Reactive arthritis pathophysiology: Difference between revisions
Akshun Kalia (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Akshun Kalia (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
It is thought that reactive arthritis is the result of previous gastrointestinal or genitourinary infections, which results in an autoimmune condition. The most commonly associated organisms include Chlamydia, Yersinia, Salmonella, Shigella, and Campylobacter infection. It is estimated around 75% patients of reactive arthritis are positive for HLA-B27. The exact mechanism by which infecting organism cause reactive arthritis is not fully understood. It is thought that microbial antigens are similar to certain body proteins (self proteins). When an immune response is mounted against the microbial proteins, the antibodies produced against microbial proteins also reacts with the self proteins of the body causing reactive arthritis. | It is thought that reactive arthritis is the result of previous [[Gastrointestinal tract|gastrointestinal]] or [[genitourinary]] infections, which results in an [[autoimmune]] condition. The most commonly associated [[organisms]] include [[Chlamydia]], [[Yersinia]], [[Salmonella]], [[Shigella]], and [[Campylobacter]] infection. It is estimated around 75% patients of reactive arthritis are positive for [[HLA-B27]]. The exact mechanism by which infecting organism cause reactive arthritis is not fully understood. It is thought that [[microbial]] [[antigens]] are similar to certain body proteins (self proteins). When an immune response is mounted against the [[microbial]] proteins, the [[antibodies]] produced against [[microbial]] proteins also reacts with the self proteins of the body causing reactive arthritis. | ||
==Pathophysiology== | ==Pathophysiology== | ||
It is thought that reactive arthritis is the result of previous gastrointestinal or genitourinary infections, which results in an autoimmune condition. The most commonly associated organisms include Chlamydia, Yersinia, Salmonella, Shigella, and Campylobacter infection.<ref name="pmid16195157">{{cite journal |vauthors=Leirisalo-Repo M |title=Reactive arthritis |journal=Scand. J. Rheumatol. |volume=34 |issue=4 |pages=251–9 |date=2005 |pmid=16195157 |doi=10.1080/03009740500202540 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid8129453">{{cite journal |vauthors=Braun J, Laitko S, Treharne J, Eggens U, Wu P, Distler A, Sieper J |title=Chlamydia pneumoniae--a new causative agent of reactive arthritis and undifferentiated oligoarthritis |journal=Ann. Rheum. Dis. |volume=53 |issue=2 |pages=100–5 |date=February 1994 |pmid=8129453 |pmc=1005260 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid19480995">{{cite journal |vauthors=Carter JD, Hudson AP |title=Reactive arthritis: clinical aspects and medical management |journal=Rheum. Dis. Clin. North Am. |volume=35 |issue=1 |pages=21–44 |date=February 2009 |pmid=19480995 |doi=10.1016/j.rdc.2009.03.010 |url=}}</ref> | It is thought that reactive arthritis is the result of previous [[gastrointestinal]] or [[genitourinary]] infections, which results in an [[autoimmune]] condition. The most commonly associated organisms include [[Chlamydia]], [[Yersinia]], [[Salmonella]], [[Shigella]], and [[Campylobacter]] infection.<ref name="pmid16195157">{{cite journal |vauthors=Leirisalo-Repo M |title=Reactive arthritis |journal=Scand. J. Rheumatol. |volume=34 |issue=4 |pages=251–9 |date=2005 |pmid=16195157 |doi=10.1080/03009740500202540 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid8129453">{{cite journal |vauthors=Braun J, Laitko S, Treharne J, Eggens U, Wu P, Distler A, Sieper J |title=Chlamydia pneumoniae--a new causative agent of reactive arthritis and undifferentiated oligoarthritis |journal=Ann. Rheum. Dis. |volume=53 |issue=2 |pages=100–5 |date=February 1994 |pmid=8129453 |pmc=1005260 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid19480995">{{cite journal |vauthors=Carter JD, Hudson AP |title=Reactive arthritis: clinical aspects and medical management |journal=Rheum. Dis. Clin. North Am. |volume=35 |issue=1 |pages=21–44 |date=February 2009 |pmid=19480995 |doi=10.1016/j.rdc.2009.03.010 |url=}}</ref> | ||
*Reactive arthritis is associated with HLA-B27 (MHC class I molecule). | *Reactive arthritis is associated with [[HLA-B27]] ([[MHC class I|MHC class I molecule]]). | ||
