Tetralogy of fallot echocardiography
|
Tetralogy of fallot Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
|
|
Tetralogy of fallot echocardiography On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Tetralogy of fallot echocardiography |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Tetralogy of fallot echocardiography |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Associate Editors-In-Chief: Keri Shafer, M.D. [2], Priyamvada Singh, MBBS
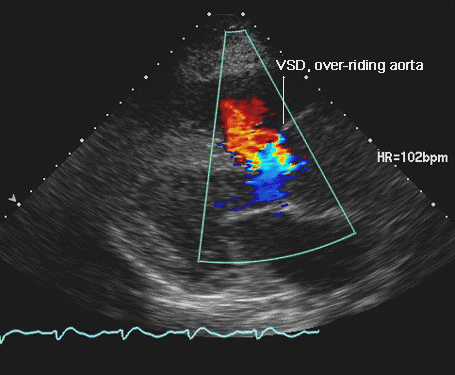
Echocardiogram is helpful in characterizing the defects as well as better understanding the hemodynamics in the heart. Right to left shunting through the VSD can be visualized by color Doppler imaging, and the severity of right ventricular outflow tract obstruction can be determined by spectral Doppler measurementsFor more info and images, see Tetralogy of fallot echocardiography
|
Tetralogy of fallot Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
|
|
Tetralogy of fallot echocardiography On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Tetralogy of fallot echocardiography |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Tetralogy of fallot echocardiography |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [3]
Associate Editors-In-Chief:Cafer Zorkun, M.D., Ph.D. [4], Priyamvada Singh, MBBS
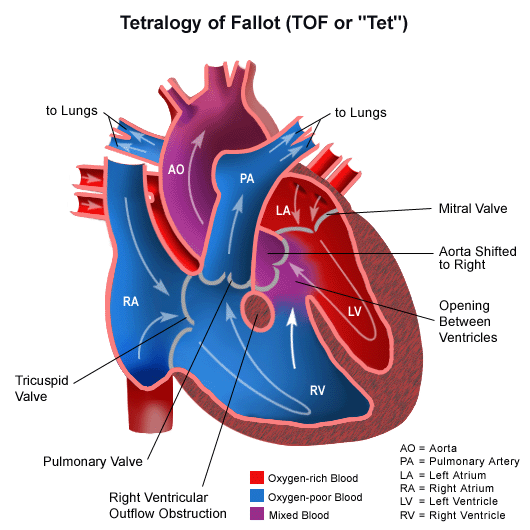
Tetralogy of Fallot
Tetralogy of fallot is a congenital heart disease comprised of four anatomic features stemming from the malalignment of the infundibular septum:
- Right ventrifular outflow obstruction (pulmonic stenosis)
- Ventricular Septal Defect
- Overriding aorta
- Right ventricular hypertrophy
- Clinically, it is a cyanotic heart defect and generally is diagnosed in infancy or early childhood.
Echo functions in Tetralogy of Fallot
- Characterization of defects
- Options for surgical intervention
- Post-operative repair function
Best evaluated by:
- parasternal long-axis view
- short-axis view (to evaluate size of septal defect)
Post surgical evaluation should include:
- Evaluation of VSD repair
- Residual shunting
- Right ventricular size and contractility
- Right ventricular outflow tract for residual stenosis
- Severity of pulmonary regurgitation
Additional Resource
Yale University School of Medicine Congenital Heart Disease: Tetralogy of Fallot