Tibial plateau fracture physical examination: Difference between revisions
(Created page with " __NOTOC__ {{Tibial plateau fracture}} {{CMG}} {{AE}} {{Rohan}} ==Overview== Patients with tibial plateau fracture usually appears well. Physical examination of patients with...") |
m (Bot: Removing from Primary care) |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | |||
{{Tibial plateau fracture}} | {{Tibial plateau fracture}} | ||
{{CMG}} {{AE}} {{Rohan}} | {{CMG}} {{AE}} {{Rohan}} | ||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
==Physical Examination== | ==Physical Examination== | ||
Physical examination of patients with tibial plateau fracture is usually remarkable for [[swelling]], [[tenderness]], [[Bruise|bruises]], [[ecchymosis]], {| align="right" | Physical examination of patients with tibial plateau fracture is usually remarkable for [[swelling]], [[tenderness]], [[Bruise|bruises]], [[ecchymosis]], | ||
{| align="right" | |||
| | | | ||
[[File:Tibia clinical image.JPG|400px|thumb|Clinical image of tibial plateau fracture showing swelling and ecchymosis. Source: Case courtesy by: [[User:Rohan Bhimani|Dr. Rohan A. Bhimani]]]] | [[File:Tibia clinical image.JPG|400px|thumb|Clinical image of tibial plateau fracture showing swelling and ecchymosis. Source: Case courtesy by: [[User:Rohan Bhimani|Dr. Rohan A. Bhimani]]]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 24: | Line 23: | ||
===Skin=== | ===Skin=== | ||
* Skin examination of patients with distal radius fracture includes: | * [[Skin]] examination of patients with distal radius fracture includes: | ||
** [[Bruise|Bruises]] | ** [[Bruise|Bruises]] | ||
** [[Ecchymosis]] | ** [[Ecchymosis]] | ||
| Line 33: | Line 32: | ||
===Neck=== | ===Neck=== | ||
* Neck examination of patients with tibial plateau fracture is normal. | * [[Neck]] examination of patients with tibial plateau fracture is normal. | ||
===Lungs=== | ===Lungs=== | ||
* Pulmonary examination of patients with tibial plateau fracture is usually normal. | * [[Pulmonary]] examination of patients with tibial plateau fracture is usually normal. | ||
===Heart=== | ===Heart=== | ||
* Cardiovascular examination of patients with tibial plateau fracture is usually normal. | * [[Cardiovascular]] examination of patients with tibial plateau fracture is usually normal. | ||
===Abdomen=== | ===Abdomen=== | ||
* Abdominal examination of patients with tibial plateau fracture is usually normal. | * [[Abdomen|Abdominal]] examination of patients with tibial plateau fracture is usually normal. | ||
===Back=== | ===Back=== | ||
* Back examination of patients with tibial plateau fracture is usually normal. | * [[Back]] examination of patients with tibial plateau fracture is usually normal. | ||
===Genitourinary=== | ===Genitourinary=== | ||
* Genitourinary examination of patients with tibial plateau fracture is usually normal. | * [[Genitourinary]] examination of patients with tibial plateau fracture is usually normal. | ||
===Neuromuscular=== | ===Neuromuscular=== | ||
* Neuromuscular examination of patients with tibial plateau fracture is usually normal. | * [[Neuromuscular]] examination of patients with tibial plateau fracture is usually normal. | ||
* However, some patients may develop [[neuropraxia]] of the [[deep peroneal nerve]] and [[tibial nerve]] resulting in decreased sensation of toes, foot and leg. | * However, some patients may develop [[neuropraxia]] of the [[deep peroneal nerve]] and [[tibial nerve]] resulting in decreased sensation of toes, foot and leg. | ||
===Extremities=== | ===Extremities=== | ||
