Legionellosis differential diagnosis: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 70: | Line 70: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! align="center" style="background:#DCDCDC;" |[[Chlamydia pneumonia]] | ! align="center" style="background:#DCDCDC;" |[[Chlamydia pneumonia]] | ||
| | | align="left" style="background:#F5F5F5;" | | ||
* | * No specific clinical features of [[chlamydia pneumonia]]. | ||
* | * Gradual symptoms | ||
* | * Associated with [[upper respiratory tract]] symptoms | ||
* | * Associated with extrapulmonary maifestations such as: | ||
| | **[[Meningitis]] | ||
* | **[[Guillain-Barre syndrome]] | ||
* | | align="left" style="background:#F5F5F5;" | | ||
| | * Normal WBC count | ||
| | * Positive [[Antibody|antichlamydial antibody]] | ||
| align="left" style="background:#F5F5F5;" | | |||
| align="center" style="background:#F5F5F5;" | | |||
[[Image:Chlamydia-pneumonia - Case courtesy of Dr Andrew Dixon, Radiopaedia.org, rID 14567.jpg|center|300px|thumb|Chlamydia-pneumonia - Case courtesy of Dr Andrew Dixon, Radiopaedia.org, rID 14567]] | [[Image:Chlamydia-pneumonia - Case courtesy of Dr Andrew Dixon, Radiopaedia.org, rID 14567.jpg|center|300px|thumb|Chlamydia-pneumonia - Case courtesy of Dr Andrew Dixon, Radiopaedia.org, rID 14567]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