*It is estimated around 75% patients of reactive arthritis are positive for HLA-B27. Other alleles associated with reactive arthritis include HLA-B51 and HLA-DRB1.<ref name="pmid19296404">{{cite journal |vauthors=Savolainen E, Kettunen A, Närvänen A, Kautiainen H, Kärkkäinen U, Luosujärvi R, Kaipiainen-Seppänen O |title=Prevalence of antibodies against Chlamydia trachomatis and incidence of C. trachomatis-induced reactive arthritis in an early arthritis series in Finland in 2000 |journal=Scand. J. Rheumatol. |volume=38 |issue=5 |pages=353–6 |date=2009 |pmid=19296404 |doi=10.1080/03009740902769559 |url=}}</ref> | *It is estimated around 75% patients of reactive arthritis are positive for [[HLA-B27]]. Other alleles associated with reactive arthritis include HLA-B51 and [[HLA-DRB1]].<ref name="pmid19296404">{{cite journal |vauthors=Savolainen E, Kettunen A, Närvänen A, Kautiainen H, Kärkkäinen U, Luosujärvi R, Kaipiainen-Seppänen O |title=Prevalence of antibodies against Chlamydia trachomatis and incidence of C. trachomatis-induced reactive arthritis in an early arthritis series in Finland in 2000 |journal=Scand. J. Rheumatol. |volume=38 |issue=5 |pages=353–6 |date=2009 |pmid=19296404 |doi=10.1080/03009740902769559 |url=}}</ref> | ||
*HLA B27 association with reactive arthritis can also be attributed to the fact that patients with family history of reactive arthritis tend to have a more severe form of disease.<ref name="pmid19473576">{{cite journal |vauthors=Kaarela K, Jäntti JK, Kotaniemi KM |title=Similarity between chronic reactive arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis.A 32-35-year follow-up study |journal=Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. |volume=27 |issue=2 |pages=325–8 |date=2009 |pmid=19473576 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | *[[HLA-B27|HLA B27]] association with reactive arthritis can also be attributed to the fact that patients with family history of reactive arthritis tend to have a more severe form of disease.<ref name="pmid19473576">{{cite journal |vauthors=Kaarela K, Jäntti JK, Kotaniemi KM |title=Similarity between chronic reactive arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis.A 32-35-year follow-up study |journal=Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. |volume=27 |issue=2 |pages=325–8 |date=2009 |pmid=19473576 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
*The exact mechanism by which infecting organism cause reactive arthritis is not fully understood. It is thought that microbial antigens are similar to certain body proteins (self proteins). When an immune response is mounted against the microbial proteins, the antibodies produced against microbial proteins also reacts with the self proteins of the body causing reactive arthritis. | *The exact mechanism by which infecting organism cause reactive arthritis is not fully understood. It is thought that [[microbial]] antigens are similar to certain body proteins (self proteins). When an [[immune]] response is mounted against the [[microbial]] proteins, the [[antibodies]] produced against [[microbial]] proteins also reacts with the self proteins of the body causing reactive arthritis. | ||
**HLA-B27 incorporated MHC class I molecule presents microbial antigens to CD8 cytotoxic T cells. | **[[HLA-B27]] incorporated [[MHC class I]] molecule presents [[microbial]] antigens to [[CD8]] cytotoxic T cells. | ||
**Antigen presenting cells (APCs) present microbial antigens to T helper cells which leads to their activation. | **[[Antigen presenting cells]] (APCs) present [[microbial]] antigens to [[T helper cells]] which leads to their activation. | ||
**T helper cells then differentiates into TH1 cells and TH2 cells which leads to secretion of interleukins (IL-2, IL-3, IL-4, IL-6),TNF-alpha, TGF-β and | **[[T helper cells]] then differentiates into [[TH1]] cells and [[TH2-cells|TH2]] cells which leads to secretion of [[interleukins]] ([[IL-2]], [[IL-3]], [[IL-4]], [[IL-6]]),[[TNF-alpha]], [[TGF-β]] and [[Th17]] cells. | ||
**Interleukins IL-3, IL-4, IL-6 leads to increased production of antibodies from plasma cells. | **[[Interleukins]] [[IL-3]], [[IL-4]], [[IL-6]] leads to increased production of [[antibodies]] from [[plasma cells]]. | ||
**Th17 cells release IL-17 which is also a major pro-inflammatory cytokine.<ref name="pmid21181220">{{cite journal |vauthors=Singh AK, Misra R, Aggarwal A |title=Th-17 associated cytokines in patients with reactive arthritis/undifferentiated spondyloarthropathy |journal=Clin. Rheumatol. |volume=30 |issue=6 |pages=771–6 |date=June 2011 |pmid=21181220 |doi=10.1007/s10067-010-1646-5 |url=}}</ref> | **[[Th17]] cells release IL-17 which is also a major pro-inflammatory [[cytokine]].<ref name="pmid21181220">{{cite journal |vauthors=Singh AK, Misra R, Aggarwal A |title=Th-17 associated cytokines in patients with reactive arthritis/undifferentiated spondyloarthropathy |journal=Clin. Rheumatol. |volume=30 |issue=6 |pages=771–6 |date=June 2011 |pmid=21181220 |doi=10.1007/s10067-010-1646-5 |url=}}</ref> | ||
**Patients with defects in T cell regulatory function may lead to more severe inflammatory process and cytokine production.