* [[Knee]] examination of patients with tibial plateau fracture include:<ref name="pmid30059369">{{cite journal| author=Ramponi DR, McSwigan T| title=Tibial Plateau Fractures. | journal=Adv Emerg Nurs J | year= 2018 | volume= 40 | issue= 3 | pages= 155-161 | pmid=30059369 | doi=10.1097/TME.0000000000000194 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=30059369 }} </ref><ref>{{cite book | last = Rockwood | first = Charles | title = Rockwood and Green's fractures in adults | publisher = Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins | location = Philadelphia, PA | year = 2010 | isbn = 9781605476773 }}</ref><ref name="pmid27984441">{{cite journal| author=Singleton N, Sahakian V, Muir D| title=Outcome After Tibial Plateau Fracture: How Important Is Restoration of Articular Congruity? | journal=J Orthop Trauma | year= 2017 | volume= 31 | issue= 3 | pages= 158-163 | pmid=27984441 | doi=10.1097/BOT.0000000000000762 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=27984441 }} </ref><ref name="pmid27914662">{{cite journal| author=Dubina AG, Paryavi E, Manson TT, Allmon C, O'Toole RV| title=Surgical site infection in tibial plateau fractures with ipsilateral compartment syndrome. | journal=Injury | year= 2017 | volume= 48 | issue= 2 | pages= 495-500 | pmid=27914662 | doi=10.1016/j.injury.2016.10.017 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=27914662 }} </ref> | |||
* [[Knee]] examination of patients with tibial plateau fracture include:<ref name=" | |||
** [[Edema|Swelling]] | ** [[Edema|Swelling]] | ||
** [[Tenderness]] | ** [[Tenderness]] | ||
** [[Deformity]] | ** [[Deformity]] | ||
** [[Knee Dislocation]] | ** [[Knee Dislocation]] | ||
** Restricted [[range of motion]] | ** Restricted [[range of motion]] | ||
** [[Tingling]] and decreased [[sensation]] of toes, foot and leg | ** [[Tingling]] and decreased [[sensation]] of toes, foot and leg | ||
** Decreased [[sensation]] over the shin and the calf can be due to [[nerve]] injury | ** Decreased [[sensation]] over the shin and the calf can be due to [[nerve]] injury | ||
** Weakness in leg | ** [[Weakness]] in [[leg]] | ||
** Acute [[carpal tunnel syndrome]] | ** Acute [[carpal tunnel syndrome]] | ||
*** Pulselessness in the leg | *** [[Pulselessness]] in the [[leg]] | ||
*** Skin pallor | *** [[Skin]] [[pallor]] | ||
*** Parasthesias | *** [[Paresthesia|Parasthesias]] | ||
** Internal Derangement of the Knee | ** Internal Derangement of the Knee | ||
*** Meniscal Injury | *** [[Meniscal tear|Meniscal]] Injury | ||
**** Positive McMurray's test | **** Positive [[McMurray's test]] | ||
** | ** [[Ligament|Ligamentous]] Injury | ||
*** Anterior Cruciate Ligament and Posterior Cruciate Ligament | *** Anterior Cruciate Ligament and Posterior Cruciate Ligament | ||
**** Positive Drawer test | **** Positive [[Drawer test]] | ||
**** Positive Lachman test | **** Positive [[Lachman test]] | ||
**** Positive Dial test | **** Positive Dial test | ||
*** Medial Collateral Ligament and Lateral Collateral Ligament | *** Medial Collateral Ligament and Lateral Collateral Ligament | ||
**** Positive Valgus and varus stress test | **** Positive [[Valgus]] and [[varus]] stress test | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| Line 88: | Line 82: | ||
{{WH}} | {{WH}} | ||
{{WS}} | {{WS}} | ||
[[Category:Needs content]] | [[Category:Needs content]] | ||
[[Category:Orthopedics]] | [[Category:Orthopedics]] | ||
[[Category:Orthopedic surgery]] | [[Category:Orthopedic surgery]] | ||
[[Category:Fractures]] | [[Category:Fractures]] | ||
[[Category:Bone fractures]] | [[Category:Bone fractures]] | ||
Latest revision as of 00:25, 30 July 2020
|
Tibial plateau fracture Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Tibial plateau fracture physical examination On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Tibial plateau fracture physical examination |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Tibial plateau fracture physical examination |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Rohan A. Bhimani, M.B.B.S., D.N.B., M.Ch.[2]
Overview
Patients with tibial plateau fracture usually appears well. Physical examination of patients with tibial plateau fracture is usually remarkable for swelling, tenderness, bruises, ecchymosis, deformity and restricted range of motion of the leg.