! align="center" style="background:#DCDCDC;" |Acute interstitial pneumonia | ! align="center" style="background:#DCDCDC;" |Acute interstitial pneumonia | ||
| | | align="left" style="background:#F5F5F5;" | | ||
*[[Dry cough]] | *[[Dry cough]] | ||
*[[Dyspnea|Progressive dyspnea]] | *[[Dyspnea|Progressive dyspnea]] | ||
| | | align="left" style="background:#F5F5F5;" | | ||
*Nonspecific | *Nonspecific | ||
| | | align="left" style="background:#F5F5F5;" | | ||
*Disseminated [[Consolidation (medicine)|consolidation]] on [[chest radiograph]] | *Disseminated [[Consolidation (medicine)|consolidation]] on [[chest radiograph]] | ||
*Interstitial infiltrate on chest radiograph | *Interstitial infiltrate on chest radiograph | ||
*Increased uptake on gallium scan | *Increased uptake on gallium scan | ||
| | | align="center" style="background:#F5F5F5;" | | ||
|- | |- | ||
! align="center" style="background:#DCDCDC;" |Pneumococcal pneumonia | ! align="center" style="background:#DCDCDC;" |Pneumococcal pneumonia | ||
| | | align="left" style="background:#F5F5F5;" | | ||
*[[Fever|High grade fever]] | *[[Fever|High grade fever]] | ||
*[[Hemoptysis]] | *[[Hemoptysis]] | ||
| Line 109: | Line 111: | ||
