Antihemophilic Factor (recombinant)
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Aparna Vuppala, M.B.B.S. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Antihemophilic Factor (recombinant) is an Antihemophilic Agent that is FDA approved for the prevention of of bleeding episodes in adults and children (0-16 years) with Hemophilia A, Perioperative management in adults and children (0-16 years) with Hemophilia A and indicated for routine prophylaxis to prevent or reduce the frequency of bleeding episodes in adults and children (0-16 years) with Hemophilia A. Common adverse reactions include arthralgia, headache, cough, nasopharyngitis, fever, anaphylaxis, and hypersensitivity reaction..
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Control and Prevention of Bleeding Episodes
- ADVATE [Antihemophilic Factor (Recombinant), Plasma/Albumin-Free Method] is an Antihemophilic Factor (Recombinant) indicated for control and prevention of bleeding episodes in adults and children (0-16 years) with Hemophilia A.
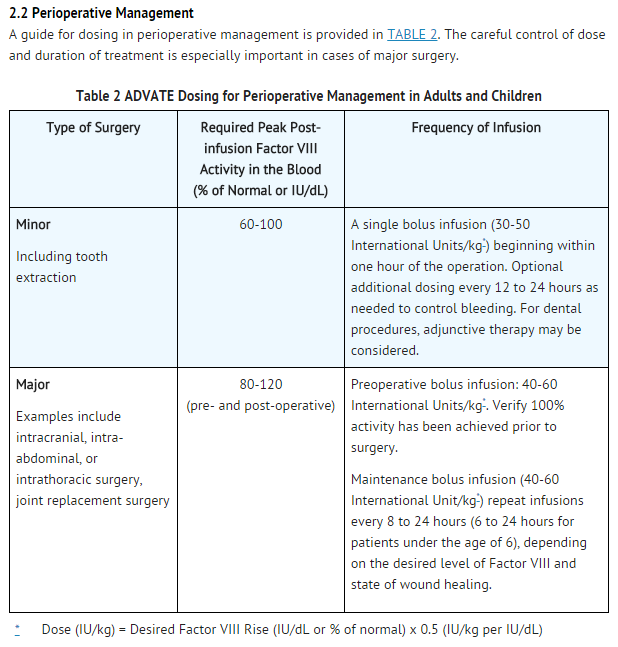
Perioperative Management
- ADVATE is indicated in the perioperative management in adults and children (0-16 years) with Hemophilia A.
Routine Prophylaxis
- ADVATE is indicated for routine prophylaxis to prevent or reduce the frequency of bleeding episodes in adults and children (0-16 years) with Hemophilia A.
- ADVATE is not indicated for the treatment of von Willebrand disease.
For Intravenous Use after Reconstitution Only
- Initiate treatment with ADVATE under the supervision of a physician experienced in the treatment of Hemophilia A.
- Each vial of ADVATE has the recombinant Factor VIII potency in International Units stated on the label. The expected in vivo peak increase in Factor VIII level expressed as IU/dL of plasma or percent normal can be estimated by multiplying the dose administered per kg body weight (IU/kg) by 2.
- The dosage and duration of treatment depend on the severity of Factor VIII deficiency, the location and extent of the bleeding, and the patient's clinical condition. Careful control of replacement therapy is especially important in cases of major surgery or life-threatening bleeding episodes.
The expected in vivo peak increase in Factor VIII level expressed as IU/dL (or % of normal) can be estimated using the following formulas:
- IU/dL (or % of normal) = [Total Dose (IU)/body weight (kg)] × 2 [IU/dL]/[IU/kg]
OR
- Dose (International Unit) = body weight (kg) × Desired Factor VIII Rise (IU/dL or % of normal) × 0.5 (IU/kg per IU/dL)
Examples (assuming patient's baseline Factor VIII level is < 1% of normal):
- A dose of 1750 IU ADVATE administered to a 70 kg patient should be expected to result in a peak post-infusion Factor VIII increase of 1750 IU × {[2 IU/dL]/[IU/kg]}/[70 kg] = 50 IU/dL (50% of normal).
- A peak level of 70% is required in a 40 kg child. In this situation, the appropriate dose would be 40 kg × 70 IU/dL/{[2 IU/dL]/[IU/kg]} = 1400 IU.
Base the dose and frequency on the individual clinical response. Patients may vary in their pharmacokinetic (e.g., half-life, in vivo recovery) and clinical responses to ADVATE. Although you can estimate the dose by the calculations above, whenever possible, perform appropriate laboratory tests including serial Factor VIII activity assays
Control and Prevention of Bleeding Episodes
- A guide for dosing in the treatment of bleeding episodes is provided in TABLE 1. The careful control of treatment dose is especially important in cases of life-threatening bleeding episodes.

Routine Prophylaxis
- For prevention of bleeding episodes, doses between 20 to 40 International Units of Factor VIII per kg body weight every other day (3 to 4 times weekly) may be utilized. Alternatively, an every third day dosing regimen targeted to maintain FVIII trough levels ≥ 1% may be employed. Adjust dose based on the patient’s clinical response.
