Restrictive cardiomyopathy
| https://https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JONXrVH4jQU%7C350}} |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Synonyms and keywords: Infiltrative cardiomyopathy; RCM; stiff heart; stiffening of the heart; heart stiffening; stiffened heart
Overview
Historical Perspective
Classification
Pathophysiology
Physiology
The normal physiology of [name of process] can be understood as follows:
Pathogenesis
- The exact pathogenesis of [disease name] is not completely understood.
OR
- It is understood that [disease name] is the result of / is mediated by / is produced by / is caused by either [hypothesis 1], [hypothesis 2], or [hypothesis 3].
- [Pathogen name] is usually transmitted via the [transmission route] route to the human host.
- Following transmission/ingestion, the [pathogen] uses the [entry site] to invade the [cell name] cell.
- [Disease or malignancy name] arises from [cell name]s, which are [cell type] cells that are normally involved in [function of cells].
- The progression to [disease name] usually involves the [molecular pathway].
- The pathophysiology of [disease/malignancy] depends on the histological subtype.
Genetics
Genes involved in the pathogenesis of restrictive cardiomyopathy include[1][2][3][4]:
- Cardiac genes for desmin, α-actin, troponin I and troponin T.
- Missense mutation (D190H) in the region of the cTnI gene (TNNI3).
- De novo mutations (R192H and K178E) in the TNNI3 gene.
- Mutations in the α-cardiac actin (ACTC), β-myosin heavy chain (β-MHC), and cTnT (TNNT2) genes have been noticed to have etiological causes of restrictive cardiomyopathy.
Associated Conditions
Conditions associated with [disease name] include:
- [Condition 1]
- [Condition 2]
- [Condition 3]
Gross Pathology
On gross pathology, [feature1], [feature2], and [feature3] are characteristic findings of [disease name].
Microscopic Pathology
On microscopic histopathological analysis, [feature1], [feature2], and [feature3] are characteristic findings of [disease name].
Causes
The main Causes of restrictive cardiomyopathy are enlisted below:[5][6]
- Amyloidosis (AL, ATTR, SSA)
- Sarcoidosis
- Hemochromatosis
- Eosinophilic myocardial disease
- Idiopathic RCM
- Progressive systemic sclerosis (scleroderma)
- Postradiation therapy (Hodgkin's lymphoma, breast cancer etc)
- Anderson Fabry disease
- Danon's disease
- Friedreich's ataxia
- Diabetic cardiomyopathy (restrictive phenotype)
- Drug induced (anthracycline toxicity, methysergide, ergotamine, mercurial agents, etc.)
- Mucopolysaccharidoses (Hurler's cardiomyopathy)
- Myocardial oxalosis
- Wegener's granulomatosis
- Metastatic malignancies
Differentiating restrictive cardiomyopathy from Other Diseases
Restrictive cardiomyopathy should be differentiated from dilated cardiomyopathy, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, congestive heart failure ect [6],[5]
| Type of disease | History | Physical examination | Chest X-ray | ECG | 2D echo | Doppler echo | CT | MRI | Catheterization hemodynamics | Biopsy |
| Restrictive cardiomyopathy[6][1] | Systemic disease (e.g., sarcoidosis, hemochromatosis). |
|
Atrial dilatation | Low QRS voltages (mainly amyloidosis), conduction disturbances, nonspecific ST abnormalities | ± Wall and valvular thickening, sparkling myocardium | Decreased variation in mitral and/or tricuspid inflow E velocity, increased hepatic vein inspiratory diastolic flow reversal, presence of mitral and tricuspid regurgitation | Normal pericardium | Measurement of iron overload, various types of LGE (late gadolinium enhancement) | LVEDP – RVEDP ≥ 5 mmHg
RVSP ≥ 55 mmHg RVEDP/RVSP ≤ 0.33 |
May reveal underlying cause. |
| Constrictive pericarditis[7][8][8] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy(HCM)[9][10] |
|
|
|
|
| |||||
| Dilated Cardiomyopathy[11][12][13][14] | Alcohol, HIV, Cocaine, CAD |
|
|
T wave and ST segment changes to septal pathological Q waves, wide QRS complex in patients with LV fibrosis might be present | LV dilation with diffuse hypokinetic walls | functional mitral and tricuspid regurgitation and a different degree of diastolic dysfunction | increased LV end-diastolic pressure and pulmonary artery wedge pressure. Left ventriculography may show ventricular dilation with global hypokinesis | |||
Epidemiology and Demographics
Risk Factors
Screening
Natural History, Complications, and Prognosis
Diagnosis
Diagnostic Study of Choice
History and Symptoms
- The majority of patients with [disease name] are asymptomatic.
