Fexinidazole
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Tejasvi Aryaputra
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Fexinidazole is a nitroimidazole antimicrobial that is FDA approved for the treatment of human African trypanosomiasis caused by the parasite Trypanosoma brucei gambiense. Common adverse reactions include hypocalcemia, upper abdominal pain, insomnia, dyspepsia, decreased appetite, hyperkalemia, back pain, nausea, dizziness, asthenia, tremor, and headache..
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
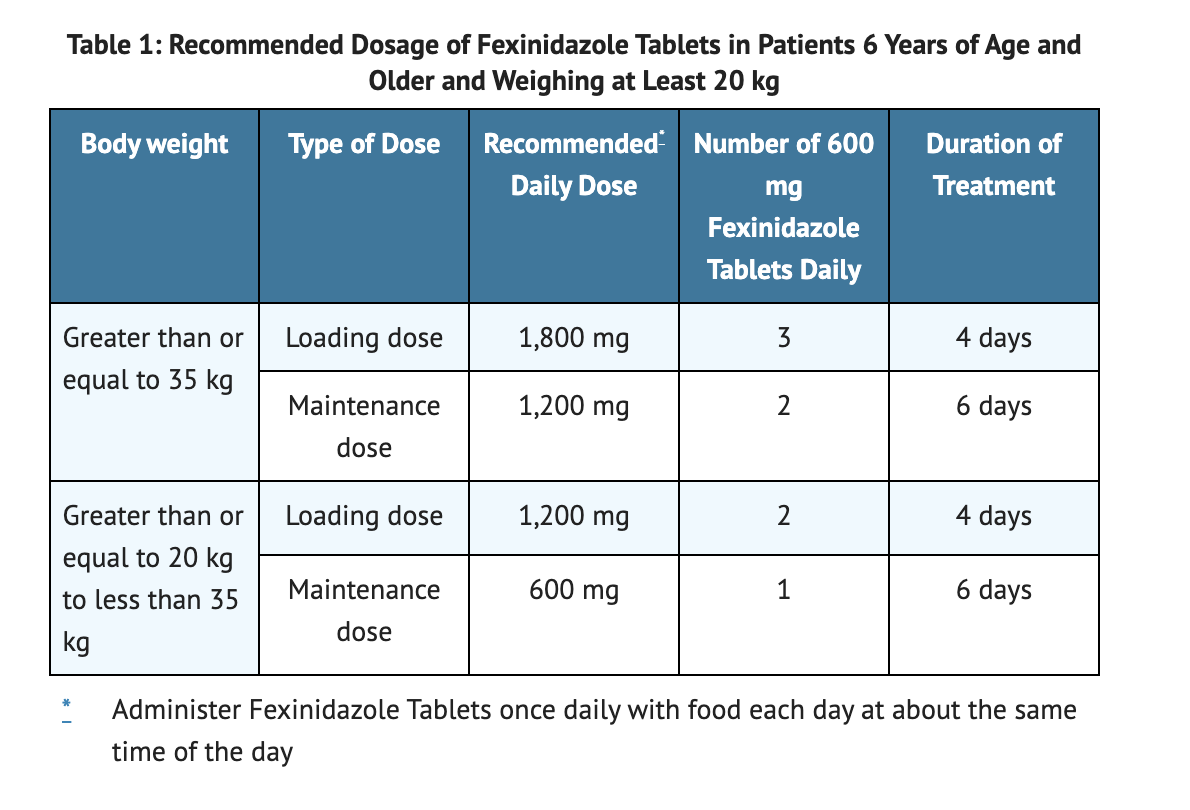
- Administer Fexinidazole dosage once daily for a total of 10 days.
- Administer Fexinidazole dosage with food at around the same time each day.
Table 1 summarizes Recommended Dosage of Fexinidazole Tablets in Patients 6 Years of Age and Older and Weighing at Least 20 kg.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Fexinidazole in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Fexinidazole in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
There is limited information regarding Fexinidazole FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric) in the drug label.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Fexinidazole in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Fexinidazole in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- Patients with known hypersensitivity to any nitroimidazole-class drugs or Fexinidazole Tablets.
- Patients with hepatic impairment.
- Patients with Cockayne syndrome.
Warnings
Decreased Efficacy in Severe Human African Trypanosomiasis Caused by Trypanosoma brucei gambiense
- In a clinical study, patients treated with Fexinidazole Tablets observed a decreased efficacy in comparison to patients treated with nifurtimox-eflornithine combination therapy.