Instruction for Use
- Administer ADVATE by intravenous (IV) injection after reconstitution. Ask patients to follow the specific preparation and administration procedures provided by their physicians.
- For instructions, ask patients to follow the recommendations in the FDA-approved patient labeling .
- Perform reconstitution, product administration, and handling of the administration set and needles with caution. Percutaneous puncture with a needle contaminated with blood can transmit infectious viruses including HIV (AIDS) and hepatitis. Obtain immediate medical attention if injury occurs. Place needles in a sharps container after single use. Discard all equipment, including any reconstituted ADVATE, in an appropriate container.
Preparation and Reconstitution
- The procedures below are provided as general guidelines for the preparation and reconstitution of ADVATE. Always work on a clean surface and wash your hands before performing the following procedures:
- Bring the ADVATE (dry factor concentrate) and Sterile Water for Injection, USP (diluent) to room temperature.
- Remove caps from the factor concentrate and diluent vials.
- Cleanse stoppers with germicidal solution and allow to dry prior to use. Place the vials on a flat surface.
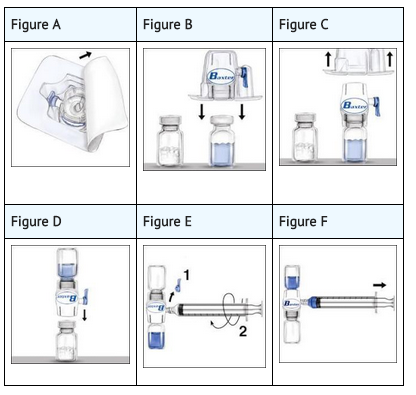
- Open the BAXJECT II device package by peeling away the lid, without touching the inside (Figure A).Do not remove the device from the package.
- Turn the package over. Press straight down to fully insert the clear plastic spike through the diluent vial stopper (Figure B).
- Grip the BAXJECT II package at its edge and pull the package off the device (Figure C). Do not remove the blue cap from the BAXJECT II device. Do not touch the exposed white plastic spike.
- Turn the system over so that the diluent vial is on top. Quickly insert the white plastic spike fully into the ADVATE vial stopper by pushing straight down (Figure D). The vacuum will draw the diluent into the ADVATE vial.
- Swirl gently until ADVATE is completely dissolved. Do not refrigerate after reconstitution.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Antihemophilic Factor (recombinant) in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Antihemophilic Factor (recombinant) in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
There is limited information regarding FDA-Labeled Use of Antihemophilic Factor (recombinant) in pediatric patients.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Antihemophilic Factor (recombinant) in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Antihemophilic Factor (recombinant) in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- Known anaphylaxis to mouse or hamster protein or other constituents of the product.
Warnings
Anaphylaxis and Hypersensitivity Reactions
- Allergic-type hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, are possible and have been reported with ADVATE. Symptoms have manifested as dizziness, paresthesias, rash, flushing, face swelling, urticaria, dypsnea, and pruritus.
- ADVATE contains trace amounts of mouse immunoglobulin G (MuIgG): maximum of 0.1 ng/IU ADVATE, and hamster proteins: maximum of 1.5 ng/IU ADVATE. Patients treated with this product may develop hypersensitivity to these non-human mammalian proteins.
- Discontinue ADVATE if hypersensitivity symptoms occur and administer appropriate emergency treatment.
Neutralizing Antibodies
- Carefully monitor patients treated with AHF products for the development of Factor VIII inhibitors by appropriate clinical observations and laboratory tests. Inhibitors have been reported following administration of ADVATE predominantly in previously untreated patients (PUPs) and previously minimally treated patients (MTPs). If expected plasma Factor VIII activity levels are not attained, or if bleeding is not controlled with an expected dose, perform an assay that measures Factor VIII inhibitor concentration.
Precautions
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
- The serious adverse drug reactions (ADRs) seen with ADVATE are hypersensitivity reactions and the development of high-titer inhibitors necessitating alternative treatments to Factor VIII.
- The most common ADRs observed in clinical trials (frequency ≥ 10% of subjects) were pyrexia, headache, cough, nasopharyngitis, vomiting, arthralgia, limb injury.
- Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
- ADVATE has been evaluated in five completed studies in previously treated patients (PTPs) and one ongoing study in previously untreated patients (PUPs) with severe to moderately severe Hemophilia A (Factor VIII ≤ 2% of normal). A total of 234 subjects have been treated with ADVATE as of March 2006. Total exposure to ADVATE was 44,926 infusions. The median duration of participation per subject was 370.5 (range: 1 to 1,256) days and the median number of exposure days to ADVATE per subject was 128.0 (range: 1 to 598).3
- The summary of adverse reactions (ADRs) with a frequency >5% (defined as adverse events occurring within 24 hours of infusion or any event causally related (ADR) occurring within study period) is shown in TABLE 3. No subject was withdrawn from a study due to an ADR. There were no deaths in any of the clinical studies.

