Neisseria gonorrhoeae: Difference between revisions
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
:::* Preferred regimen:[[Ceftriaxone]] 250 mg IM in a single dose {{and}} [[Azithromycin]] 1 g PO in a single dose | :::* Preferred regimen:[[Ceftriaxone]] 250 mg IM in a single dose {{and}} [[Azithromycin]] 1 g PO in a single dose | ||
::* | ::* Gonococcal Conjunctivitis Disseminated Gonococcal Infection | ||
:::* Preferred regimen :[[Azithromycin]] 1 g PO in a single dose | :::* Preferred regimen :[[Ceftriaxone]] 250 mg IM in a single dose {{and}} [[Azithromycin]] 1 g PO in a single dose | ||
:*Disseminated Gonococcal Infection | |||
::* Treatment of Arthritis and Arthritis-Dermatitis Syndrome | |||
:::* Preferred regimen :[[Ceftriaxone]] 1 g IM/IV q24h for 7 days{{and}} [[Azithromycin]] 1 g PO in a single dose | |||
:::* Alternative regimen :[[Cefotaxime]] 1 g IV q8h for 7 days {{or}} [[Ceftizoxime]] 1 g IV q 8 h for 7 days {{and}} [[Azithromycin]] 1 g PO in a single dose | |||
:::* Alternative regimen (1):[[ Amoxicillin]] 500 mg PO tid for 7 days | :::* Alternative regimen (1):[[ Amoxicillin]] 500 mg PO tid for 7 days | ||
:::* Alternative regimen (2):[[ Erythromycin]] base 500 mg PO qid for 7 days {{or}} [[Erythromycin]]base 250 mg PO qid for 14 days | :::* Alternative regimen (2):[[ Erythromycin]] base 500 mg PO qid for 7 days {{or}} [[Erythromycin]]base 250 mg PO qid for 14 days | ||
:::* Alternative regimen (3):[[ Erythromycin]] ethylsuccinate 800 mg PO qid for 7 days {{or}} [[Erythromycin]] ethylsuccinate 400 mg PO four qid for 14days | :::* Alternative regimen (3):[[ Erythromycin]] ethylsuccinate 800 mg PO qid for 7 days {{or}} [[Erythromycin]] ethylsuccinate 400 mg PO four qid for 14days | ||
:::* Note:[[ Doxycycline]], [[Ofloxacin]], and [[Levofloxacin]] are contraindicated in pregnant women. | :::* Note:[[ Doxycycline]], [[Ofloxacin]], and [[Levofloxacin]] are contraindicated in pregnant women. | ||
::* '''Chlamydial infection among neonates''' | ::* '''Chlamydial infection among neonates''' ::* '''Pregancy'''::* '''Chlamydial Infections in patients with HIV Infection' | ||
::* '''Ophthalmia Neonatorum'''caused by ''C. trachomatis'' | ::* '''Ophthalmia Neonatorum'''caused by ''C. trachomatis'' | ||
:::* Preferred regimen :[[ Erythromycin]] base or ethylsuccinate ,PO 50 mg/kg/ day divided into 4 doses daily for 14 days | :::* Preferred regimen :[[ Erythromycin]] base or ethylsuccinate ,PO 50 mg/kg/ day divided into 4 doses daily for 14 days | ||
Revision as of 14:31, 26 June 2015
| Neisseria gonorrhoeae | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
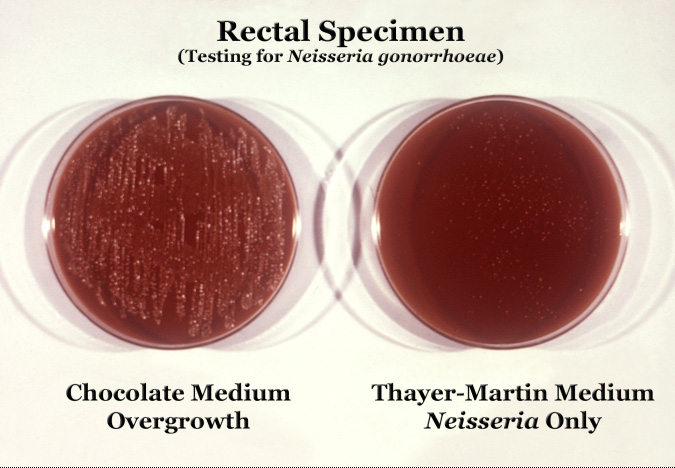 Neisseria gonorrhoeae cultured on two different media types.
| ||||||||||||||
| Scientific classification | ||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||
| Binomial name | ||||||||||||||
| Neisseria gonorrhoeae Zopf, 1885 |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
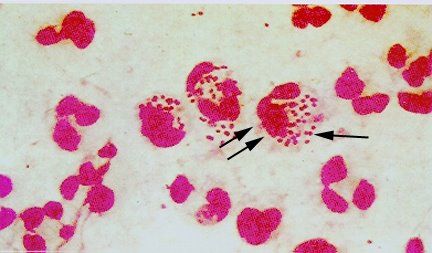
Neisseria gonorrhoeae (also known as Gonococci) is a species of Gram-negative bacteria responsible for the sexually transmitted disease gonorrhoea.[1] Neisseria are highly fastidious cocci, requiring nutrient supplementation to survive. Thus, they grow on Chocolate agar (heated blood agar) with carbon dioxide. These cocci are facultatively intracellular and typically appear in pairs (diplococci).