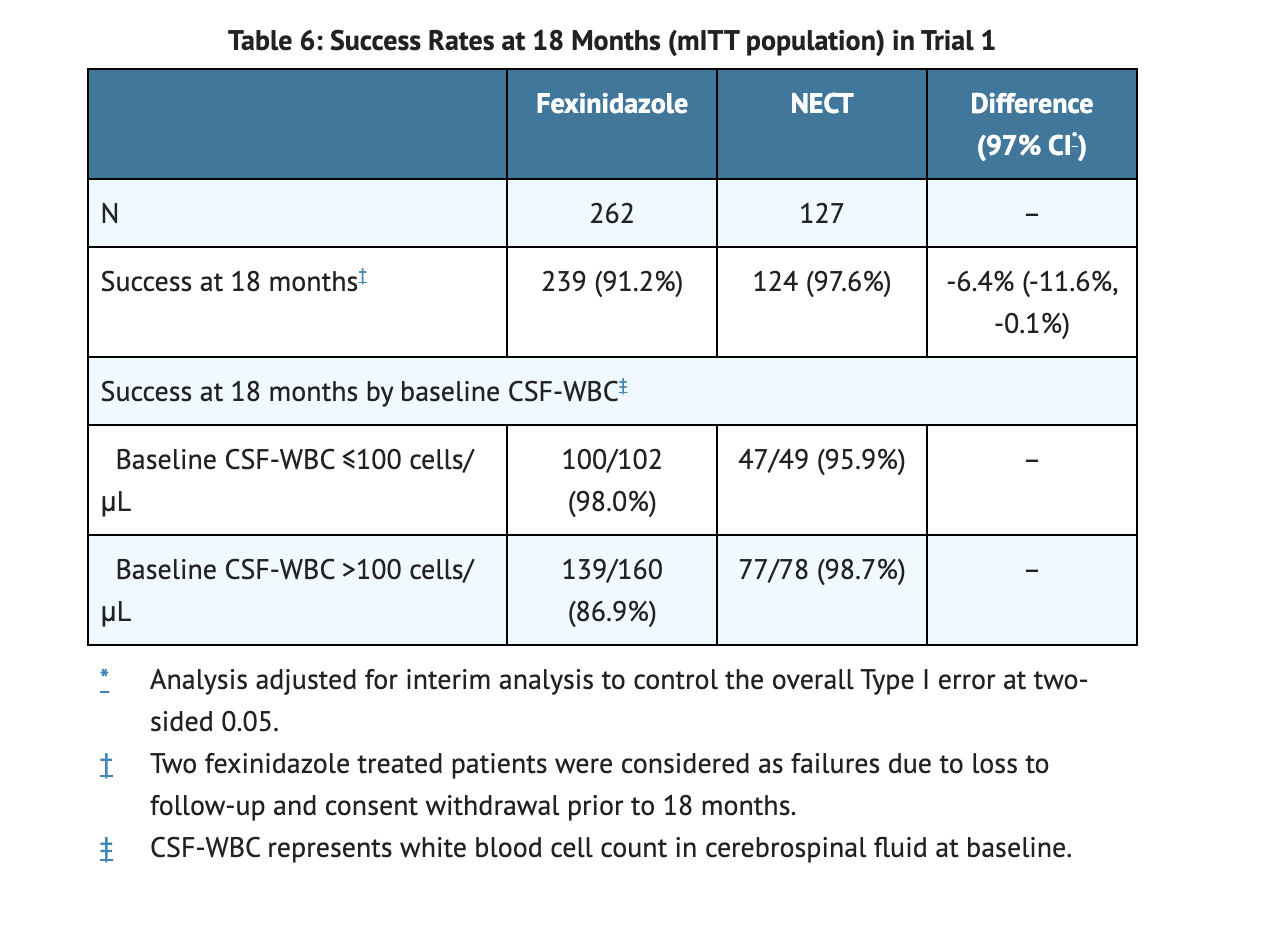
- 86.9% with Fexinidazole Tablets is the 18-month success rate for patients with severe second stage disease.
- 98.7% with NECT is the 18-month success rate for patients with severe second stage disease.
- Use of Fexinidazole Tablets are recommended for treatment in patients with severe second stage HAT due to T. brucei gambiense disease.
QT Interval Prolongation
- QT interval is prolonged in Fexinidazole Tablets in a concentration-dependent manner.
- 19 msec increase was seen in the QTcF interval due to the Fexinidazole Tablets.
- Advise patients with QTcF interval greater than 470 msec to avoid Fexinidazole treatment.
- Advise patients with a history of torsade de pointes, congenital long QT syndrome, cardiac arrhythmias, uncompensated heart failure, or family history of sudden death to avoid Fexinidazole treatment.
- Advise patients with uncorrected hypokalemia to avoid Fexinidazole treatment.
- Advise patients to avoid concomitant administration of inducers of hepatic CYP450 and Fexinidazole.
