Nomifensine
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Elimination half-life | 1.5-4 hours |
| Excretion | Kidney (88%) within 24 hours[1] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| E number | {{#property:P628}} |
| ECHA InfoCard | {{#property:P2566}}Lua error in Module:EditAtWikidata at line 36: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C16H18N2 |
| Molar mass | 238.328 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
|
WikiDoc Resources for Nomifensine |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Nomifensine Most cited articles on Nomifensine |
|
Media |
|
Powerpoint slides on Nomifensine |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Nomifensine at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Nomifensine at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Nomifensine
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Nomifensine Discussion groups on Nomifensine Patient Handouts on Nomifensine Directions to Hospitals Treating Nomifensine Risk calculators and risk factors for Nomifensine
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Nomifensine |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
Nomifensine (Merital, Alival) is a norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor developed by a team at Hoechst AG in the 1960s.[2] The drug was test marketed in the United States by Hoechst AG (now Sanofi-Aventis), i.e. a drug that increases the amount of synaptic norepinephrine and dopamine available to receptors by blocking the dopamine and norepinephrine reuptake transporters.[3] This is a mechanism of action shared by some recreational drugs like cocaine and the medication Tametraline (see DRI). Research showed that the (S) isomer is responsible for activity.[4] The drug was an effective antidepressant, without sedative effects. Nomifensine did not interact significantly with alcohol and lacked anticholinergic effects. No withdrawal symptoms were seen after 6 months treatment. The drug was however considered not suitable for agitated patients as it presumably made agitation worse.[5][6] In January 1986 the drug was withdraw by its manufacturers for safety reasons.[7]
Some case reports in the 1980s suggested that there was potential for psychological dependence on nomifensine, typically in patients with a history of stimulant addiction, or when the drug was used in very high doses (400–600 mg per day).[8]
In a 1989 study it has been investigated for use in treating adult ADHD and proven successful.[9] In a 1977 study it has not proven of benefit in advanced parkinsonism, except for depression associated with the parkinsonism.[10]
Clinical uses
Nomifensine was investigated for use as an antidepressant in the 1970s, and was found to be a useful antidepressant at doses of 50–225 mg per day, both motivating and anxiolytic.
Side effects
During treatment with nomifensine there were relatively few adverse effects mainly renal failure, paranoid symptoms, drowsiness or insomnia, headache, and dry mouth. Side effects affecting the cardiovascular system included tachycardia and palpitations, but nomifensine was significantly less cardiotoxic than the standard triciclyc antidepressants.[11]
Due to the risk of a risk of haemolytic anaemia, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) withdrew approval for nomifensine on March 20, 1992. Nomifensine has subsequently been withdrawn from the Canadian and UK markets as well.[12] Some deaths were linked to immunohaemolytic anemia caused by this compound although the mechanism remained unclear.[13]
In 2012 structure–affinity relationship data (compare SAR) were published.[14]
Synthesis
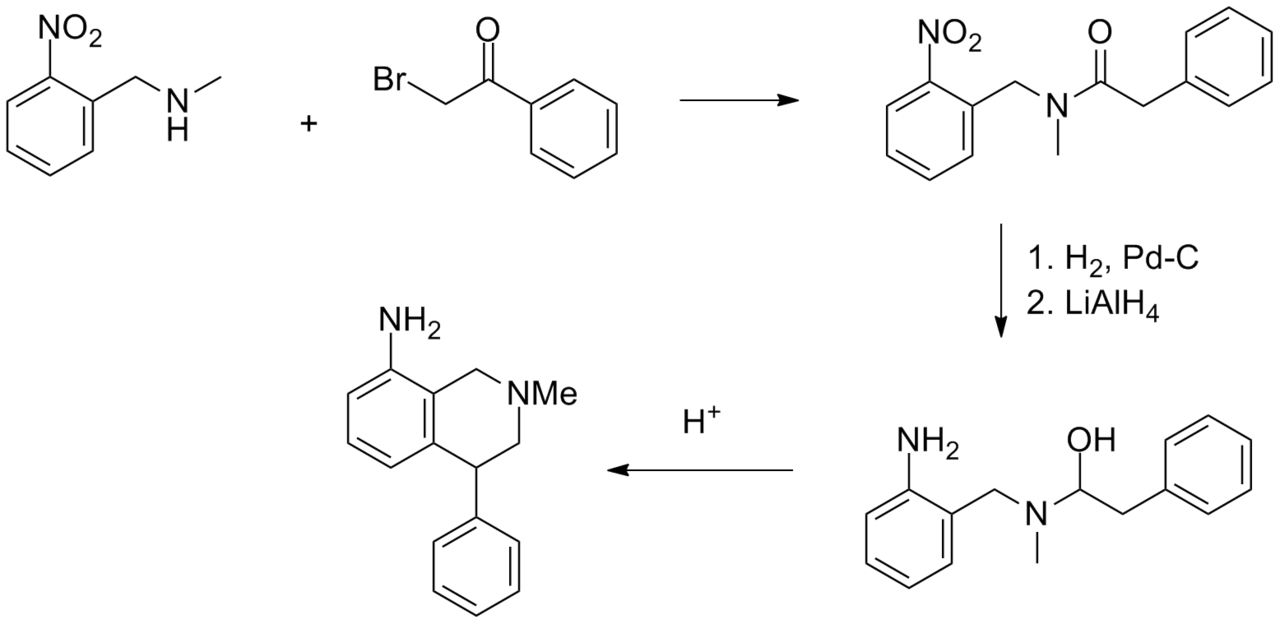
See also
References
- ↑ Heptner W, Hornke I, Uihlein M (April 1984). "Kinetics and metabolism of nomifensine". The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 45 (4 Pt 2): 21–5. PMID 6370971.
|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ↑ US patent 3577424, "4-Phenyl-8-Amino Tetrahydroisoquinolines", issued 1971-05-04, assigned to Farbwerke Hoechst
- ↑ PMID 477572 (PMID 477572)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ 'Chirality and Biological Activity of Drugs' page 138
- ↑ PMID 334230 (PMID 334230)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ PMID 6370985 (PMID 6370985)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ "CSM Update: Withdrawal of nomifensine". British Medical Journal (Clinical Research Ed.). 293 (6538): 41. July 1986. doi:10.1136/bmj.293.6538.41. PMC 1340782. PMID 20742679.
|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ↑ PMID 3774872 (PMID 3774872)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ PMID 2651559 (PMID 2651559)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ PMID 334223 (PMID 334223)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ Hanks GW (1977). "A profile of nomifensine". British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 4Suppl 2: 243S–248S. PMC 1429121. PMID 911653.
|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ↑ "Nomifensine DB04821". Drugbank.ca.
- ↑ PMID 3058454 (PMID 3058454)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ Pechulis AD et al (2012): "4-Phenyl tetrahydroisoquinolines as dual norepinephrine and dopamine reuptake inhibitors", Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 7219. PMID 23084899
- ↑ Template:Cite doi
- Pages with script errors
- Pages using citations with accessdate and no URL
- CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list
- Pages with incomplete PMID references
- Drugs with non-standard legal status
- Articles with changed CASNo identifier
- E number from Wikidata
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Chemical articles with unknown parameter in Infobox drug
- Articles without KEGG source
- Drugboxes which contain changes to verified fields
- Drugboxes which contain changes to watched fields
- Antidepressants
- Stimulants
- Withdrawn drugs
- Drug