*[[Productive cough]] | *[[Productive cough]] | ||
*[[Egophony]] | *[[Egophony]] | ||
| | | align="left" style="background:#F5F5F5;" | | ||
*[[Gram positive bacteria|Gram positive]] [[diplococci]] on sputum Gram stain | *[[Gram positive bacteria|Gram positive]] [[diplococci]] on sputum Gram stain | ||
*[[Pleural effusion]] ([[exudative]]) | *[[Pleural effusion]] ([[exudative]]) | ||
*Respiratory alkalosis | *Respiratory alkalosis | ||
| | | align="left" style="background:#F5F5F5;" | | ||
*Parenchymal hyperlucency on [[chest radiograph]] | *Parenchymal hyperlucency on [[chest radiograph]] | ||
*Increased uptake on [[gallium scan]] | *Increased uptake on [[gallium scan]] | ||
| Line 119: | Line 121: | ||
*Alveolar [[Consolidation (medicine)|consolidation]] on [[chest radiograph]] | *Alveolar [[Consolidation (medicine)|consolidation]] on [[chest radiograph]] | ||
*Lobar [[Consolidation (medicine)|consolidation]] on [[chest radiograph]] | *Lobar [[Consolidation (medicine)|consolidation]] on [[chest radiograph]] | ||
| | | align="center" style="background:#F5F5F5;" | | ||
|- | |- | ||
! align="center" style="background:#DCDCDC;" |Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia | ! align="center" style="background:#DCDCDC;" |Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia | ||
