Organogenesis
In animal development, organogenesis is the process by which the ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm develop into the internal organs of the organism. Internal organs initiate development in humans within the 3rd to 8th weeks in utero.The germ layers in organogenesis differ by three processes: folds, splits, and condensation. Developing early during this stage in chordate animals are the neural tube and notochord. Vertebrate animals all differentiate from the gastrula the same way. Vertebrates develop a neural crest that differentiates into many structures, including some bones, muscles, and components of the peripheral nervous system. The coelom of the body forms from a split of the mesoderm along the somite axis.
Production
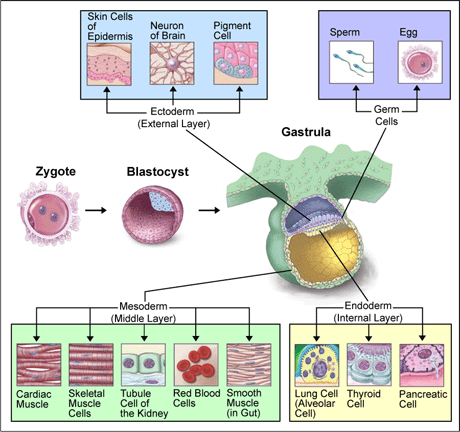
The proceeding graph represents the products produced by the three germ layers.
| Germ Layer | Category | Product |
|---|---|---|
| Endoderm | General[1] | Gastrointestinal tract |
| Endodern | General | Respiratory tract |
| Endoderm | General | Endocrine glands and organs (liver and pancreas) |
| Mesoderm | General | Bones |
| Mesoderm | General | Most of the Circulatory system |
| Mesoderm | General | Connective tissues of the gut and integuments |
| Mesoderm | General | Excretory Tract |
| Mesoderm | General | Mesenchyme |
| Mesoderm | General | Mesothelium |
| Mesoderm | General | Muscles |
| Mesoderm | General | Peritoneum |
| Mesoderm | General | Reproductive System |
| Mesoderm | General | Urinary System |
| Mesoderm | Vertebrate[2] | Chordamesoderm |
| Mesoderm | Vertebrate | Paraxial mesoderm |
| Mesoderm | Vertebrate | Intermediate mesoderm |
| Mesoderm | Vertebrate | Lateral plate mesoderm |
| Ectoderm | General | Nervous system |
| Ectoderm | General | Outer part of integument |
| Ectoderm | Vertebrate | Skin (along with glands, hair, nails) |
| Ectoderm | Vertebrate | Epithelium of the mouth and nasal cavity |
| Ectoderm | Vertebrate | Lens and cornea of the eye |
| Ectoderm | Vertebrate | Melanocytes |
| Ectoderm | Vertebrate | Peripheral nervous system |
| Ectoderm | Vertebrate | Facial cartilage |
| Ectoderm | Vertebrate | Dentin (in teeth) |
| Ectoderm | Vertebrate | Brain (rhombencephalon, mesencephalon and prosencephalon) |
| Ectoderm | Vertebrate | Spinal cord and motor neurons |
| Ectoderm | Vertebrate | Retina |
| Ectoderm | Vertebrate | Posterior pituitary |
See also
- Ectoderm
- Embryogenesis
- Endoderm
- Eye development
- Germ layer
- Germ line development
- Heart development
- Histogenesis
- Limb development
- Mesoderm
- Morphogenesis
Notes
- ↑ The General category denotes that all or most of the animals containing this layer produce the adjacent product.
- ↑ The Vertebrate category denotes that all or most of the vertebrates containing this layer produce the adjacent product.
References
| File:Wiktionary-logo-en-v2.svg | Look up organogenesis in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
- Evers, Christine A., Lisa Starr. Biology:Concepts and Applications. 6th ed. United States:Thomson, 2006. ISBN 0-534-46224-3.
Template:Embryology Template:Germ layer
de:Organogenese nl:Organogenese sr:Органогенеза fi:Organogeneesi sk:Organogenéza Template:WikiDoc Sources