Physical Examination
Physical examination of patients with tibial plateau fracture is usually remarkable for swelling, tenderness, bruises, ecchymosis,
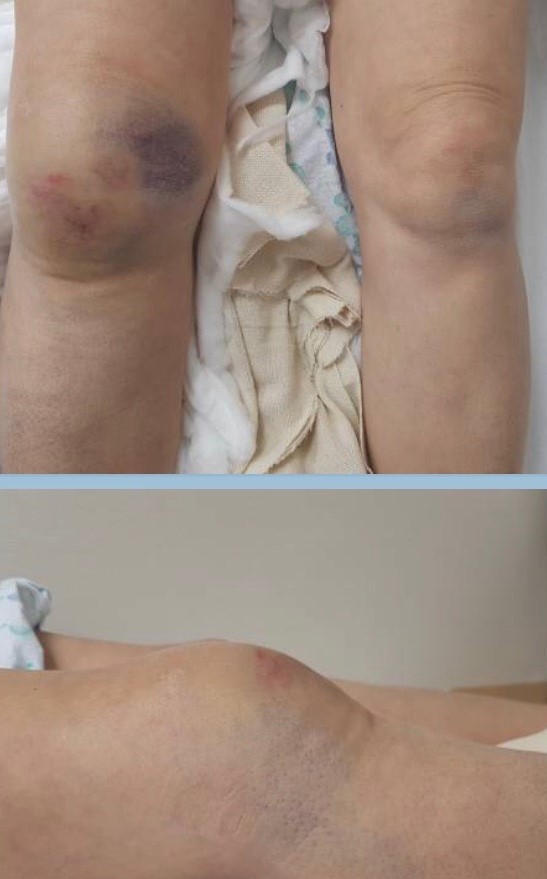 |
Appearance of the Patient
- Patients with tibial plateau fracture usually appears well.
Vital Signs
- Weak pulse may be seen when associated with polytrauma.
- Low blood pressure with normal pulse pressure may be present due to compound fracture with blood loss.
Skin
- Skin examination of patients with distal radius fracture includes:
HEENT
- HEENT examination of patients with tibial plateau fracture is usually normal.
Neck
- Neck examination of patients with tibial plateau fracture is normal.
Lungs
- Pulmonary examination of patients with tibial plateau fracture is usually normal.
Heart
- Cardiovascular examination of patients with tibial plateau fracture is usually normal.
Abdomen
- Abdominal examination of patients with tibial plateau fracture is usually normal.
Back
- Back examination of patients with tibial plateau fracture is usually normal.
Genitourinary
- Genitourinary examination of patients with tibial plateau fracture is usually normal.
Neuromuscular
- Neuromuscular examination of patients with tibial plateau fracture is usually normal.
- However, some patients may develop neuropraxia of the deep peroneal nerve and tibial nerve resulting in decreased sensation of toes, foot and leg.
Extremities
- Knee examination of patients with tibial plateau fracture include:[1][2][3][4]
- Swelling
- Tenderness
- Deformity
- Knee Dislocation
- Restricted range of motion
- Tingling and decreased sensation of toes, foot and leg
- Decreased sensation over the shin and the calf can be due to nerve injury
- Weakness in leg
- Acute carpal tunnel syndrome
- Pulselessness in the leg
- Skin pallor
- Parasthesias
- Internal Derangement of the Knee
- Meniscal Injury
- Positive McMurray's test
- Meniscal Injury
- Ligamentous Injury
- Anterior Cruciate Ligament and Posterior Cruciate Ligament
- Positive Drawer test
- Positive Lachman test
- Positive Dial test
- Medial Collateral Ligament and Lateral Collateral Ligament
- Anterior Cruciate Ligament and Posterior Cruciate Ligament
References
- ↑ Ramponi DR, McSwigan T (2018). "Tibial Plateau Fractures". Adv Emerg Nurs J. 40 (3): 155–161. doi:10.1097/TME.0000000000000194. PMID 30059369.
- ↑ Rockwood, Charles (2010). Rockwood and Green's fractures in adults. Philadelphia, PA: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 9781605476773.
- ↑ Singleton N, Sahakian V, Muir D (2017). "Outcome After Tibial Plateau Fracture: How Important Is Restoration of Articular Congruity?". J Orthop Trauma. 31 (3): 158–163. doi:10.1097/BOT.0000000000000762. PMID 27984441.
- ↑ Dubina AG, Paryavi E, Manson TT, Allmon C, O'Toole RV (2017). "Surgical site infection in tibial plateau fractures with ipsilateral compartment syndrome". Injury. 48 (2): 495–500. doi:10.1016/j.injury.2016.10.017. PMID 27914662.