| | | align="left" style="background:#F5F5F5;" | | ||
*[[Immunosuppressive]] state | *[[Immunosuppressive]] state | ||
*[[Subcutaneous emphysema]] | *[[Subcutaneous emphysema]] | ||
*[[Cough|Hacking cough]] | *[[Cough|Hacking cough]] | ||
*[[Dyspnea|Progressive dyspnea]] | *[[Dyspnea|Progressive dyspnea]] | ||
| | | align="left" style="background:#F5F5F5;" | | ||
*[[Respiratory alkalosis]] | *[[Respiratory alkalosis]] | ||
*Serum beta-D-glucan elevation | *Serum beta-D-glucan elevation | ||
| | | align="left" style="background:#F5F5F5;" | | ||
*[[Alveolar]] [[Consolidation (medicine)|consolidation]] on [[chest radiograph]] | *[[Alveolar]] [[Consolidation (medicine)|consolidation]] on [[chest radiograph]] | ||
*Lobar [[Consolidation (medicine)|consolidation]] on [[chest radiograph]] | *Lobar [[Consolidation (medicine)|consolidation]] on [[chest radiograph]] | ||
*Interstitial infiltrate on [[chest radiograph]] | *Interstitial infiltrate on [[chest radiograph]] | ||
*[[Pneumomediastinum]] on [[chest radiograph]] | *[[Pneumomediastinum]] on [[chest radiograph]] | ||
| | | align="center" style="background:#F5F5F5;" | | ||
|- | |- | ||
! align="center" style="background:#DCDCDC;" |Pulmonary embolism | ! align="center" style="background:#DCDCDC;" |Pulmonary embolism | ||
