Celiac artery
|
WikiDoc Resources for Celiac artery |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Celiac artery Most cited articles on Celiac artery |
|
Media |
|
Powerpoint slides on Celiac artery |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Celiac artery at Clinical Trials.gov Trial results on Celiac artery Clinical Trials on Celiac artery at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Celiac artery NICE Guidance on Celiac artery
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Celiac artery Discussion groups on Celiac artery Patient Handouts on Celiac artery Directions to Hospitals Treating Celiac artery Risk calculators and risk factors for Celiac artery
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Celiac artery |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
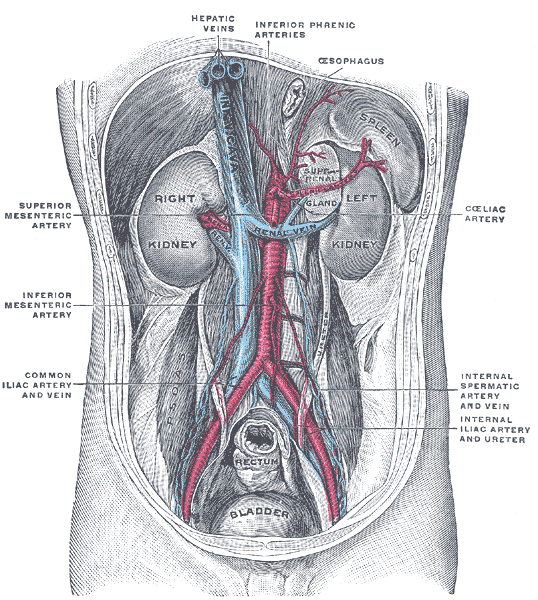
The celiac artery, also known as the celiac trunk and also spelled as coeliac, is the first major branch of the abdominal aorta and branches from the aorta around the level of the T12 vertebra in humans. It is one of three anterior/ midline branches of the abdominal aorta (the others are the superior and inferior mesenteric arteries).
Region supplied
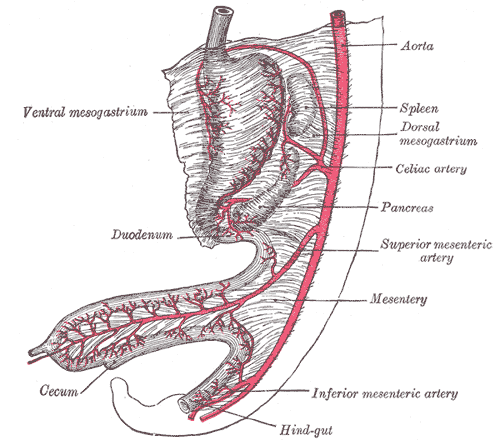
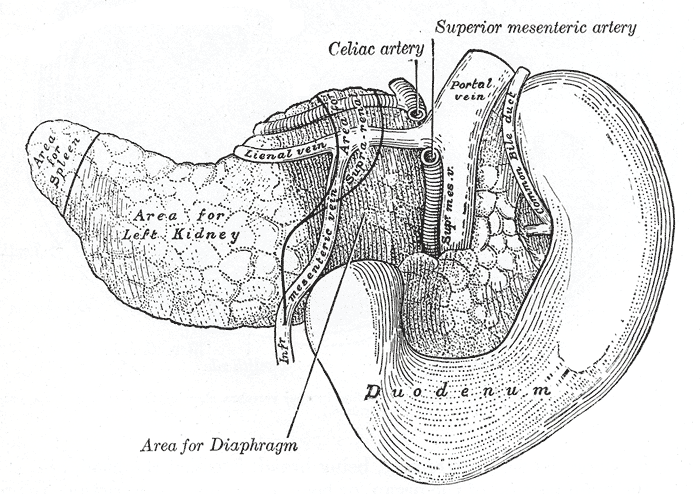
The celiac artery supplies oxygenated blood to the liver, stomach, abdominal oesophagus, spleen and the superior half of both the duodenum and the pancreas. These structures correspond to the embryonic foregut. (Similarly, the superior mesenteric artery and inferior mesenteric artery feed structures arising from the embryonic midgut and hindgut respectively. Note that these three anterior branches of the abdominal aorta are distinct and cannot substitute for one another, although there are limited connections between their terminal branches.)