Immunogenicity
- The development of Factor VIII inhibitors with the use of ADVATE was evaluated in clinical studies with pediatric PTPs (<6 years of age with >50 Factor VIII exposures) and PTPs (>10 years of age with >150 Factor VIII exposures). Of 198 subjects who were treated for at least 10 exposure days or on study for a minimum of 120 days, 1 adult developed a low-titer inhibitor (2.0 [BU] in the Bethesda assay) after 26 exposure days. Eight weeks later, the inhibitor was no longer detectable, and in vivorecovery was normal at 1 and 3 hours after infusion of another marketed recombinant Factor VIII concentrate. This single event results in a Factor VIII inhibitor frequency in PTPs of 0.51% (95% CI of 0.03 and 2.91% for the risk of any Factor VIII inhibitor development).3,4 No Factor VIII inhibitors were detected in the 53 treated pediatric PTPs.
- In clinical studies that enrolled previously untreated subjects (defined as having had up to 3 exposures to a Factor VIII product at the time of enrollment), 5 (20%) of 25 subjects who received ADVATE developed inhibitors to Factor VIII.3 Four patients developed high titer ( > 5 BU) and one patient developed low-titer inhibitors. Inhibitors were detected at a median of 11 exposure days (range 7 to 13 exposure days) to investigational product.
- Immunogenicity also was evaluated by measuring the development of antibodies to heterologous proteins. 182 treated subjects were assessed for anti-Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell protein antibodies. Of these patients, 3 showed an upward trend in antibody titer over time and 4 showed repeated but transient elevations of antibodies. 182 treated subjects were assessed for muIgG protein antibodies. Of these, 10 showed an upward trend in anti-muIgG antibody titer over time and 2 showed repeated but transient elevations of antibodies. Four subjects who demonstrated antibody elevations reported isolated events of urticaria, pruritus, rash, and slightly elevated eosinophil counts. All of these subjects had numerous repeat exposures to the study product without recurrence of the events and a causal relationship between the antibody findings and these clinical events has not been established.
- Of the 181 subjects who were treated and assessed for the presence of anti-human von Willebrand Factor (VWF) antibodies, none displayed laboratory evidence indicative of a positive serologic response.
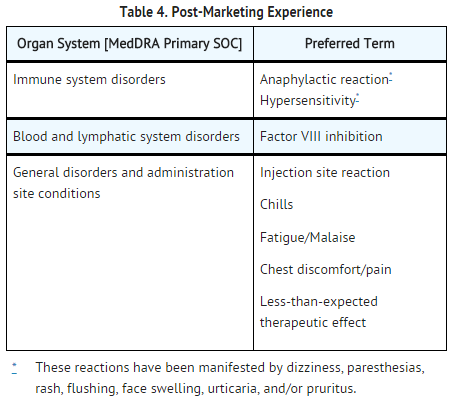
Postmarketing Experience
- The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of ADVATE. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Among patients treated with ADVATE, cases of serious allergic/hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis have been reported and Factor VIII inhibitor formation (observed predominantly in PUPs).TABLE 4 represents the most frequently reported post-marketing adverse reactions as MedDRA Preferred Terms.
Drug Interactions
- There are no known drug interactions reported with ADVATE. Drug interaction studies have not been performed.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Category C. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with ADVATE. It is not known whether ADVATE can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or whether it can affect reproductive capacity. Prescribe ADVATE only if clinically needed.
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Antihemophilic Factor (recombinant) in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
- There are no adequate and well-controlled human studies that have investigated the effects of ADVATE during labor and delivery. Prescribe ADVATE only if clinically needed.
Nursing Mothers
- It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when ADVATE is administered to a nursing woman. Prescribe ADVATE only if clinically needed.
Pediatric Use
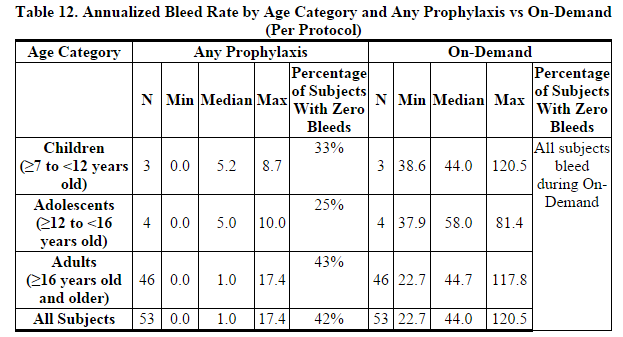
- In comparison to adults, children present with higher Factor VIII clearance (based on per kg body weight) values and thus lower half-life and recovery of Factor VIII. This may be explained by differences in body composition and should be taken into account when dosing or following Factor VIII levels in the pediatric population5 . Because clearance (based on per kg body weight) has been demonstrated to be higher in the pediatric population, larger or more frequent dosing based on per kg body weight may be needed in this population. In the ADVATE Routine Prophylaxis Clinical Study, 3 children aged 7 to <12 and 4 adolescents aged 12 to < 16 were included in the per-protocol analysis. The reductions in annualized bleeding rate per subject per year during any prophylaxis regimen as compared to during on-demand therapy were similar among children, adolescents, and adults.