OR
- The hallmark of [disease name] is [finding]. A positive history of [finding 1] and [finding 2] is suggestive of [disease name]. The most common symptoms of [disease name] include [symptom 1], [symptom 2], and [symptom 3].
- Symptoms of [disease name] include [symptom 1], [symptom 2], and [symptom 3].
History
Patients with [disease name]] may have a positive history of:
- [History finding 1]
- [History finding 2]
- [History finding 3]
Common Symptoms
Common symptoms of [disease] include:
- Dyspnea
- Fatigue
- Limited exercise capacity
- Palpitations
- Syncope
Less Common Symptoms
Less common symptoms of restrictive cardiomyopathy include
- Angina
Physical Examination
Physical examination of patients with [disease name] is usually normal.
OR
Physical examination of patients with [disease name] is usually remarkable for [finding 1], [finding 2], and [finding 3].
OR
The presence of [finding(s)] on physical examination is diagnostic of [disease name].
OR
The presence of [finding(s)] on physical examination is highly suggestive of [disease name].
Appearance of the Patient
- Patients with [disease name] usually appear [general appearance].
Vital Signs
- High-grade / low-grade fever
- Hypothermia / hyperthermia may be present
- Tachycardia with regular pulse or (ir)regularly irregular pulse
- Bradycardia with regular pulse or (ir)regularly irregular pulse
- Tachypnea / bradypnea
- Kussmal respirations may be present in _____ (advanced disease state)
- Weak/bounding pulse / pulsus alternans / paradoxical pulse / asymmetric pulse
- High/low blood pressure with normal pulse pressure / wide pulse pressure / narrow pulse pressure
Skin
- Skin examination of patients with restrictive cardiomyopathy is usually normal.
HEENT
- HEENT examination of patients with restrictive cardiomyopathy is usually normal.
Neck
- Jugular venous distension is noted sometimes with kussmaul sign
- Hepatojugular reflux
Lungs
- Fine/coarse crackles upon auscultation of the lung bases/apices unilaterally/bilaterally
- Rhonchi
Heart
Abdomen
Back
- Back examination of patients with restrictive cardiomyopathy is usually normal.
Genitourinary
- Genitourinary examination of patients with restrictive cardiomyopathy is usually normal.
Neuromuscular
- Neuromuscular examination of patients with restrictive cardiomyopathy is usually normal.
Extremities
- Peripheral edema of the lower extremities
Laboratory Findings
Electrocardiogram
X-ray
Echocardiography and Ultrasound
CT scan
MRI
Other Imaging Findings
Other Diagnostic Studies
Treatment
Medical Therapy
Interventions
Surgery
Primary Prevention
Secondary Prevention
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Mogensen J, Kubo T, Duque M, Uribe W, Shaw A, Murphy R, Gimeno JR, Elliott P, McKenna WJ (January 2003). "Idiopathic restrictive cardiomyopathy is part of the clinical expression of cardiac troponin I mutations". J. Clin. Invest. 111 (2): 209–16. doi:10.1172/JCI16336. PMC 151864. PMID 12531876.
- ↑ Burke MA, Cook SA, Seidman JG, Seidman CE (December 2016). "Clinical and Mechanistic Insights Into the Genetics of Cardiomyopathy". J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 68 (25): 2871–2886. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2016.08.079. PMC 5843375. PMID 28007147.
- ↑ Parvatiyar MS, Pinto JR, Dweck D, Potter JD (2010). "Cardiac troponin mutations and restrictive cardiomyopathy". J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2010: 350706. doi:10.1155/2010/350706. PMC 2896668. PMID 20617149.
- ↑ Kostareva A, Gudkova A, Sjöberg G, Mörner S, Semernin E, Krutikov A, Shlyakhto E, Sejersen T (January 2009). "Deletion in TNNI3 gene is associated with restrictive cardiomyopathy". Int. J. Cardiol. 131 (3): 410–2. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2007.07.108. PMID 18006163.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Hong JA, Kim MS, Cho MS, Choi HI, Kang DH, Lee SE, Lee GY, Jeon ES, Cho JY, Kim KH, Yoo BS, Lee JY, Kim WJ, Kim KH, Chung WJ, Lee JH, Cho MC, Kim JJ (September 2017). "Clinical features of idiopathic restrictive cardiomyopathy: A retrospective multicenter cohort study over 2 decades". Medicine (Baltimore). 96 (36): e7886. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000007886. PMC 6393124. PMID 28885342.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Rammos A, Meladinis V, Vovas G, Patsouras D (2017). "Restrictive Cardiomyopathies: The Importance of Noninvasive Cardiac Imaging Modalities in Diagnosis and Treatment-A Systematic Review". Radiol Res Pract. 2017: 2874902. doi:10.1155/2017/2874902. PMC 5705874. PMID 29270320.
