkeley, University of California Press, 2000.
| |
|
| |
| - Hardy, A. Beriberi, White Rice, and Vitamin B: A disease, a cause, and a cure N Engl J Med 343:588, August 24, 2000. Book review.
| |
|
| |
| - Gubler, CJ. Thiamin. In: Handbook of vitamins: Nutritional, biochemical, and clinical aspects, Machlin, LJ (Ed), Marcel Dekker, New York 1984. p.245.
| |
|
| |
| - Rindi, G. Thiamine. In: Present knowledge in nutrition, 7th edn. Washington, DC: International Life Sciences Institute, 1996: 160-6.
| |
|
| |
| - Thiamine deficiency and its prevention and control in major emergenciesWHO/NHD/99.13
| |
|
| |
| - Clements RH, Katasani VG, Palepu R, Leeth RR, Leath TD, Roy BP, Vickers SM. Incidence of vitamin deficiency after laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass in a university hospital setting. Am Surg 2006; 72(12): 1196 1202.
| |
|
| |
| - S. Lakhani, H. Shah, K. Alexander, F. Finelli, J. Kirkpatrick, T. Koch. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth and thiamine deficiency after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery in obese patients. Nutrition Research, Volume 28, Issue 5, Pages 293-298
| |
|
| |
|
| - Wei Jiang, M.D., Jane P. Gagliardi, M.D., Y. Pritham Raj, M.D., Erin J. Silvertooth, M.D., Eric J. Christopher, M.D., and K. Ranga R. Krishnan, M.D. Acute Psychotic Disorder After Gastric Bypass Surgery: Differential Diagnosis and Treatment. Am J Psychiatry 163:15-19, January 2006. | | [[Beriberi medical therapy|Medical Therapy]] | [[Beriberi primary prevention|Primary Prevention]] | [[Beriberi secondary prevention|Secondary Prevention]] | [[Beriberi cost-effectiveness of therapy|Cost-Effectiveness of Therapy]] | [[Beriberi future or investigational therapies|Future or Investigational Therapies]] |
|
| |
|
| - Bikram Bal, Timothy R. Koch, Frederick C. Finelli & Michael G. Sarr .Managing medical and surgical disorders after divided Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology and Hepatology 7, 320-334 June 2010
| | ==Case Studies== |
| | [[Beriberi case study one|Case #1]] |
|
| |
|
| ==See also== | | ==See also== |
| Line 104: |
Line 60: |
| {{Nutritional pathology}} | | {{Nutritional pathology}} |
|
| |
|
| | [[Category:Disease]] |
| [[Category:Malnutrition]] | | [[Category:Malnutrition]] |
| [[Category:Reduplicants]] | | [[Category:Reduplicants]] |