- Advise patients to avoid concomitant administration with drugs that block cardiac potassium channels, prolong the QT interval, or those that induce bradycardia with Fexinidazole.
Neuropsychiatric Adverse Reactions
- In clinical studies, a higher percentage of psychiatric-related adverse reactions and Central Nervous System adverse reactions were reported in patients part of the group receiving Fexinidazole than those receiving nifurtimox eflornithine combination therapy.
- Headaches, insomnia, and tremor were more reported in patients part of the group receiving Fexinidazole than those receiving nifurtimox eflornithine combination therapy.
- Some patients reported suicidal ideation when treated with Fexinidazole.
- Advise patients who are about to start Fexinidazole treatment about potential neuropsychiatric adverse reactions.
- Alternative therapy or extreme monitoring of patient may needed if patient currently have or a history of psychiatric disorders.
Neutropenia
- Patients have reported experiencing neutropenia when treated with Fexinidazole.
- Patients with a baseline absolute neutrophil count of less than 5,000 cells/mm3 experienced adverse reactions in Trial 1 studies.
- Advise patients to avoid concomitant administration with drugs that may cause neutropenia with Fexinidazole.
- Monitor patients leukocyte count periodically when they are taking Fexinidazole.
- Advise patients to seek proper treatment if they experience fever or other symptoms or signs of infection.
Potential for Hepatotoxicity
- Less than 2% of patients receiving Fexinidazole experienced elevations in liver transaminases.
- Monitor lab results of the liver in patients both baseline and during Fexinidazole treatment.
- Monitor patients for abnormal liver-related laboratory tests during Fexinidazole treatment.
Risk of Disulfiram-like Reaction Due to Concomitant Use with Alcohol
- Disulfiram-like reactions may occur in patients who consume alcohol.
- Advise patients to avoid during and 48 hours after completing Fexinidazole treatment the consumption of alcohol.
Risk of Psychotic Reactions Due to Concomitant Use with Disulfiram
- Advise patients that the concomitant administration of nitroimidazole or disulfiram drugs with Fexinidazole may cause psychotic reactions.
- If patients have taken disulfiram during the last two weeks, avoid administration of Fexinidazole.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
Clinical Trials Experience
- Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions and durations of follow up, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