<ref name="pmid20810989">{{cite journal |vauthors=Eliçabe RJ, Cargnelutti E, Serer MI, Stege PW, Valdez SR, Toscano MA, Rabinovich GA, Di Genaro MS |title=Lack of TNFR p55 results in heightened expression of IFN-γ and IL-17 during the development of reactive arthritis |journal=J. Immunol. |volume=185 |issue=7 |pages=4485–95 |date=October 2010 |pmid=20810989 |doi=10.4049/jimmunol.0902245 |url=}}</ref> | **Patients with defects in [[T cell]] regulatory function may lead to more severe [[inflammatory]] process and [[cytokine]] production.<ref name="pmid20810989">{{cite journal |vauthors=Eliçabe RJ, Cargnelutti E, Serer MI, Stege PW, Valdez SR, Toscano MA, Rabinovich GA, Di Genaro MS |title=Lack of TNFR p55 results in heightened expression of IFN-γ and IL-17 during the development of reactive arthritis |journal=J. Immunol. |volume=185 |issue=7 |pages=4485–95 |date=October 2010 |pmid=20810989 |doi=10.4049/jimmunol.0902245 |url=}}</ref> | ||
**The increased cytokine and antibody production leads to destruction of microbial proteins as well as self proteins causing an autoimmune reaction. | **The increased [[cytokine]] and [[antibody]] production leads to destruction of [[microbial]] proteins as well as self proteins causing an [[autoimmune]] reaction. | ||
**Furthermore, studies have shown the presence of T cells and intra-articular antibodies on synovial fluid analysis. | **Furthermore, studies have shown the presence of [[T cells]] and intra-articular [[antibodies]] on [[synovial fluid]] analysis. | ||
[[image:T cell activation1111.png|thumb|center|Activation of CD4 and CD8 cells ([By CNX OpenStax [CC BY 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0)], via Wikimedia Commons])]] | [[image:T cell activation1111.png|thumb|center|Activation of CD4 and CD8 cells ([By CNX OpenStax [CC BY 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0)], via Wikimedia Commons])]] | ||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
===Reactive Arthritis in HIV patients=== | ===Reactive Arthritis in HIV patients=== | ||
*Patients with HIV who later on develop reactive arthritis tend to have a more serious presentation. | *Patients with [[HIV]] who later on develop reactive arthritis tend to have a more serious presentation. | ||
*These patients present with severe generalised rash resembling psoriasis (pink color and scaly), severe arthritis and other AIDS related symptoms. | *These patients present with severe generalised [[rash]] resembling [[psoriasis]] (pink color and scaly), severe arthritis and other [[AIDS]] related symptoms. | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 15:15, 12 April 2018
|
Reactive arthritis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Reactive arthritis pathophysiology On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Reactive arthritis pathophysiology |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors forReactive arthritis pathophysiology |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1];Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Akshun Kalia M.B.B.S.[2]
Overview
It is thought that reactive arthritis is the result of previous gastrointestinal or genitourinary infections, which results in an autoimmune condition. The most commonly associated organisms include Chlamydia, Yersinia, Salmonella, Shigella, and Campylobacter infection. It is estimated around 75% patients of reactive arthritis are positive for HLA-B27. The exact mechanism by which infecting organism cause reactive arthritis is not fully understood. It is thought that microbial antigens are similar to certain body proteins (self proteins). When an immune response is mounted against the microbial proteins, the antibodies produced against microbial proteins also reacts with the self proteins of the body causing reactive arthritis.
Pathophysiology
It is thought that reactive arthritis is the result of previous gastrointestinal or genitourinary infections, which results in an autoimmune condition. The most commonly associated organisms include Chlamydia, Yersinia, Salmonella, Shigella, and Campylobacter infection.[1][2][3]
- Reactive arthritis is associated with HLA-B27 (MHC class I molecule).
- It is estimated around 75% patients of reactive arthritis are positive for HLA-B27. Other alleles associated with reactive arthritis include HLA-B51 and HLA-DRB1.[4]
- HLA B27 association with reactive arthritis can also be attributed to the fact that patients with family history of reactive arthritis tend to have a more severe form of disease.[5]
- The exact mechanism by which infecting organism cause reactive arthritis is not fully understood. It is thought that microbial antigens are similar to certain body proteins (self proteins). When an immune response is mounted against the microbial proteins, the antibodies produced against microbial proteins also reacts with the self proteins of the body causing reactive arthritis.