Geriatic Use
- Clinical studies of ADVATE did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently compared to younger subjects. Individualize dose selection for geriatric patients.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Antihemophilic Factor (recombinant) with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Antihemophilic Factor (recombinant) with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Antihemophilic Factor (recombinant) in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Antihemophilic Factor (recombinant) in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Antihemophilic Factor (recombinant) in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Antihemophilic Factor (recombinant) in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- ADVATE is for intravenous use after reconstitution only.
- Inspect parenteral drug products for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. The solution should be clear and colorless in appearance. If not, do not use the solution and notify Baxter immediately.
- Administer ADVATE at room temperature within 3 hours of reconstitution.
- Use plastic syringes with this product because proteins in the product tend to stick to the surface of glass syringes.
- Use aseptic technique.
- Remove the blue cap from the BAXJECT II device. Connect the syringe to the BAXJECT II device (Figure E). Do not inject air.
- Turn the system upside down (factor concentrate vial now on top). Draw the factor concentrate into the syringe by pulling the plunger back slowly (Figure F).
- Disconnect the syringe; attach a suitable needle and inject intravenously as instructed under Administration by Bolus Infusion. If a patient is to receive more than one vial of ADVATE, the contents of multiple vials may be drawn into the same syringe. Please note that the BAXJECT II device is intended for use with a single vial of ADVATE and Sterile Water for Injection, USP, only; therefore, reconstituting and withdrawing a second vial into the syringe requires a second BAXJECT II device.
- Administer ADVATE over a period of ≤ 5 minutes (maximum infusion rate 10 mL/min). Determine the pulse rate before and during administration of ADVATE. Should a significant increase in pulse rate occur, reducing the rate of administration or temporarily halting the injection usually allows the symptoms to disappear promptly.
Monitoring
- The clinical response to ADVATE may vary. If bleeding is not controlled with the recommended dose, determine the plasma level of Factor VIII and administer a sufficient dose of ADVATE to achieve a satisfactory clinical response. If the patient’s plasma Factor VIII level fails to increase as expected or if bleeding is not controlled after the expected dose, suspect the presence of an inhibitor (neutralizing antibodies) and perform appropriate tests as follows:
- Monitor plasma Factor VIII activity levels by the one-stage clotting assay to confirm the adequate Factor VIII levels have been achieved and maintained when clinically indicated .
- Perform the Bethesda assay to determine if Factor VIII inhibitor is present. If expected Factor VIII activity plasma levels are not attained, or if bleeding is not controlled with the expected dose of ADVATE, use Bethesda Units (BU) to titer inhibitors.
- If the inhibitor titer is less than 10 BU per mL, the administration of additional Antihemophilic Factor concentrate may neutralize the inhibitor and may permit an appropriate hemostatic response.
- If the inhibitor titer is above 10 BU per mL adequate hemostasis may not be achieved. The inhibitor titer may rise following ADVATE infusion as a result of an anamnestic response to Factor VIII. The treatment or prevention of bleeding in such patients requires the use of alternative therapeutic approaches and agents.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Antihemophilic Factor (recombinant) in the drug label.
Overdosage
- No symptoms of overdose with ADVATE have been reported.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding Antihemophilic Factor (recombinant) Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
- ADVATE temporarily replaces the missing coagulation Factor VIII that is needed for effective hemostasis.
Structure
- ADVATE is a purified glycoprotein consisting of 2,332 amino acids that is synthesized by a genetically engineered CHO cell line. In culture, the CHO cell line expresses rAHF into the cell culture medium. The rAHF is purified from the culture medium using a series of chromatography columns. The purification process includes an immunoaffinity chromatography step in which a monoclonal antibody directed against Factor VIII is employed to selectively isolate the rAHF from the medium. The cell culture and purification processes used in the manufacture of ADVATE employ no additives of human or animal origin. The production process includes a dedicated, viral inactivation solvent-detergent treatment step. The rAHF synthesized by the CHO cells has the same biological effects on clotting as human Antihemophilic Factor (Human) [hAHF ]. Structurally the recombinant protein has a similar combination of heterogeneous heavy and light chains as found in AHF (Human).