- ↑ Ramasamy V, Mayosi BM, Sturrock ED, Ntsekhe M (September 2018). "Established and novel pathophysiological mechanisms of pericardial injury and constrictive pericarditis". World J Cardiol. 10 (9): 87–96. doi:10.4330/wjc.v10.i9.87. PMC 6189073. PMID 30344956.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Biçer M, Özdemir B, Kan İ, Yüksel A, Tok M, Şenkaya I (November 2015). "Long-term outcomes of pericardiectomy for constrictive pericarditis". J Cardiothorac Surg. 10: 177. doi:10.1186/s13019-015-0385-8. PMC 4662820. PMID 26613929.
- ↑ Kubo T, Gimeno JR, Bahl A, Steffensen U, Steffensen M, Osman E, Thaman R, Mogensen J, Elliott PM, Doi Y, McKenna WJ (June 2007). "Prevalence, clinical significance, and genetic basis of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy with restrictive phenotype". J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 49 (25): 2419–26. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2007.02.061. PMID 17599605.
- ↑ Marian AJ, Braunwald E (September 2017). "Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: Genetics, Pathogenesis, Clinical Manifestations, Diagnosis, and Therapy". Circ. Res. 121 (7): 749–770. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.311059. PMC 5654557. PMID 28912181.
- ↑ Francone M (2014). "Role of cardiac magnetic resonance in the evaluation of dilated cardiomyopathy: diagnostic contribution and prognostic significance". ISRN Radiol. 2014: 365404. doi:10.1155/2014/365404. PMC 4045555. PMID 24967294.
- ↑ McNally EM, Mestroni L (September 2017). "Dilated Cardiomyopathy: Genetic Determinants and Mechanisms". Circ. Res. 121 (7): 731–748. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.309396. PMC 5626020. PMID 28912180.
- ↑ Tayal U, Prasad S, Cook SA (February 2017). "Genetics and genomics of dilated cardiomyopathy and systolic heart failure". Genome Med. 9 (1): 20. doi:10.1186/s13073-017-0410-8. PMC 5322656. PMID 28228157.
- ↑ Mitrut R, Stepan AE, Pirici D (2018). "Histopathological Aspects of the Myocardium in Dilated Cardiomyopathy". Curr Health Sci J. 44 (3): 243–249. doi:10.12865/CHSJ.44.03.07. PMC 6311227. PMID 30647944.
Overview
Restrictive cardiomyopathy is the least common cardiomyopathy. It is called this because it restricts the heart from stretching and filling with blood properly. Rhythmicity and contractility of the heart may be normal, but the stiff walls of the heart chambers (atria and ventricles) keep them from adequately filling. So blood flow is reduced, and blood that would normally enter the heart is backed up in the circulatory system. In time, restrictive cardiomyopathy patients develop heart failure.
Causes
Life Threatening Causes
Life-threatening causes include conditions which may result in death or permanent disability within 24 hours if left untreated. There are no known life threatening causes of restrictive cardiomyopathy that may result in death within 24 hours if not treated.
Common Causes
Causes by Organ System
Causes in Alphabetical Order
Diagnosis
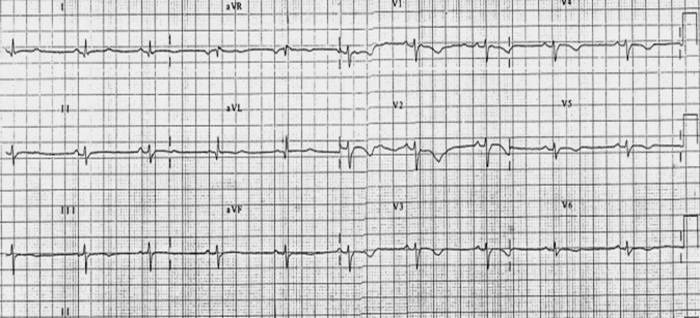
Electrocardiogram
Shown below is an example of restrictive cardiomyopathy with low voltage and flipped anterior T waves.