- Trial 1 looked at 394 patients with second stage, meningoencephalitic HAT to understand the safety of Fexinidazole in comparison to nifurtimox-eflornithine combination therapy.
- 264 patients in Trial 1 were part of the group receiving Fexinidazole while the other 130 patients were part of nifurtimox-eflornithine combination therapy.
- Trial 2 looked into the safety of Fexinidazole for 230 patients with stage 1 hemolymphatic and early stage 2 HAT.
- Trial 3 looked into the safety of Fexinidazole for pediatric patients that had any stage of HAT with an age older than 6 years of age.
- The patient population tended to be more males than females in Trial 1 and 3 while it was equally distributed in Trial 2.
- 16.1 to 19.3 kg/m2 is the mean BMI in all trials being conducted.
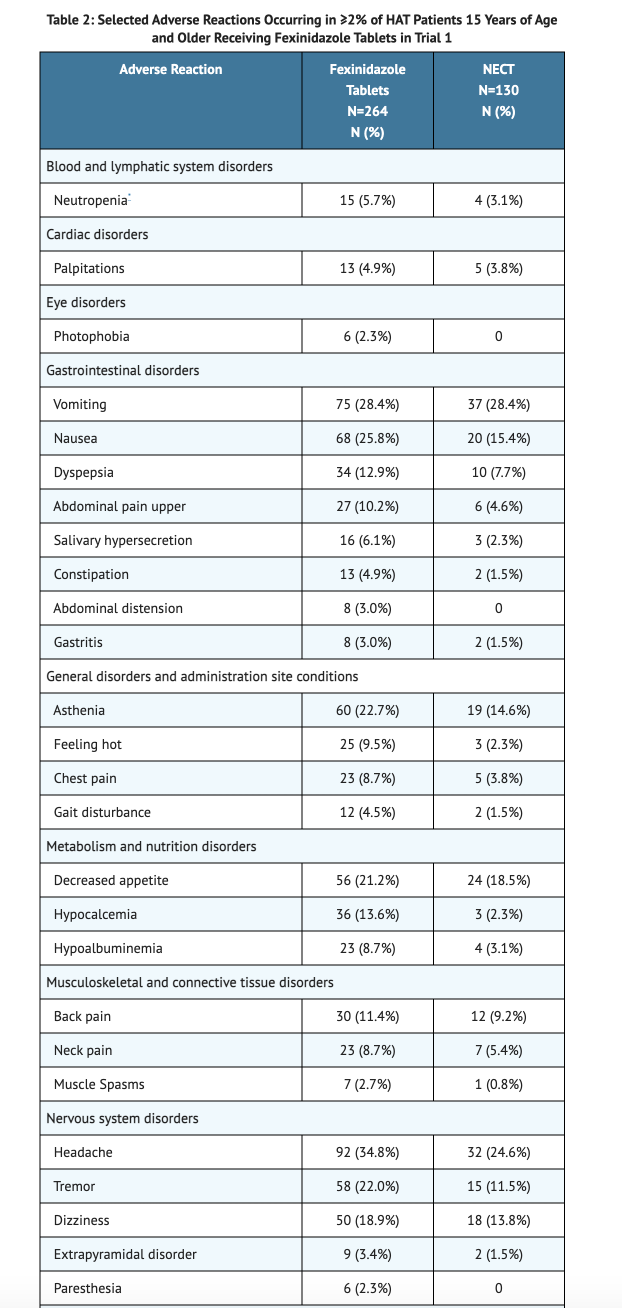
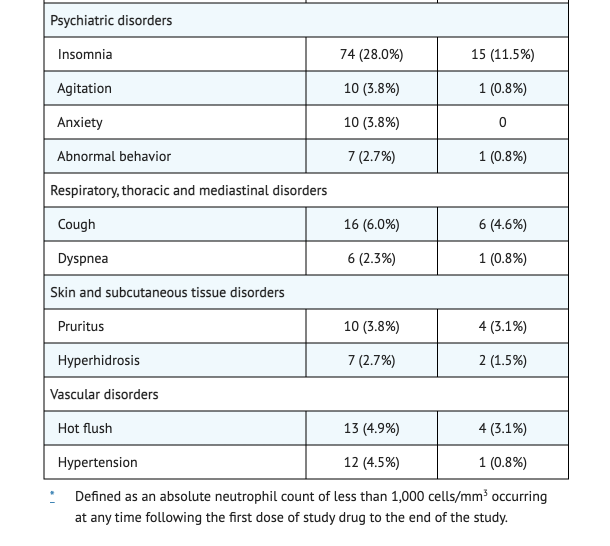
- Dizziness, hypocalcemia, dyspepsia, back pain, insomnia, nausea, asthenia, tremor, decreased appetite, hyperkalemia, upper abdominal pain, vomiting, and headaches were the most common adverse reactions reported in Trial 1 studies.
- Elevated liver transaminases and pychiatric disorders were reported in less 2% of patients for Trial 1 studies.
- Vomiting occurred more in pediatric patients taking Fexinidazole than adult patients taking Fexinidazole.
Table 2 shows the Selected Adverse Reactions Occurring in ≥2% of HAT Patients 15 Years of Age and Older Receiving Fexinidazole Tablets in Trial 1.
Postmarketing Experience
- Patients with Cockayne syndrome experienced acute liver failure and severe irreversible hepatotoxicity after use of metronidazole.
Drug Interactions
Pharmacodynamic Interactions
- Herbal medicines/supplements with Fexinidazole has the potential for pharmacodynamic interactions and/or toxicities.
- Advise patients to avoid concomitant administration with herbal medicines/supplements with Fexinidazole.
- Avoid co-administration of block potassium channels and Fexinidazole as it prolongs the QT interval.
Pharmacokinetic Drug Interactions
Table 3 shows Effect of Fexinidazole on other Drugs.
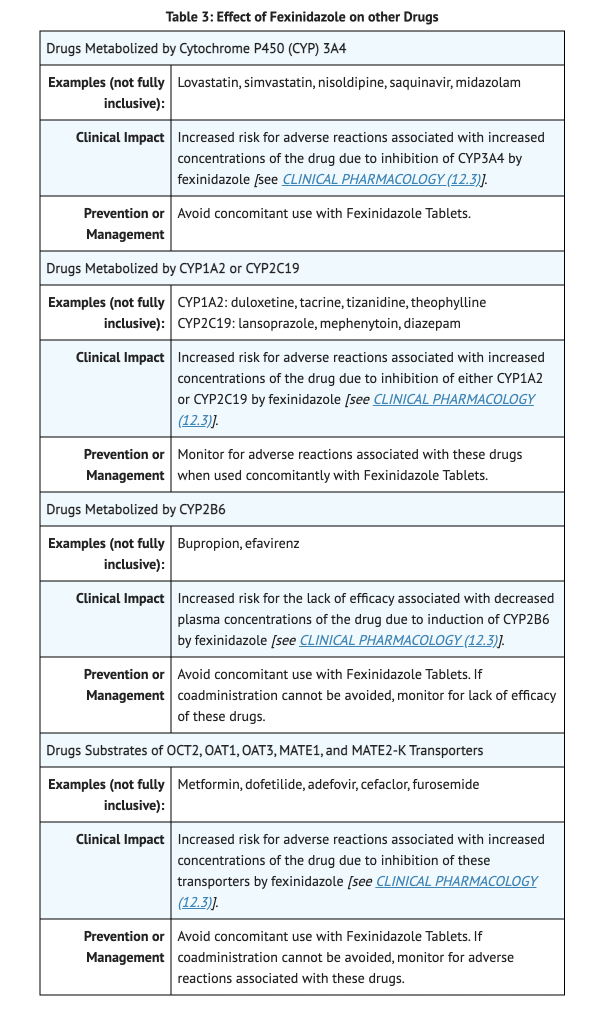
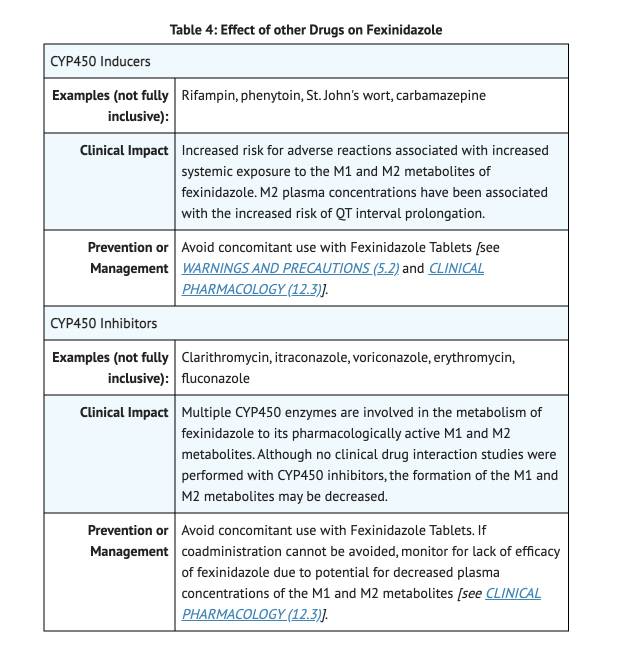
Table 4 shows Effect of other Drugs on Fexinidazole.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category (FDA):
During pregnancy, both the mother and fetus are at risk with untreated HAT due to T. brucei gambiense. Insufficient data has been conducted looking into the risk of major birth defects or miscarriage of pregnant women. Animal studies done on pregnant rats given oral Fexinidazole showed no effects on prenatal development. Lower body weights were observed in first generation offspring when pregnant rats were given oral Fexinidazole. Advise pregnant women with HAT due to T. brucei gambiense, to be treated which can prevent vertical transmission.