Gonorrhoea symptoms include a purulent (or pus-like) discharge from the genitals which may be foul smelling, a burning sensation during urination and conjunctivitis commonly in neonates; that's why silver nitrate is used as a preventive measure. It also occurs occasionally in adults. Neisseria is usually isolated on a Thayer-Martin agar — an agar plate with 3 different antibiotics and nutrients which not only facilitate the growth of Neisseria species, but inhibit the growth of Gram-positive organisms and most bacilli and fungi. Further testing to differentiate the species includes testing for oxidase (all Neisseria show a positive reaction) and the carbohydrates maltose, sucrose, and glucose test in which N. gonorrhoeae will only oxidize (that is, utilize) the glucose.
If N. gonorrhoeae is resistant to the penicillin family of antibiotics, then ceftriaxone (a third-generation cephalosporin) is often used.
Patients should also be tested for Chlamydia infections, since co-infection is frequent.
Diagnosis
Pathology
Treatment
- Gonococcal Infections
- Gonococcal Infections [3]
- Gonococcal Infections in Adolescents and Adults
- Uncomplicated Gonococcal Infections of the Cervix, Urethra, and Rectum
- Preferred regimen : Ceftriaxone 250 mg IM in a single dose AND Azithromycin 1g PO in a single dose
- Alternative regimen:Cefixime 400 mg PO single dose AND Azithromycin 1 g PO single dose.(If ceftriaxone is not available)
- Uncomplicated Gonococcal Infections of the Pharynx
- Preferred regimen:Ceftriaxone 250 mg IM in a single dose AND Azithromycin 1 g PO in a single dose
- Gonococcal Conjunctivitis Disseminated Gonococcal Infection
- Preferred regimen :Ceftriaxone 250 mg IM in a single dose AND Azithromycin 1 g PO in a single dose
- Disseminated Gonococcal Infection
- Treatment of Arthritis and Arthritis-Dermatitis Syndrome
- Preferred regimen :Ceftriaxone 1 g IM/IV q24h for 7 daysAND Azithromycin 1 g PO in a single dose
- Alternative regimen :Cefotaxime 1 g IV q8h for 7 days OR Ceftizoxime 1 g IV q 8 h for 7 days AND Azithromycin 1 g PO in a single dose
- Alternative regimen (1):Amoxicillin 500 mg PO tid for 7 days
- Alternative regimen (2):Erythromycin base 500 mg PO qid for 7 days OR Erythromycinbase 250 mg PO qid for 14 days
- Alternative regimen (3):Erythromycin ethylsuccinate 800 mg PO qid for 7 days OR Erythromycin ethylsuccinate 400 mg PO four qid for 14days
- Note:Doxycycline, Ofloxacin, and Levofloxacin are contraindicated in pregnant women.
- Chlamydial infection among neonates ::* Pregancy::* Chlamydial Infections in patients with HIV Infection'
- Ophthalmia Neonatorumcaused by C. trachomatis
- Preferred regimen :Erythromycin base or ethylsuccinate ,PO 50 mg/kg/ day divided into 4 doses daily for 14 days
- Alternative regimen : Azithromycin suspension, PO 20 mg/kg /day qd for 3 days
- Note: The mothers of infants who have chlamydial infection and the sex partners of these women should be evaluated and treated.
- Infant Pneumonia
- Preferred regimen :Erythromycin base or ethylsuccinate PO 50 mg/kg/ day divided into 4 doses daily for 14 days
- Alternative regimen : Azithromycin suspension, PO 20 mg/kg /day qd for 3 days
- Chlamydial infection among infants and childern
- Infants and childern who weigh < 45 kg
- Preferred regimen :Erythromycin base or ethylsuccinate PO 50 mg/kg/ day divided into 4 doses daily for 14 days
- Infants and childern who weigh ≥45 kg but who are aged <8 years
- Preferred regimen :Azithromycin 1 g PO in a single dose
- Infants and childern aged ≥8 years
- Preferred regimen :Azithromycin 1 g PO in a single dose OR Doxycycline 100 mg PO bid for 7 days
References
- ↑ Ryan KJ, Ray CG (editors) (2004). Sherris Medical Microbiology (4th ed. ed.). McGraw Hill. ISBN 0838585299.
- ↑ http://picasaweb.google.com/mcmumbi/USMLEIIImages
- ↑ "Chlamydial Infections".
de:Neisseria gonorrhoeae it:Neisseria gonorrhoeae hu:Neisseria gonorrhoeae nl:Neisseria gonorrhea no:Neisseria gonorrhoeae