| | | align="left" style="background:#F5F5F5;" | | ||
*Calf [[pain]] or [[swelling]] | *Calf [[pain]] or [[swelling]] | ||
*Decreased [[pulse pressure]] | *Decreased [[pulse pressure]] | ||
| Line 156: | Line 158: | ||
*[[Venous stasis]] | *[[Venous stasis]] | ||
*[[Bone fracture]] | *[[Bone fracture]] | ||
| | | align="left" style="background:#F5F5F5;" | | ||
*[[D-dimer]] elevation | *[[D-dimer]] elevation | ||
*[[Hypocapnia]] | *[[Hypocapnia]] | ||
| Line 164: | Line 166: | ||
*[[Right axis deviation]] on ECG | *[[Right axis deviation]] on ECG | ||
*Right ventricular overload on ECG | *Right ventricular overload on ECG | ||
| | | align="left" style="background:#F5F5F5;" | | ||
*Normal [[chest radiograph]] | *Normal [[chest radiograph]] | ||
*[[Atelectasis]] on [[chest radiograph]] | *[[Atelectasis]] on [[chest radiograph]] | ||
| Line 174: | Line 176: | ||
*Segmental [[perfusion]] defect on lung scan | *Segmental [[perfusion]] defect on lung scan | ||
*[[V/Q scan|V/Q]] mismatch on lung scan | *[[V/Q scan|V/Q]] mismatch on lung scan | ||
| | | align="center" style="background:#F5F5F5;" | | ||
|- | |- | ||
! align="center" style="background:#DCDCDC;" |Streptococcal pneumonia | ! align="center" style="background:#DCDCDC;" |Streptococcal pneumonia | ||