- ADVATE is formulated as a sterile, non-pyrogenic, white to off-white powder for intravenous injection. When reconstituted with the provided Sterile Water for Injection, USP, the product contains the following stabilizers and excipients in targeted amounts:
- ADVATE is available in single-dose vials that contain nominally 250, 500, 1000, 1500, 2000, 3000 or 4000 International Units (IU) per vial. The product contains the following stabilizers and excipients: mannitol, trehalose, sodium chloride, histidine, Tris, calcium chloride, polysorbate-80, and glutathione. VWF is co-expressed with Factor VIII and helps to stabilize it in culture. The final product contains no more than 2 ng VWF/IU rAHF, which will not have any clinically relevant effect in patients with von Willebrand disease. The product contains no preservative.
- Each vial of ADVATE is labeled with the rAHF activity expressed in International Units per vial. Biological potency is determined by an in vitro assay, which employs a Factor VIII concentrate standard that is referenced to a WHO International Standard for Factor VIII concentrates. One international unit, as defined by the WHO standard for blood coagulation Factor VIII, human, is approximately equal to the level of Factor VIII activity found in 1 mL of fresh pooled human plasma. The specific activity of ADVATE is 4000 to 10000 International Units per milligram of protein.
Pharmacodynamics
- The activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) is prolonged in patients with hemophilia. Determination of aPTT is a conventional in vitro assay for biological activity of Factor VIII. Treatment with ADVATE normalizes the aPTT over the effective dosing period.
Pharmacokinetics
- A randomized, crossover pharmacokinetic study of ADVATE produced at Orth, Austria (test) and RECOMBINATE [Antihemophilic Factor (Recombinant)] (reference) was conducted in 56 non-bleeding subjects. The subjects received either of the products as an IV infusion (50 ± 5 IU/kg body weight) and there was a washout period of 72 hours to 4 weeks between the two infusions. The pharmacokinetic parameters were calculated from Factor VIII activity measurements in blood samples obtained up to 48 hours following each infusion.4 Pharmacokinetic parameters for adults for each study preparation in the per-protocol analysis are presented in TABLE 6.

- The 90% confidence intervals for the ratios of the mean AUC(0-48h) and in vivo recovery values for the test and control products were within the pre-established limits of 0.80 and 1.25. In addition, in vivorecoveries at the onset of treatment and after 75 exposure days were compared for 62 subjects. Results of this analysis indicated no significant change in the in vivo recovery at the onset of treatment and after ≥ 75 exposure days.
- See the description of the clinical study results for a discussion of the effect of long-term exposure on the pharmacokinetic properties of ADVATE .
- In an analysis of data from 58 unique subjects with 65 surgical procedures in the perioperative management study, the target Factor VIII level was met or exceeded in all cases following a single loading dose ranging from 29 to 104 IU/kg.
- Pharmacokinetic parameters calculated from interim pharmacokinetic data for 51 subjects ≤ 16 years of age (per-protocol analysis) are available for 0 neonates, 3 infants, 21 children, and 27 adolescents as shown in TABLE 7. The clearance of ADVATE in infants, children, older children, and adolescents was 26%, 23%, 42%, and 23% higher than adults (0.031 dL/hr/kg). The half-life of ADVATE in infants, children, older children, and adolescents was 27%, 15%, 10%, and 3% lower than adults (12.08 hours). The extent to which these differences may be clinically significant is not known.

- In a crossover pharmacokinetic study of rAHF-PFM reconstituted in 2 mL versus 5 mL Sterile Water for Injection, USP, (sWFI) in previously treated severe Hemophilia A adult and adolescent patients, the AUCs of the two formulations were comparable and the 90% confidence interval ranged from 90.4 to 102.6, indicating that the two formulations are pharmacokinetically equivalent.
Nonclinical Toxicology
- Single doses, severalfold higher than the recommended clinical dose (related to body weight), did not demonstrate any acute or toxic effect for ADVATE in laboratory animals (mouse, rat, rabbit, and dog). Multiple dose studies were not performed with ADVATE but were performed with the related product, RECOMBINATE, and with formulation buffers of ADVATE.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
- No studies have been conducted with the active ingredient in ADVATE to assess its mutagenic or carcinogenic potential. The CHO cell line employed in the production of ADVATE is derived from that used in the biosynthesis of RECOMBINATE [Antihemophilic Factor (Recombinant)]. ADVATE has been shown to be comparable to RECOMBINATE with respect to its biochemical and physicochemical properties, as well as its non-clinical in vivo pharmacology.
- RECOMBINATE was tested for mutagenicity at doses considerably exceeding plasma concentrations in vitro, and at doses up to ten times the expected maximal clinical dose in vivo. At that concentration, it did not cause reverse mutations, chromosomal aberrations, or an increase in micronuclei formation in bone marrow polychromatic erythrocytes. Studies in animals have not been performed to evaluate carcinogenic potential.
