Gallstone disease causes
|
Gallstone disease Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Surgery |
|
Case Studies |
|
Gallstone disease causes On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Gallstone disease causes |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Gallstone disease causes |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
Causes
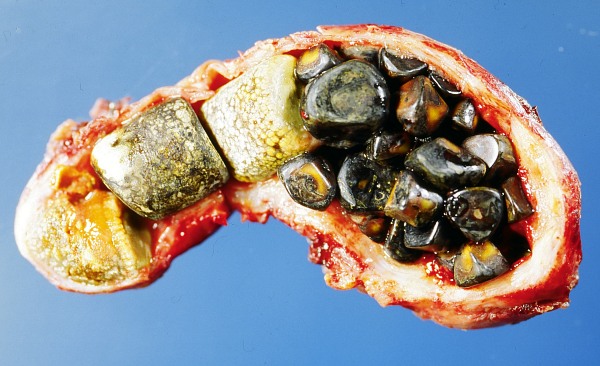
Progress has been made in understanding the process of gallstone formation. Researchers believe that gallstones may be caused by a combination of factors, including inherited body chemistry, body weight, gallbladder motility (movement), and perhaps diet. Additionally, people with erythropoietic protoporphyria (EPP) are at increased risk to develop gallstones.[1]
Cholesterol gallstones develop when bile contains too much cholesterol and not enough bile salts. Besides a high concentration of cholesterol, two other factors seem to be important in causing gallstones. The first is how often and how well the gallbladder contracts; incomplete and infrequent emptying of the gallbladder may cause the bile to become overconcentrated and contribute to gallstone formation. The second factor is the presence of proteins in the liver and bile that either promote or inhibit cholesterol crystallization into gallstones.
In addition, increased levels of the hormone estrogen as a result of pregnancy, hormone therapy, or the use of combined (estrogen-containing) forms of hormonal contraception, may increase cholesterol levels in bile and also decrease gallbladder movement, resulting in gallstone formation.
No clear relationship has been proven between diet and gallstone formation. However, low-fiber, high-cholesterol diets, and diets high in starchy foods have been suggested as contributing to gallstone formation. Other nutritional factors that may increase risk of gallstones include rapid weight loss, constipation, eating fewer meals per day, eating less fish, and low intakes of the nutrients folate, magnesium, calcium, and vitamin C.[2] On the other hand, wine and whole grain bread may decrease the risk of gallstones.[3]
Common Causes
- Aging
- Clofibrate
- Combined oral contraceptive pill
- Diabetes
- Fasting
- Hemolytic anemia
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Obesity
- Pregnancy
Causes by Organ System
Causes in Alphabetical Order
References
- ↑ "Erythropoietic Protoporphyria". Merck Manual. Retrieved 2007-08-25.
- ↑ R.M. Ortega (1997). "Differences in diet and food habits between patients with gallstones and controls". Journal of the American College of Nutrition. 16: 88–95. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (help);|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ↑ European Journal Gastroenterology & Hepatology. 6: 585–593. 1995. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help);|access-date=requires|url=(help)