Right heart failure electrocardiogram
|
Right heart failure Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Right heart failure electrocardiogram On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Right heart failure electrocardiogram |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Right heart failure electrocardiogram |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
Right heart failure is often accompanied by right ventricular hypertrophy and right ventricular dilatation. The general electrocardiographic findings of right ventricular hypertrophy include right axis deviation, an R/S ratio > 1 in V1, and the presence of P pulmonale.
Electrocardiogram
Summary of EKG Criteria for RVH
- Right axis deviation of +90 degrees or more
- The R wave in V1 is 7 mm or more in height
- RV1 + SV5 or SV6 = 10 mm or more
- R/S ratio in V1 = 1.0 or more
- S/R ratio in V6 = 1.0 or more
- Late intrinsicoid deflection in V1 (0.035+)
- Incomplete RBBB pattern
- ST T strain pattern in 2,3,aVF
- P pulmonale or P congenitale
- S1 S2 S3 pattern in children
Differential Diagnosis of R>S in V1
- RVH
- Posterior MI
- WPW
- HCM (septal hypertrophy)
- Kulbertus' block (septal fascicular block)
- Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
- Normal variant
- V4r may be a more useful and reliable than lead V1 in that it often reveals an r>s while v1 remains normal
- An incomplete right bundle branch block in the right precordial chest leads may signal the development of RVH
- In the limb leads right axis deviation develops and at times prominent Q waves simulating an IMI appear in leads 2,3, and aVF.
- In children an S1 S2 S3 pattern (i.e. an S wave deeper than R in all 3 standard leads) is a reliable index of RVH
- RV strain can be seen in leads V1 and V2 but also in leads 2,3, aVF
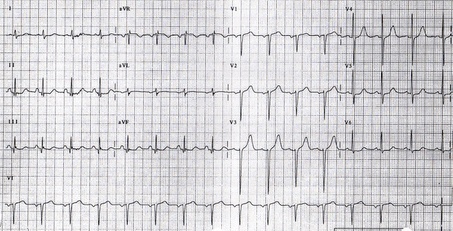
EKG in Right Ventricular Hypertrophy
Shown below are images illustrating right ventricular hypertrophy and its EKG findings.
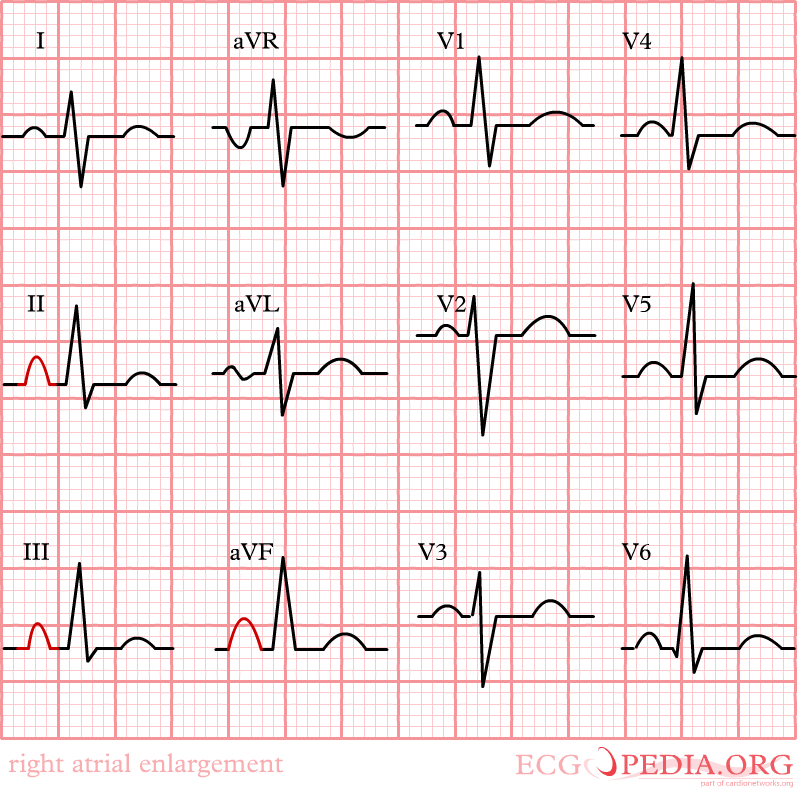
EKG in Right Atrial Enlargement
Right atrial enlargement is defined as either:
Shown below are images illustrating right atrial enlargement and its EKG findings.