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Fexinidazole in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Fexinidazole during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
No data is present on the effects done on the breastfed child and the effects on milk production when treated with Fexinidazole. Animal studies done on nursing rats show that rat milk contains Fexinidazole. Advise patients about potential adverse reactions associated with Fexinidazole on the breastfed child.
Pediatric Use
Studies done on pediatric patients aged 6 years and older have tested the safety and effectiveness of Fexinidazole. Pediatric patients were more likely to experience vomiting. When comparing pediatric patients and adults, the safety profile of Fexinidazole was similar in both.
Geriatic Use
There is not enough elderly patients to look into the safety and effectiveness of Fexinidazole when comparing young and elderly patients.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Fexinidazole with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Fexinidazole with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
Patients with mild to moderate renal impairment do not need to adjust dosage of Fexinidazole. Advise patients to avoid use of Fexinidazole if they have severe renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
The pharmacokinetics of Fexinidazole is unknown in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Fexinidazole in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Fexinidazole in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Advise patients to eat food when taking Fexinidazole.
- Advise patients to avoid alcoholic beverages during and 48 hours after completing Fexinidazole treatment.
- Advise patients do not re-dose on Fexinidazole tablets if they vomit for the first time.
Monitoring
- Monitor patients signs and symptoms during Fexinidazole treatment.
- If a dosage is missed on a day, advise patients to continue normal Fexinidazole dosing next day.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding the compatibility of Fexinidazole and IV administrations.
Overdosage
- In clinical studies, males given up to 3,600 mg of Fexinidazole daily for 14 days experienced adverse reactions such as vomiting, increased transaminases, and panic attack.
- Vomiting, decreased calcium levels, and increased potassium levels are symptoms of overdosage.