| | | align="left" style="background:#F5F5F5;" | | ||
*Pectoriloquy | *Pectoriloquy | ||
*Bronchial [[breath sounds]] | *Bronchial [[breath sounds]] | ||
| Line 186: | Line 188: | ||
*[[Pleuritic chest pain]] | *[[Pleuritic chest pain]] | ||
*[[Egophony]] | *[[Egophony]] | ||
| | | align="left" style="background:#F5F5F5;" | | ||
*[[Gram-positive cocci]] in chains on sputum [[Gram stain]] | *[[Gram-positive cocci]] in chains on sputum [[Gram stain]] | ||
*[[Respiratory alkalosis]] | *[[Respiratory alkalosis]] | ||
*[[Pleural effusion]] (exudative) | *[[Pleural effusion]] (exudative) | ||
| | | align="left" style="background:#F5F5F5;" | | ||
*Alveolar consolidation on chest radiograph | *Alveolar consolidation on chest radiograph | ||
*Lobar consolidation on chest radiograph | *Lobar consolidation on chest radiograph | ||
*[[Empyema]] on chest radiograph | *[[Empyema]] on chest radiograph | ||
*Increased uptake on [[gallium scan]] | *Increased uptake on [[gallium scan]] | ||
| | | align="center" style="background:#F5F5F5;" | | ||
|- | |- | ||
! align="center" style="background:#DCDCDC;" |Viral pneumonia | ! align="center" style="background:#DCDCDC;" |Viral pneumonia | ||
| | | align="left" style="background:#F5F5F5;" | | ||
