Nasal cavity
|
WikiDoc Resources for Nasal cavity |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Nasal cavity Most cited articles on Nasal cavity |
|
Media |
|
Powerpoint slides on Nasal cavity |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Nasal cavity at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Nasal cavity at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Nasal cavity
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Nasal cavity Discussion groups on Nasal cavity Patient Handouts on Nasal cavity Directions to Hospitals Treating Nasal cavity Risk calculators and risk factors for Nasal cavity
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Nasal cavity |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
The nasal cavity (or nasal fossa) is a large air-filled space above and behind the nose in the middle of the face.
Function
The nasal cavity conditions the air to be received by the areas of the respiratory tract and nose. Owing to the large surface area provided by the conchae, the air passing through the nasal cavity is warmed or cooled to within 1 degree of body temperature. In addition, the air is humidified, and dust and other particulate matter is removed by vibrissae, short, thick hairs, present in the vestibule. The cilia of the respiratory epithelium move the particulate matter towards the pharynx where it is swallowed.
Borders
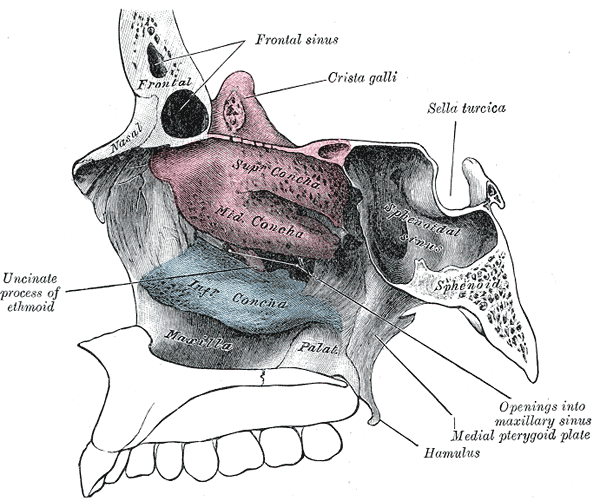
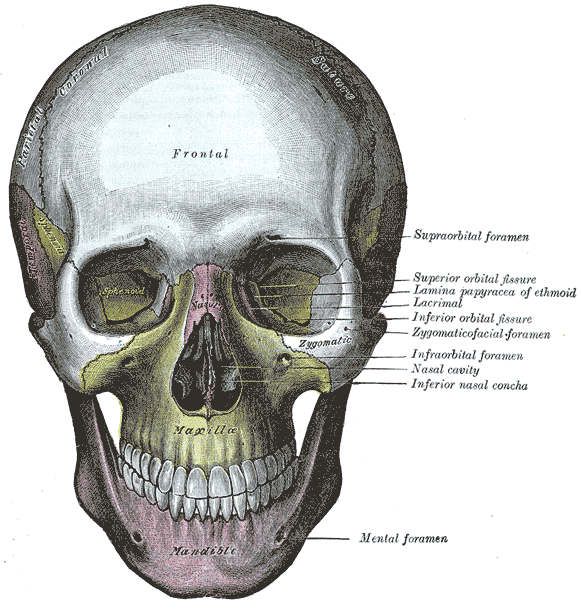
The lateral wall of the nasal cavity is mainly made up by the maxilla, however there is a deficiency that is compensated by: the perpendicular plate of the palatine bone, the medial pterygoid plate, the labyrinth of the ethmoid and the inferior concha. The nasal cavity is enclosed by the nasal bone above. The floor of the nasal cavity, which forms the roof of the mouth, is made up by the bones of the hard palate: the horizontal plate of the palatine bone posteriorly and the palatine process of the maxilla anteriorly. To the front of the nasal cavity is the nose, while the back is continuous with the pharynx. The paranasal sinuses are connected to the nasal cavity through small orifices called ostia.
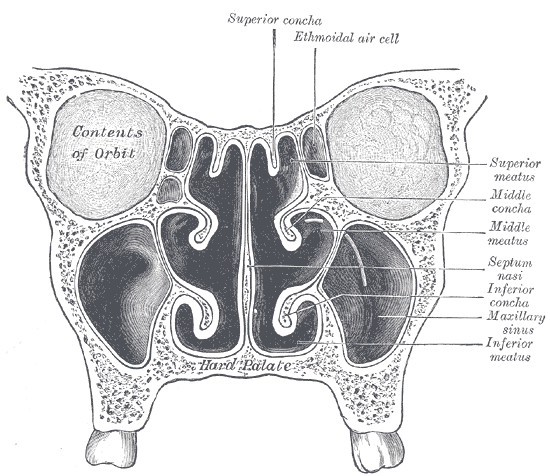
The nasal cavity is divided in two by a vertical fin called the nasal septum. On the sides of the nasal cavity are three horizontal outgrowths called turbinates or conchae (singular "concha"). These turbinates disrupt the airflow, directing air toward the olfactory epithelium on the surface of the turbinates and the septum. The vomeronasal organ is located at the back of the septum and has a role in pheromone detection.