Pharmacology
| |
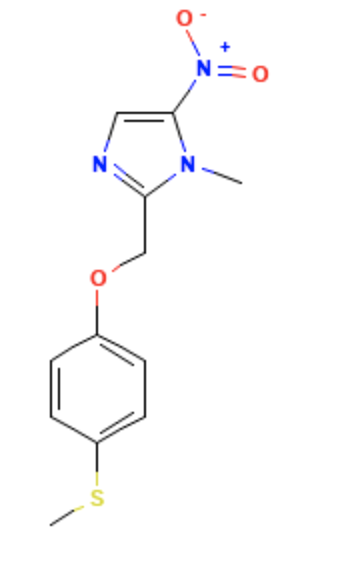
Fexinidazole
| |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| 1-Methyl-2-{[4-(methylsulfanyl)phenoxy] | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | |
| ATC code | P01 |
| PubChem | |
| DrugBank | |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | Template:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox |
| Mol. mass | ? |
| Synonyms | Template:Ubl |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ? |
| Metabolism | ? |
| Half life | ? |
| Excretion | ? |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. |
? |
| Legal status |
[[Prescription drug|Template:Unicode-only]](US) |
| Routes | By mouth |
Mechanism of Action
- Fexinidazole is an antiprotozoal drug.
Structure
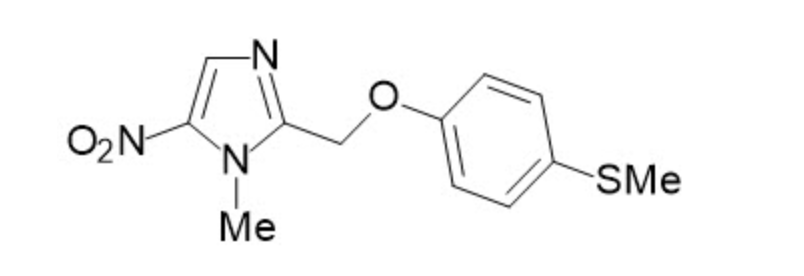
- Fexinidazole is a nitroimidazole antimicrobial drug. It has an empirical formula of C12H13N3O3S and a molecular weight of 279.3 g/mol.
Pharmacodynamics
Cardiac Electrophysiology
- 19.0 msec is the mean increase in QTcF for the recommended dosage of Fexinidazole.
- M2 metabolite is the potential reason for the increase in QTcF.
Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics
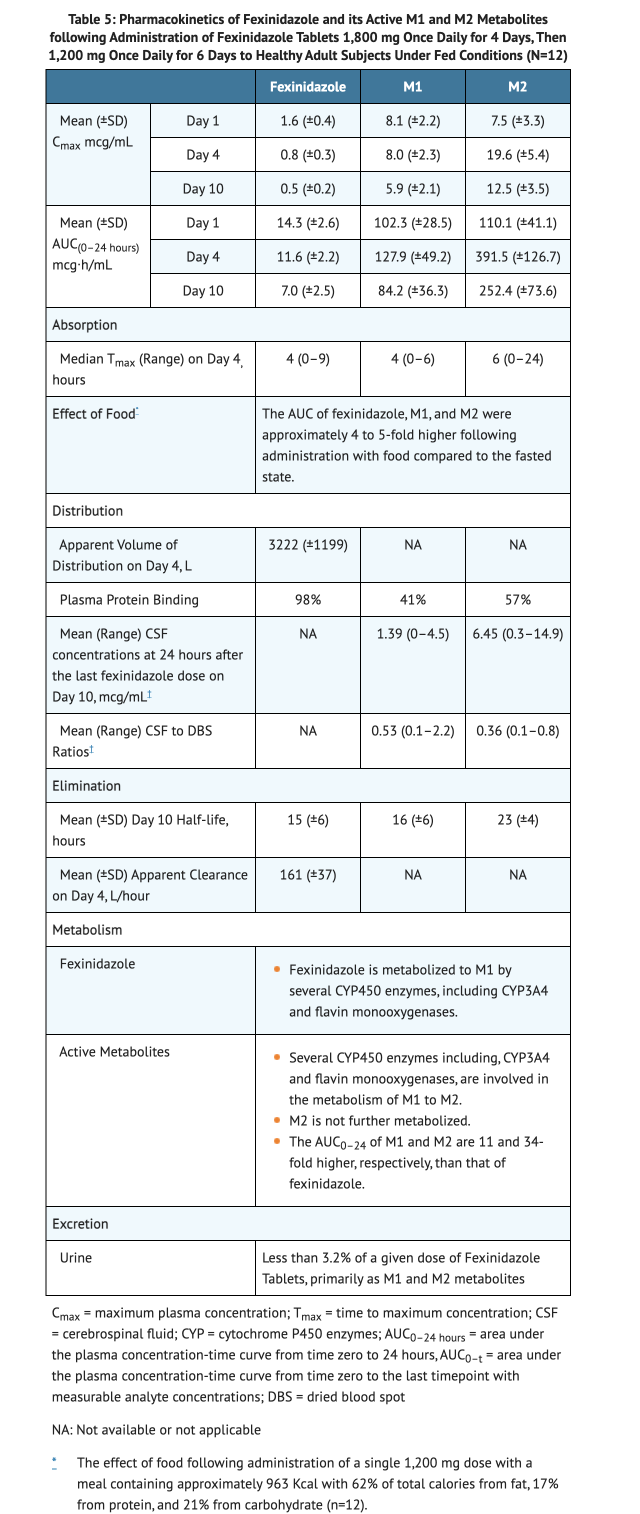
Table 5 summarizes the Pharmacokinetics of Fexinidazole and its two pharmacologically active M1 and M2 metabolites.