Clinical Studies
Original Safety and Efficacy Study
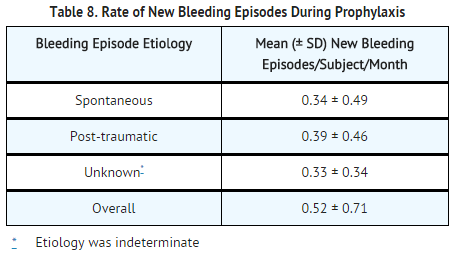
- The original safety and efficacy study evaluated the pharmacokinetics (double-blinded, randomized, cross-over), safety, immunogenicity, and hemostatic efficacy (open-label) of ADVATE in 111 subjects. The study was conducted with 103 Caucasian; 7 Black and 1 Asian US and European previously treated subjects (PTPs with ≥ 150 exposure days) diagnosed with moderate to severe hemophilia A (FVIII level ≤ 2% of normal), who were ≥ 10 years of age (20 were 10 to <13, 22 were 13 to <16, and 69 were 16 years and older). Subjects with a history of or a detectable FVIII inhibitor, portal vein hypertension (INR >1.4), presence of splenomegaly, spider angiomata, history of esophageal hemorrhage or documented esophageal varices, hypersensitivity to RECOMBINATE rAHF, or scheduled to receive immunomodulating drug were excluded. Subjects self-administered ADVATE for routine prophylaxis and for the treatment of bleeding episodes. A global assessment of efficacy was rendered by the subject (for home treatment) or study site investigator (for treatment under medical supervision) using an ordinal scale of excellent, good, fair, or none, based on the quality of hemostasis achieved with ADVATE produced in the Orth facility for the treatment of each new bleeding episode. A total of 510 bleeding episodes were reported, with a mean (± SD) of 6.1 ± 8.2 bleeding episodes per subject. Of these 510 episodes, 439 (86%) were rated excellent or good in their response to treatment with ADVATE, 61 (12%) were rated fair, 1 (0.2%) was rated as having no response, and for 9 (2%), the response to treatment was unknown. A total of 411 (81%) bleeding episodes were managed with a single infusion, 62 (12%) required 2 infusions, 15 (3%) required 3 infusions, and 22 (4%) required 4 or more infusions of ADVATE for satisfactory resolution. A total of 162 (32%) bleeding episodes occurred spontaneously, 228 (45%) were the result of antecedent trauma, and for 120 (24%) bleeding episodes, the etiology was unknown.4
- The rate of new bleeding episodes during the protocol-mandated 75 exposure day prophylactic regimen (≥ 25 IU/kg body weight 3-4 times per week) was calculated as a function of the etiology of bleeding episodes for 107 evaluable subjects (n = 274 new bleeding episodes).4 These rates are presented in TABLE 8.
The pharmacokinetic properties of ADVATE were investigated at the beginning of treatment in a multicenter study of previously treated subjects and at the end of treatment in a subset of subjects (N=13) who had completed at least 75 exposure days of treatment with ADVATE. Post-infusion levels and clearance of Factor VIII during the perioperative period were examined in an interim analysis of subjects enrolled in an ongoing surgery study. The pharmacokinetics of ADVATE were investigated in an interim analysis of a study of pediatric previously treated subjects < 6 years of age .
Continuation Study
- Additional (open-label) safety and efficacy data were based on 82 subjects who continued with treatment following participation in the pivotal study. An interim analysis of efficacy from the continuation study was conducted for 27 subjects who self-administered ADVATE produced in Neuchâtel on a routine prophylactic regimen during a minimum period of 50 exposure days to ADVATE. New bleeding episodes were treated with ADVATE and the outcome of treatment was rated as excellent, good, fair, or none, based on the quality of hemostasis achieved. A total of 51 new bleeding episodes occurred in 13 of the 27 subjects being treated with ADVATE. By etiology, 53% of these bleeding events resulted from trauma and 27% occurred spontaneously; the other 20% had an undetermined etiology. The response to treatment with ADVATE for the majority (63%) of all new bleeding episodes was rated as excellent or good. 86% of the bleeding episodes resolved with only 1 infusion and an additional 6% were resolved by a second infusion.
- In vivo recoveries at the onset of treatment and after 75 exposure days were compared for 62 subjects. There were no significant differences between the in vivo recoveries at the onset of treatment and thein vivo recoveries after ≥ 75 exposure days.
Perioperative Management Study
- The study design, key inclusion and exclusion criteria, treatment, number of subjects and age range for the original perioperative management study can be found in TABLE 9.

- An interim analysis of the hemostatic efficacy of ADVATE during the perioperative management of subjects undergoing surgical procedures was conducted for 10 of 25 planned subjects. Ten subjects underwent 10 surgical procedures while receiving ADVATE. Eight subjects received the ADVATE by intermittent bolus infusion and 2 subjects received a combination of continuous and intermittent bolus infusion. Nine of the 10 subjects completed the study. Six of the surgical procedures were classified as major, and 4 were minor. Of the 6 major surgeries, 5 were for orthopedic complications of hemophilia. A brief description of each surgical procedure, along with study duration and study medication exposure, is presented in TABLE 10.