The celiac artery is an essential source of blood, since the interconnections with the other major arteries of the gut are not sufficient to sustain adequate perfusion. Thus it cannot be safely ligated in a living person, and obstruction of the celiac artery will lead to necrosis of the structures it supplies.
Branches
There are three main divisions of the celiac artery, and each in turn has its own named branches.
| Artery | Branches |
| left gastric artery | esophageal branch, hepatic branch |
| common hepatic artery | proper hepatic artery,right gastric artery, gastroduodenal artery |
| splenic artery | dorsal pancreatic artery, short gastric arteries, left gastro-omental artery |
The celiac artery may also give rise to the inferior phrenic arteries.
Drainage
The celiac artery is the only major artery that nourishes the abdominal digestive organs that does not have a similarly-named vein.
Most blood returning from the digestive organs (including from the area of distribution of the celiac artery) is diverted to the liver via the portal venous system for further processing and detoxification in the liver before returning to the systemic circulation via the hepatic veins.
In contrast to the drainage of midgut and hindgut structures by the superior mesenteric vein and inferior mesenteric vein respectively, venous return from the celiac artery is through either the splenic vein emptying into the hepatic portal vein or via smaller tributaries of the portal venous system.
Notably, the splenic vein carries bilirubin (the waste product of hemoglobin metabolism) to the liver for excretion via the bile duct.
Additional images
-
Abdominal part of digestive tube and its attachment to the primitive or common mesentery. Human embryo of six weeks.
-
The pancreas and duodenum from behind.
-
Posterior abdominal wall, after removal of the peritoneum, showing kidneys, suprarenal capsules, and great vessels.
-
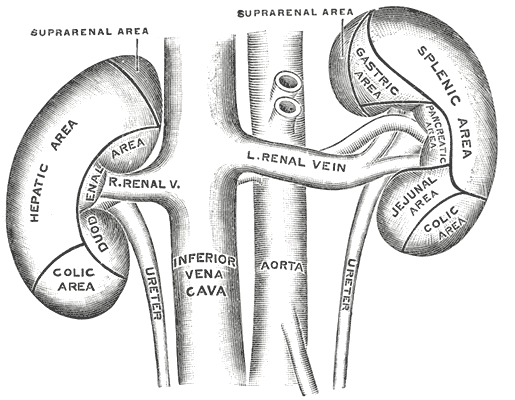
The anterior surfaces of the kidneys, showing the areas of contact of neighboring viscera.
-
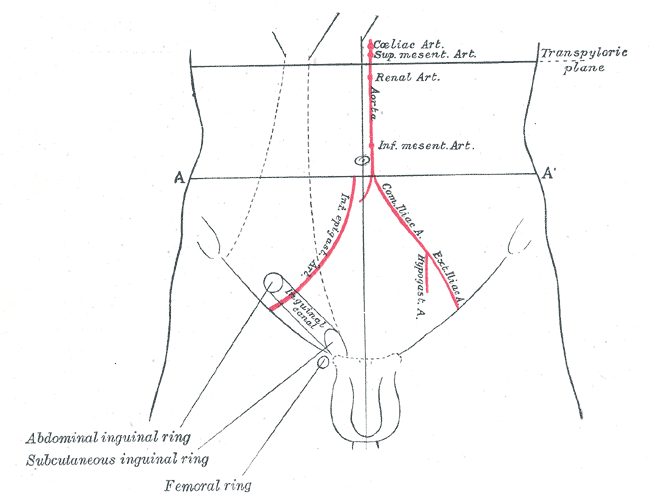
Front of abdomen, showing surface markings for arteries and inguinal canal.
External links
- Template:SUNYAnatomyFigs - "Branches of the celiac trunk."
- Template:SUNYAnatomyFigs - "Parietal and visceral branches of the abdominal aorta."
- Template:EMedicineDictionary
- Template:NormanAnatomy
- Template:LoyolaMedEd