Specific Populations
Elderly patients:
- Pharmacokinetic studies have not been done patients older than 65 years of age.
- No significant covariate affecting the PK of fexinidazole was due to age.
Pediatric patients:
- Similar systemic exposures of plasma AUC values was seen in both adult and pediatric patients.
Hepatic impairment:
- Studies on patients with hepatic impairment have not been conducted that look at the pharmacokinetics.
Renal Impairment:
- Clinical studies show similar AUC0–24 for Fexinidazole and its metabolites between patients without renal impairment and patients with mild or moderate renal impairment.
Race/ethnicity:
- When looking at race and ethnicity, no studies have been conducted to make any conclusions on its effects of the pharmacokinetics of Fexinidazole.
Drug Interaction Studies
In vitro studies:
- CYP2B6, CYP3A4/5, CYP2C19, CYP1A2, and CYP2D6 are potentially inhibited by Fexinidazole.
- CYP2C19 is potentially inhibited by M1.
- CYPs are not inhibited by M2.
- CYP3A4 is not induced by Fexinidazole, M1, or M2.
- CYP2B6 and CYP1A2 are potentially induced by Fexinidazole and M1.
- OCT2, OAT1, OAT3, MATE2-K, OATP1B1, MATE1, and OATP1B3 are inhibited by Fexinidazole.
- MATE1, OAT3, and MATE2-K are inhibited by M1.
- OAT1, OAT3, MATE2-K, OCT2, and MATE1 are inhibited M2.
- P-gp or BCRP is not inhibited by Fexinidazole, M1, or M2.
Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenicity
- When looking into Fexinidazole, no carcinogenicity study was conducted.
Mutagenesis
- In the Ames test, Fexinidazole and the M2 metabolite were mutagenic.
- In the rat liver unscheduled DNA synthesis assay, in the in vitro micronucleus test, and in the vivo mouse micronucleus assay, Fexinidazole was negative.
Impairment of Fertility
- In animal studies, there is no effect on fertility parameters and no evidence of impairment of reproductive performance in rats given Fexinidazole.
Clinical Studies
Trial 1
- A randomized, comparative open-label trial that looked into the safety and effectiveness of Fexinidazole.
- Trial included 394 patients with late second-stage HAT due to T. brucei gambiense.
- Patients in the trial either received Fexinidazole Tablets (264) or Nifurtimox-eflornithine combination therapy (130).
- Patient population of the trial had a mean age of 35 years of age and mostly consisted of men (61%).
- The trial looked at success rate of patients in each group.
- Success is defined as a patient that is alive with no evidence of trypanosomes in any body fluid and CSF WBC ≤20 cells/µL. Another definition of success was patients had no parasites in the blood or lymph and a satisfactory clinical condition without clinical signs or symptoms.
Table 6 summarizes the success rate in Trial 1 at 18 months.
Trial 2 and Trial 3
- Trial 2 was a single-arm trial in adult patients with in early stage HAT due to T. brucei gambiense that looked into the efficacy of Fexinidazole.
- 98.7% is the success rate of Fexinidazole treatment in Trial 2 patients.
- Trial 3 was a single-arm trial in pediatric patients with in early stage HAT due to T. brucei gambiense that looked into the efficacy of Fexinidazole.
- 97.6% is the success rate of Fexinidazole treatment in Trial 3 patients.