- For each of the 10 subjects, intra- and post-operative quality of hemostasis achieved with ADVATE was assessed by the operating surgeon and study site investigator, respectively, using an ordinal scale of excellent, good, fair, or none. The same rating scale was used to evaluate control of hemorrhage from a surgical drain placed at the incision site in one subject. The quality of hemostasis achieved with ADVATE was rated as excellent or good for all assessments.
Routine Prophylaxis Study
- In a multicenter, open-label, prospective, randomized, controlled postmarketing clinical study of the relative efficacy of ADVATE use in 2 prophylactic treatment regimens compared to that of on-demand treatment, 53 PTPs with severe to moderately severe Hemophilia A (FVIII level ≤2 IU/dL) were analyzed in the per-protocol group. Subjects were initially treated for 6 months of on-demand therapy and then randomized to 12 months of either a standard prophylaxis regimen (20-40 IU/kg every 48 hours) or PK-driven prophylaxis regimen (20-80 IU/kg every 72 hours). All subjects had a history of at least 8 joint hemorrhages per year upon entering the study. Each subject in the per protocol group was adherent to > 90% of the prescribed number of prophylactic infusions; no subject in the study surpassed the upper boundary of 110% of the prescribed number of prophylactic infusions.
- The median annual bleed rate during the on-demand therapy period was 44 bleeds per subject per year compared to 1 bleed per subject per year while on either prophylaxis regimen, which was a statistically significant difference (p<0.0001). 22 of 53 (42%) subjects experienced no bleeding episodes while on prophylaxis for one year. While there was no statistically significant difference in bleeding frequency observed between the two prophylaxis regimens studied, the study was not powered to demonstrate equivalence in bleeding rate between the two prophylaxis arms.
- The equation used to determine the weight-adjusted dose of the product used in the PK-driven prophylaxis arm, as calculated from the individual subject’s incremental recovery and half-life values to achieve a trough level of ≥ 1 IU/dL at the inter-dosing interval of 72 hours is defined as follows:
D i = (2) 72/t i / r i. (i is the subject)
D = target FVIII dose (IU/kg) that ensures that a trough level of ≥1 IU/dL is achieved after 72 hours
r = FVIII incremental recovery (IU/dL / IU/kg) as determined by the subject’s PK analysis
t = FVIII half-life (hrs) as determined by the subject’s PK analysis


How Supplied
- ADVATE is available in single-dose vials that contain the following nominal product strengths:
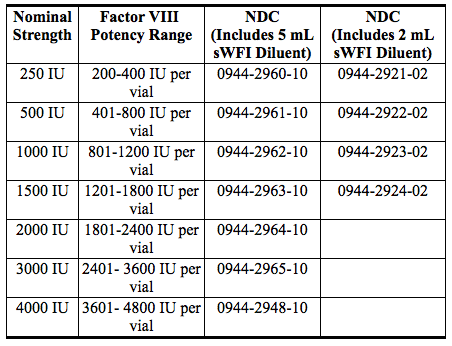
- Actual Factor VIII activity in International Units is stated on the label of each ADVATE carton and vial.
Storage and Handling
- ADVATE is packaged with 5 mL or 2 mL of Sterile Water for Injection, USP, a BAXJECT II Needleless Transfer Device, one Terumo Microbore Infusion set (2 mL only), one full prescribing physician insert, and one patient insert.
- ADVATE should be refrigerated (2° - 8°C [36° - 46°F]) in powder form.
- ADVATE may be stored at room temperature (up to 30°C [86°F]) for a period of up to 6 months not to exceed the expiration date.
- The date that ADVATE is removed from refrigeration should be noted on the carton.
- Do not use beyond the expiration date printed on the vial or six months after date noted on the carton, whichever is earlier. After storage at room temperature, the product must not be returned to the refrigerator. Avoid freezing to prevent damage to the diluent vial.
