Gallstone disease physical examination: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
m (Bot: Removing from Primary care) |
||
| (29 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
Patients with gallstones are usually not ill-appearing and don't have [[fever]] or [[tachycardia]]. Physical examination of patients with gallstones is sometimes remarkable for [[Abdominal pain|right upper quadrant pain]], [[epigastric]] tenderness, [[Abdominal guarding|guarding]] and [[jaundice]]. Symptoms occurs when stones reach more than 8 mm in size. [[Courvoisier's sign]] (a [[palpable]] [[gallbladder]] on physical examination) may be [[Palpate|palpated]] when the [[common bile duct]] becomes obstructed and the [[gallbladder]] becomes dilated. This mostly occurs with [[malignant]] [[common bile duct]] obstruction, but has been reported with gallstone disease. | |||
==Physical Examination== | |||
*Gallstones are usually [[asymptomatic]]. | |||
*This means that gallstones are discovered incidentally when [[imaging studies]] are obtained for another reason. | |||
*Physical findings become relevant when a stone blocks the [[common bile duct]], this could lead to the development of [[biliary colic]] up to [[Jaundice|obstructive jaundice]]. | |||
*The pain is usually referred to the back, ordinarily between the shoulder blades, or there is pain under the right shoulder (Collins' sign). Eventually, the [[pain]] subsides.<ref name="pmid18000708">{{cite journal |vauthors=Yang MH, Chen TH, Wang SE, Tsai YF, Su CH, Wu CW, Lui WY, Shyr YM |title=Biochemical predictors for absence of common bile duct stones in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy |journal=Surg Endosc |volume=22 |issue=7 |pages=1620–4 |year=2008 |pmid=18000708 |doi=10.1007/s00464-007-9665-2 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid19190960">{{cite journal |vauthors=Fitzgerald JE, White MJ, Lobo DN |title=Courvoisier's gallbladder: law or sign? |journal=World J Surg |volume=33 |issue=4 |pages=886–91 |year=2009 |pmid=19190960 |doi=10.1007/s00268-008-9908-y |url=}}</ref> | |||
[[Image:jaundice.jpg|thumb|center|200px|Source: Wikipedia. Patient with jaundice<ref name="urlJaundice - Wikipedia">{{cite web |url=https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jaundice#/media/File:Jaundice08.jpg |title=Jaundice - Wikipedia |format= |work= |accessdate=}}</ref>]] | |||
===Appearance of the Patient=== | ===Appearance of the Patient=== | ||
*Patients with [ | *Patients with gallstones usually appear to be well. | ||
*Patients with [[obstructive jaundice]] may exhibit a yellowish discoloration of the [[skin]] and [[sclera]] of the eyes. | |||
[[Image:jaundice1.jpg|thumb|center|500px|Source: Wikipedia. Patient with scleral icterus<ref name="urlJaundice - Wikipedia">{{cite web |url=https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jaundice#/media/File:Jaundice08.jpg |title=Jaundice - Wikipedia |format= |work= |accessdate=}}</ref>]] | |||
===Vital Signs=== | ===Vital Signs=== | ||
*[[Fever]] | |||
*[[Tachycardia]] with regular pulse | |||
*[[ | |||
*[[Tachycardia]] with regular pulse | |||
===Skin=== | ===Skin=== | ||
*[[Jaundice]] | *[[Jaundice]] | ||
===Abdomen=== | ===Abdomen=== | ||
*[[Abdominal distention]] | *[[Abdominal distention]] | ||
*[[Abdominal tenderness]] in the right | *[[Abdominal tenderness]] in the right upper abdominal quadrant | ||
*[[Rebound tenderness]] (positive Blumberg sign) | *[[Rebound tenderness]] (positive [[Blumberg sign]]) | ||
*A palpable abdominal mass in the right | *A palpable [[abdominal mass]] in the right upper abdominal quadrant (positive [[Courvoisier's sign]]) | ||
*[[Guarding]] may be present | |||
=== | ===HEENT=== | ||
*[[Jaundice|Icteric sclera]] | |||
*[[ | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| Line 140: | Line 42: | ||
{{WH}} | {{WH}} | ||
{{WS}} | {{WS}} | ||
[[Category: | |||
[[Category:Gastroenterology]] | |||
[[Category:Hepatology]] | |||
[[Category:Surgery]] | |||
[[Category:Disease]] | |||
Latest revision as of 21:48, 29 July 2020
|
Gallstone disease Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Surgery |
|
Case Studies |
|
Gallstone disease physical examination On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Gallstone disease physical examination |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Gallstone disease physical examination |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Hadeel Maksoud M.D.[2]
Overview
Patients with gallstones are usually not ill-appearing and don't have fever or tachycardia. Physical examination of patients with gallstones is sometimes remarkable for right upper quadrant pain, epigastric tenderness, guarding and jaundice. Symptoms occurs when stones reach more than 8 mm in size. Courvoisier's sign (a palpable gallbladder on physical examination) may be palpated when the common bile duct becomes obstructed and the gallbladder becomes dilated. This mostly occurs with malignant common bile duct obstruction, but has been reported with gallstone disease.
Physical Examination
- Gallstones are usually asymptomatic.
- This means that gallstones are discovered incidentally when imaging studies are obtained for another reason.
- Physical findings become relevant when a stone blocks the common bile duct, this could lead to the development of biliary colic up to obstructive jaundice.
- The pain is usually referred to the back, ordinarily between the shoulder blades, or there is pain under the right shoulder (Collins' sign). Eventually, the pain subsides.[1][2]
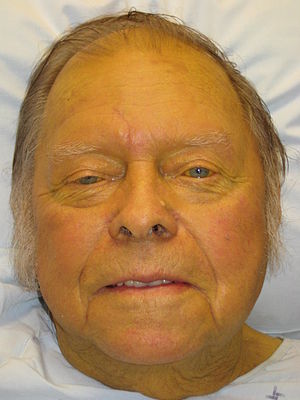
Appearance of the Patient
- Patients with gallstones usually appear to be well.
- Patients with obstructive jaundice may exhibit a yellowish discoloration of the skin and sclera of the eyes.
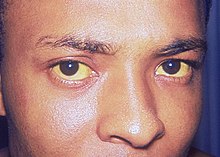
Vital Signs
- Fever
- Tachycardia with regular pulse
Skin
Abdomen
- Abdominal distention
- Abdominal tenderness in the right upper abdominal quadrant
- Rebound tenderness (positive Blumberg sign)
- A palpable abdominal mass in the right upper abdominal quadrant (positive Courvoisier's sign)
- Guarding may be present
HEENT
References
- ↑ Yang MH, Chen TH, Wang SE, Tsai YF, Su CH, Wu CW, Lui WY, Shyr YM (2008). "Biochemical predictors for absence of common bile duct stones in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy". Surg Endosc. 22 (7): 1620–4. doi:10.1007/s00464-007-9665-2. PMID 18000708.
- ↑ Fitzgerald JE, White MJ, Lobo DN (2009). "Courvoisier's gallbladder: law or sign?". World J Surg. 33 (4): 886–91. doi:10.1007/s00268-008-9908-y. PMID 19190960.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Jaundice - Wikipedia".