How Supplied
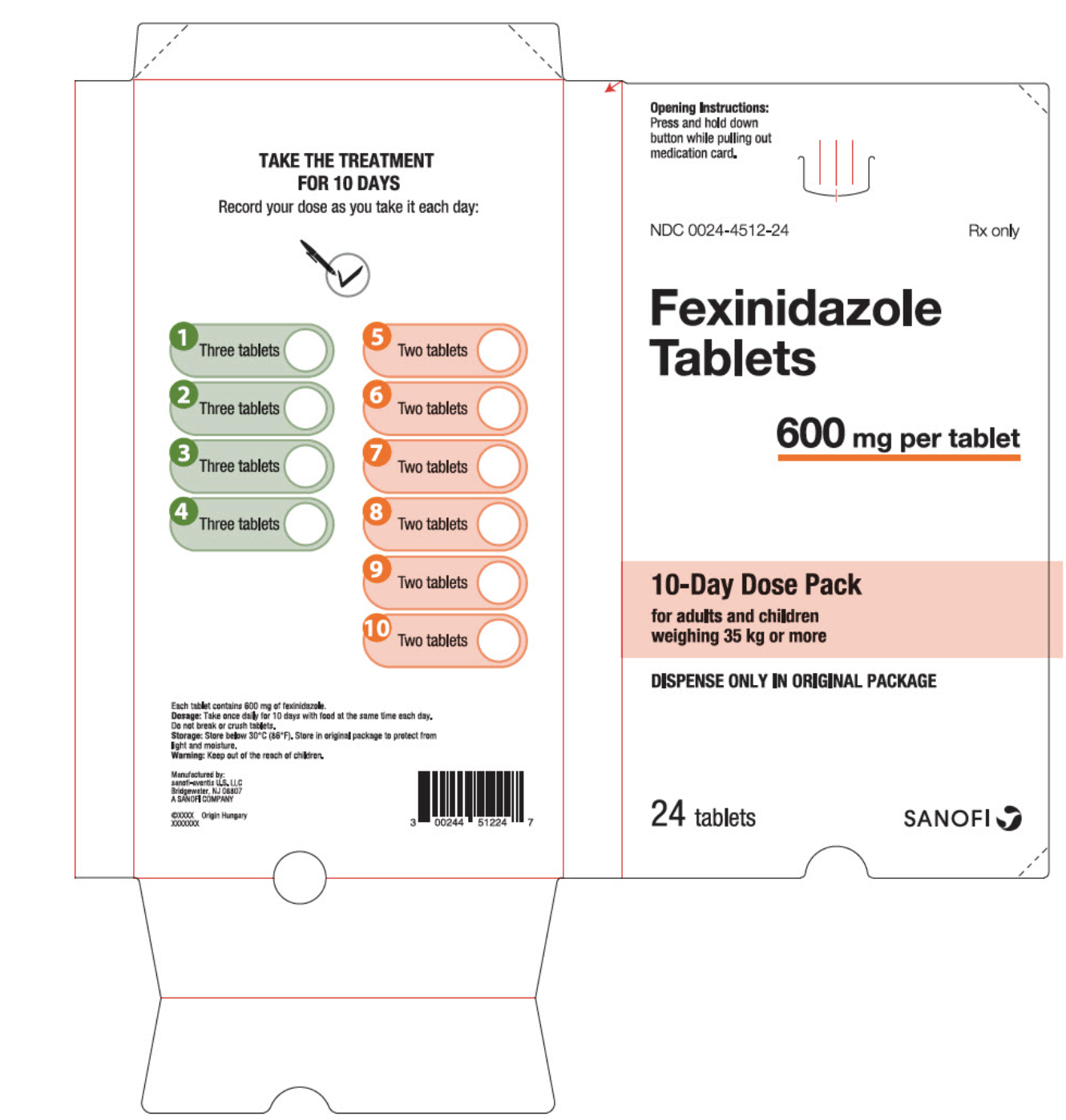
- 600 mg yellow/pale tablets as either a 14 pack for pediatric patients older than 6 years weighing 20 kg to less than 35 kg.
- 600 mg yellow/pale tablets as either a 24 pack for adult and pediatric patients weighing 35 kg or more.
Storage
- Store below 30°C.
- To protect against moisture or light, store Fexinidazole tablets in original packaging.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Fexinidazole |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Fexinidazole |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
Administration with Food
- Advise patients that Fexinidazole should be taken at the same time each day with a meal.
Alcohol Consumption
- Advise patients during and 48 hours after Fexinidazole treatment to refrain from alcohol consumption.
Vomiting
- Advise patients if vomiting occurs to not take an additional dosage, but to take the next scheduled dosage.
- Advise patients to seek medical counseling if vomiting occurs more than once.
Missed Doses
- Advise patients to resume dosage the next day if a scheduled dosage is missed.
Neuropsychiatric Adverse Reactions
- Advise patients when taking Fexinidazole about the neuropsychiatric adverse reactions that may occur.
- Headache, mood changes, insomnia, suicidal ideation, psychiatric disorders, and tremors are some of the neuropsychiatric adverse reactions when taking Fexinidazole that may occur.
- Advise patients to seek medical consultation if they experience neuropsychiatric adverse reactions.
Dizziness
- Advise patients to avoid driving if experiencing dizziness or tiredness.
- Advise patients that side effects of taking Fexinidazole include asthenia, dizziness, somnolence, and fatigue.
Drug Interactions
- Advise patients who are taking other medications to consult with their medical provider.
Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-Fexinidazole interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- Fexinidazole
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Fexinidazole Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.