Storage
There is limited information regarding Antihemophilic Factor (recombinant) Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Antihemophilic Factor (recombinant) |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel

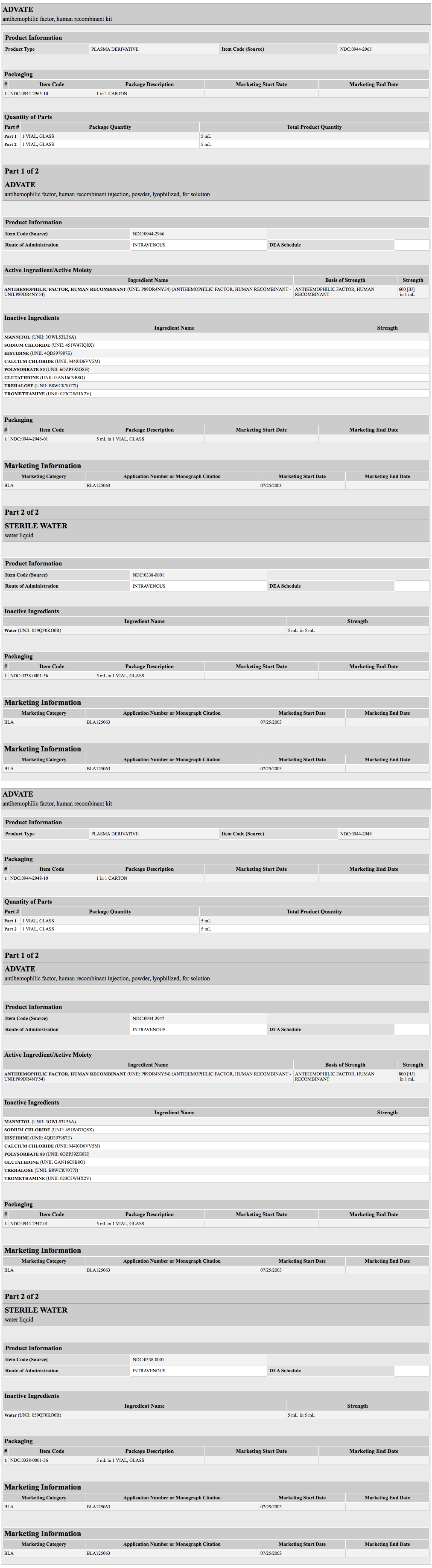

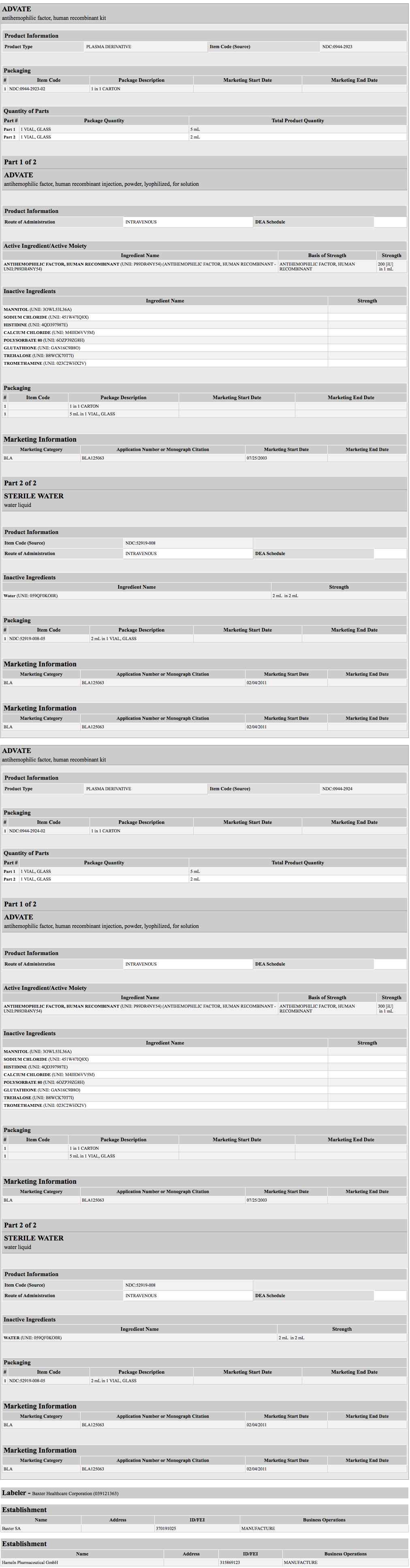
{{#ask: Label Page::Antihemophilic Factor (recombinant) |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
- See FDA approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use)
- Advise patients to report any adverse reactions or problems following ADVATE administration to their physician or healthcare provider.
- Allergic-type hypersensitivity reactions have been reported with ADVATE. Warn patients of the early signs of hypersensitivity reactions, including hives, pruritus, generalized urticaria, angioedema, hypotension, shock, anaphylaxis and acute respiratory distress. Advise patients to discontinue use of the product if these symptoms occur and seek immediate emergency treatment with resuscitative measures such as the administration of epinephrine and oxygen.
- Inhibitor formation may occur with the treatment of a patient with Hemophilia A. Advise patients to contact their physician or treatment center for further treatment and/or assessment if they experience a lack of clinical response to Factor VIII replacement therapy, as this may be a manifestation of an inhibitor.
- Advise patients to consult with their physicians or healthcare provider prior to travel.
- While traveling advise patients to bring an adequate supply of ADVATE, based on their current regimen of treatment.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Antihemophilic Factor (recombinant) interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- ADVATE®[1]
- Advate
- Xyntha
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Antihemophilic Factor (recombinant) Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Antihemophilic Factor (recombinant)
|Pill Name=No image.jpg
|Drug Name=
|Pill Ingred=|+sep=;
|Pill Imprint=
|Pill Dosage={{{dosageValue}}} {{{dosageUnit}}}
|Pill Color=|+sep=;
|Pill Shape=
|Pill Size (mm)=
|Pill Scoring=
|Pill Image=
|Drug Author=
|NDC=
}}