Cilia and mucus along the inside wall of the nasal cavity trap and remove dust and pathogens from the air as it flows through the nasal cavity. The cilia move the mucus down the nasal cavity to the pharynx, where it can be swallowed.
The nasal cavity is divided into two segments: the respiratory segment and the olfactory segment. The respiratory segment is lined with ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium (also called respiratory epithelium). The conchae are located in this region. The respiratory segment has a very vascularized lamina propria allowing the venous plexuses of the conchal mucosa to engorge with blood, restricting airflow and causing air to be directed to the other side of the nose. This cycle occurs approximately every 20-30 minutes. Nose bleeds in the inferior concha are common in this region. The olfactory segment is lined with a specialized type of pseudostratified columnar epithelium, known as olfactory epithelium, which contains receptors for the sense of the smell. This segment is located along the dorsal roof of the nasal cavity. Histological sections appear yellowish-brown due to the presence of lipofuscin pigments. Olfactory mucosal cell types include: bipolar neurons, supporting (sustentacular) cells, basal cells, and Bowman's glands. The axons of the bipolar neurons form the olfactory nerve (cranial nerve I) which enters the brain through the cribiform plate. Bowman's glands are serous glands in the lamina propria, whose secretions trap and dissolve oderiferous substances.
Blood and nerve supply
There is a rich blood supply to the nasal cavity. In some animals, such as dogs, the capillary beds flowing through the nasal cavity help cool the blood flow to the brain.
Blood supply comes from branches of both the internal and external carotid artery, including branches of the facial artery and maxillary artery. The named arteries of the nose are:
- Sphenopalatine artery, a branch of the maxillary artery.
- Anterior ethmoidal artery, a branch of the ophthalmic artery
- Branches of facial artery supplying the vestibule of the nasal cavity.
Innervation
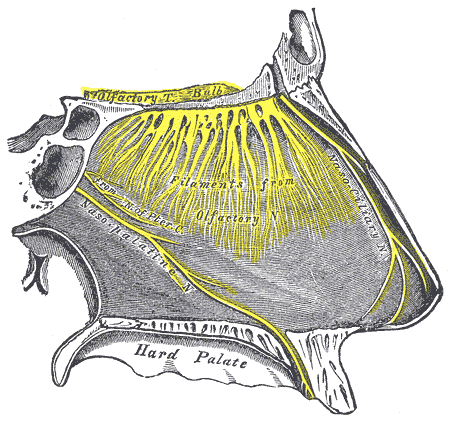
Innervation of the nasal cavity responsible for the sense of smell is via the olfactory nerve, which sends microscopic fibers from the olfactory bulb through the cribiform plate to reach the top of the nasal cavity.
General sensory innervation is by branches of the trigeminal nerve (V1 & V2):
- Nasociliary nerve (V1)
- Nasopalatine nerve (V2)
- Posterior nasal branches of Maxillary nerve (V2)
The entire nasal cavity is innervated by autonomic fibers. Sympathetic innervation to the blood vessels of the mucosa causes them to constrict, while parasympathetic innervation of the mucosa controls secrection by mucous glands.
Diseases
Diseases of the nasal cavity include viral infections and nasal cavity cancer.
Additional images
-
Nose and nasal cavities
-
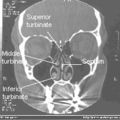
Normal Nose CT Front cross section
-
Coronal section of nasal cavities.
-
Anatomy of the nasal cavity
-
The skull from the front.
-
Left orbicularis oculi, seen from behind.
-
Lateral wall of nasal cavity.
-
Nerves of the wall of the nasal cavity
See also
External links
Template:Respiratory system Template:Head and neck general
ar:جوف الأنف ca:Cavitat nasal dv:ނޭފަތުގެ މަގު gl:Foxa nasal it:Fosse nasali lv:Deguna dobums lt:Nosies ertmė simple:Nasal cavity sk:Nosová dutina fi:Nenäontelo yi:נאז לעכער