*[[Pleuritic chest pain]] | *[[Pleuritic chest pain]] | ||
*[[Breath sounds|Bronchial breath sounds]] | *[[Breath sounds|Bronchial breath sounds]] | ||
| Line 204: | Line 206: | ||
*Fine [[rales]] | *Fine [[rales]] | ||
*[[Breath sounds|Bronchovesicular breath sounds]] | *[[Breath sounds|Bronchovesicular breath sounds]] | ||
| | | align="left" style="background:#F5F5F5;" | | ||
*[[Lymphocytosis]] | *[[Lymphocytosis]] | ||
*[[Respiratory alkalosis]] | *[[Respiratory alkalosis]] | ||
| | | align="left" style="background:#F5F5F5;" | | ||
*Lobar [[Consolidation (medicine)|consolidation]] on [[chest radiograph]] | *Lobar [[Consolidation (medicine)|consolidation]] on [[chest radiograph]] | ||
*Interstitial infiltrate on [[chest radiograph]] | *Interstitial infiltrate on [[chest radiograph]] | ||
| | | align="center" style="background:#F5F5F5;" | | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 18:15, 2 November 2018
|
Legionellosis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Legionellosis differential diagnosis On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Legionellosis differential diagnosis |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Legionellosis differential diagnosis |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
Legionellosis must be differentiated from other causes of fever, dyspnea, cough, and sputum production, such as bacterial pneumonia, viral pneumonia, and other causes of atypical pneumonia.
Differential Diagnosis
Legionellosis must be differentiated from other causes of fever, dyspnea, cough, and sputum production, such as bacterial pneumonia, viral pneumonia, and other causes of atypical pneumonia.[1]
| Disease | Clinical manifestation | Lab findings | Imaging findings | Chest X-ray |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Legionellosis |
|
|
||
| Q fever |
|
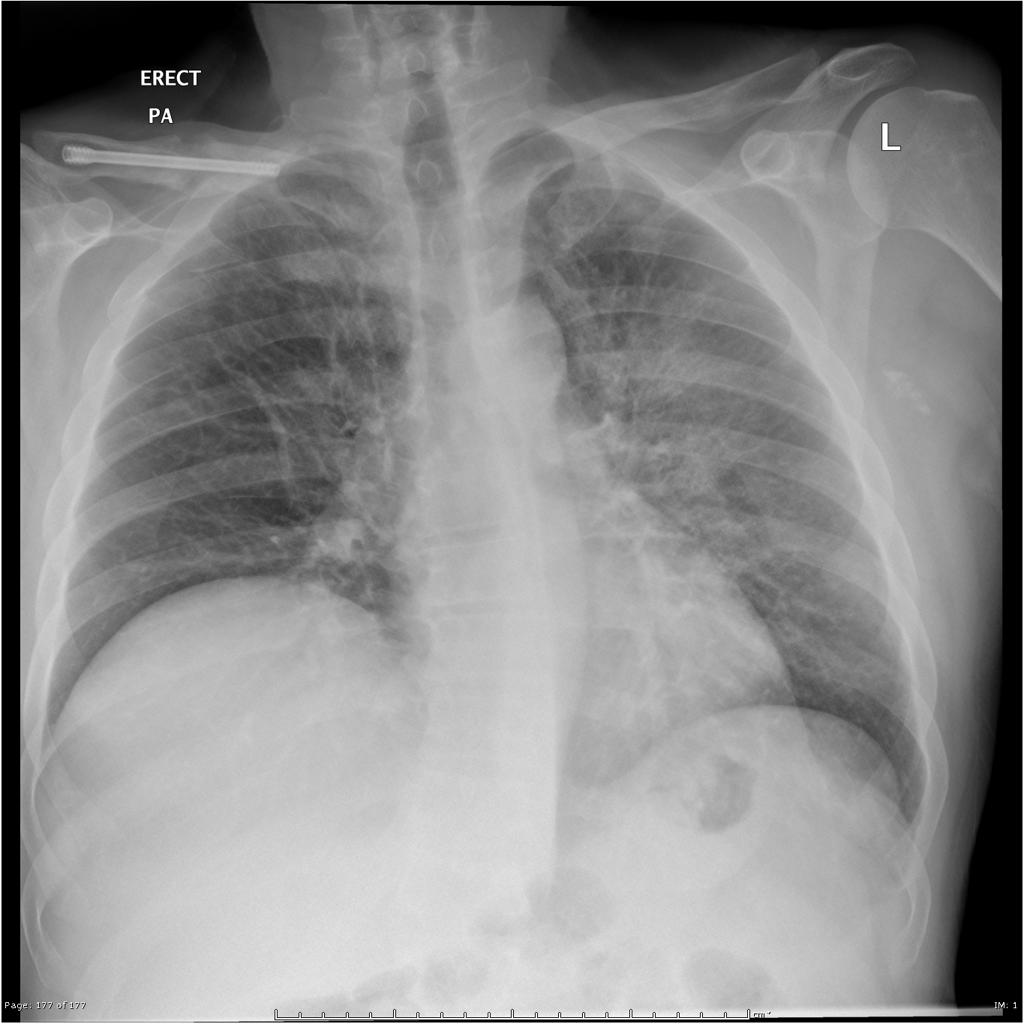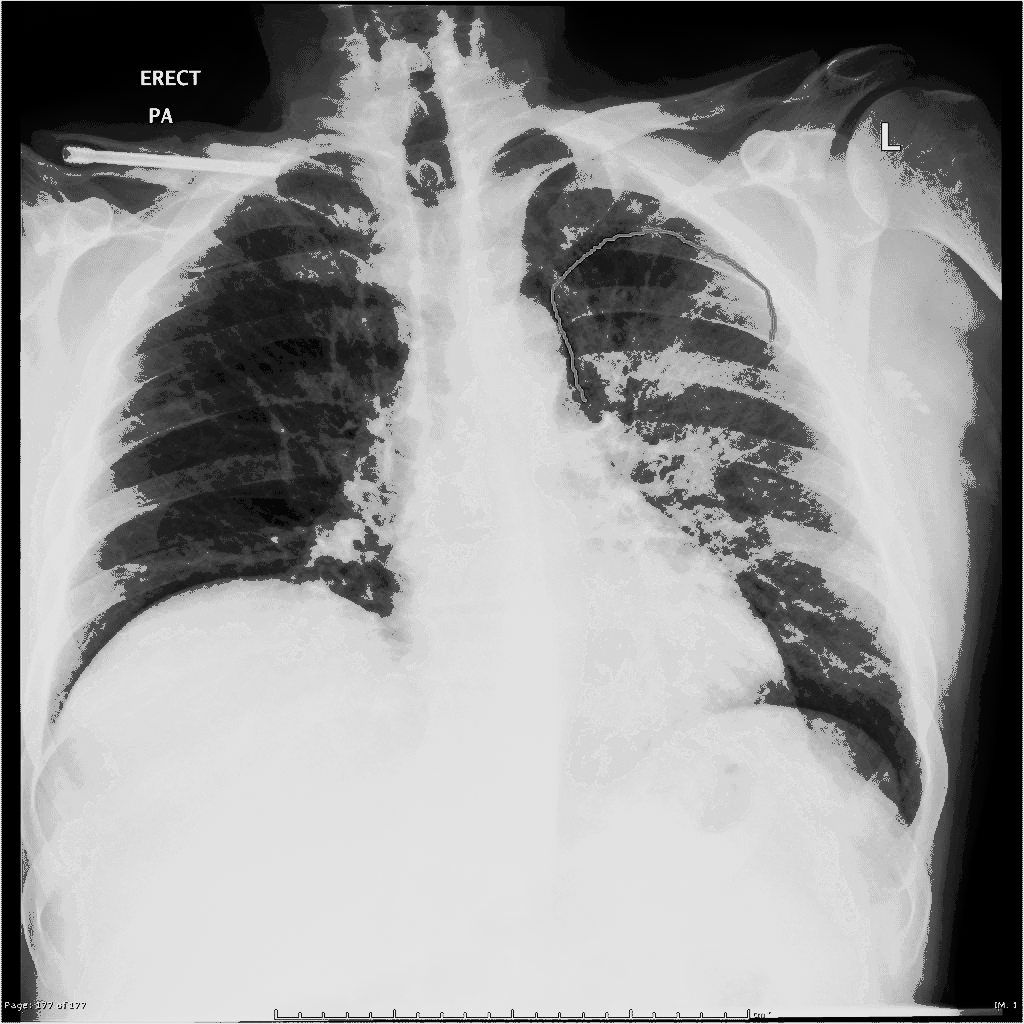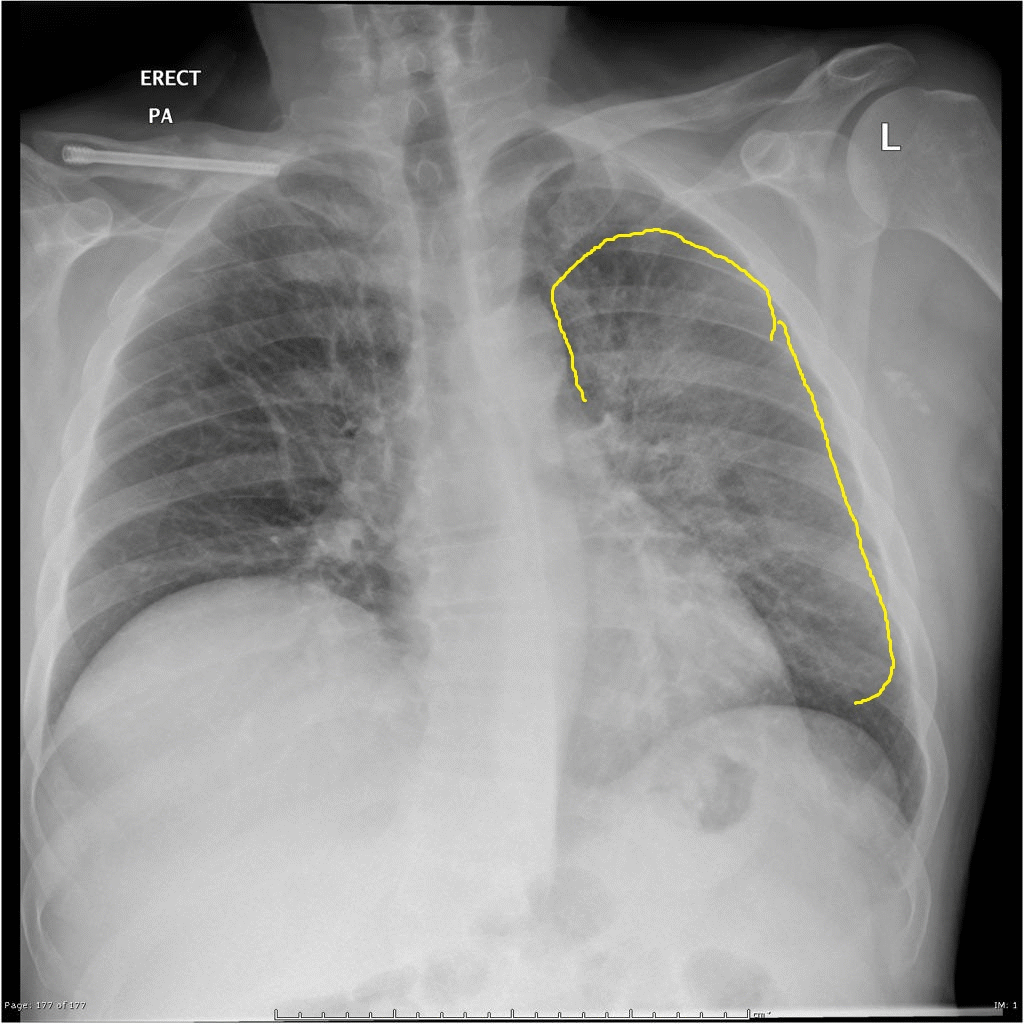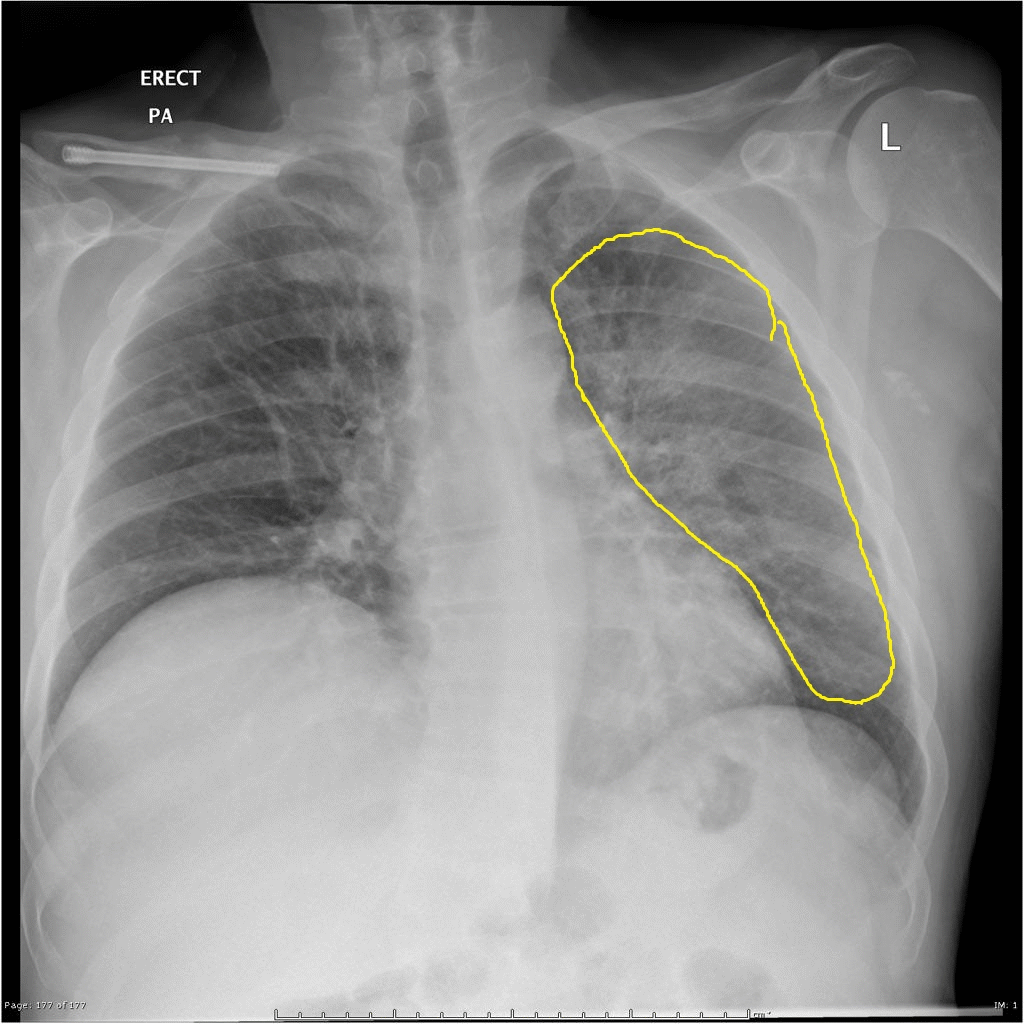 | ||
| Mycoplasma pneumonia |
|
|
|
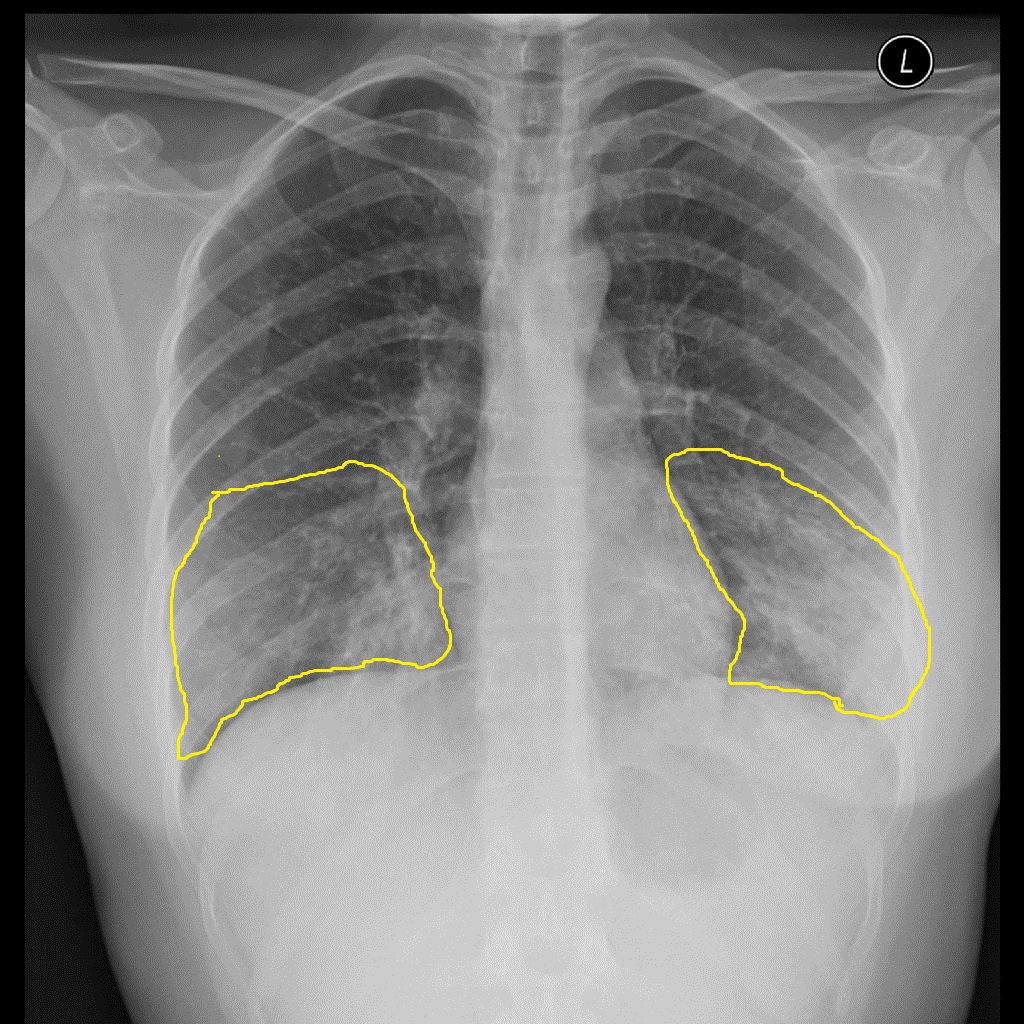 |
| Chlamydia pneumonia |
|
|
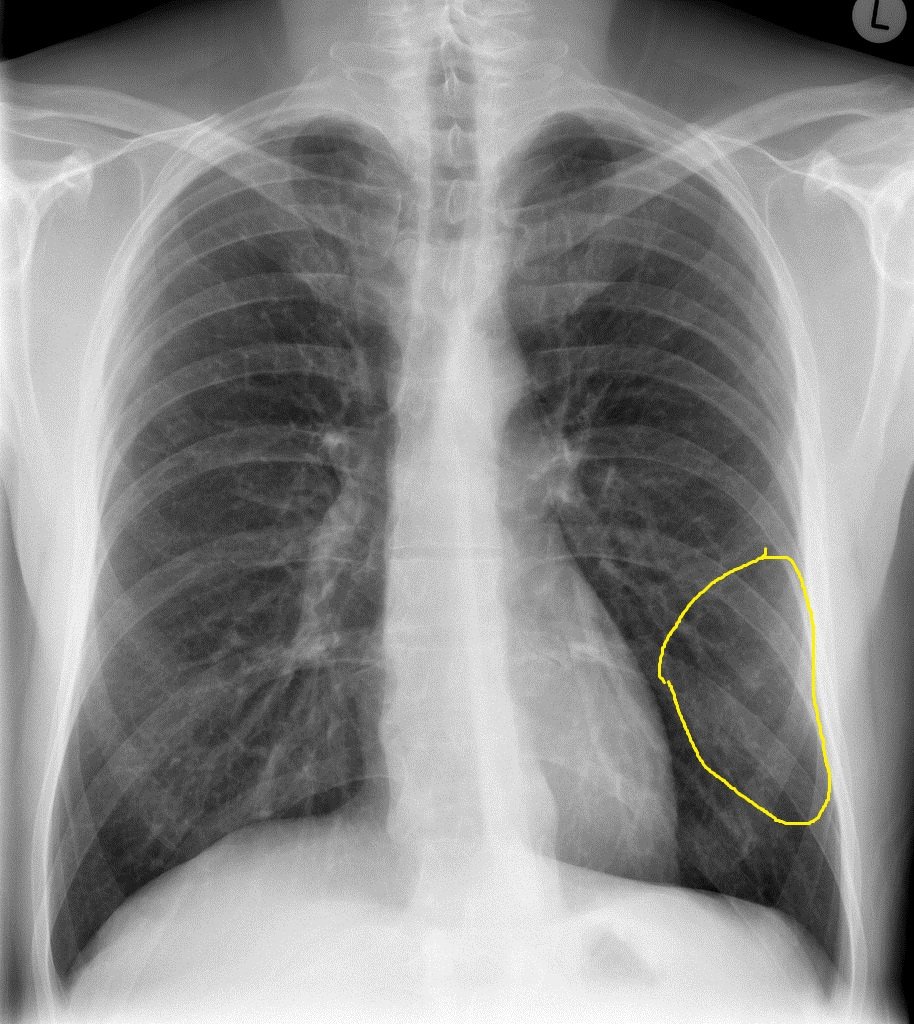 | |
| Acute interstitial pneumonia |
|
|
||
| Pneumococcal pneumonia |
|
|
|
|
| Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia |
|
|
||
| Pulmonary embolism |
|
|
|
|
| Streptococcal pneumonia |
|
|
|
|
| Viral pneumonia |
|
References
- ↑ Irfan M, Farooqi J, Hasan R (2013). "Community-acquired pneumonia". Curr Opin Pulm Med. 19 (3): 198–208. doi:10.1097/MCP.0b013e32835f1d12. PMID 23422417.