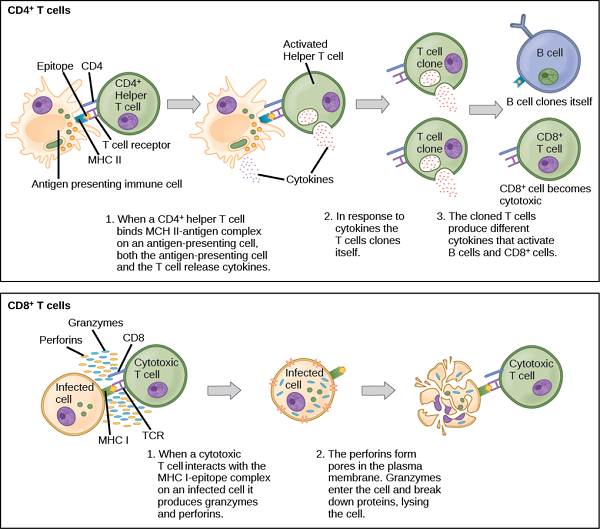
- HLA-B27 incorporated MHC class I molecule presents microbial antigens to CD8 cytotoxic T cells.
- Antigen presenting cells (APCs) present microbial antigens to T helper cells which leads to their activation.
- T helper cells then differentiates into TH1 cells and TH2 cells which leads to secretion of interleukins (IL-2, IL-3, IL-4, IL-6),TNF-alpha, TGF-β and Th17 cells.
- Interleukins IL-3, IL-4, IL-6 leads to increased production of antibodies from plasma cells.
- Th17 cells release IL-17 which is also a major pro-inflammatory cytokine.[6]
- Patients with defects in T cell regulatory function may lead to more severe inflammatory process and cytokine production.[7]
- The increased cytokine and antibody production leads to destruction of microbial proteins as well as self proteins causing an autoimmune reaction.
- Furthermore, studies have shown the presence of T cells and intra-articular antibodies on synovial fluid analysis.
Reactive Arthritis in HIV patients
- Patients with HIV who later on develop reactive arthritis tend to have a more serious presentation.
- These patients present with severe generalised rash resembling psoriasis (pink color and scaly), severe arthritis and other AIDS related symptoms.
References
- ↑ Leirisalo-Repo M (2005). "Reactive arthritis". Scand. J. Rheumatol. 34 (4): 251–9. doi:10.1080/03009740500202540. PMID 16195157.
- ↑ Braun J, Laitko S, Treharne J, Eggens U, Wu P, Distler A, Sieper J (February 1994). "Chlamydia pneumoniae--a new causative agent of reactive arthritis and undifferentiated oligoarthritis". Ann. Rheum. Dis. 53 (2): 100–5. PMC 1005260. PMID 8129453.
- ↑ Carter JD, Hudson AP (February 2009). "Reactive arthritis: clinical aspects and medical management". Rheum. Dis. Clin. North Am. 35 (1): 21–44. doi:10.1016/j.rdc.2009.03.010. PMID 19480995.
- ↑ Savolainen E, Kettunen A, Närvänen A, Kautiainen H, Kärkkäinen U, Luosujärvi R, Kaipiainen-Seppänen O (2009). "Prevalence of antibodies against Chlamydia trachomatis and incidence of C. trachomatis-induced reactive arthritis in an early arthritis series in Finland in 2000". Scand. J. Rheumatol. 38 (5): 353–6. doi:10.1080/03009740902769559. PMID 19296404.
- ↑ Kaarela K, Jäntti JK, Kotaniemi KM (2009). "Similarity between chronic reactive arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis.A 32-35-year follow-up study". Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 27 (2): 325–8. PMID 19473576.
- ↑ Singh AK, Misra R, Aggarwal A (June 2011). "Th-17 associated cytokines in patients with reactive arthritis/undifferentiated spondyloarthropathy". Clin. Rheumatol. 30 (6): 771–6. doi:10.1007/s10067-010-1646-5. PMID 21181220.
- ↑ Eliçabe RJ, Cargnelutti E, Serer MI, Stege PW, Valdez SR, Toscano MA, Rabinovich GA, Di Genaro MS (October 2010). "Lack of TNFR p55 results in heightened expression of IFN-γ and IL-17 during the development of reactive arthritis". J. Immunol. 185 (7): 4485–95. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0902245. PMID 20810989.